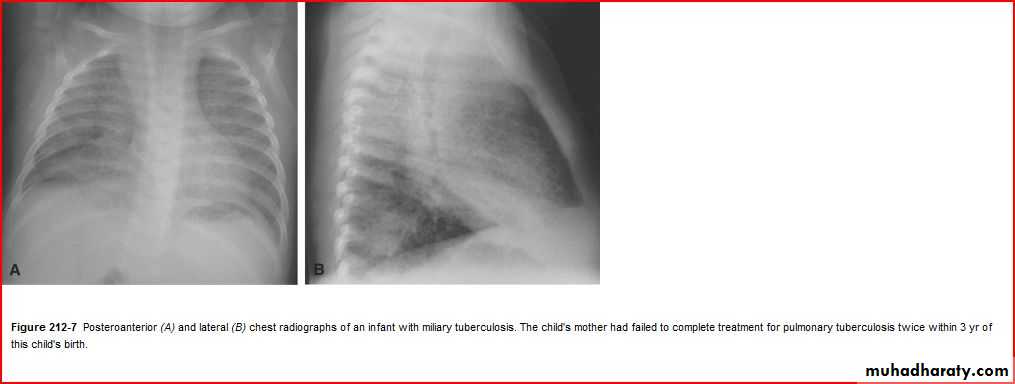
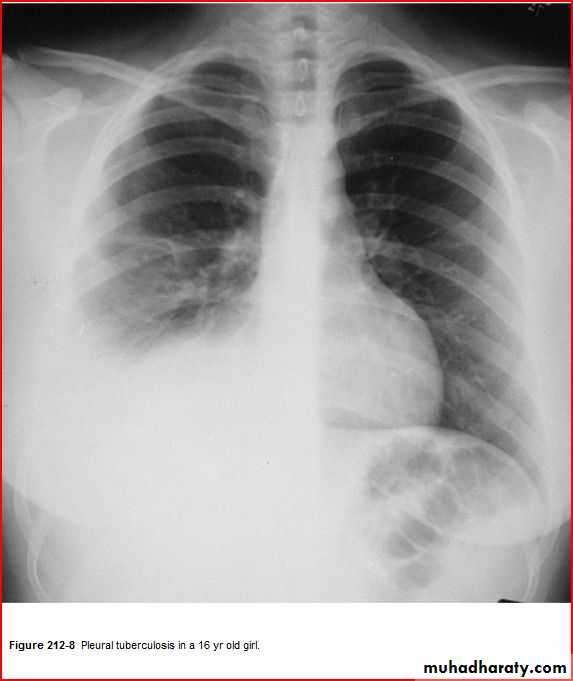
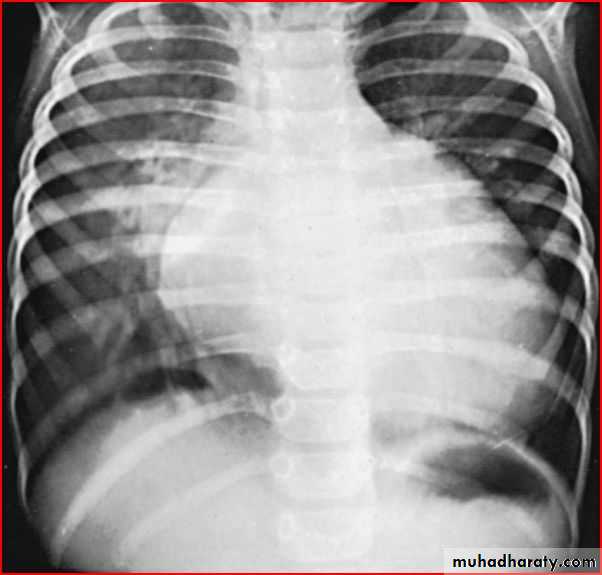
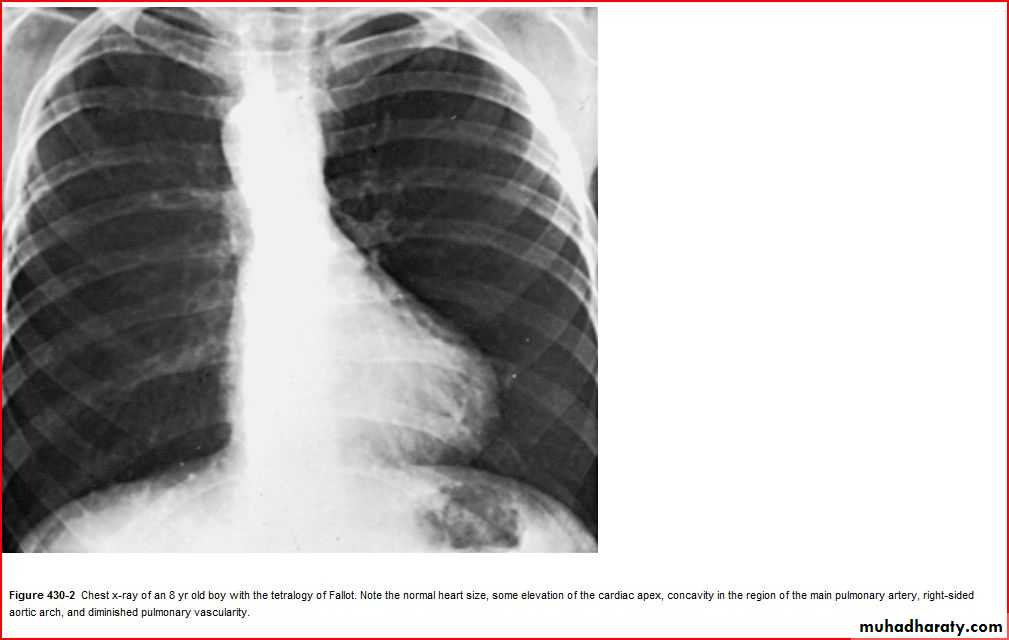
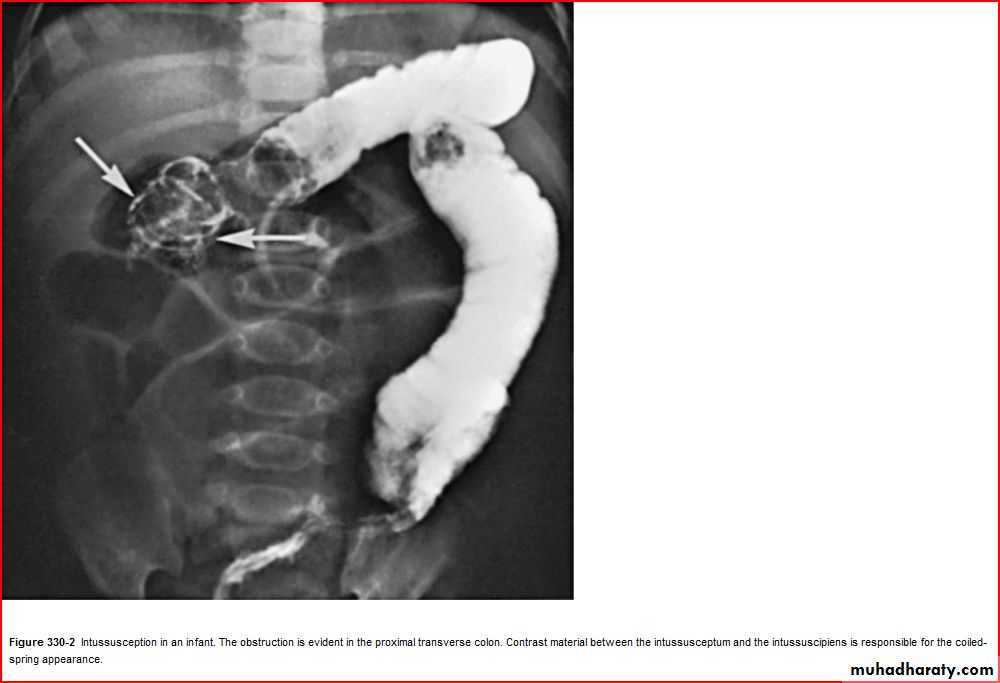
Pediatric E.C.G
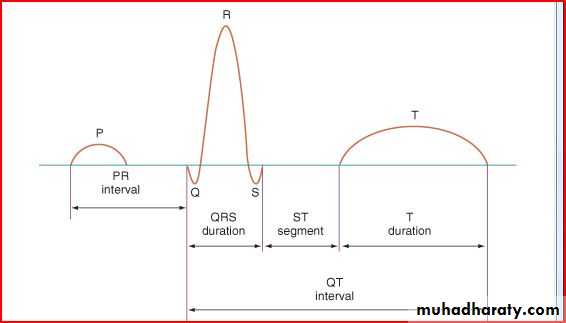
The electrocardiogram should be read systematicallyHeart rate (300/no.of large squares between R-R)OR(1500/NO.of small squares between R-R)
P wave axis (the P wave should be upright in leads I and aVF and inverted in lead Avr)-Normally less than 2-3 small squares (0.08-0.12 sec) wide and tall
Rhythm
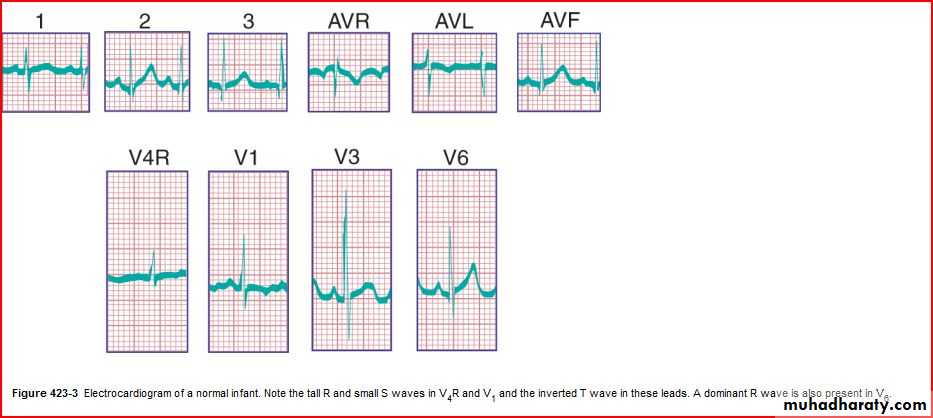
QRS axis (In a newborn, the mean QRS frontal-plane axis normally lies in the range of +110 to +180 degrees. The right-sided chest leads reveal a larger positive (R) than negative (S) wave and may do so for months or years because the right ventricle remains relatively thick throughout infancy-Over the years, the QRS axis gradually shifts leftward, and the right ventricular forces slowly regress. Leads V1, V3R, and V4R display a prominent R wave until 6 mo to 8 yr of age)
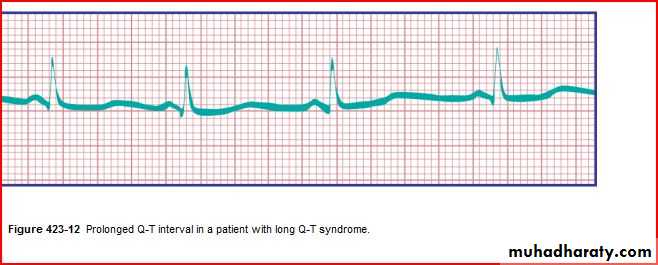
Intervals PR, QRS, QT/QTc (PR 3-5 SMALL SEQUARES)(QRS If longer than 2-3 square (0.08-0.12 sec), that's bundle branch block (BBB).
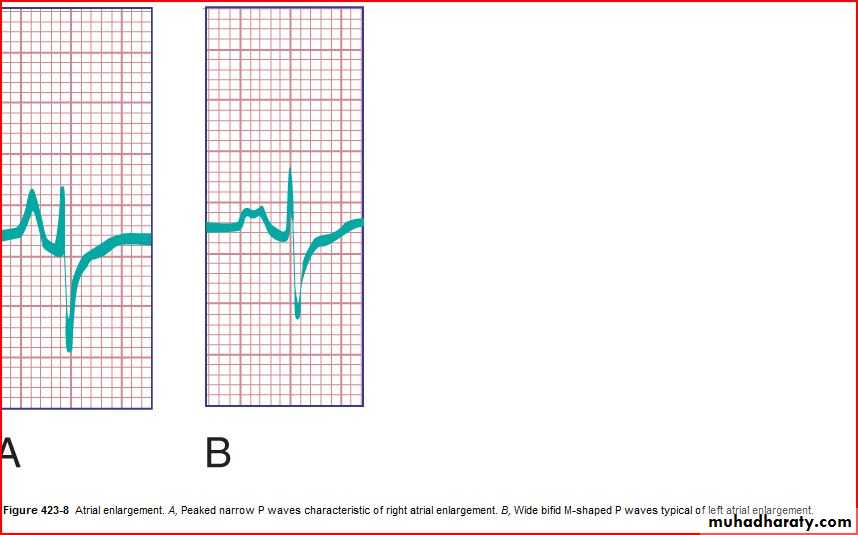
P wave amplitude and duration (RA and LA enlargement)
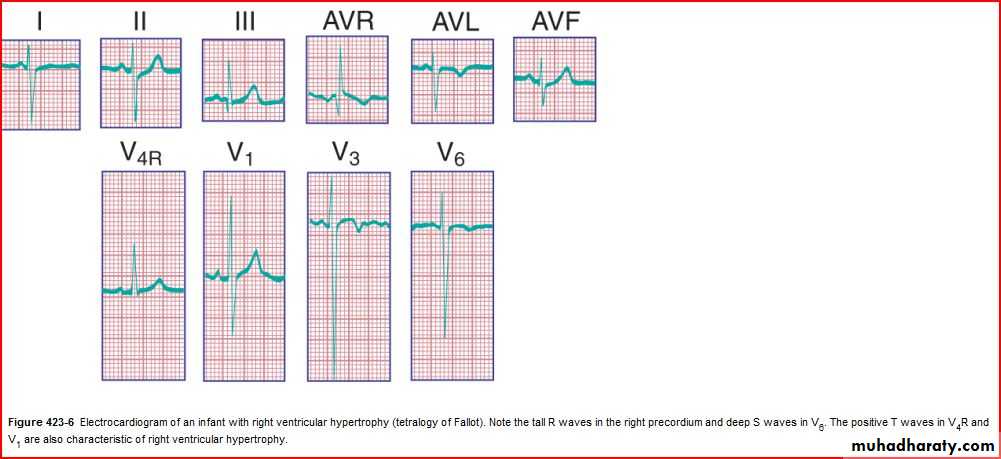
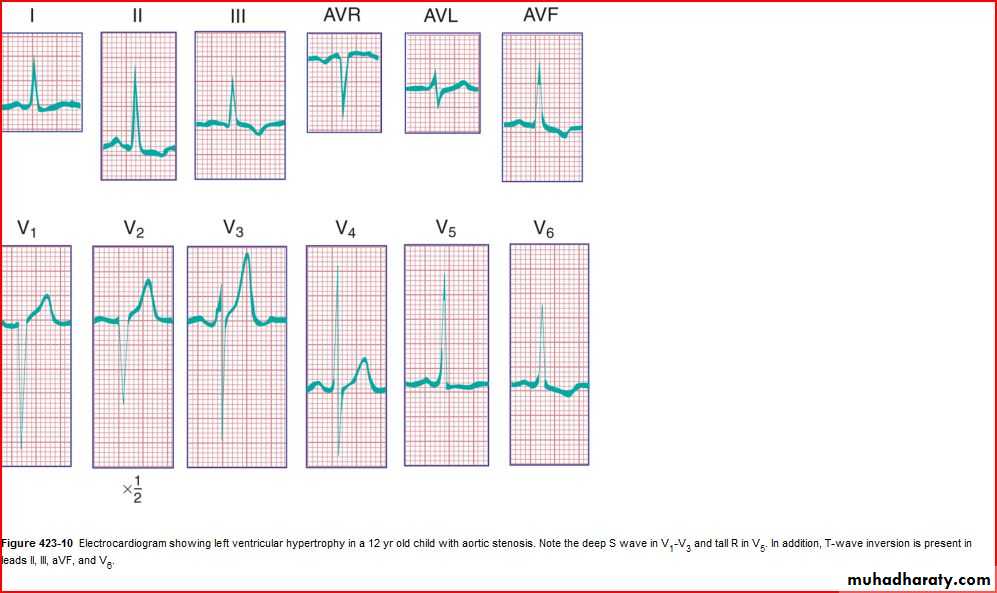
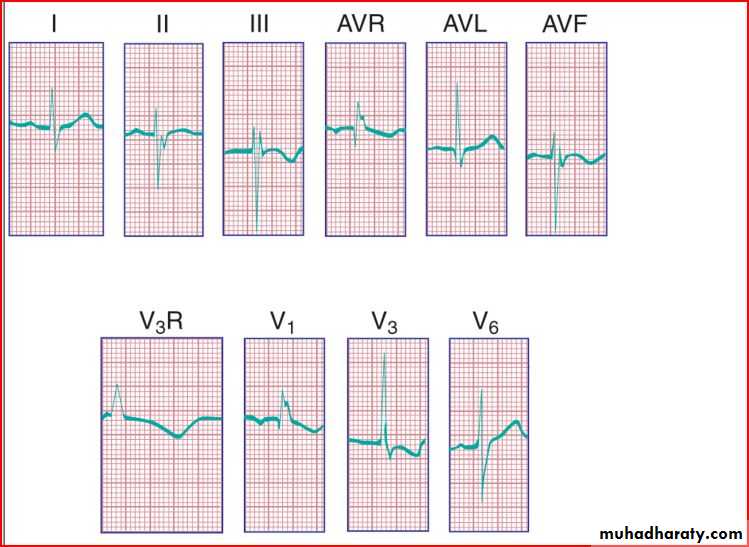
QRS amplitude, R/S ratio, Q waves (RVH – LVH)
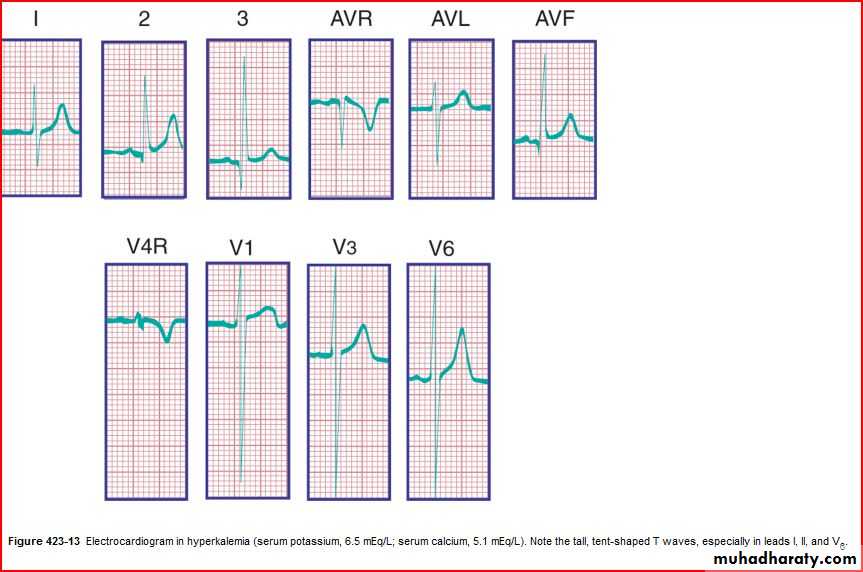
ST segments and T wave
T wave inversion: Infants older than 48 hours of age should have inverted T waves in the right praecordial leads. These findings persist throughout childhood with inversion to V4 being accepted as normal. There is a progressive change to an upright T wave across the praecordial leads from left to right as the child grows older. Until 8 years of age an upright T wave in V1 is considered a sign of right ventricular hypertrophy. Many children will show persistence of an inverted T wave in V1 until their late teens
PR interval if > 5 small sequares is prolonged
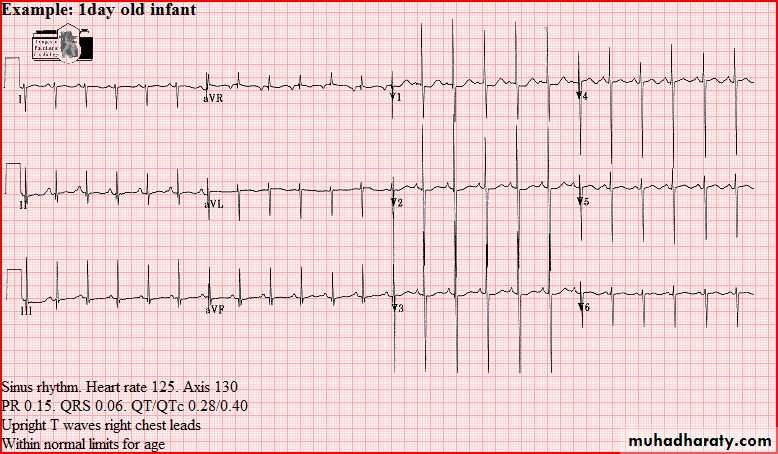
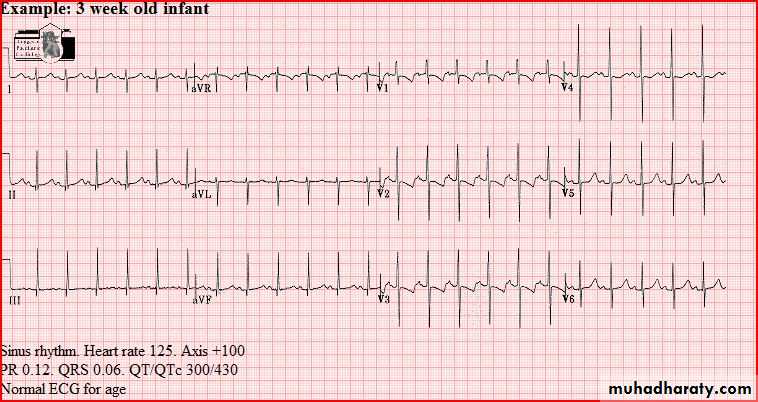
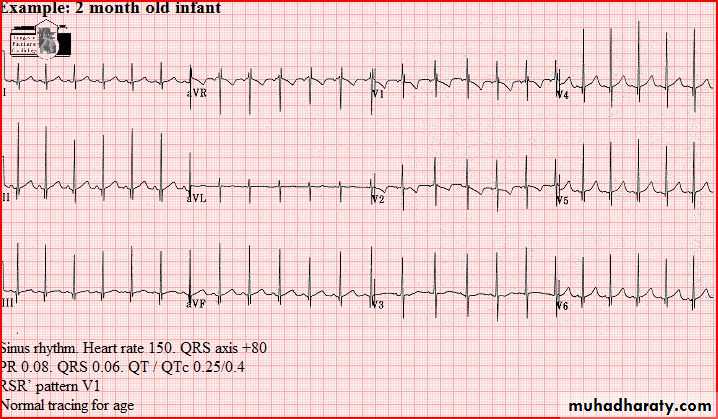
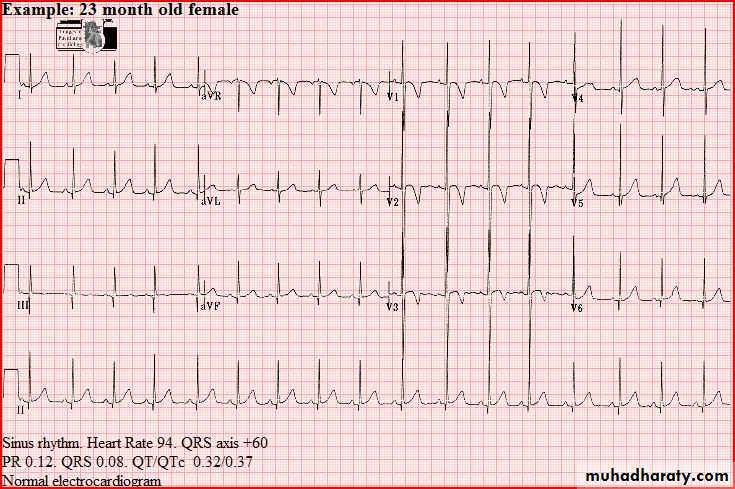
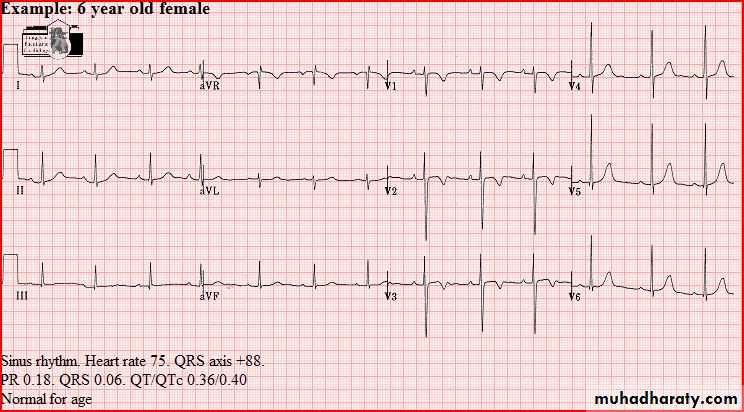
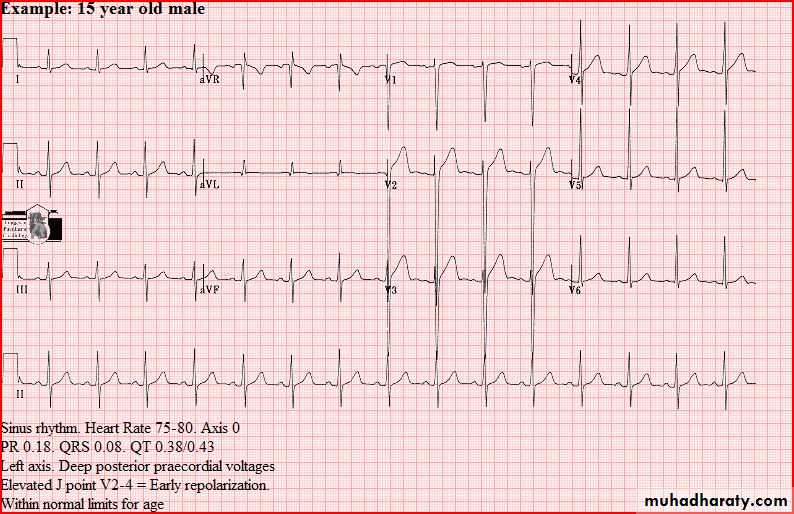
Normal tracings Examples of normal tracings for the different age groups follow, preceded by a general description of the characteristics of that age group.
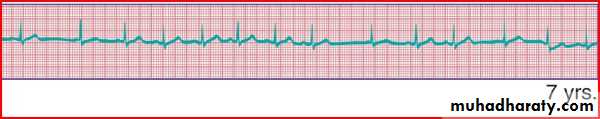
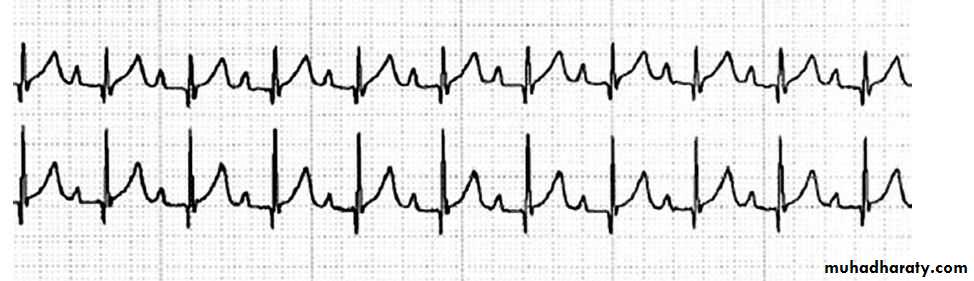
Sinus arrythmia : occur during inspiration by increased heart beats
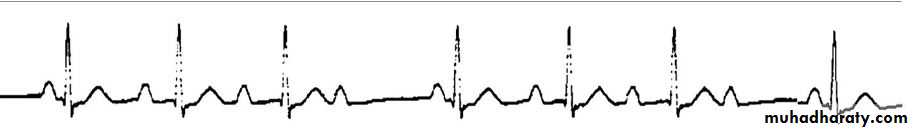
Complete heart blick
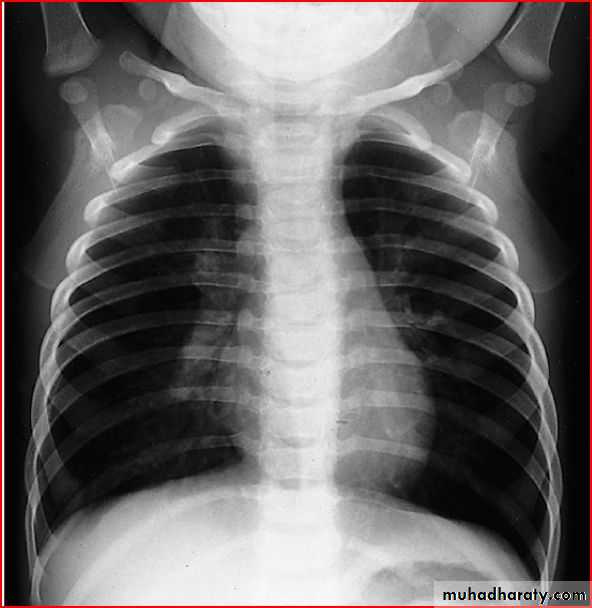
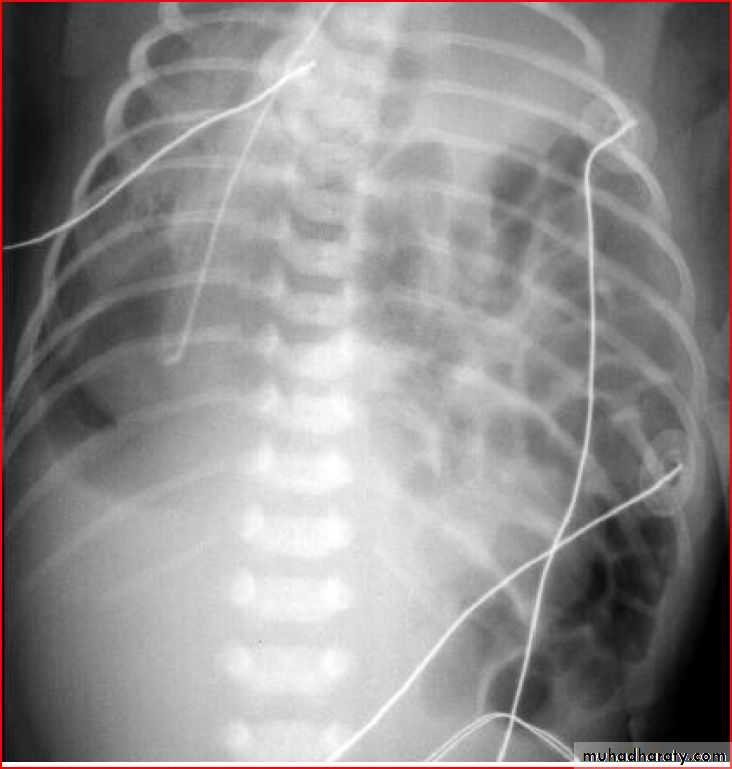
Bronchoilitis
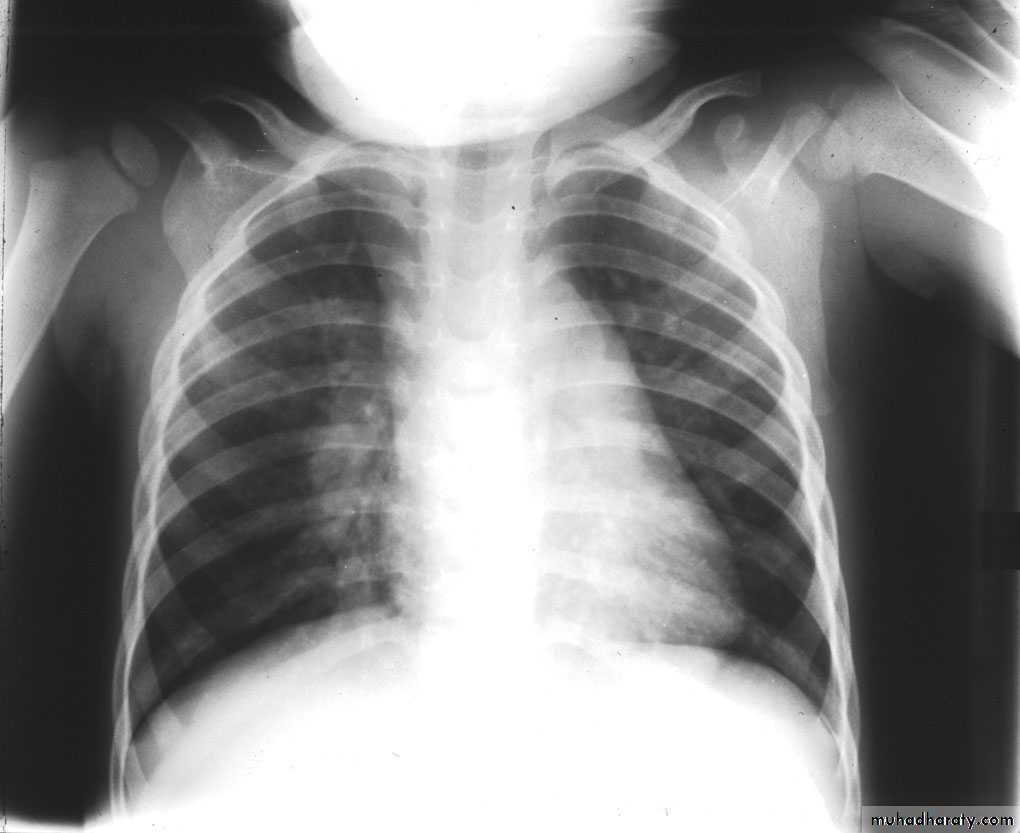
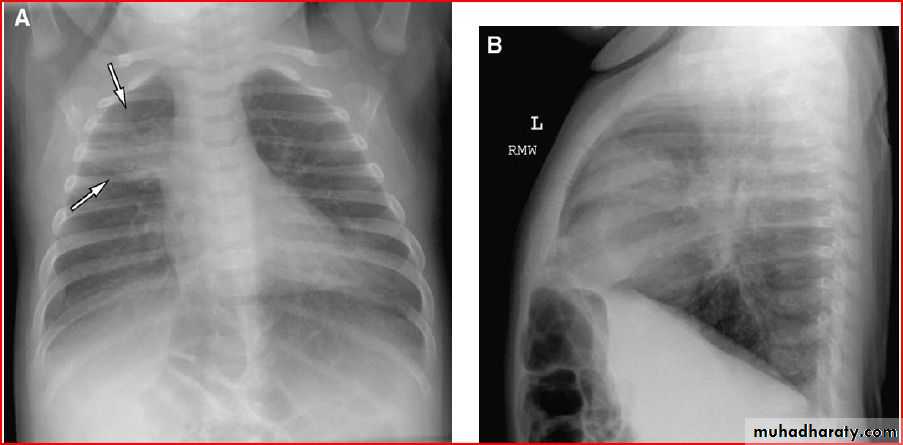
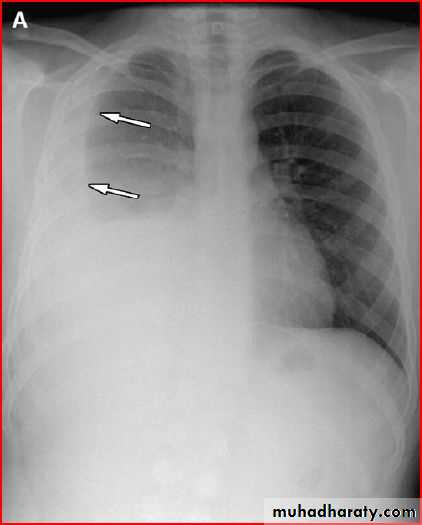
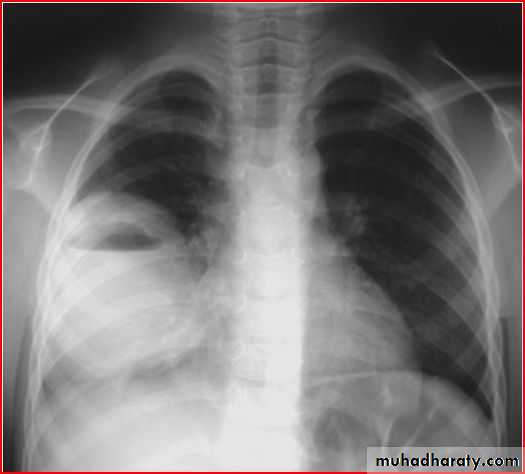
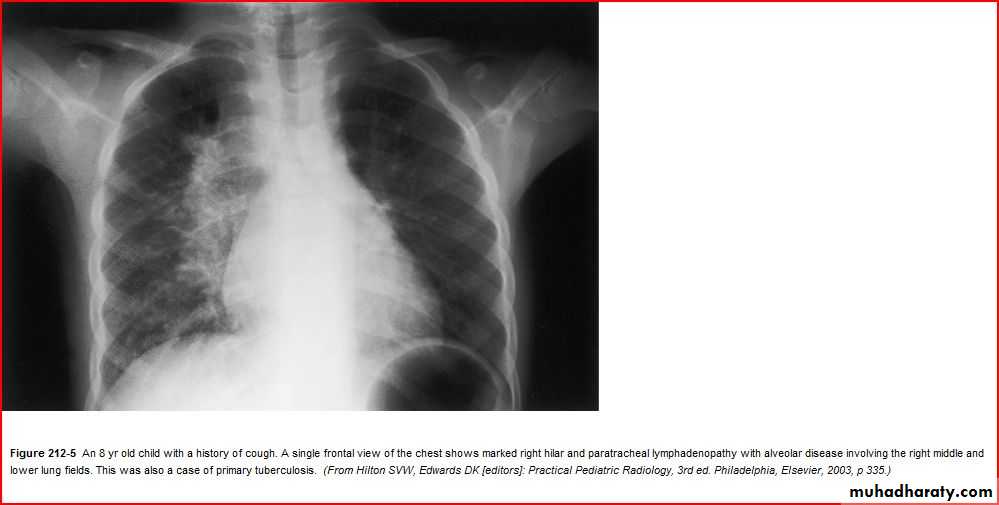
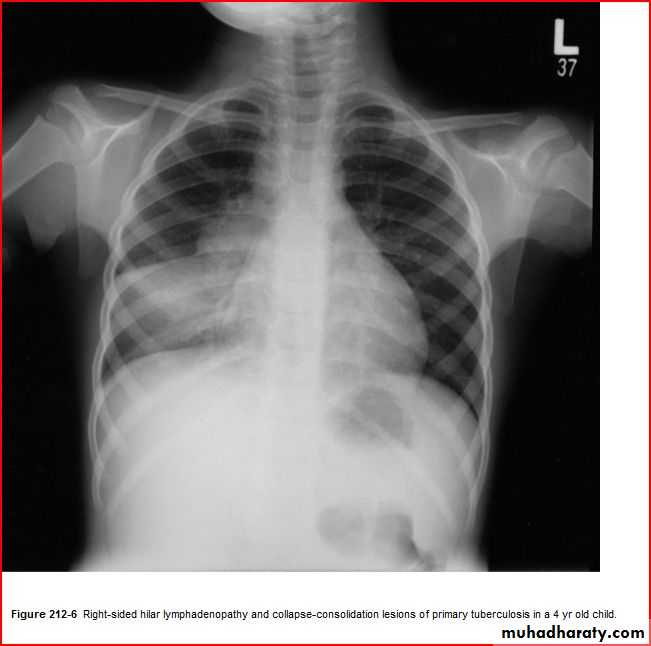
Middle lobe pneumonia
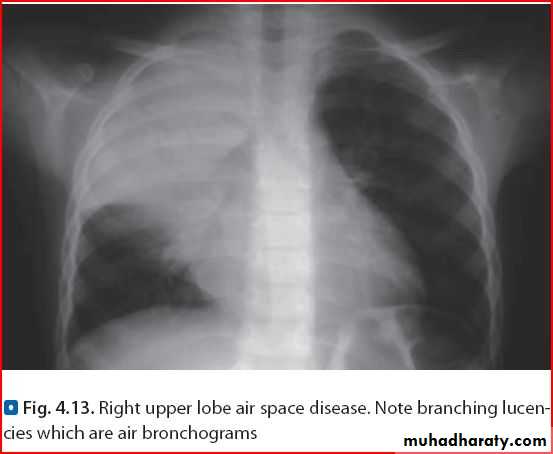
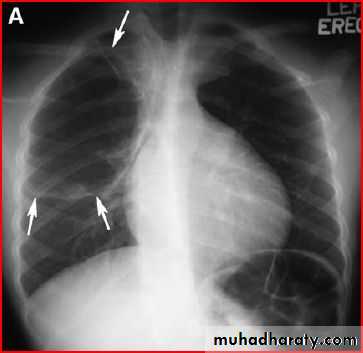
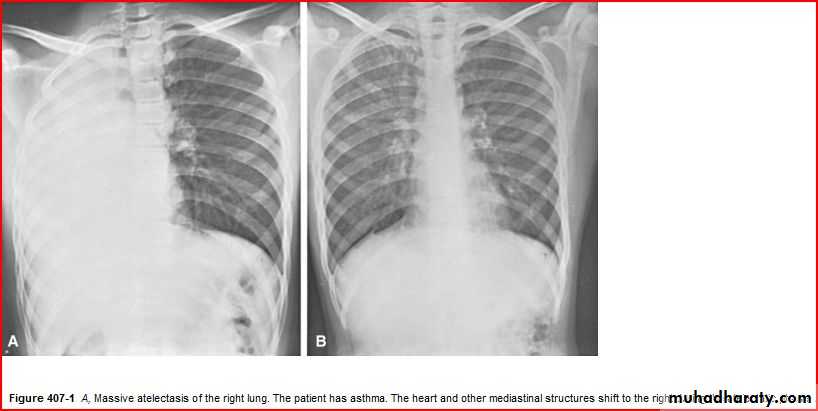
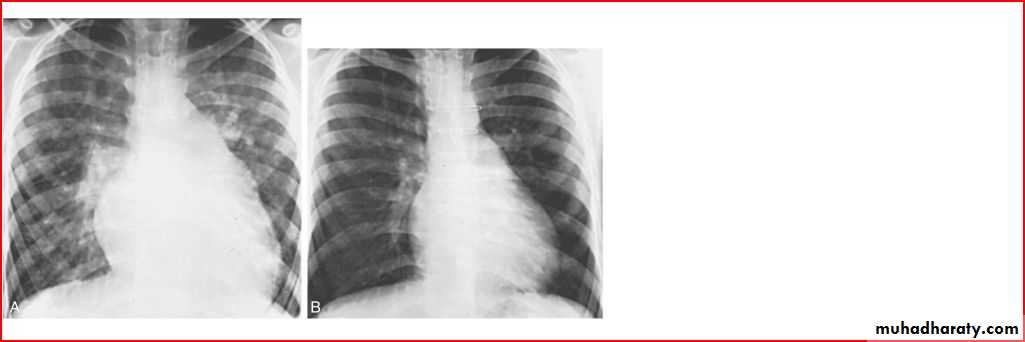
Whole right lung pneumonia
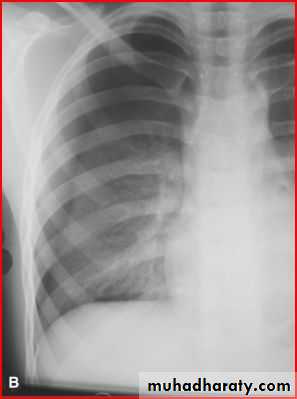
Normal after the tratment
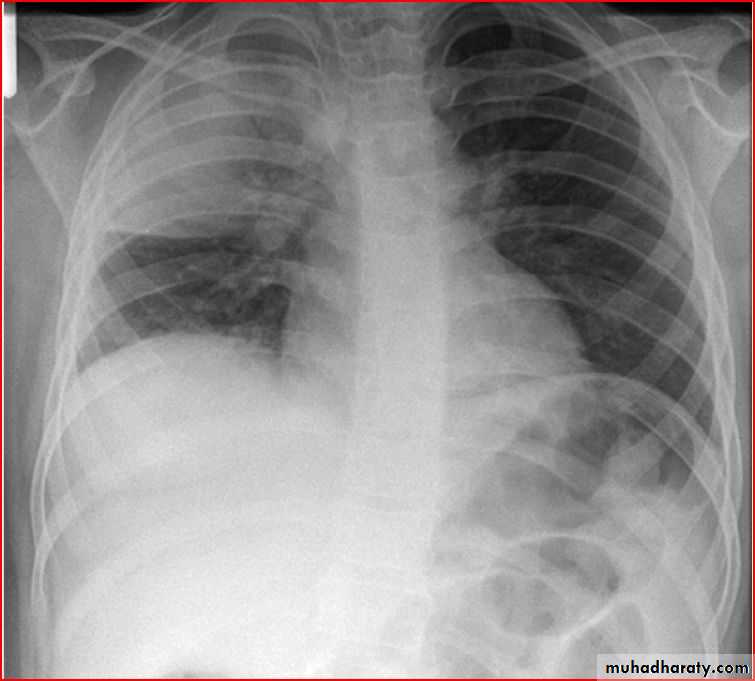
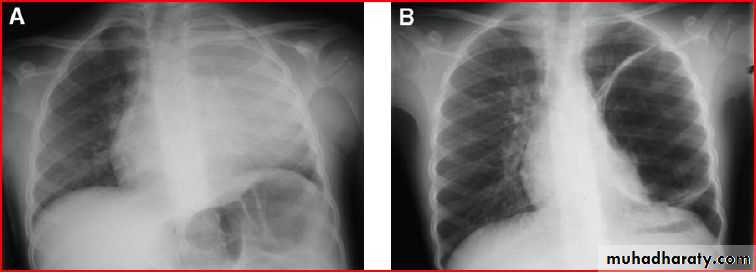
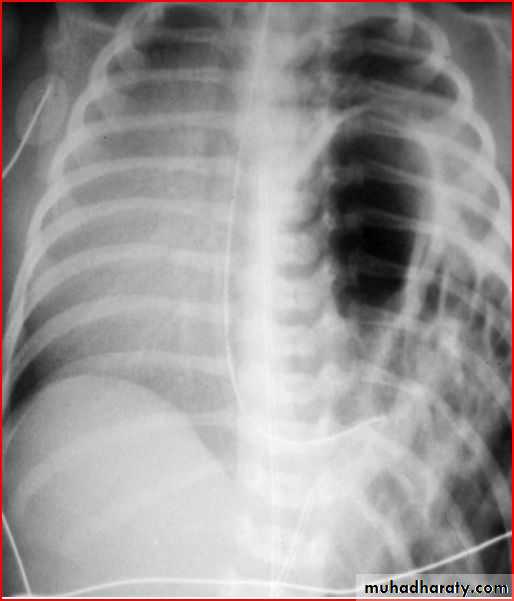
Basal left lobe pneumonia
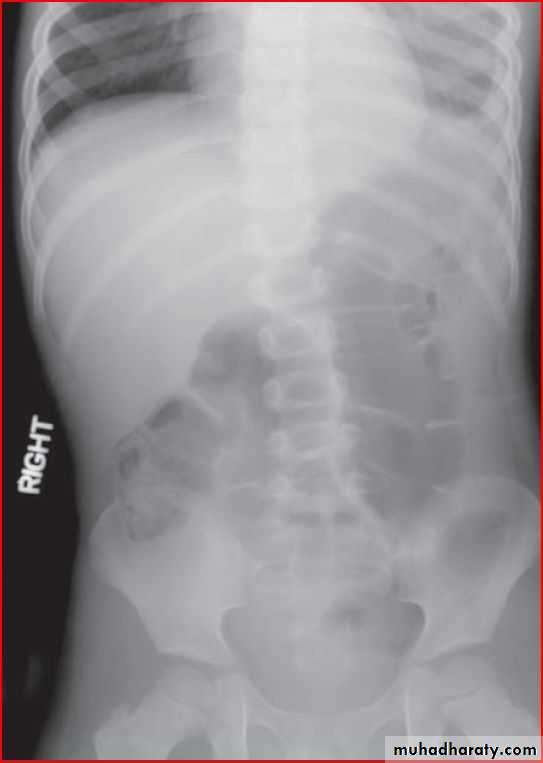
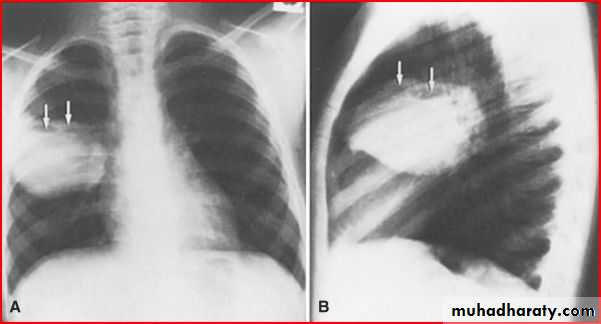
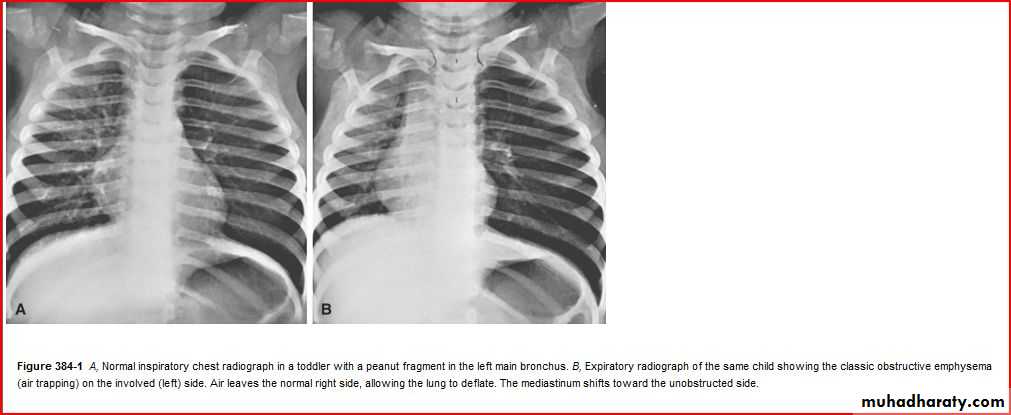
May be presented as abdomial painPneumatocele ( air lined wall
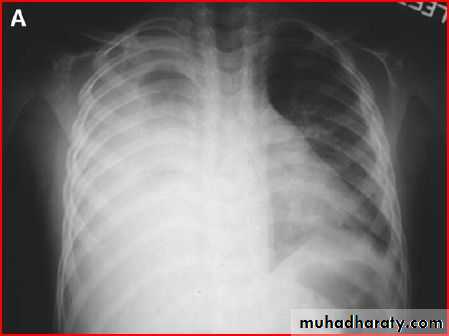
Cause : staph aureus infectionpneumothorax
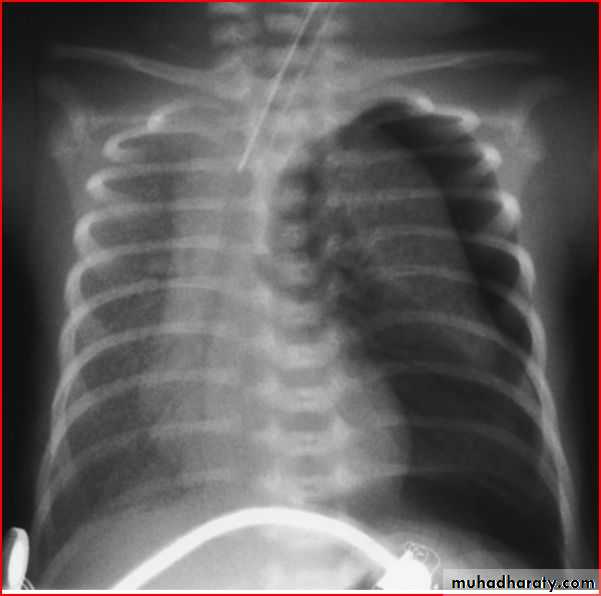
Tension pneumothorax
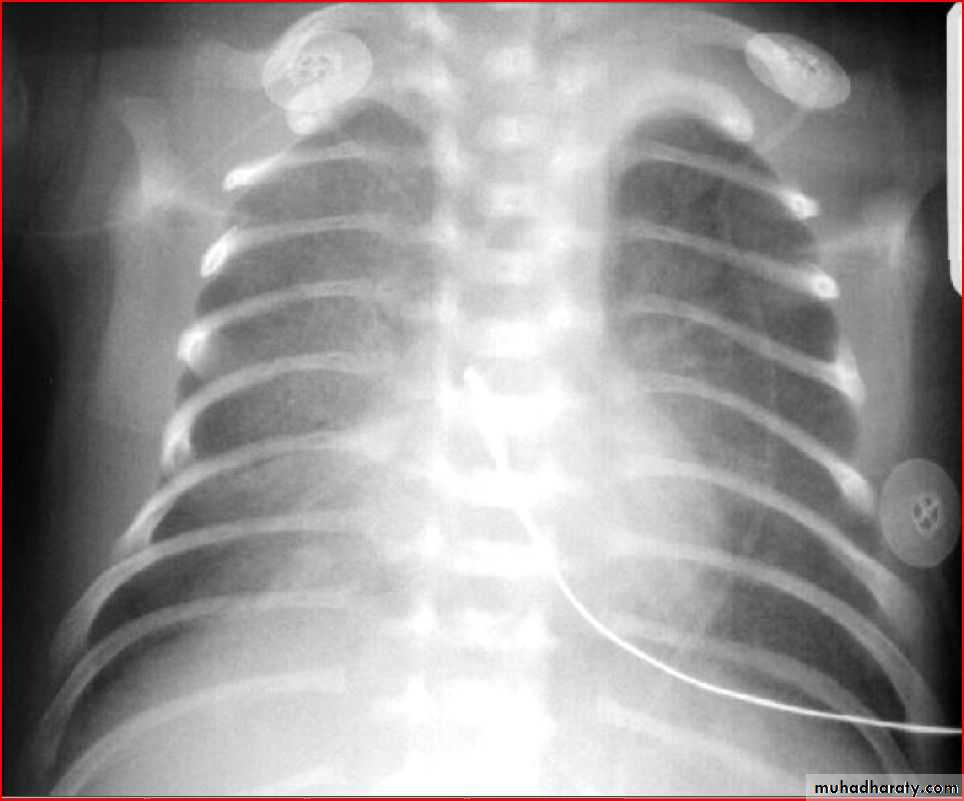
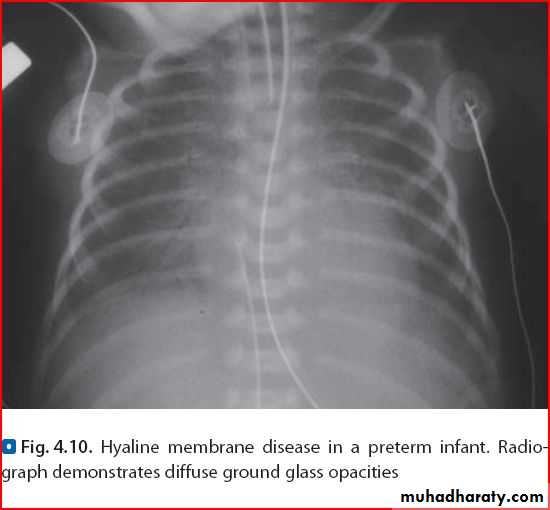
Respiratory distress syndrome ( hyaline membrane disease )
Radiological features : glasss ground appearanceLung abcess
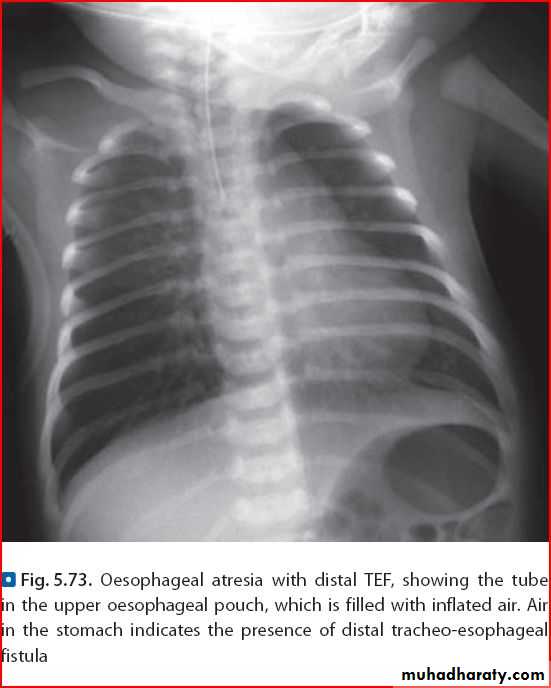
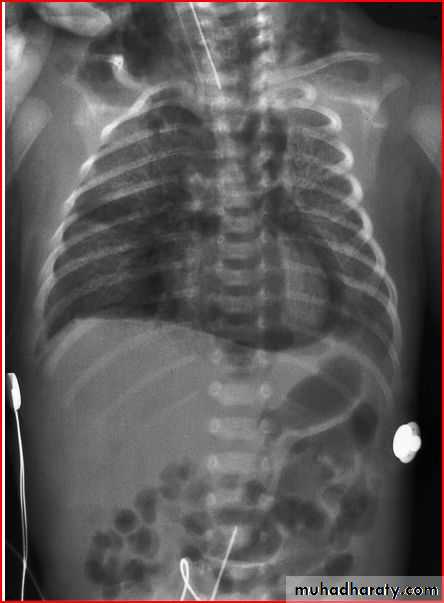
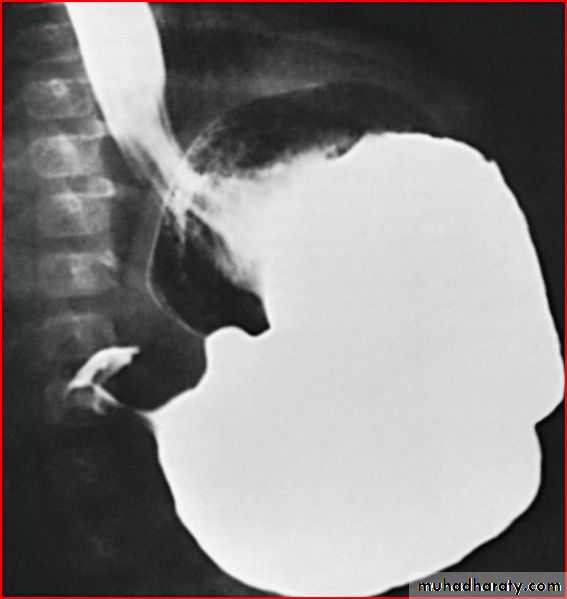
Diaphgramtic hernia
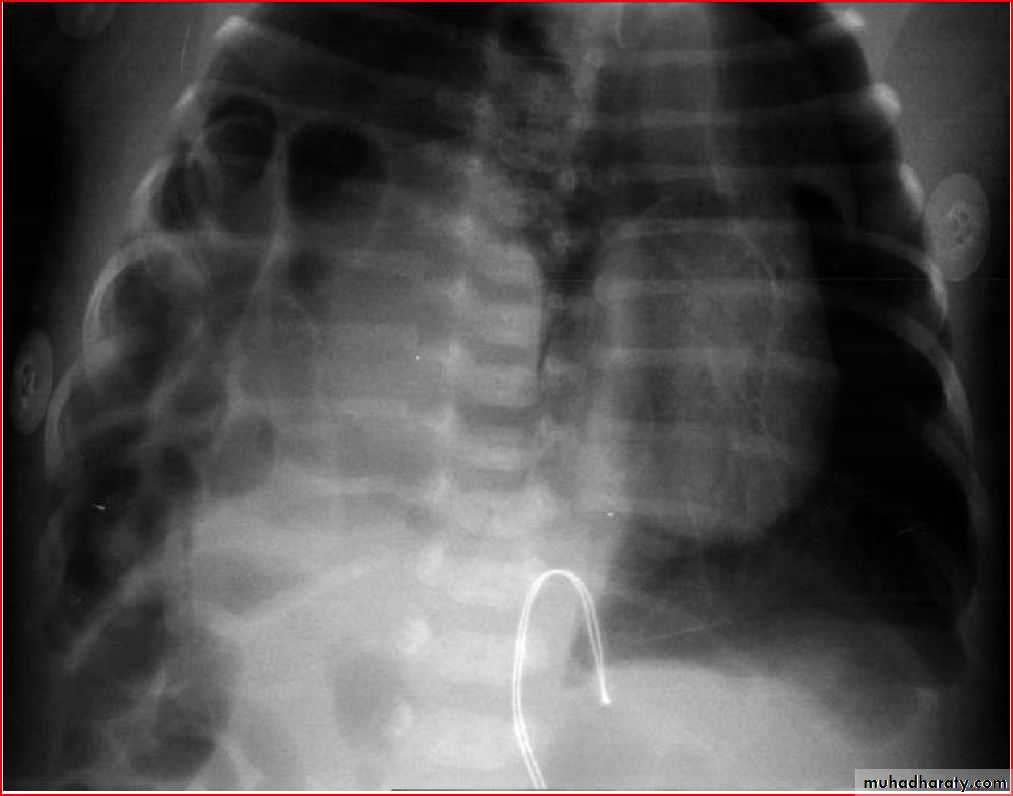
Lung abcess