Prematurity
Premature (preterm) baby:Birth before 37 completed weeks gestation. 8% of all births. Most problems seen in with infants born <32 completed weeks.
Predisposing factors:
-Idiopathic (40%).-Previous preterm birth.
-Multiple pregnancy.
-Maternal illness, e.g. chorioamnionitis, polyhydramnios, pre-
eclampsia,
-diabetes mellitus.
-Premature rupture of membranes.
-Uterine malformation or cervical incompetence.
-Placental disease, e.g. dysfunction, antepartum haemorrhage.
-Poor maternal health or socio-economic status
Complications of prematurity:
Respiratory: surfactant deficiency causing respiratory distresssyndrome, apnoea of prematurity, chronic lung disease / bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
CNS: intraventricular haemorrhage, periventricular leucomalacia;
retinopathy of prematurity.
GIT: necrotizing enterocolitis ,inability to suck, and poor milk
tolerance.Hypothermia.
Immuno-compromise resulting in recurrent infections.
Impaired fluid/electrolyte homeostasis skin water loss, poor renal function.
Patent ductus arteriosus.Anaemia of prematurity.
Jaundice liver enzyme immaturity.Birth trauma.
Perinatal hypoxia.Later: increased risk of adverse neurodevelopmental outcome,
behavioural problems and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Signs of prematurity:
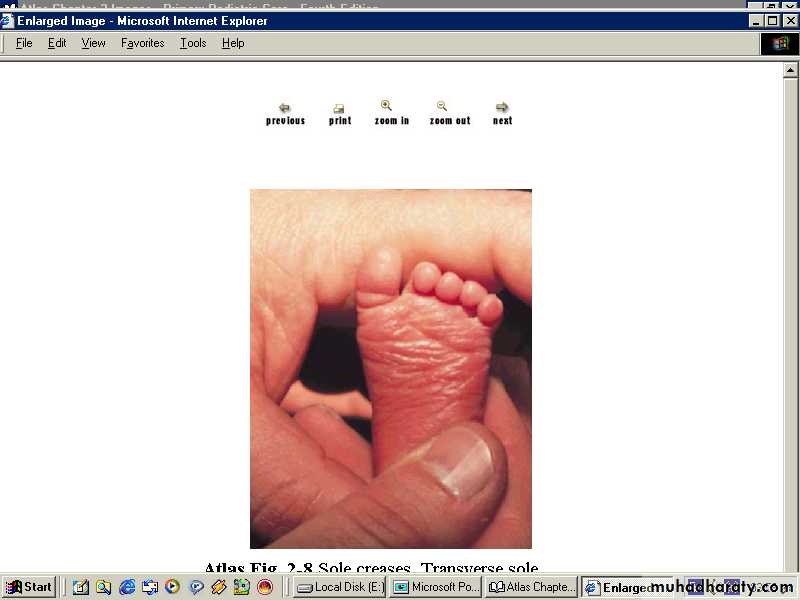
-Thin gelatinous skin and dark red in color.-Poorly developed breast tissue, no palpable breast tissue or it is flat
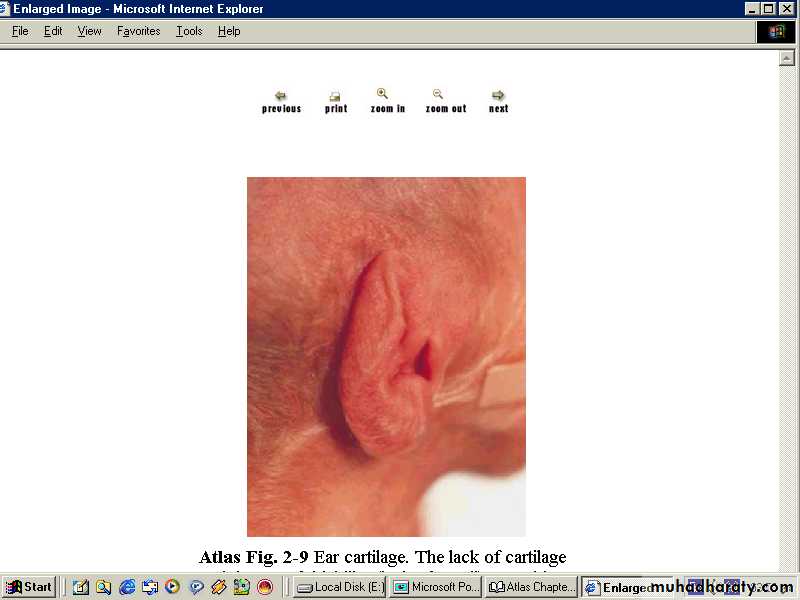
and less than 1cm in diameter.- The ear auricle is soft, no cartilage and there is slow or no recoil.
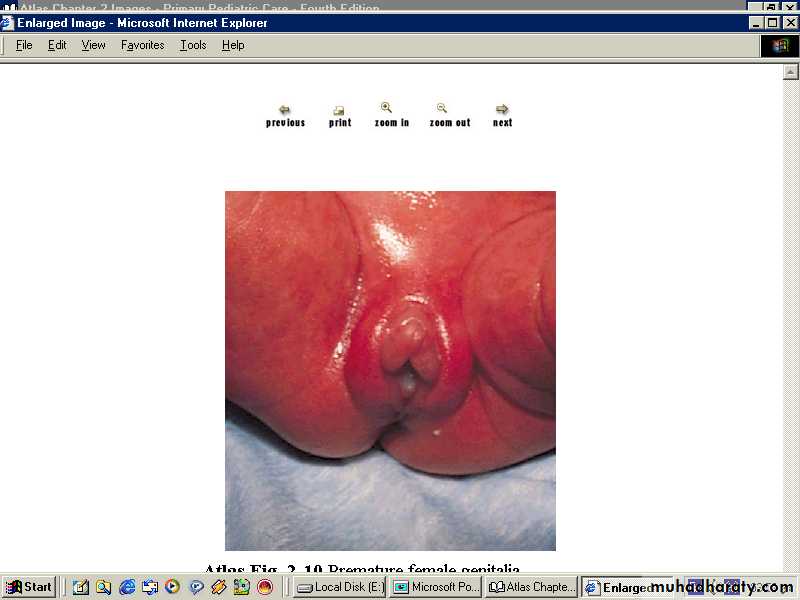
-soft auricle no cartilge slow recoil.-Genitalia:-
male: the testes are not descended in the scrotum and no creaseson the scrotum.
Female: labia majora are not covering completely labia minora.