siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
1
The Joint
Objective :
Know :
*Definition of joint
*Structural &functional classification of the joints
*Features of synovial joint
*Types of synovial joint
The Joint
Joint or articulation is the site where two or more bones come together.
Joint is usually movable, but that is but many joints exhibit limited
movement ,and others are completely immovable.
o
:
Classification of joints
1-Functional classification
, based on degree of movement:
Synarthrosis----non-movable joint.
Amphiarthrosis-----slightly movable joint.
Diarthrosis ----freely movable joint.
o
2-Structural
classification
, based on the major connective tissue type
that
connect the bones together:
Fibrous joints
; Consists of 2 bones united by fibrous tissue,
exhibit little or no movement. It is subdivided into :
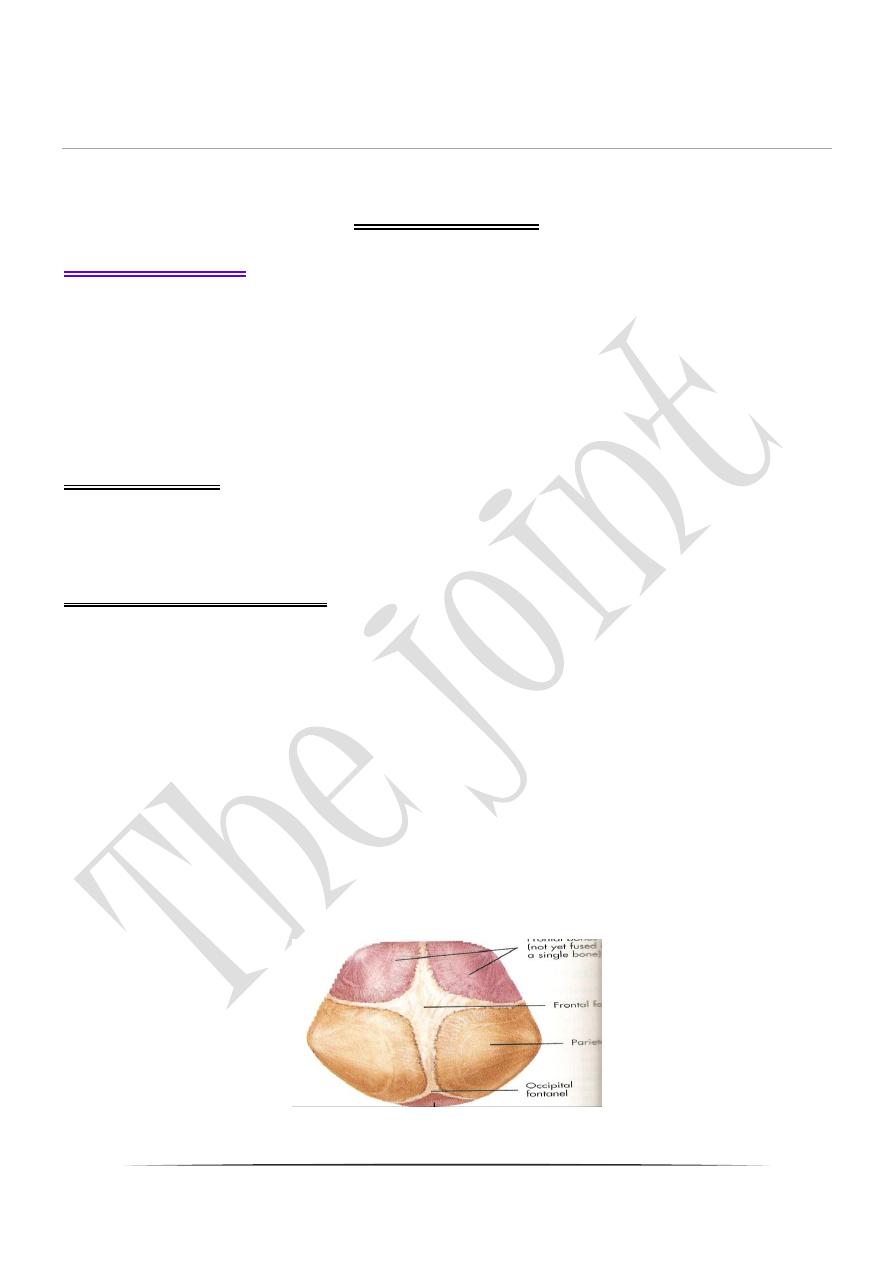
a-Sutures --- the bones are closely adjacent, and firmly
o
interlocking as in the flat bones of the skull.
o
siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
2
o
b-Syndesmosis--- bone are separated by some distance and held
together by ligaments. Little movement is possible as in distal
tibiofibular joint.
o
o
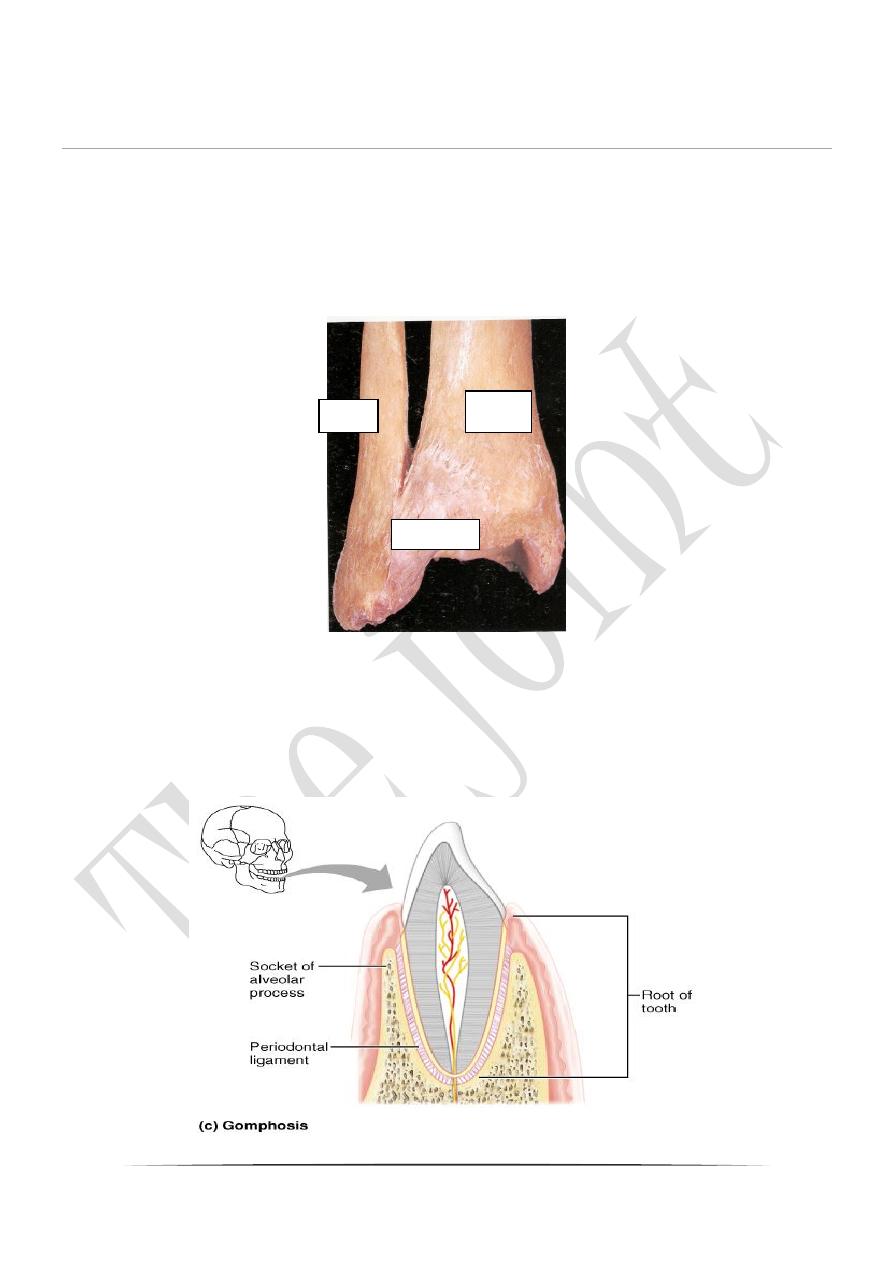
c-Gomphosis----consists of pegs fitted into sockets and held in place by
ligaments, as the joints between the teeth and the bone of the jaw.
aibi
fibul
a
Ligamen
t
ligament
siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
3
o
Cartilaginous joints
; the union of the bones by acartilage.Only
slight movement can occur. It is of two types:
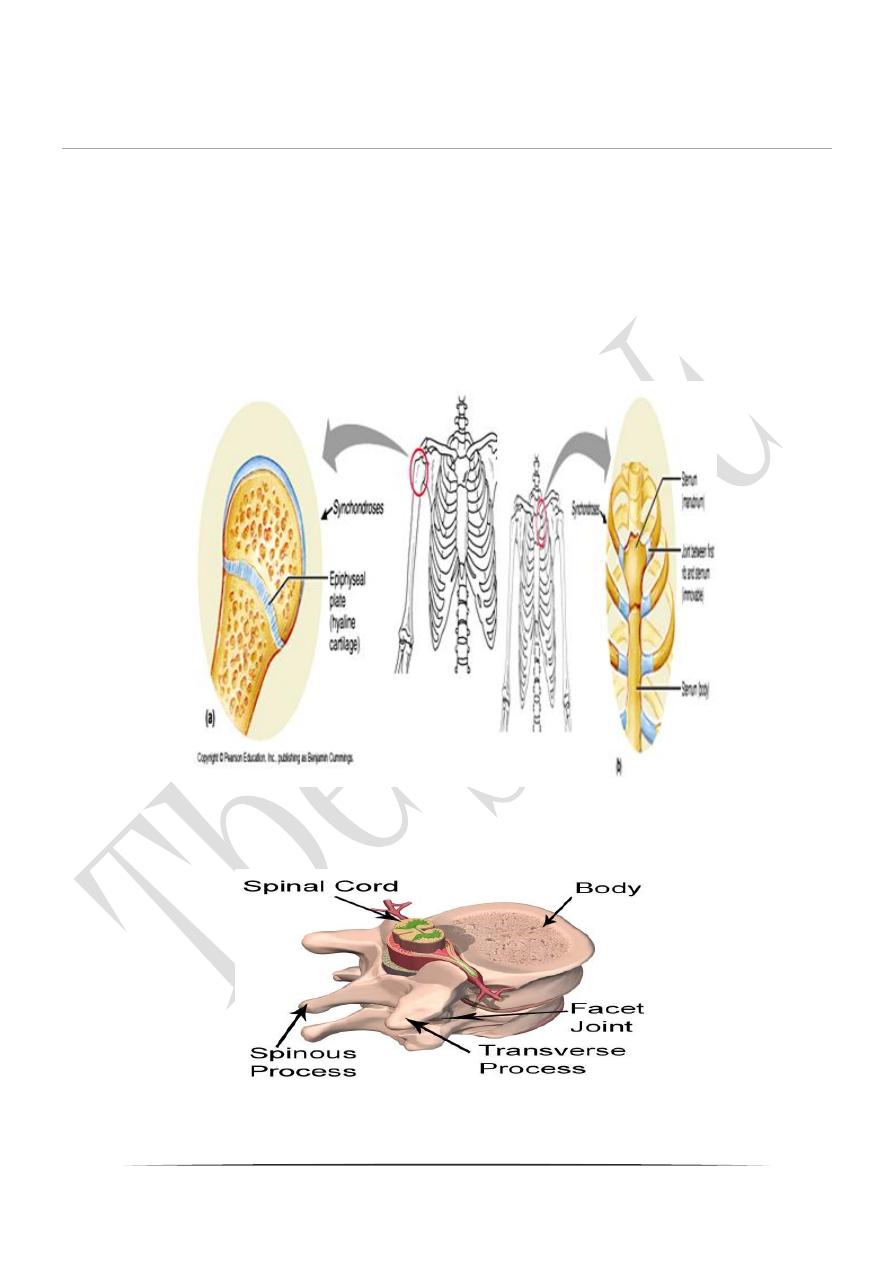
a- Synchondrosis ( primary )The two bones united by a cartilages ,only
slight movement can occur, as in the cartilages between the first rib
and maniburium sterni.
b-Symphysis ( secondary ); The bones are joined together by
fibrocartilage,which allow a limited movement, as in joint between
vertebral bodies and symphysis pubis.

siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
4
Synovial joints
;
freely movable joints that contain synovial fluid
in a cavity surrounding the end of articulating bones. Most joints that unit
the appendicular skeleton are Synovial, this reflects the greater mobility of
the appendicular skeleton compared to the axil skeleton. .
o
Features of synovial joints:
1.The articular surface is covered by articular cartilages which provides a
smooth surface .
2-presence of joint cavity which is filled by Synovial fluid. This fluid is a
complex mixture of polysaccharides, proteins fat, and cells, forming thin
lubricating film covering the articular surface. .
3.The cavity is enclosed by a joint capsule, which helps to hold bones
together.
4-A portion of the capsule thickened to form a ligaments.
5-Synovial membrane lines the cavity except the articular cartilages. This
membrane produces synovial fluid..
6-In some synovial joints the synovial membrane extend as a sac to form a
bursa close to the joint filled with fluid and slippery inner surface presents
between:
•
*two bones
o
•
* tendon and bone
o
•
*Ligament and bone
o
•
* muscle and bone
o
*skin and bone .
o
•
It acts to prevent friction between these structures during movement
of the adjacent joint.
o

siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
5
o
The synovial joint classified according to
Types of synovial joins:
the shape of the adjoining articular surface.
o
1-Gliding joints; two flat surfaces gliding on each other e.g. articular
process between vertebrae, joints between intercarpal bone, joints
between intertarsal bone
o
.
o
2-Saddle joint; two saddle-shaped articulating surfaces oriented at a right
angle on each other,e.g.is the joint between the carpal and metacarpal of
thumb.
siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
6
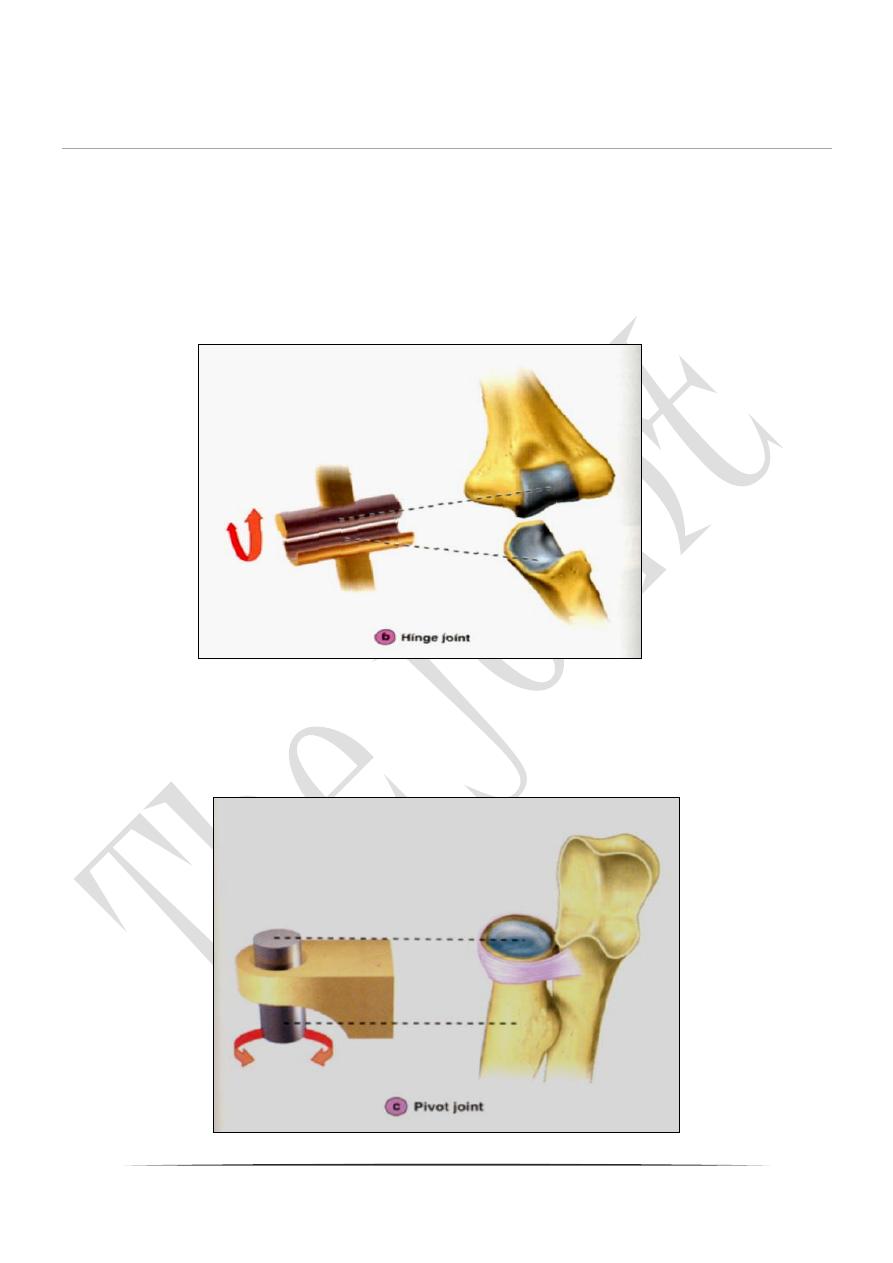
3-Hinge joint; at this joint the convexity of one bone applied on the
concavity of the others in the elbow, knee joints .
4-Pivot joints; Cylindrical bony process rotates with in a ring of bone and
ligaments as in rotation of axis vertebra against the atlas when shaking the
head, proximal radioulnar joint(head of radius rotates against the ulna).
siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
7
o
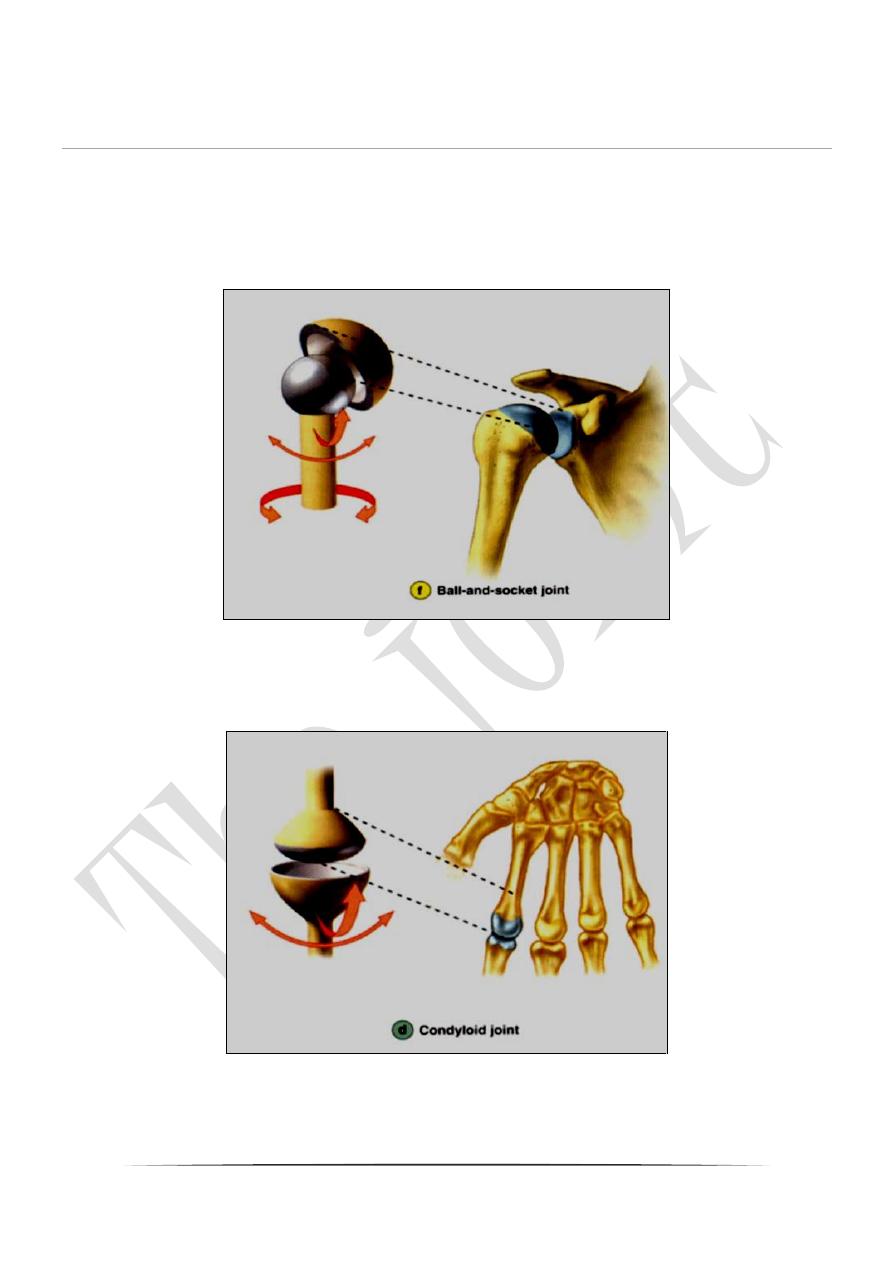
5-Ball and socket joints; a head of one bone fits into socket of other bone
as in shoulder and hip joint.
o
6-Ellipsoid or condyloid joints; are elongated ball and socket joint as in
the joint between the occipital condoyle of skull and atlas vertebra.
,metacarpal and phalanges.
o

siBa ouric la imoBcsi cisaB
oooooooooooooo
staoo arcB
rDd B nns H :rD
8
Biomechanical classification
Joints can also be classified based on their anatomy into:
*Simple Joint: 2 articulation surfaces (e,g.shoulder & hip joints )
* Compound Joint: 3 or more articulation surfaces (e.g. Radio carpal joint
* Complex Joint: 2 or more articulation surfaces and an articular disc or
meniscus (e.g. Knee joint )
