
1
Fifth stage
Medicine
Lec-11
د . منوع
1/1/2014
Cancer Chemotherapy
Vinka alkaloids (animation and ADR)
•
Microtubule Synthesis animation
•
Inhibition of spindle function
ADR
• Severe neurotoxicity
– Paresthesias
– Loss of reflexes
– Foot drop
– Ataxia
–
VinBlastine
Uses ; (ABVD)
Hodgkin’s disease Lymphomas
Carcinoma Breast
Testicular tumors
Toxicity:
Bone marrow
suppression, anorexia,
nausea, vomiting &
Diarrhea, Alopecia
VinCristine (oncovan)
Uses: (MOPP)
Childhood leukemias
Childhood tumors-Wilm’s tumor, Neuroblastoma, Hodgkin’s disease
2
Toxicity:
Peripheral neuritis with
Paresthesia, Muscle weakness
***Vincristine has marrow sparing effect
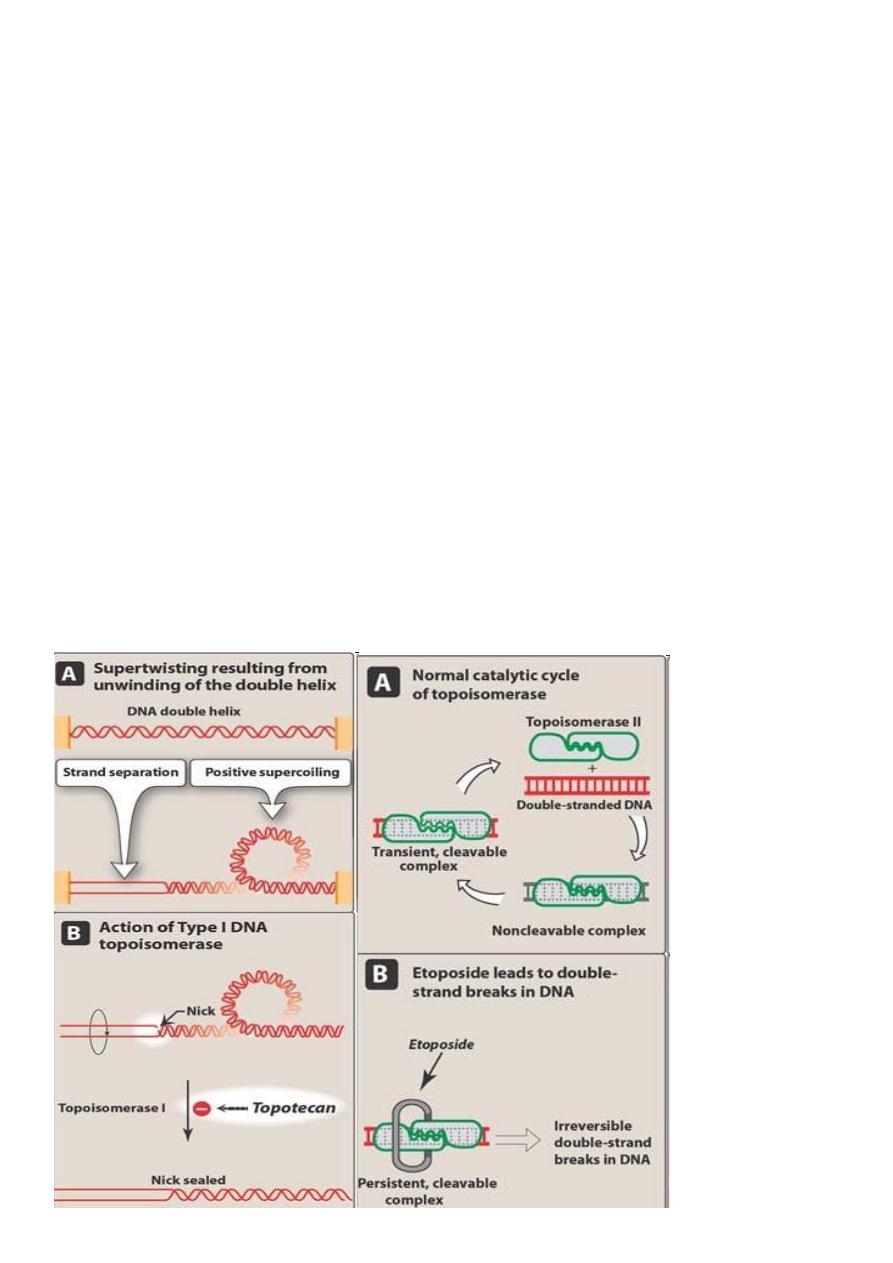
Etoposide & Teniposide
• Acts by inhibiting topoisomerase II
• These drugs are most active in late S and early G2 phase
• Used in combination Tx of small cell carcinoma of lung, prostrate and testicular
carcinomas
Other topoisomerase inhibitors:
• Topotecan, Irinotecan
– Both act by inhibiting topoisomerase-I
Topoisomerase inhibitors

3
Paclitaxel & Docetaxel
• These drugs act by interfering with mitotic spindle
• They prevent micotubule disassembly into tubulin monomers
•
ADR
• Neutropenia
• Peripheral neuropathy
Questions
• What is the diff between MOA of taxanes and Vinca alkaloids
• Which is the marrow sparing anticancer drug
• Topoisomerase-1 inhibitors
• Topoisomerase-2 inhibitors

4
Anticancer Antibiotics
• Anthracyclines:
– Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
– Daunorubicin
• Bleomysin
• Dactinomycin
• Mitomycin
Doxorubicin & Daunorubicin
• These drugs intercalate between base pairs, inhibit topoisomerase II and also generate
free radicals
• They block RNA and DNA synthesis and cause strand scission
• *These are CCNS drugs
• Used as a component in ABVD regimen in Hodgkin’s lymphoma
ADR
• Cardiac toxicity (due to generation of free radicals)
• Acute form: arrthythmias, ECG changes, pericarditis, myocarditis

5
• Chronic form: ***Dilated cardiomyopathy, heart failure
• ****Rx with dexrazoxane
– This is an inhibitor of iron mediated free radical generation
• Bone marrow depression, Total alopecia
• Radiation recall reaction
Bleomycin
• Acts through binding to DNA, which results in single and double strand breaks
following free radical formation and inhibition of DNA synthesis
• The DNA fragmentation is due to oxidation of a DNA-bleomycin-Fe(II) complex and
leads to chromosomal aberrations
• CCS drug that causes accumulation of cells in G
2
Uses
• ABVD regimen for Hodgkin’s
• Intracavitary therapy in ovarian and breast cancers (Sclerosing agent)
ADR
• ***Pulmonary fibrosis
Questions
• ADR of anthracyclines? (clinical symptoms)
• Why ADR with anthracyclines?
• How to treat it?
• ADR of bleomycin?

6
Hormonal agents
• Glucocorticoids
• Sex hormone antagonists
• GnRH analogs
• Aromatase inhibitors
Glucocorticoids (Prednisone)
• Because of their marked lympholytic action, they are used in acute leukemias and
lymphomas.
• Have anti-inflammatory effect
• Increase appetite
• Produce euphoria (feeling of well being)
• Increase body weight
• Suppress hypersensitivity reaction due to certain anticancer drugs
• Control hypercalcemia
• Control bleeding
• Have non-specific antipyretic effect
• Increase the antiemetic effect of ondansetron/granisetron/ metoclopramide
7
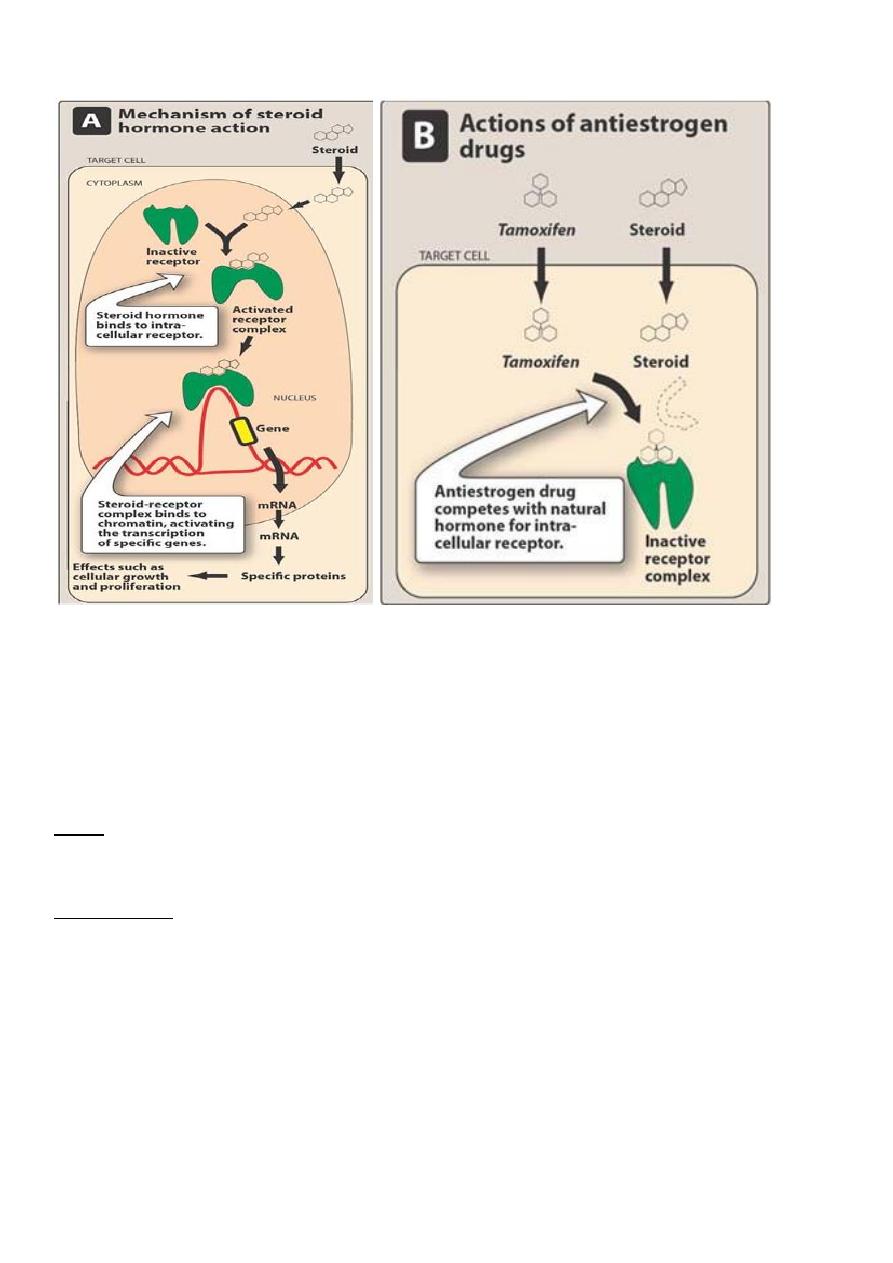
Sex hormone antagonists
Tamoxifen
• Blocks the binding of estrogen to receptors of estrogen sensitive cancer cells in bresat
tissue
• It is used in receptor positive breast carcinoma
• Also useful in progestin resistant endometrial carcinoma
ADR:
• Hot flushes, vaginal bleeding and venous thrombosis
Other drugs
• Flutamide: androgen receptor antagonist used in prostatic carconima
• ADR for flutamide includes: gynecomastia, hot flushes
8
MOA of drugs
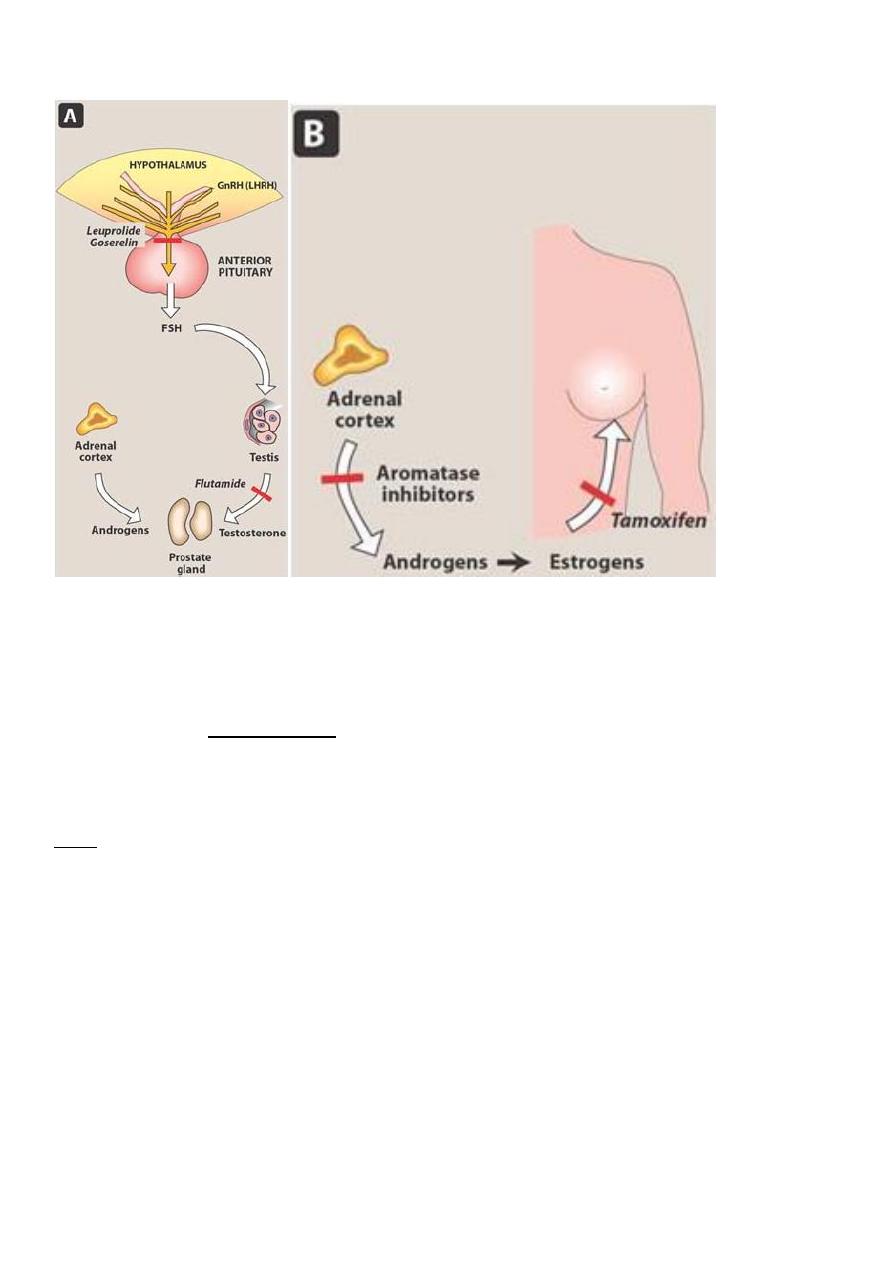
GnRH analogs
• Leuprolide, gosarelin and naferelin
• Effective in management of Prostatic carcinomas
• When given in constant doses they inhibit release of pituitary LH and FSH
• These drugs suppress gonadal function due to down regulation and desensitization of
Gn-RH receptors
ADR
• Leuprolide may cause gynecomastia, hematuria, impotence and testicular atrophy
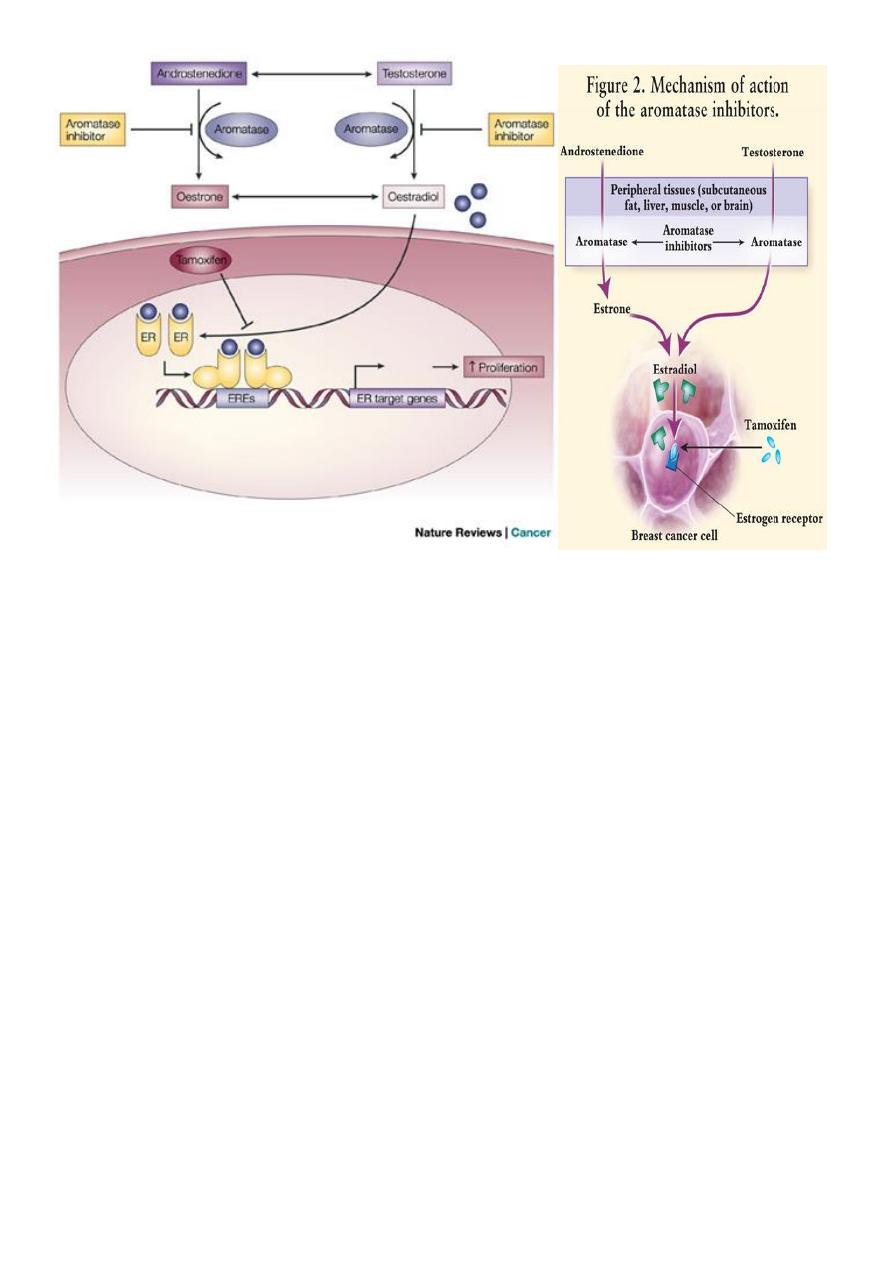
Aromatase inhibitors
• The aromatase reaction is responsible for the extra-adrenal synthesis of estrogen from
androstenedione
• This takes place in liver, fat, muscle, skin, and breast tissue, including breast
malignancies.
• Peripheral aromatization is an important source of estrogen in postmenopausal women.
• Aromatase inhibitors decrease the production of estrogen in these women.
9
• Anastrozole and Letrozole
• These drugs inhibit the aromatase enzyme
• ****Used in Tx of postmenopausal women with metastatic breast ca (1
st
line drug)
• ADR includes: bone pain and peripheral edema
Miscellaneous agents Asparaginase, imatinib, interferons, monoclonal
antibodies
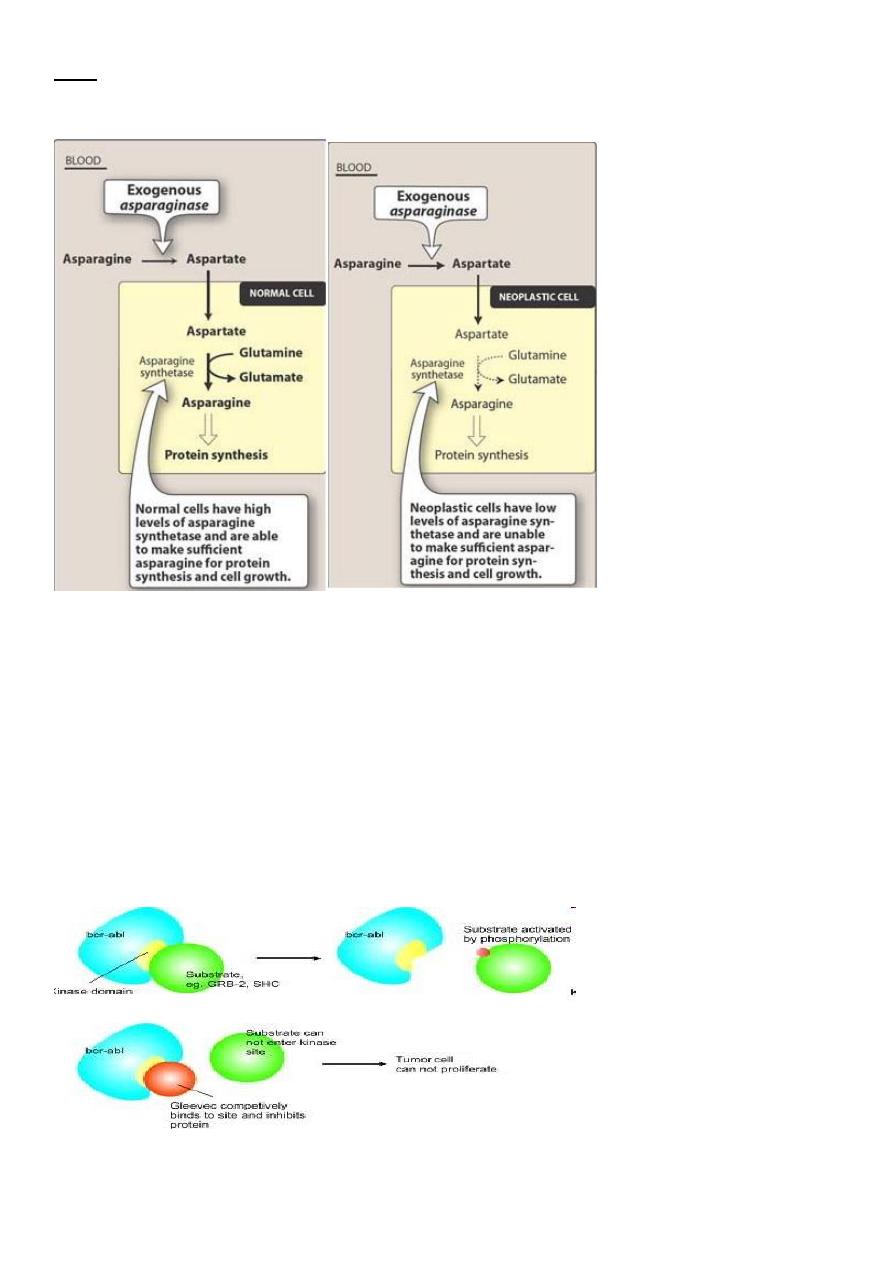
Asparaginase
• L-Asparaginase catalyzes the deamination of asparagine to aspartic acid and
ammonia.
• L-Asparaginase is used in combination therapy to treat childhood acute lymphocytic
leukemia
• Its mechanism of action is based on the fact that some neoplastic cells require an
external source of asparagine because of their limited capacity to synthesize
sufficient amounts of that amino acid to support growth and function.
• L-Asparaginase hydrolyzes blood asparagine and, thus, deprives the tumor cells of
this amino acid, which is needed for protein synthesis
11
ADR
• Acute pancreatitis*****
Imatinib
• Example of a drug, whose development was guided by knowledge of a specific
oncogene
• Used for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia
• Acts by inhibiting tyrosine kinase activity of the protein product of the Bcr-Abl
oncogene
• This gene is expressed in CML
MOA of imatinib

11
Interferons
• Human interferons have been classified into three types—α, β, and
—on the basis of
their antigenicity.
• The α interferons are primarily leukocytic, whereas the β and
interferons are produced
by connective tissue fibroblasts and T lymphocytes, respectively.
• Recombinant DNA techniques in bacteria have made it possible to produce two species
designated interferon-α-2a and -2b used in Tx of neoplastic diseases.
• ***Interferon-α-2a is presently approved for the management of hairy-cell leukemia,
chronic myeloid leukemia, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)–related
Kaposi sarcoma.
• ***Interferon-α-2b is approved for the treatment of hairy-cell leukemia, melanoma,
AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, and follicular lymphoma.
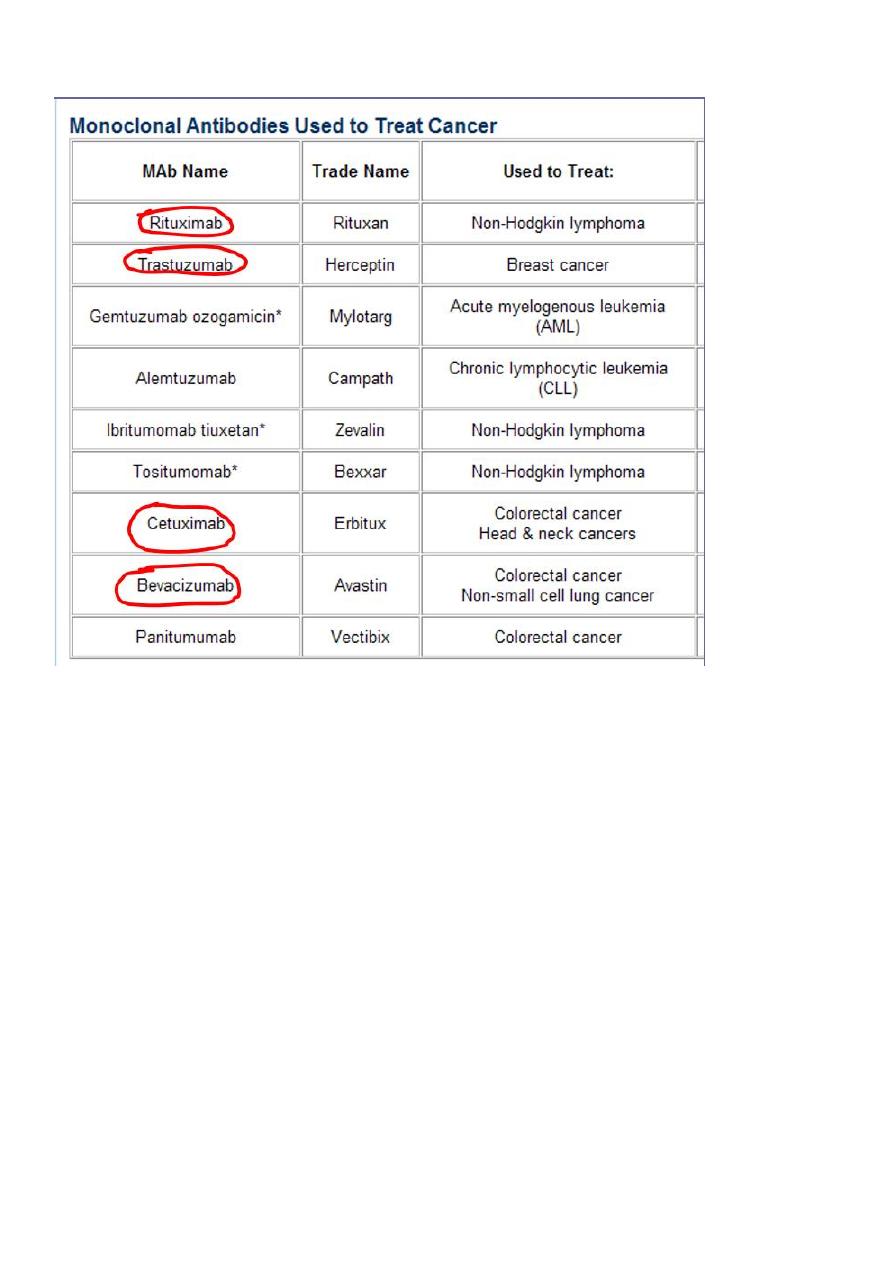
Monoclonal Antibodies
• They are created from B lymphocytes (from immunized mice or hamsters) fused with
“immortal” B-lymphocyte tumor cells.
• The resulting hybrid cells can be individually cloned, and each clone will produce
antibodies directed against a single antigen type.
• Recombinant technology has led to the creation of “humanized” antibodies that
overcome the immunologic problems previously observed following administration of
mouse (murine) antibodies.
• Currently, several monoclonal antibodies are available in the United States for the
treatment of cancer.
• Trastuzumab, rituximab, bevacizumab, and cetuximab
Trastuzumab
• In patients with metastatic breast cancer, overexpression of transmembrane human
epidermal growth factor–receptor protein 2 (HER2) is seen in 25 to 30 % of patients.
• Trastuzumab is a recombinant DNA–produced, humanized monoclonal antibody,
specifically targets the extracellular domain of the HER2 growth receptor that has
intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity.
• Trastuzumab binds to HER2 sites in breast cancer tissue and inhibits the proliferation of
cells that overexpress the HER2 protein, thereby decreasing the number of cells in the S
phase.
12
FDA approved MAb
Questions???
• What are Flutamide and Leuprolide and mention their uses?
• MOA of tamoxifen?
• MOA of anastrozole and letrozole?
– Important clinical indication for these drugs?
• Important ADR of L-asparaginase?
– Clinical symptoms of ADR (including lab)
• MOA and use of imatinib?
• MABs used in cancer chemotherapy (know four of them circled above)

13
Treatment of Specific cancers
Hodgkin’s disease:
• ABVD regimen (doxorubicin,bleomycin,vinblastine,dacarbazine)
• MOPP regimen (mechorethamine,vincristine,procarbazine,prednisone)
• NHL: CHOP regimen (cyclophosphamide,doxorubicin,vincristine,prednisone)
• Multiple myeloma : MP protocol (melphalan and prednisone)
Breast ca:
• CMF protocol (cyclophosphamide-MTX-fluorouracil)
• Tamoxifen
• Anastrozole, letrozole
