
1
Parasitology
P
ractical
l
abs
http://goo.gl/rjRf4F
I
LOKA
©
http://www.muhadharaty.com/Parasitology
I

2
Content
Topics:
Page:
E.coli
3
E. histolytica
4
Giardia lambilia
5
Triechomonus
7
Trypanosoma
8
Lishmania
10
P.vivax
11
P. malariae + P.falciparum
12
Sexual cycle of malaria
13
B.coli + Toxoplasma
14
Ascaris + enterobius
16
A.duodenale + T.trichiura
18
Trichinella + wuchereria
19
Taenia saginata
21
Taenia solium
22
Echinococcus granulosus
23
D.latum + H.nana
25
Schistosoma haematobium
27
Schistosoma mansoni
28
F. hepatica + H. heterophyes
30
Mosquito + sand-fly + fleas
31
Sarcoptes scabiei + lice + Ticks
33
Summary
35

3
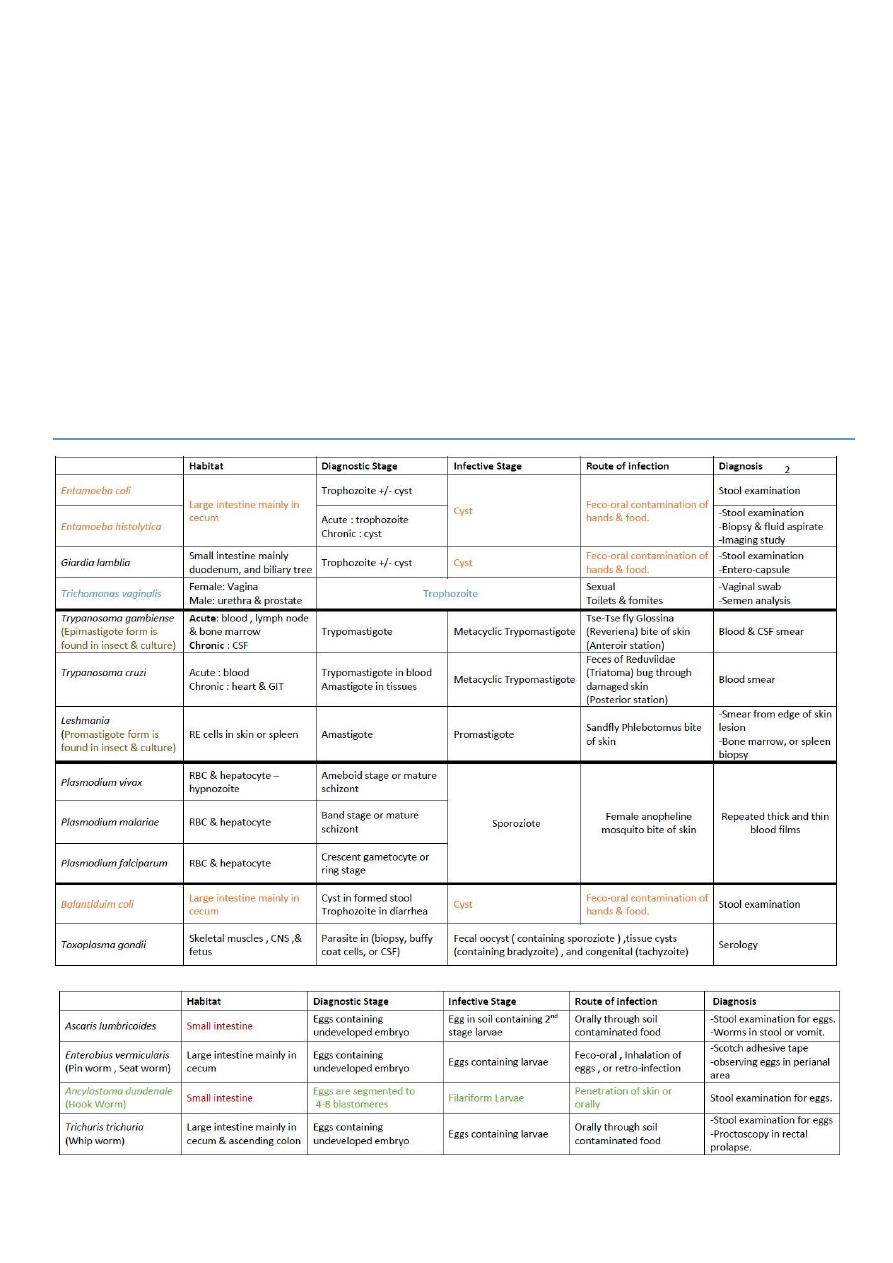
Parasite1:
E.coli
#Introduction:
Classification of parasites
Diagnosis of parasite ( by stool examination , blood examination , x-ray ,…….)
General stool examination (GSE)----- if the test is positive that means there are
pathogenic parasites but when the test is negative that means there are non-
pathogenic parasites or food particles or waste products in the stool
Preparation of (GSE)----- (1)without iodine stain to see the motile trophozoite
(2) with iodine stain to see dead trophozoite but it use to see cyst and eggs
#E.coli:
non-pathogenic parasite
10%-20% of population have E.coli without any symptoms
habitat : lumen of large intestine mainly in cecum
route of infection : feco-oral route
infective stage : cyst
diagnostic stage : tropozoite (-)+ cyst
morphology :
#Trophozoite:
It has more granular endoplasm containing ingested bacteria and debris and food
particles (no RBCs) .
The ectoplasm is not clear. and it has short and wide pseudopodia.
It has one nucleus contain large eccentric karyosome, and large chromatin granules
arranged irregularly beneath nuclear membrane.
size: 10-50 microns
#Mature Cyst:
small , spherical to oval in shape , containing 4-8 nuclei , usually found in feces
size: 10-30 microns
nuclear morphology of the cyst is similar to that of trophozoite but they are smaller
#Immature Cyst:
containing 2-4 nuclei
chromatoid bodies
glycogen

4
Parasite2:
E. histolytica
#E. histolytica:
1- pathogenic parasite
2- trophzoite acute
هذه
االشياء هي سبب خطورة هذه المرحلة من الطفيلي
has :-1-pseudopodia for motile activity -2- centric karyosom and regular chromatin for protolytic
enzymes and toxic sub.
3-infective stage : cyst
4-diagnostic stage : chroniccyst acutetrophozoite
5-cyst and trophozoite diagnosis by : biopsy and stool examination and imaging study
6- diseases :
a. acute dysntric diarrhea
يوجد فقط تروفوزويت
b. chronic diarrhea ( perforation , ulceration of colon and peritoneal region)
يوجد تروفوزويت و سست
c. toxic colon
d. liver abscess
e. lung and brain (rare)
7- route of infection :: feco-oral route ( water-food-flies-carriers)
8- habitat : large intestine mainly in cecum
9- treatment : metronidazole - tinidazole
10- E.histolyic is epidemic because it infect only human
11- morphology :
#Trophozoite:
ليس لديه شكل ثابت
1- Clear ectoplasm .
2- Large finger – like pseudopdia
3- The endoplasm is granular and may contain RBCs.
4- It has one nucleous, contain small central keryosome and fine chromatin granules
arrenged regularly beneath nuclear membrane.
5- size: 30-50 microns

5
#Mature Cyst:
1- small , spherical in shape , containing 1-4 nuclei
.
Each nucleous contain similar nuclear
morphology like the trophozoite but smaller , usually found in feces .
2- size: 10 microns
#Immature Cyst:
1- containing 1-2 nuclei
2- chromatoid bodies
3- glycogen
#For diagnosis of any parasite, depend on the following tests:
1- history (clinical presentation)
2- imaging technology
3- histological examination
4- serological examination
5- stool , urine and CSF examination
Parasite3:
Giardia lambilia
#Giardia lambilia:
1- reproduction : by binary fission ( in normal condition)
2- common in our society and it infect all ages ,, it make endemic diseases .
3- habitat : lumen of small intestine mainly in duodenum and in the biliary tree .
4- route of infection : feco-oral route
5- infective stage : cyst
6- diagnostic stage : tropozoite (-)+ cyst
7- morphology :

6
#Trophozoite:
1- small –> 12-15 micron
2- tear or piriform in shape
3- anterior rounded end and posterior tapered or pointed end
4- two large anterior nuclei with central karyosome .
5- has 2 axostyle
6- has 3-5 anterior flagella with single posterior flagella
7- has blepharoplast(sucking disc) and two parabasal bodies
8- dorsal convex surface and ventral flat surface
All these features is called (( ugly monkey face ))
#Cyst:
1- small , oval in shape , containing 4 nuclei one pair on each side of the axostyle
2- size: 10-12 microns
3- has 2 axostyle
4- it contain the remaining parts of trophozoite
#The disease of Giardia lambilia:
1- steatorrhea
2- gallstones ( sever case )
3- lactose tolerance ( rare case )
4- diarrhea
5- weight loss
Giardia lambilia is mild but in rare conditions it make (( post giardial infection chronic fatigue
syndrome )) which may lead to death
#The diagnosis of Giardia lambilia:
1- most common is stool examination for trophozoite or cyst but most of cases is lead to negative
result with this examination
2- the best examination is by enterocapsule
3- endoscope
4- duodenal aspiration

7
#The treatment of Giardia lambilia:
1- metronidazole
2- tinidazole
Parasite4:
Triechomonus
#Triechomonus:
1- T.vaginalis ( for human)
2- T.tonex ( in crural areas – make bad breathe odor – does not make infection)
3- T.hominis (nonpathogenic – but in large number in colon lead to diarrhea )
#T.vaginalis:
1-Morphology ( of trophozoite )
1- undulating membrane
2- large single anterior nucleus
3- 18-20 microns
4- single posterior flagella with 3 anterior
5- has axostyle
6- has hydrogenosome
7- piriform shape
8- sometimes it contain viral particles (HIV)
2- no cyst stage ( only trophozoite )
3- in female it infect the vagina but in male it infect the urethra and prostate
4- in female it secret toxic substances that make hemorrhage and damage to the epth. Of the
vagina and make a lot of exudate
5- in male it make urgency and irritation of urethra and infertility and little exudate
6- Diagnosis of T.vaginalis
1- Swap from the wall of the vagina

8
2- Semen analysis
7- Infection route ::
1- sexual way ( portal of entry is genitalia )
2- close contact to the patient
3- toilet
4- clothes
8- diagnostic and infected stage is trophozoite
9- The treatment of T.vaginalis:
1- metronidazole
2- tinidazole
Parasite5:
Trypanosoma
#T. gambiense:
1- located in Africa
2- morphology of the trypomastigoid :
1-pointed anteriorly
2- centered elongated nucleus
3- kinetoplast ( posterior)
4- flagella ( anterior)
5- undulating membrane
6- length 15-30 microns
7- elongated and fusiform shape
3- life cycle :: from the biological vector (glossina tse tse fly {reveriena type}) to human
4- acute form (trypomasigoid) present in blood, lymph, bone marrow
5- chronic form present in C.S.F because it affect the C.N.S
6- it is ( anterior station ) because it multiple in the salivary gland of the insect
7- morphology of the epimastigoid : is the same as morphology of the trypomastigoid except ::
kinetoplast become anterior to the nucleus

9
8- trypomastigoid located in human but epimastigoid located in insect and it found intracellular in
human ( we can see the epimastigoid in the insect and culture)
9- the culture is 3N media
10- infective stage :: metacyclic trypomastigoid { epimastigoid } that present in the saliva of
insect and transmit to the human by bite
11- disease : it cause Gambian trypanosomasis or mid African sleeping sickness
12- Treatment : suramine ( I.V )
#T. cruzi:
1- present in America
2- morphology: is the same as morphology of the T. gambiense except :: kinetoplast become very
dominant ) (واضح جدا في الخلفand sometimes it become u or c shape
3- vector : reduvid bug ( Triatoma )
4- it is ( posterior station ) because it multiple in the hind gut of the bug and transmitted to
human by the feces of the bug
5- diagnosis :: blood examination
6- Route of infection : reduvid bug bite – blood transmission
7- infective stage : metacyclic trypomastigoid { epimastigoid }
7- diagnostic stage : Trypomastigoid in the blood – amastigoide in the tissues
8- habitat : Acute : blood
Chronic : heart and GIT
9- disease : it cause American trypanosomasis or chagas disease
10 treatment : Nitrofurane
:::::: مالحظات هامة:::::::
1- endemic : المرض موجود في منطقة معينة طوال السنة
2- epidemic : يأتي المرض على شكل موجة الى منطقة معينة ثم يذهب
3- pandemic : المرض ينتشر في كل أنحاء العالم
4- sleeping sickness is endemic in Africa and America
5- thin blood film is used in this lab ::: the RBCs are clear and the parasite located between them
and there are few WBCs

11
Parasite6:
Lishmania
1-hemoflagellate ( lishmania and trypanosoma ) have Amastigote , promastigote , epimastigote
and trypomastigote stages .
2- Lishmania :
-- L. Donovane. (kala azar, Visceral leishmaniasis)
-- L. Tropica. ( Oriental sore, Baghdad boil, cutanous leishmaniasis)
-- L. barazerliensis (cutanous leishmaniasis )
-- L . Mexicana ( cutanous leishmaniasis )
3- morphology of all Lishmania
1- Amastigote :: intracellutlar – round(ovale) – 2 to 4 microns – has nucleus and kinetoplast –
short internal flagellat – not motile
2- promastigote :: spindle - has nucleus and kinetoplast – short external flagellate – motile – 15
to 25 microns
5- diagnostic stage is Amastigote (( in skin or RES ))
6- infective stage is promastigote (( in the insect or the culture ))
7- life cycle :: transfer from man as amastigote to the vector(insect) then developed into
promastigote then transfer to man again
8- vector is sand-fly ( phlebotomas )
9- reservoir is man
10 – route of infection ::: skin bite – blood transmission – congenital(rare)
11- diagnosis :: 1- smear from the margin of ulcer ( see amastigote )
2- incubation in experimental animals
3- culture ( nnn media)
4- biopsy from ulcer
5- serological test ( PCR – skin test - ……… )
12- treatment : antimonials ( sodium stibogluconate )
13- habitat : in the RES ( liver – spleen – L.N – B.M ) and in skin
:: مالحظات
1
-
ال
amastigote
تكون صغيرة جدا جدا و تحتوي على غشاء رفيع جدا يحيط بها و
بالوسط يوجد نقطتان هما النواة والل
kinetoplast
2
-
ال
promastigote
تظهر احيانا على شكل وردة
rosette
3
-
اذا كانت ال
amastigote
موجودة
في ال
skin
فهذا يعني
L.Tropica
و اذا كانت
موجودة بال
spleen
فهذا يعني
other Lishmanias

11
Parasite7:
P.vivax
#P.vivax:
1- Plasmodium has two stages : -1- Vertebrate host---asexual cycle---schizogony
-2- Invertebrate host---sexual cycle---sporogony
2- schizogony divided into two stages :
-1- exoerythrocytic stage (hepatic stage)( in the liver ) (( not see in this lab ))
-2- erythrocytic stage ( in the RBCs ) (( see in this lab ))
3- infective stage is sporozoites which seen in the salivary gland of the insect only
4- diagnostic stage of p.vivax is ameboid stage
5- why we see large RBCs in p.vivax infection ???? because
-1- the merosoite enter inside the RBCs and cause swelling of them
- 2- vivax infect reticulocyte (large immature RBC)
6- the cycle ( )نفس النظري-------
vivaxmerozoiteenter the RBCring stage formation of schuffiners dots(use for diagnosis of
vivax)active cytoplasm movementameboid stageimmature stage(nuclear division)mature
stage(cytoplasmic division )formation of 12-16 merozoite repeat the cycle or lead to formation
of gametocyte (female macrogametocyte and male microgametocyte)
7- vivax cause tertian fever ( every three day )
8- diagnosis by :
-1-thick blood film : to recognize the presence of parasite ( in lite infection
and in endemic area because it is easy and fast )
-2-thin blood film : to differentiate between species
-3-serodiagnosis
9- malaria only occur inside the cells (intracellular)
10- you can not see multiple un-sequential stages in the same slide
ال يمكن رؤية عدة مراحل غير متسلسلة في نفس الساليد
11- route of infection: bite of female anopheles mosquito - sometimes blood transfusion
12- habitat : liver – RBC
13- the stages :::>>>
-1- ring stage : one nucleus + schuffiners dots { pink or red color }
-2- ameboid stage : one nucleus + schuffiners dots + irregular cytoplasm

12
-3- immature stage : more than one nucleus + schuffiners dots + irregular cytoplasm
-4- mature stage : multiple nucleus with their cytoplasm + schuffiners dots
Parasite8:
P. malariae + P.falciparum
#P. malariae:
1- route of infection :: bite of female mosquito
2- it has no hypnozoite but p.vivax has hypnozoite
3- has dark brown to black malarian pigments
4- gametocyte are rounded
5- infective stage is sporozoites
6- diagnostic stage of p.malariae is band stage and rosette mature schzonite stage
7- it infect mature RBCs and the size of RBC still normal
8- the cycle:
malariaemerozoiteenter the RBCring stage (no schuffiners dots)(small and compact ring)
band stage (diagnostic stage) immature stage(nuclear division)mature stage(sometimes
has rosette shape with malarian pigment in the center and the merozoite around it) formation
of 6-10 merozoite repeat the cycle or lead to formation of gametocyte (female
macrogametocyte with compact nucleus and male microgametocyte with diffuse nucleus)
9- malariae cause quatrain malaria ( every four day )
10- diagnosis by :
-1-thick blood film : to recognize the presence of parasite ( in lite infection
and in endemic area because it is easy and fast )
-2-thin blood film : to differentiate between species
-3-serodiagnosis
11- malaria only occur inside the cells (intracellular)
12 - erythrocytic sch. Cycle in P. malariae take 72 hours but in P.vivax take 42 hour
13 - exoerythrocytic sch. Cycle in P. malariae take 2 weeks but in P.vivax take 10 day
14- the stages :::>>>
-1- ring stage : small compact ring + no schuffiners dots + normal size RBCs
-2- band stage : diagnostic
-3- mature stage : 6-10 merozoite + sometimes rosette
13
#P. falciparum:
1- cause Malignant tertian + Subtertian malaria
2- infect all types of RBCs
3- sometimes multiple infection in single RBC
4- sometimes the ring stage has two nucleus
5- in the peripheral blood see the ring and gametocyte only but in sever state we can see the
other stages
6- gametocyte crescent in shape ( diagnostic )
7- ring stage very small
8- mature schizonte has 8-32 merozoite
9- the stages :::>>>
-1- ring stage : very small
-2- gametocyte : crescent shape
Parasite9:
Sexual cycle of malaria
1- definitive host :: female anopheles mosquito ---- the male feed on plants not blood
2- intermediate host :: human
3- infective stage of all malaria :: sporozoite (present in the saliva of female anopheles mosquito )
4- the sexual cycle occur in the mosquito as follow ::: the mosquito bite the skin of infected human
and take all stages of malaria inside the blood but all these stages are digested in the small intestine
of the mosquito except the gametocyte which form the zygote and after one hour the zygote form
the ookenite then it go to the gut of the mosquito to form the oocyst which go below the basement
membrane of the gut and increase in number and make nuclear division then rapture and release
the sporozoite which go to the body cavity then to the salivary gland then go to other human by
bite of the skin to repeat the asexual cycle in the human
5- sexual cycle ( sporogony ) in the female anopheles mosquito
6- asexual cycle ( schizogony ) in human
7- the slides :::
-1- oocyst :: 50 microns ,, spherical ,, in the intestine of mosquito
-2- ookinete :: small ,, motile(the zygote is immotile) ,, contain vacuoles ,, central
nucleus ,, anterior pointed end ,, posterior rounded end
-3- sporozoite:: elongated spindle shape ,, motile ,,central nucleus ,,10-15 micron

14
The differences between the sporozoite and the gametocyte of P. falciparum :::
Sporozoite gametocyte of P. falciparum
Larger smaller
Without RBCs with RBCs
Contain vacuoles no vacuoles
Central nucleus elongated nucleus
Note :: هام لإلمتحان
1- p.malariae ::: low degree of movement so it form band stage
2- p.vivax ::: high degree of movement so it form amoeboid stage
P.vivax Benign tertian malaria
P.malariae Quartan malaria
P.falciparum Malignant tertian malaria ( Subtertian malaria )
P.ovale ovale tertian malaria ( Benign tertian malaria )
#Drugs used in treatment and prevention of malaria:
1. Quinine
2. Chloroquine
3. Sulfadoxine + pyrimethamine (fansidar)
4. Primaquine
5. Mefloquine
6. Proguanil
Parasite10:
B.coli + Toxoplasma
#Balantidium coli:
1- risk group :: farmers and people deals with farm product directly
2- Morphology ::
Trophozoite
Cyst
50-200 micron
{largest protozoa infect man}
40-50 micron
Oval or bag shape
Spherical shape
Ciliated
Ciliated
Has phagosome
No phagosme

15
Kidney shape macro-nucleus
Kidney shape macro-nucleus
spherical shape micro-nucleus
spherical shape micro-nucleus
Retractile food vacuoles
Retractile food vacuoles
No wall
Thick cyst wall
3- B.coli present mainly in pigs and can be present in cattle
4- rare in our society
5- route of infection :: contaminated food and water from the farm by oral route
6- B.coli is the only ciliated parasite that infect human
7- the cyst contain thick wall for resistance of environmental factors
8- habitat :: large intestine of man and animals ( mainly cecum )
9- diagnostic stage : cyst +/- trophozoite
10- infective stage : cyst
11- animals are reservoir for B.coli
12- it cause dysentery like that of E.histolytica but can not cause extra-intestinal disease
13- it cause acute illness in man but lead to death if it cause perforation of large intestine and the
normal flora of the large intestine invade the peritoneum and cause acute abdomen
14- stool examination for cyst and trophozoite but in E.histolytica we see trophozoite
15- treatment :: tetracycline
16- under the microscope we see:: 1-foad vacuoles 2- macronucleus 3- micronucleus
#Toxoplasma gondii:
1- common disease in our society ( 40% to 50 % of people affected )
2- it is a benign parasite in immune-competent people but can cause death in immune-deficient
people and in fetus
3- toxoplasma is intracellular parasite so it is more resistance to drug and cause more sever
disease than extracellular parasite
4- tachyzoit :: present in the blood ,, has apecomplexia that is important receptor for the target
cells + nucleus
5- bradyzoite :: present in skeletal mucles and C.N.S and it affect any nucleated tissue ,, it present
in the tissue cyst
6- oocyst :: oval shape ,, two sporocyst ( each contain 4 sporozoite )
7- acute phase of disease caused by tachyzoite (7-20 days of parasitemia )
8- chronic phase of disease caused by bradyzoite ( for years )
9- habitat : 1-tachyzoite in blood 2- bradyzoite in Skeletal M. and C.N.S
10- definitive host ::: cat

16
11- intermediate host :: man + any animal ( mammals – birds )
12- infective stage : all stages could be infective as follow :
Oocyst ingestion of contaminated food and water
Tissue stage ingestion of infected meat - organ transplantation
Tachyzoite raw goat milk – blood transfusion – congenital
13- diagnosis :: the best diagnosis is serological tests and it is the only test used in clinical
diagnosis
14- it cause abortion and congenital anomalies in fetus if the mother infected during the
pregnancy of before it for short time
15- treatment :: spiromycin – pyrimethamine
Parasite11:
Ascaris + enterobius
#Ascaris lumbricoides : ( roundworm ---- nematode ):
1- Largest nematode :::: 35cm
2- Adult females about 20 to 35 cm. long ….. Adult male about 15 to 30 cm. long
3- morphology ::: from the lecture
4- life cycle :: من محاضرة النظري ولكن الهام في العملي هي النقاط التالية
1- habitat :: small intestine (in duodenum)
2- diagnostic stage :: egg pass in stool (contain non mature embryo )
3- Infective stage :: egg in soil ( contain second stage larva )
4- route of infection :: oral route (( contaminated food-drink-hand-vegetables ))
5- why larva rapture the capillaries in the lung ??? the diameter of larva is 0.02 mm and the
diameter of capillaries is 0.01 so larva rapture the capillaries and go through the bronchial tree to
the pharynx and swallowed again.
6- it take 2 to 2.5 months from infection to adult stage under optimum conditions
7- symptoms : loss of appetite , fever , wheezing , vomiting , dyspnea , abdominal pain ,
abdominal swelling , diarrhea .
8- very dangerous in children lead to intestinal obstruction
9- diagnosis :: 1- stool examination for egg (( round or oval ,, albumin layer in the wall
Hyaline layer in the wall ,, non-mature embryo,, corticated))
2- worm in the stool or vomit
3- larva in gastric or respiratory secretions
4- eosinophilia ( blood count )
10 – treatment :: mebensazol – albensazol

17
#Enterobius vermicularis (threadworm - seat worm - pinworm Oxyuris
vermicularis ):
1- The adult female has a sharply pointed posterior end, is 8 to 13 millimeters long
2- The adult male is smaller, measuring 2 to 5 millimeters long , and it has a curved posterior end
(( we should differentiate between male and female ))
3- diagnostic characters of it :::: the esophageal bulb in adult and D shape egg
4- the uterus in female is full with eggs
5- habitat :: cecum and adjacent parts of small and large intestine
6- it need air and low temperature so it go to the perianal region during night
7- when it reach the perianal region it take 4 to 6 hours to become infective (egg containing larva
)
8- group at risk :::: children
9- source of infection (( contaminated food , drink ,hand ………..))
10 – route of infection : -1- oral route -2- retro-infection -3- inhalation of the eggs
11- diagnosis :: 1- scotch test 90%
2- stool examination 5%
3- self-diagnosis
12- diagnostic stage :: egg (contain non mature embryo )
13 - Infective stage :: egg ( contain larva )
#Important:
1- Ascaris :::: --- larva in the lung
--- adult ( male and female ) in the specimen
--- egg (( round or oval ,, albumin layer in the wall
Hyaline layer in the wall ,, contain larva,, corticated))
2- Enterobius ::: --- adult female (( larger – pointed posterior end – uterus full of egg -
esophageal bulb ))
--- adult male (( smaller – curved posterior end -- esophageal bulb ))
--- egg (( D-shape – contain larva – smooth surface – translucent
– thick outer shell ))

18
Parasite12:
A.duodenale + T.trichiura
#A.duodenale:
1-life cycle :: نفس النظريFilariform larva (( non feeding – 500 micron length ))
Rhabditiform larva (( feeding ))
2- habitat :duodenum
3- route of infection :: -- penetration of the skin -- contaminated food and drink
4- infective stage : Filariform larva
5- diagnostic stage : egg contain undeveloped embryo in stool or adult worm
6- morphology : 1- Adult female is about 9-13 mm
2- The male is smaller than female 8-10 mm
3- The anterior end have buccal capsule armed with two ventral pairs
of teeth.
4- The posterior end of the male has copulatory bursa to attach the
female during the copulation, females have simple conical tail
7- morphology of egg ( )ال يوجد ساليد
oval shape
50 micron
outer thick shell
inner translucent shell
colorless
segmented to 4-8 blastomeres
8- clinical picture
) (نفس النظريin the late stage it cause anemia because it suck the blood by the
pairs of teeth - it cause 0.25 ml/worm/day of blood ) (هام
9- diagnosis :: stool examination (( see egg and adult worm ))
10 – treatment : Mebendazole – Albendazole
#T.trichiura:
1- habitat : large intestine ( cecum and ascending colon )
2- life cycle : بالنظري
3- infective stage : developed egg ( contain larva )
4- diagnostic stage : egg in stool + adult
19
5- route of infection : feco-oral route
6- morphology : 1- female : 40-50 micron + anterior part like whip
2- male : 30-45 micron + anterior part like whip
3- posterior end : thick contain sex organ and intestine in female
pointed in male curved
7- morphology of egg ( )هام جدا1- lemon or barrel shape
2- 60 micron
3- two bulging ( protuberance )
4- outer shell
5- embryo
8- clinical picture ) (نفس النظريit cause anemia 0.005 ml/worm/day of blood )ماه(
9- diagnosis ::
stool examination (( see egg and adult worm ))
proctoscopy in rectal prolapse
10 - treatment : Mebendazole – Albendazole
Parasite13:
Trichinella + wuchereria
#Trichinella spiralis:
1-life cycle :: swine eat uncooked garbage containing pork scraps adult worm in intestine of
swine larva encysted in striated muscles of swine , bear , walrus man eat raw or undercooked
park adult warm in man intestine produce larva larvae carried in blood stream to muscles and
other organs larvae encysted in striated muscles
2- larva survive only in skeletal muscles but in other locations will destroyed
3- larva with calcified capsule can be recognized by the eye not by X-ray
4- adult have spear ( )رمحprojection in the end of the mouth that allow deep penetration in the
muscles
5- the larva surround itself by cyst that developed in the skeletal muscles
6- man is the dead end of the cycle
7- it is intestinal nematode
8- man acquired the infection by ingest the infected meat which contain larva
9- infective stage larva
10- diagnostic stage First stage-larva in the nest cells

21
11- site : from duodenum to the end of intestine
12- female is viviparous that mean it give larva directly without egg ( in 2 days)
:::Note ::: oviparous give egg ---- viviparous give larva directly without egg
13- early stage of disease diarrhea
14- late stage of disease generalized muscle pain
15- muscles affected by this parasite :: diaphragm – deltoid – calf muscles – extraocular muscles
16- man is intermediate host ( because contain larva stage ) and definitive host ( because contain
adult stage ) …… pig ,dog ,cat and other animals also intermediate and definitive host ….. birds only
definitive hosts………………man also act as harbor .
17- diagnosis the best method is muscle biopsy (100% result)….. other methods : serological
test(ELISSA) , skin test and see larva by naked eye ( adult male and female rarely seen )
18- treatment barbiturate – corticosteroids – thiabendazole
#
Wuchereria bancrofti:
1- habitat large lymph vessels and lymph nodes
2- female : 8-10 cm …. Larger than male
3- human acquired the infection by bite of all species of mosquito … most common species are :
culex , aedes and anophyles
4- life cycle : female lay microfilariae in the lymphatic of man microfilariae penetrate the lymphatic
and migrate to the blood vessels and enter the circulation microfilariae ingested by mosquito
microfilariae penetrate the small intestine of mosquito then migrate to the thoracic muscles where
they develop infective larva in the proboscis of the mosquito larva deposited on skin near bite
of mosquito go to blood larva enter lymphatic and developed to adult ( from 6 months to 1
year )
5- infective stage larva from mosquito (filariform larva L3)
6- diagnostic stage microfilariae
7- microfilariae = prelarval stage ( the number of microfilariae in night is 3 times more than day )
in the day the microfilariae go to the pulmonary and in night it go to the blood
8- female are viviparous
9- first stage asymptomatic
10 –second stage go to lymph nodes of lower limbs and external genitalia cause lymphangitis
and cause elephantiasis
11- after death of Wuchereria bancrofti it also cause disease by its toxin
::: note ::: microfilariae present in the blood of human then converted to larva in the mosquito then
to adult worm in the human (( human is definitive host ))

21
12- diagnosis : 1- blood film ( taken at night because number of microfilariae is
increased )
2- blood centrifuge ( if blood film is negative )
3- calcified cyst seen by naked eye
Parasite14:
Taenia saginata
#Cestode
( )بشكل عام: morphology of adult (( head(scolex) – short neck – mature segment –
immature segment – gravid segment ))
#Taenia saginata:
1- cause Taeniasis (beef tapeworm infection)
2-life cycle :: adult in small intestine embroynated egg after few weeks egg in stool ( or gravid
segment in the stool ) egg hatch into larva (oncosphere) in the intestine and penetrate intestinal
wall oncosphere in the muscles and other tissues after 3 months oncosphere developed into
cysticorcus bovis in the muscles cysticorcus bovis eaten by man (in insufficiency cooked beef )
scolex attach to mucosa of small intestine and developed into adult worm after 2-3 months
adult in small intestine repeat the cycle
3- habitat : small intestine (jejunum)
4- route of infection : mouth ( eating infected meat )
5- infective stage : cysticorcus bovis
6- source of infective stage : tongue of animals (cattle) that contain cysticorcus bovis and it
prevented by good cooking and deep freezing
7- cysticorcus bovis enter the body as invagenated scolex then converted to evagenated scolex that
attach to the small intestine .
8- evagenated scolex only in human
9- invagenated scolex in cattle and animals
10- definitive host : human
11- intermediate host : cattle , cow , ……..
12- Diagnosis : stool examination ( see egg , gravid segment )
13- clinical picture : abdominal pain , nausea , vomiting , intestinal obstruction and appendicitis
14- treatment : niclosmide

22
15- morphology :
A- Adult : 1- white-gray color
2- (5-6) meter long
3- head contain 4 suckers without rostelum and without niclaic
4- scolex --- a: invagenated : scolex inside the cyst ( )غير موجود بالمختبر
b: evagenated : scolex outside the cyst ( )موجود بالمختبر
5- mature segment : two lobe of ovary – uterus – testes
6- immature segment
7- gravid segment : uterus contain eggs – 15-30 uterine branches
B- Egg : 1- small size (30-40M)
2- spherical or oval shape
3- covered by thick outer sheath
4- contain hexacanth embryo
5- have 6 hooklets
6- radially straight wall
Parasite15:
Taenia solium
#Taenia solium:
((
pork tapeworm ))
1- habitat : small intestine (jejunum)
2- definitive host : man only
3- intermediate host : pig , man , sometimes dog and other animals
4- human can be intermediate host for T.solium , but only definitive host for T.saginata
5- human become intermediate host by the following ways :
1- Peristalsis in opposite side : regurgitation of the egg to the stomach Hcl intestine
bile release of oncosphere(larva) {{autoinfection}}
2- Human is carrier of adult poor hygiene egg will contaminate the food (self infection )
3- Restaurants workers poor hygiene egg will contaminate the food
6- route of infection for man and animals : oral route

23
7- infective stage to animals : egg
8- infective stage to man : cysticercus cellulose in pork meat
9- life cycle :: adult in small intestine of man emberyonated egg+ segments in feces egg and
gravid segment on soil eaten by swine or (man ) larva (oncosphere) hatch in the intestine
penetration of the wall go to blood carried by blood to other tissue cysticercus cellulose
eaten by man (raw or insufficiently cooked)evaginated scolex attach to mucosa adult in small
intestine of man
10-adult :: scolex + hooks + suckers + neck + gravid segment when gravid segment separate
from the body and go outside in feces so the egg will appear in the stool after the rapture of
gravid segment
11- Hcl of stomach + bile pigment => lead to rapture of cysticercus cellulose and release of larva
(oncosphere)
12- diagnosis : egg or gravid segment in stool
13- morphology :
1- Scolex : a- evaginated & invaginated
b- rostellum
c- double row of hooks
d- suckers
2- Gravid segment : 7-13 branch of uterus
3- Egg ( like the egg of T.saginata)
4- Mature segment: a- square shape (but T.saginata = rectangle shape)
b- accessory lobe between the uterus and the other lobe
T.saginatabi-lobed T.soliumtri-lobed
Parasite16:
Echinococcus granulosus
#Echinococcus granulosus:
1- It is the smallest tape warm can infect the human ( 8-9mm or 1cm length)
2- definitive host : dog and other canidae
3- intermediate host : human , sheep ,goats , swine and others
4- habitat : adult worm in the small intestine of dog (definitive host)
5- infective stage to man : egg in the feces of infected dog
6- infective stage to dog : larval or cystic stages in sheep
7- life cycle (( غير هامThe adult Echinococcus granulosus inhabit the upper part of small intestine
of the definitive hosts, dogs or other canids( cats, foxes and wolves). Gravid proglottids release

24
eggs that are passed in the feces as a diognostic stage for infected dogs These eggs are infective
stage to a suitable intermediate host (sheep, goat, cattle and man). After ingestion, the eggs
hatches in small intestine and releases an oncospher (emberyo) that penetrates the intestinal wall
and migrates through the circulatory system into various organs, especially the liver and lungs. In
these organs, the oncosphere develops into a hydatid cyst that enlarges gradually, producing
protoscolicis incide the cyst. The dogs ( definitive host )and other canids becomes infected by
ingesting the H. cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host. After ingestion, the scolex
evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa, and develop into adult stages in 30 to 80 days. ))
8- human is dead end of the cycle
9- oncosphere cause diseases in the human 70% in liver – 20% in lung – 10% other organs –
when reach the C.N.S it may lead to death
10- The disease called ( Hydatid disease (hydatidosis) ): Is caused by the larval stages (hydatid
cyst) ----> very common disease in Iraq ,Turkey, Syria and in country with sheep
11- This disease called belong to SOL (space occupying lesions ) this mean that the development
of disease depend on the organ which contain the hydatid cyst . and it differ from organ to another
( the parasite has no toxin )
12- Trauma and surgery lead to rapture of hydatid cyst inflammation and hypersensitivity
death of the patient
13- Diagnosis :
1. History of patients in endemic areas.
2. X-ray picture, detection of the cyst mass in organ.
3. Ultrasound scan - MRI - CT scan.
4. Biopsy not recommended before operation, but is essential to confirm
the diagnosis after surgical operation.
5. Serology tests (IHA- ELISA- PCR- Casoni skin test)
14- Treatment : surgical removal after 2 months of albendazole for shrinkage of cyst
15- morphology :
1— adult :
1
- head : contain scolex (piriform shape)+ 4 suckers + two rows of hooks +
rostellum (used to attach to intestinal mucosa )
2- Immature segment : small + not contain any differentiated organs
3- Mature segment : contain fully developed male and female sexual organs
4-Gravid segment : contain only uterus full with eggs.( 10-15 uterine branches)
2— hydatid cyst : ( size = 1cm and it may reach 50 cm )
1- Germinal layer: inner thin layer + cuboidal cells + it is primary layer of the
parasite + continuously produce protoscolecis .
2- Hyaline layer: non-nucleated + used to maintain the shape of hydatid cyst .

25
3- Fibrous tissue layer: thick + formed as a result of the defense mechanism in the
body against the hydatid cyst .
4- Outer host- tissue capsule: derived from the tissue that contain the hydatid cyst.
5- The sac : contain protoscolexs ( invagenated scolecs called hydatid sand )
3— egg :
1- Spherical
2- 35-45um in diameter .
3- Hexacanth Embryo centrally located .
4- Radially staited shell
Parasite17:
D.latum + H.nana
#Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm):
1- It is the largest human tapeworm 3-10 meters in length
2- definitive host : man , dog , cat
3- intermediate host : 1) first : freshwater crustacean (copepod)
2) Second : fresh water fish
4- habitat : small intestine ( jejunum – ilium )
5- infective stage to man : plerocercoid larvae
6- diagnostic stage to man : egg and gravid ( stool examination )
7- route of infection : eating raw or uncooked infected intermediate host fish
8- life cycle (( غير هامThe adults of D. latum attach to the mucosa of small intestine by scolex
immature eggs are passed in feces, after maturation the oncospheres develop into a coracidia
larvae After ingestion of these larvae by a suitable freshwater crustacean (the copepod first
intermediate host) After ingestion of the copepod by a suitable second intermediate host(fresh
water fish) the procercoid larvae are released from the crustacean and they develop into a
plerocercoid larvae (sparganum) which is the infective stage to humans Humans can acquire
the disease by eating raw or uncooked infected intermediate host fish the plerocercoid develop
into mature adult tapeworms in the small intestine. Maturation of the parasites occurs within 20
days and the adult worm can release the eggs in the small intestine and pass with feces as a
diagnostic stage ))
9- morphology :
1- Scolex :
almond-shape - spoon-shape - deep
longitudinal grooves(dorsal and ventral) -
no hooks - 1-2mm
2- mature segments : broader than long - contain both male and female organs

26
3- it has 3000 segment
4- egg : oval in shape with operculum at one end
10- Clinical Features: abdominal discomfort – diarrhea – vomiting - weight loss - Vitamin B12
deficiency -intestinal obstruction.
#Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm):
1- It is the smallest human tapeworm 15 to 40 mm in length
2- definitive host : man , mice , cat
3- intermediate host : none
4- habitat : small intestine ( ilium )
5- infective stage to man : cysticercoids larva - egg
6- diagnostic stage to man : egg and gravid ( stool examination )
7- route of infection : oral route - arthropod bite - autoinfection
8- life cycle (( غير هامThe adult present in small intestine of human The eggs pass as a
diagnostic stage and are immediately infective when passed with the stool of patient If the
eggs are ingested by an arthropod intermediate host, they develop into cysticercoids
larva(Infective stage), which can infect humans or rodents (Difinitive hosts ) by ingestion and
develop into adults in the small intestine If the eggs are ingested with contaminated
hands,food or water from infected feces the oncospheres (hexacanth emberyo ) inside the eggs
are released and penetrate the intestinal villus and develop into cysticercoid larva,which rupture
the villus, then return to the intestinal lumen, and develp into adult worm which attached to the
intestinal mucosa and develop into adults and start producing gravid proglottids ))
9- morphology :
1- Scolex :
1-2 mm - 4 suckers – one row of hooks – rectictile rostellum
2- mature segments : broader than long - contain both male and female reproductive
organs
3- neck
4- it has 200 segment
5- gravid segment : uterus with eggs
10- Clinical Features: weakness – headaches – anorexia - abdominal pain – diarrhea
Treatment : 1- Praziquantel is the drug of choice for Hymenolepis nana
2- Niclosamide is the drug of choice for Diphyllobothrium latum

27
Parasite18:
Schistosoma haematobium
#Trematodes:
Intestinal flukes Heterophyes heterophyes
Liver flukes Fasciola hepatica
Pulmonary flukes Paragonimus westermani
Blood flukes Schistosoma
#Schistosoma haematobium:
1- definitive host : man
2- intermediate host : snail bulinus
3- habitat : vesical plexus (veins) around the bladder
4- infective stage to man : cercaria
5- diagnostic stage to man : egg ( urine examination )
6- route of infection : skin penetration - oral route
7- life cycle (( غير هامadult in the intestine of man embryonated egg in small intestine
embryonated egg pass into lumen of bladder , out with urine into water Miracardium haches
from egg , penetrate snail in the snail mother sporocyst daughter sporocyst cercaria cercaria
leave snail into water cercaria penetrate skin of man carried by blood to the heart lungs
heart portal vessels immature worm become mature worm migrate back to vesical
veins repeat the cycle ))
8- morphology :
Adult :
1- Have separate sexes ( male and female )
2- Elongated parasite , leaf shape
3- Anteriorly it is attached to the host by ventral suckers
4- Female : longer – narrower – smooth body
5- Male : shorter – wider – body has granulations – folded body
6- They have oral and ventral suckers – mouth – pharynx - esophagus – intestine
7- The intestine end in blind loop
8- Black color of worm body due to digestion of blood
9- GIT : have two branches that fuse to make one canal
10- Male : have 3-5 testes opposite to ventral suckers
11- Female : has ovary infront of the reunion of intestine
( ovary located posteriorly – red color )
12- Female : from ovary to the end of the body there are vitellaire glands

28
Egg :
1- Oval
2- Large
3- No operculum
4- Contain fully developed Miracardium
5- Have terminal spine
Miracardium:
1. Swim very rapid searching for snails
2. Covered by cilia
Cerearia :
1. Bifurcated tail
2. Has body
3. After penetration of skin , it will lose its tail
4. Could enter through mouth or skin
9 – Symptoms : Cough &hemoptysis - Febrile reaction - Eosinophilia - Terminal hematuria -
Dysuria - frequency of micturition - Suprapubic pain - pyurea
10 - Diagnosis :
Urine examination ( see egg ----- do the test after exercise )
Biopsy
Clinical picture
Blood examination ( eosinophilia – increase WBC )
Hatching test (examination of eggs for viability )
Serological diagnosis
X-ray
UltraSound
Intradermal Skin test
11 - Treatment : Metrifonate – Niridazole – Praziquantel
Parasite19:
Schistosoma mansoni
1- definitive host : man
2- intermediate host : snail biomphalaria
3- habitat : mesenteric veins of man
4- infective stage to man :bifurcated tail cercaria (present in water)
5- diagnostic stage to man : egg ( stool examination )

29
6- route of infection : skin penetration (head only enter, but tail stay out) - oral route
7- life cycle (( غير هامadult in the mesenteric veins of man embryonated egg in small venule
embryonated egg pass into lumen of intestine , go out with stool Miracardium haches from egg
, penetrate snail in the snail mother sporocyst daughter sporocyst cercaria cercaria leave snail
into water cercaria penetrate skin of man carried by blood to the heart lungs heart
portal vessels immature worm become mature worm migrate back to mesenteric veins
repeat the cycle ))
((cercaria enter liver through the artery develop to adult leave the liver through the vein
go to intestine ))
8- morphology :
Adult :
13- Have separate sexes ( male and female )
14- Male ( oral suckers - ventral suckers - gynecophoric canal - 6-9 testes near the ventral
suckers )
15- Female ( ovary located anteriorly and it is pink in color ) in S.hematobium ovary located
posteriorly or in the middle
o S.hematobium female ovary
) قريبة من الجهة الغامقة ( بالنهاية
o S.mansoni female ovary
) قريبة من الجهة الفاتحة ( بالبداية
Egg :
6- Oval
7- Large
8- No operculum
9- Contain fully developed Miracardium
10- Have small , lateral spine
Miracardium:
3. Swim very rapid searching for snails
4. Covered by cilia
Cerearia :
5. Bifurcated tail
6. Has body
7. After penetration of skin , it will lose its tail
8. Could enter through mouth or skin
9 – Symptoms : pruritus - rashes - Cough &hemoptysis - fever - Eosinophilia - urticara - diarrhea -
dysentery - weight loss - hepatospleenomegaly - anemia - abdominal discomfort
10 - Diagnosis :
stool examination ( see egg ----- do the test after exercise )
liver Biopsy
Clinical picture
Hatching test (examination of eggs for viability – also use to check the following patients)

31
Serological diagnosis
Skin test
Sigmoidoscopy and biopsy
11 - Treatment : oxamniquine – Niridazole – Praziquantel
Parasite20:
F. hepatica + H. heterophyes
#Fasciola hepatica:
1- definitive host : man , sheep , cattle , ……..
2- intermediate host : snail lymnea
3- habitat : bile duct and biliary passages
4- infective stage to man : metacercaria (present in water vegitations)
5- diagnostic stage to man : egg ( stool examination )
6- route of infection : oral route ( eating uncooked watercress )
7- life cycle (( غير هامadult in biliary passages egg in stool miracidium in snail lymnea
sporocyst – radia – cercaria cercaria leave snail encyst as metacercaria on grass , watercress
eaten uncooked by man penetrate intestinal wall , liver capsule , biliary tree repeat the
cycle ))
8- morphology :
Adult :
16- Leaf shape with branched intestine , testes , vitallariae
17- Large ( 2-3 cm in length )
18- Has shoulders ( shouldered appearance )
19- Anteriorly wider than posteriorly
20- Oral , ventral suckers
21- Ovary
22- Short convoluted uterus ( with eggs )
Cerearia :
9. Not - bifurcated tail
10. Has body
9 – Symptoms : pruritus - fever - Eosinophilia - urticara – epigastric pain – jaundice –
hepatomegaly - cholangitis - biliary obstruction
10 - Diagnosis :
stool examination ( see egg )
duodenal aspirate
skin test
Serological diagnosis
11 - Treatment : bithionol

31
#Heterophyes heterophyes:
1- definitive host : man , cat , dog , animals that eat fish
2- intermediate host : first snail pirenella // second fish (mugil fish )
3- habitat : small intestine
4- infective stage to man : metacercaria (present on the scales , tail , gills , fins of fish)
5- diagnostic stage to man : egg fully empryonated ( stool examination )
6- route of infection : oral route ( eating uncooked fish )
7- life cycle (( غير هامadult in small intestine egg in stool fully empryonated first
intermediate host snail sporocyst , radia , cercaria cercaria encyst to metacercaria on scales ,
tail , gills , fins of mugil fish second intermediate host man eat raw fish metacercaria escape
become adult in week repeat the cycle )
8- morphology :
Adult :
1. Very small ( 1-2 mm )
2. Pyriform shape ( posterior end more rounded than anterior end )
3. Large oral sucker anteriorly
4. Large ventral sucker ( behind oral sucker )
5. Genital suckers ( behind and lateral to the ventral sucker)
6. 2 ovoid testes posteriorly
7. Ovary ( anterior to testes – oval shape – red color)
8. Polygonal Vitellarial glands ( posterior and lateral )
9. Intestine
10. Convoluted uterus ( with eggs )
Cerearia :
1. Not - bifurcated tail
2. Has body and head
9 – Symptoms : irritation - diarrhea - colicky pain - abdominal discomfort - tenderness -
eosinophilia
10 - Diagnosis :
stool examination ( see egg )
11 - Treatment : praziquantel
Parasite21:
Mosquito + sand-fly + fleas
#Mosquito:
1- only two are important Anopheles and Culex
2- morphology :

32
one pair of wings
three pairs of legs
head ( circular – one pair of eyes – contain proboscis and antennae and maxillary palp )
3- medical importance it is a vector for :
Malaria ( parasite )
Filariasis ( parasite )
Yellow fever + Denque ( viral disease )
Viral encephalitis
Anopheles male
Anopheles female
Culex male
Culex female
Hair
More hairy
Less hairy
More hairy
Less hairy
Antennae
Plumose
Pilose
Plumose
Pilose
Maxillary palps
End as club shape As long as proboscis Turned upward Short
#Sand-Fly:
1- only one is important phlebotomus papatassi
2- morphology :
one pair of wings ( V shape on resting position )
very hairy ( over all the body )
small ( 3 mm size )
yellowish in color
16 joined antennae ( with one long pair of antennae )
3- medical importance it is a vector for :
Leishmania ( barazilliasis – kala azar )
sand-fly fever ( viral )
bartonellosis ( bacillus disease )
#Fleas:
1- only one is important Siphonaptera
2- morphology :
small size ( 2 - 2.5 mm )
wingless
3-4 pairs of strong legs ( help the fleas to jump )
Compressed laterally
Mouth part and antennae are short
Small head
3- medical importance it is a vector for :
Plaque
Endemic typhus (( epidemic typhus transmitted by lice ))
Number of bacterial and viral diseases
33
Parasite22:
Sarcoptes scabiei + lice + Ticks
#Sarcoptes scabiei:
1- morphology:
Tow separated sex.
Oval in shape
Has mouth part
Gray-yellow color
Have dorsal bristles.
Four pairs of leg (tow anterior pair and tow posterior pair).
Larval stage (nymphs) has same morphology of adult except it has one posterior pair of
leg, in case of nymph develop to male only one stage will occur, but if nymph develop to
femal two stage will occur.
2- habitat : live in stratum corneum ( feed on keratinized cells – make tunnels in skin )
3- Life cycle :
Start
adult parasite make tunnels in the epidermis and eat the dead cells
mating of
adult male and female
give 50 eggs daily
eggs develop to larva
nymph
adult
repeat the cycle
female :: adult
egg
nymph 1
nymph 2
adult
male :: adult
egg
nymph
adult
4- diagnosis :
Clinically.
Scarping test. (( invasive scraping of the skin until bleeding ))
Ink test (easy & non invasive).
Laboratory test (very rare & invasive).
serology test are not found.
#Lice:
Head louse : pediculus humanus capitis
body louse : pediculus humanus corporis
pubic louse : phthirus pubis
Female
Male
0.4 mm
0.25 mm
Have long bristles
Have short bristles
Have cup like sucker in the anterior pair of leg
Have cup like sucker in anterior & posterior pair of leg

34
1- morphology :
small
ectoparasite
wingless
dorsoventrally flattened ( compressed dorsoventrally )
claw at the end of each leg ( 3 pairs of legs )
composed of head , thorax and abdomen
have mouth part ( adapted for piercing and sucking the blood from the host )
pubic louse compact body (abdomen plus thorax) + small size(0.25 mm) + large claw
on the legs so it called crab louse ( crab = ) سلطعون the claw help the lice to catch the
hair
2- area of isolation :
Head louse : found on scalp ( feed on human blood when need )
body louse : found on clothing ( feed on human blood when need )
pubic louse : found on pubic hair ( it is one of the major STDs )
lice present in crowded area and low hygiene ( handy cape -metal retarted patient )
3- clinical importance :
lead to bleeding
STD (pubic louse)
Body louse is vector for : Epidemic typhus – Relapsing fever – Trench fever
Head and pubic louse not vectors
#Ticks:
1- Hard ticks ( Ixodidae spp. )
Hard skeleton of keratinized material cover the body (in female 1/3 of the body is covered -
in male whole body is covered) this hard skeleton called scutum
Oval in shape
4 Pairs of legs
We can see mouth part from both dorsal and ventral surface
See it brown in color
2- soft ticks ( ornithodoros spp. )
Leather texture ( lack of scutum )
rounded in shape
4 Pairs of legs
Not see mouth part from dorsal surface
It is the biggest insect in low-power
35
3- ticks feed on blood ( it not need human blood but human affect accidentally )
4- clinical importance :
Neurotoxin : it is anesthetic material ( to prevent human from sense the bite )
More than 5 adult ticks produce neurotoxin will reach the C.N.S ( may lead to death ) …….
Sometimes lead to paralysis
Vector for :
1. Tularemia ( bacterial )
2. Hemorrhagic fever ( viral )
3. Babesia ( parasitic ) …… malaria like parasite that destroy the R.B.Cs
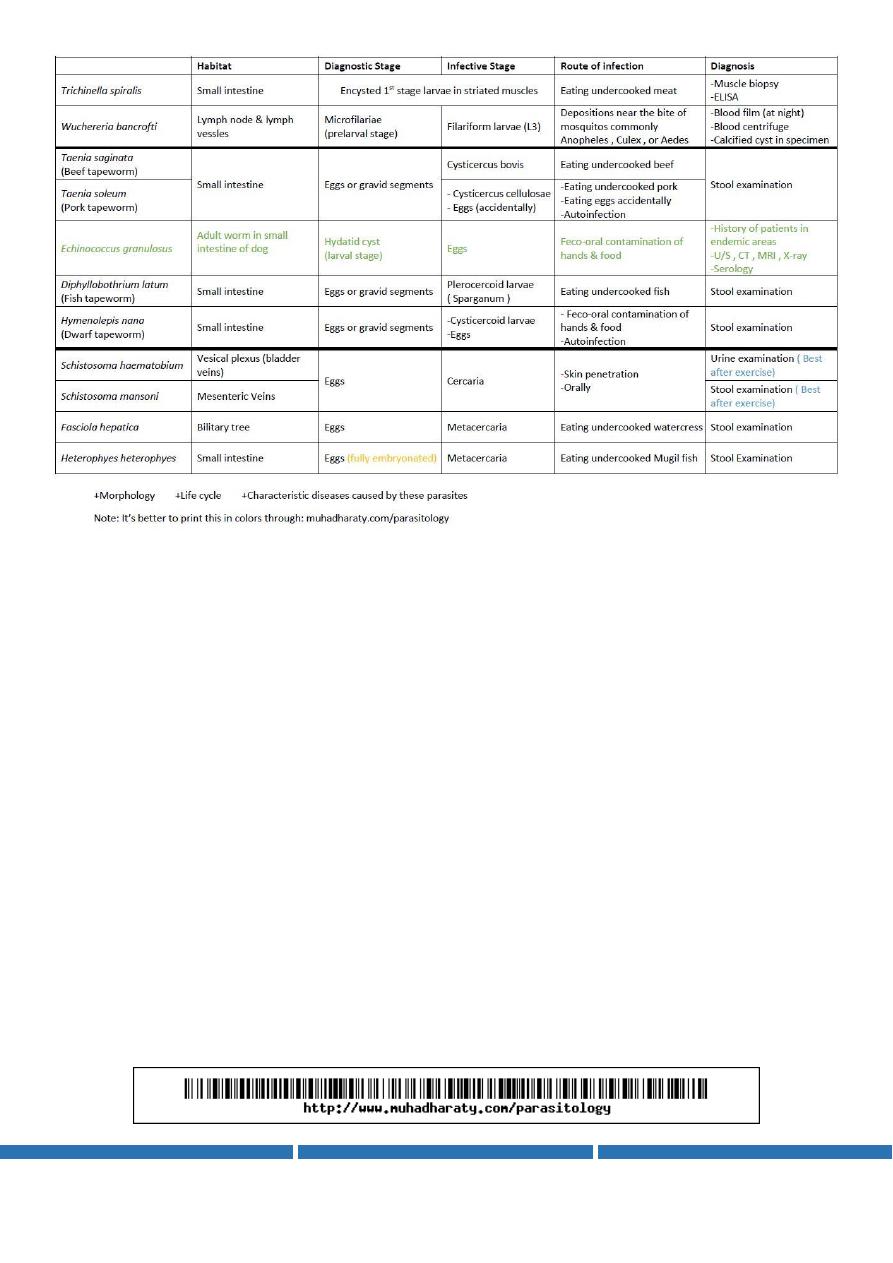
Summary:
By Ameer Saadallah
36
