Anorectal malformationsDr.Bassam Alabbasi
Introduction:-Assurbanipal library: (when a woman bears a child whose anus is closed then the whole land will suffer the want of food).
- becoming less common.
-imperforate anus wrong name ? Most have fistulous connection.
- Correction is difficult :-
1- loss of relation to sphincter.
2- abnormal muscle development.
3- abnormal nerve supply.
Incidence:-
- About 1-3000 to 1-5000 live birth.- Males affected slightly more than female.
-high lesion =male/low lesion =female
- Most cases sporadically.
- Risk of inheritance only 1%.
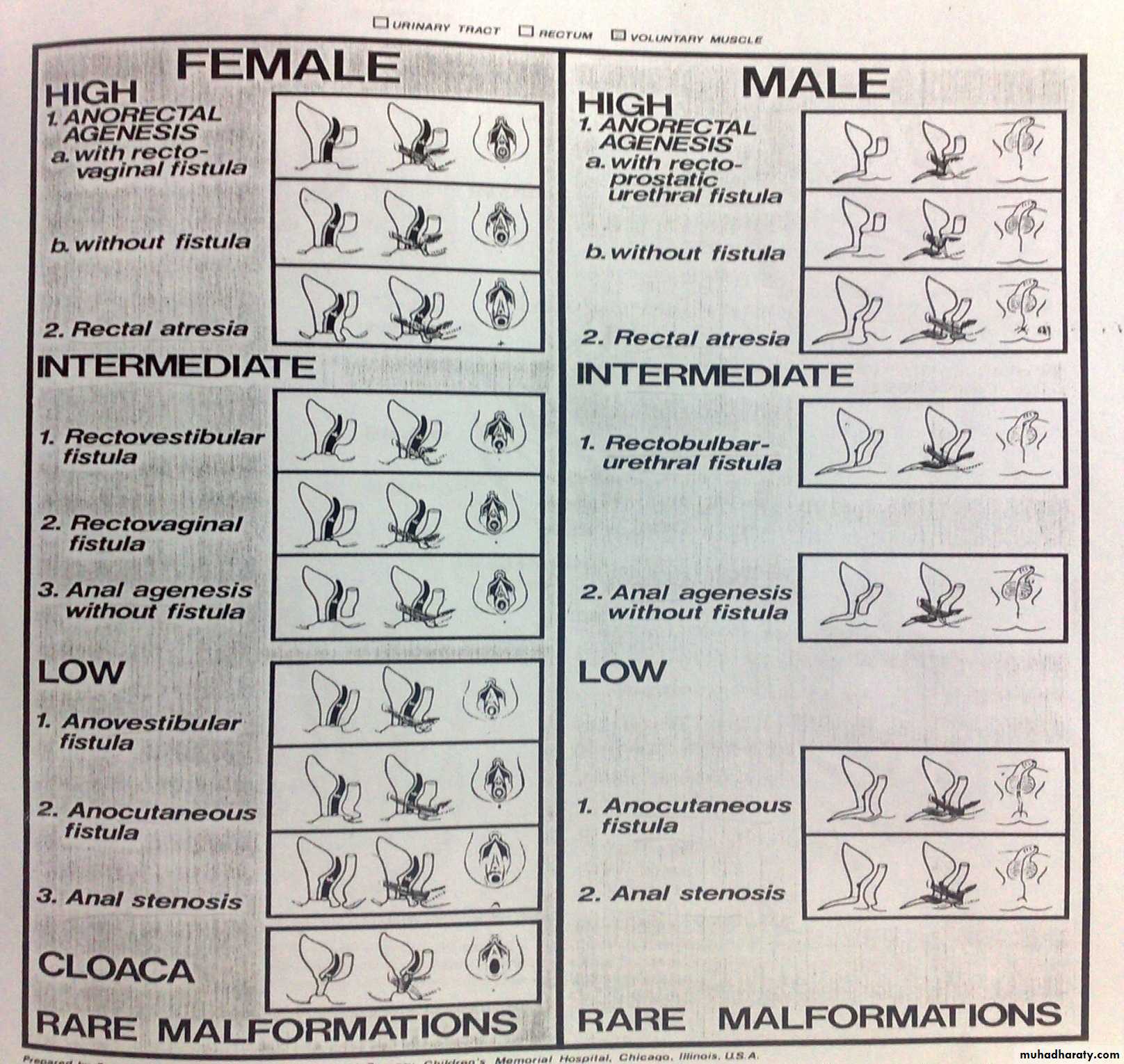
:Classification
Different sub type classified according to:-1-relation of terminal bowel to pelvic floor muscle(levator ani).
2- presence or absence of fistula(skin or uro genital).
3- conditions needs colostomy , others not need.
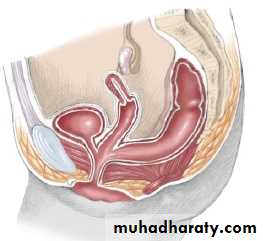
1- High type : blind end rectum above levator ani muscle
a-with fistula to-bladder or urethra in male
-vagina in female. b-without fistula(anorectal agenesis or atresia).
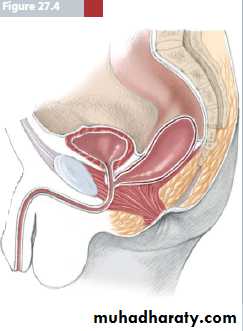
2-low type: blind end rectum below levator ani muscle.
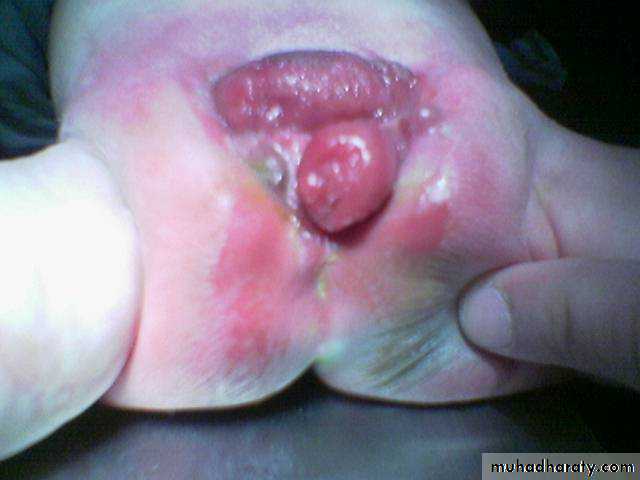
a-with fistula to- skin (cutaneous fistula) - vestibule.
b-without fistula (anal agenesis)
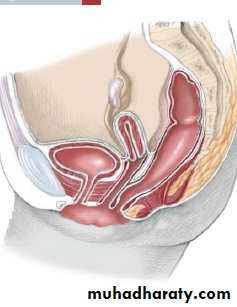
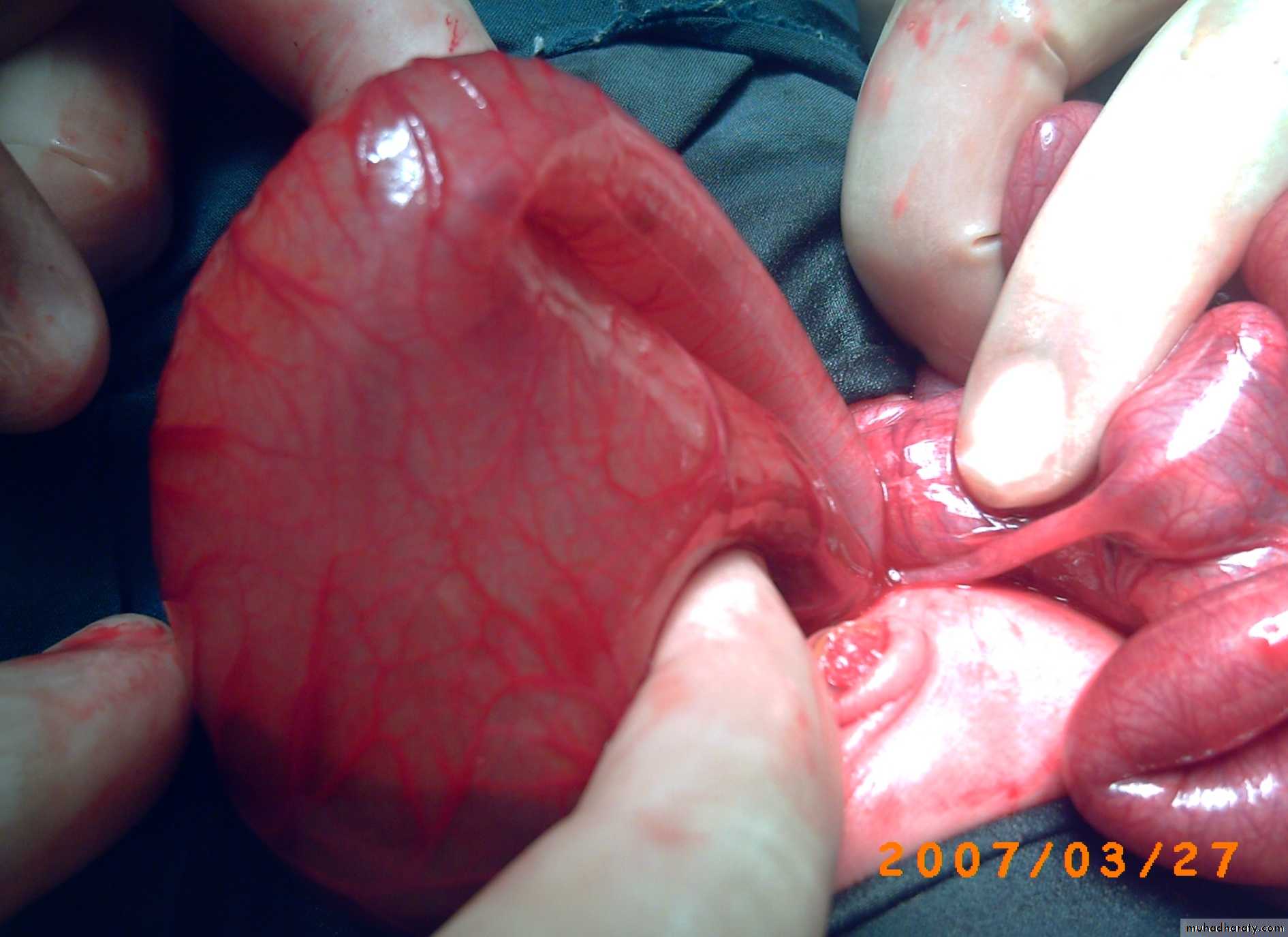
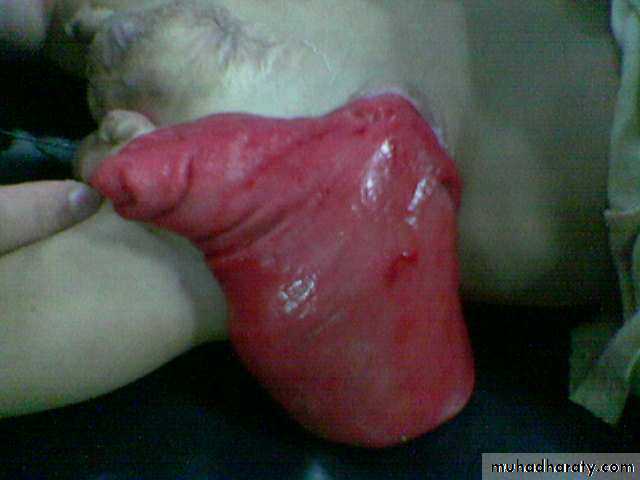
3- cloaca in female(rectum ,urethra and vagina in one opening or channal called urogenital sinus)
International classification
Associated anomalies:-
- Carful system review(very important) .More than 60% of cases have second anomalies.
: Genito urinary anomalies
-50% of cases and its include:-1-neuropathic bladder.
2-vesicoureteral reflux.
3-ureterocel.
4-ureteric duplication.
5-renal agenesis.
6-bladder or cloacal exstophy.
7-miscelaneous.
Skeletal anomalies:-
-20% of cases:-1- vertebral.
2-spinal dysraphism.
3-sacral anomalies.
4-spinal cord and pelvic nerve dysfunction.
5- pelvic floor dusfunction.
Cardiovascular anomalies:-
-12% of cases and it may be life threatening:-
1- V.S.D.
2-A.S.D.
3-A-V Canal.
4-Right aortic arch.
Gastro intestinal anomalies:-
- 10% of cases:-1-Congenital cystic colon(C.C.C.).
2-Dudenal Artesia.
3-esophageal Artesia.
4-intestinal artesian.
Syndromes or associations:-
1- Down syndrome.
2- V.A.C.T.E.R.L. association.
3- Currarino triade.
Clinical presentations
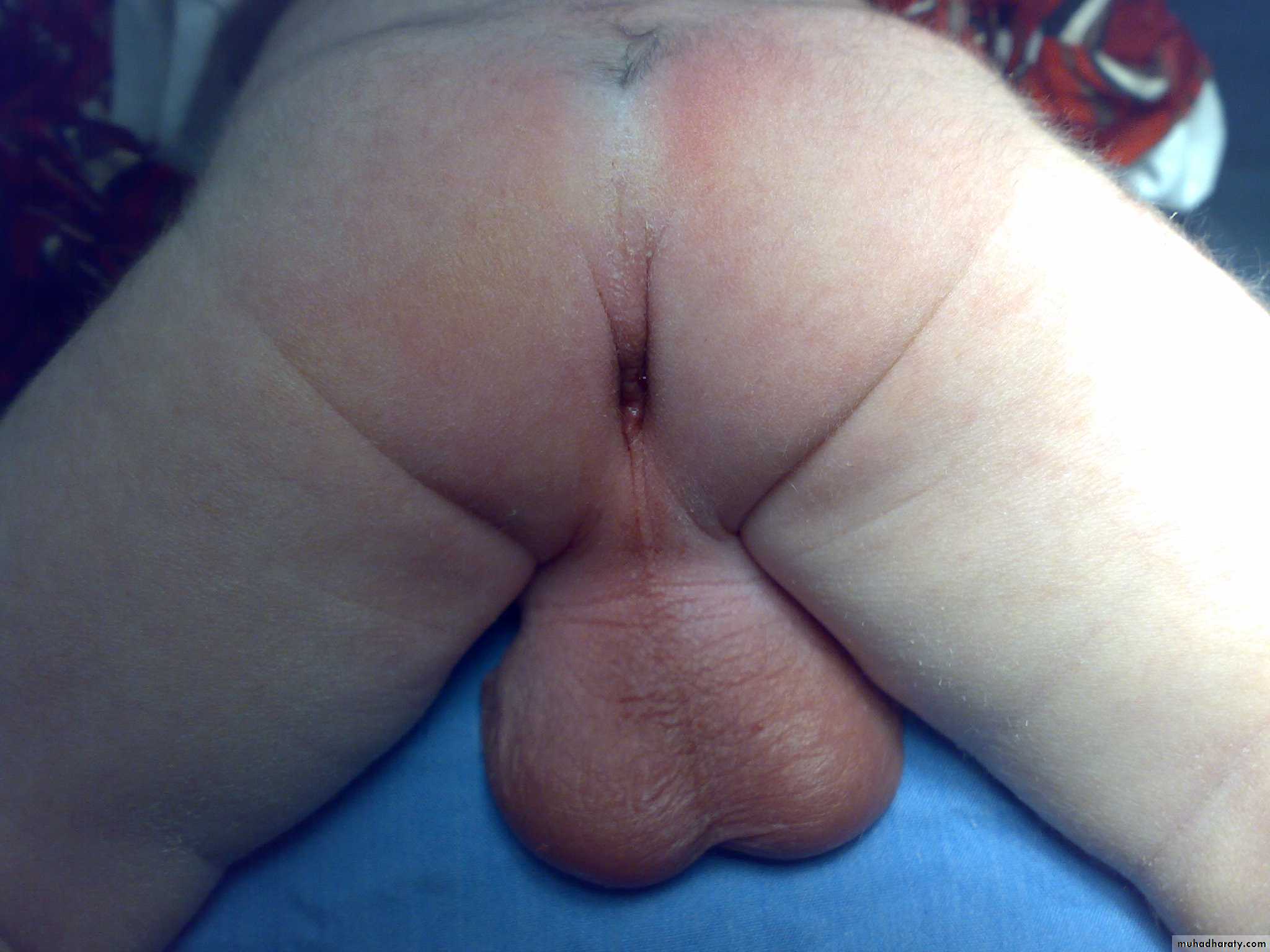
-intestinal obstruction.-simple inspection(diagnostic)/level(difficult).
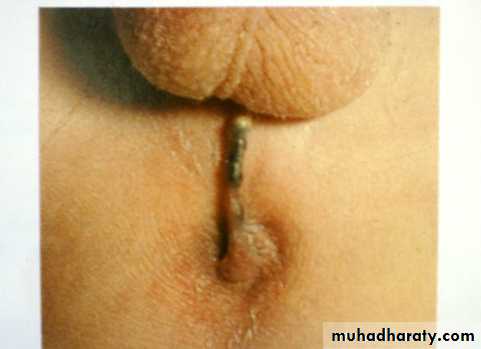
- Condition of anal dimple(well formed=low/flat=high).
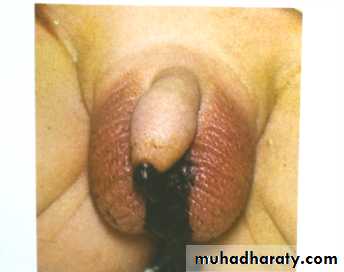
-voiding of meconium per urethra(in male) high type.
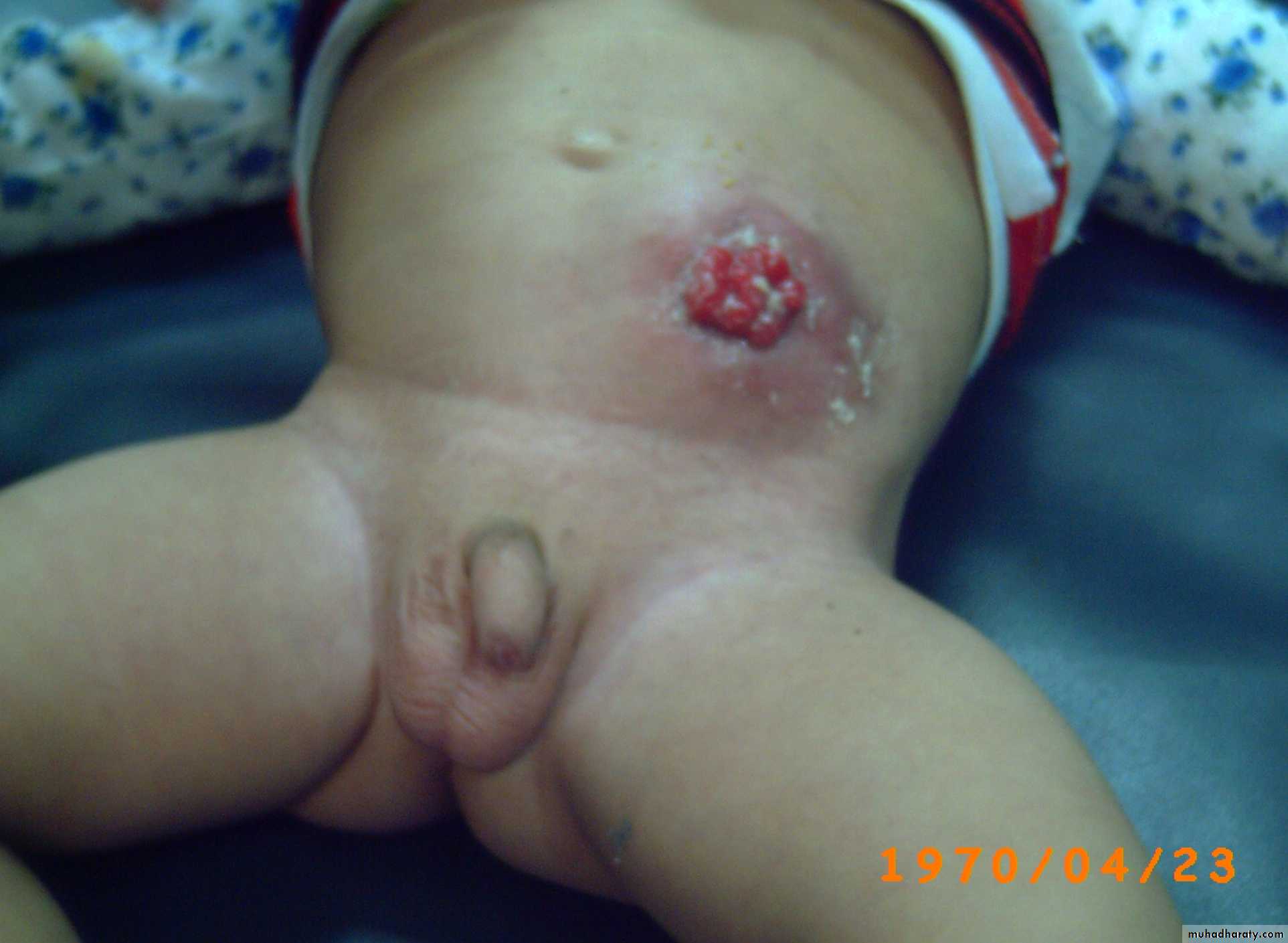
- sometime cutaneous fistula filled with meconium low type.
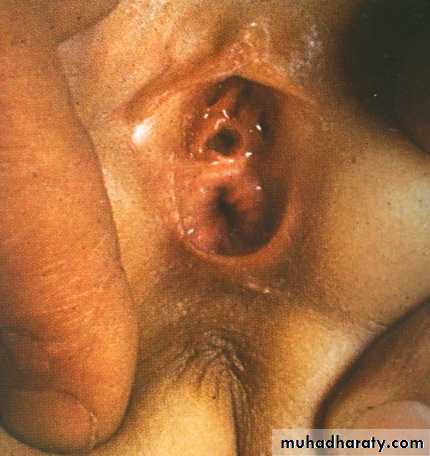
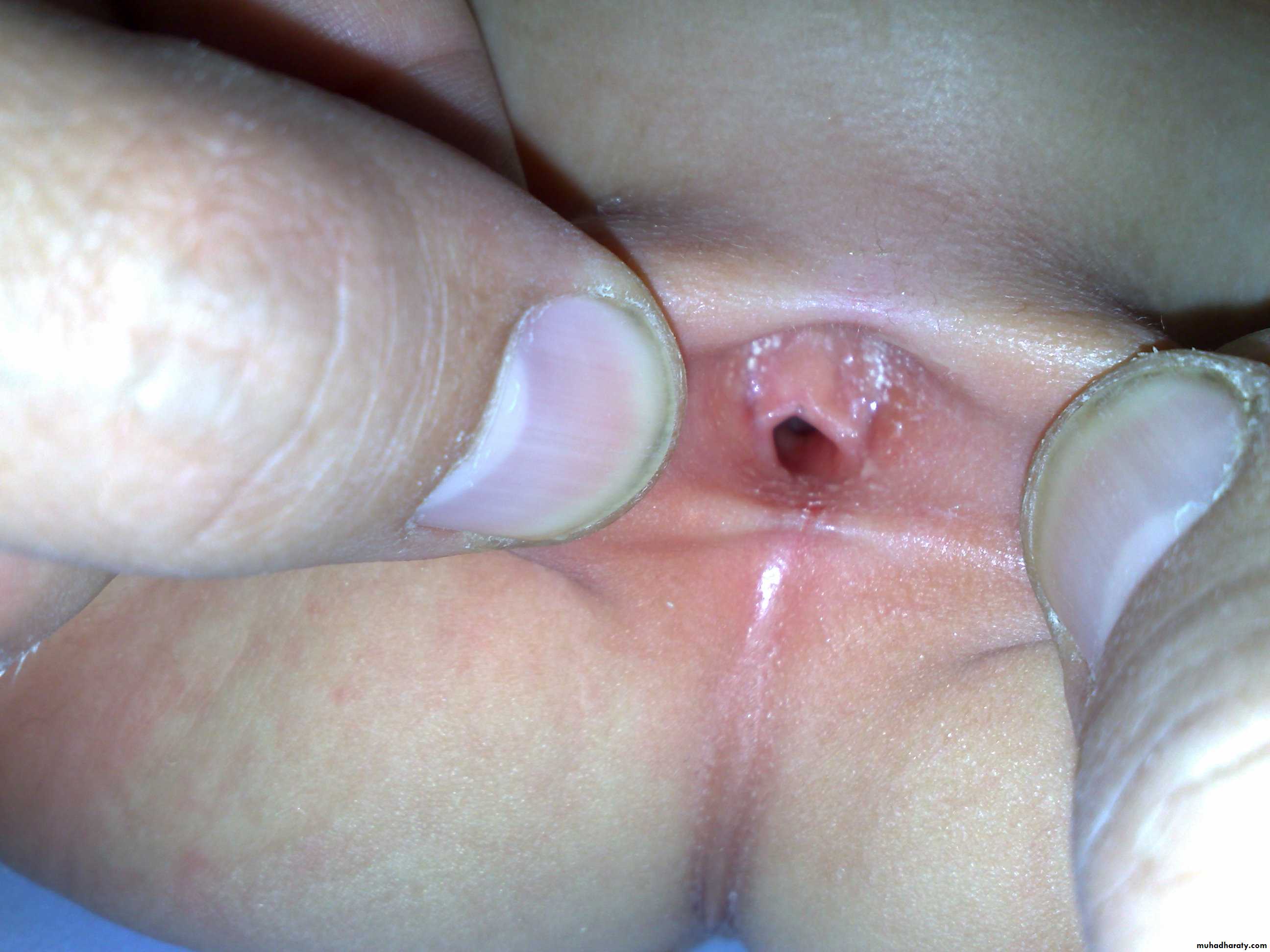
-in female carful genital examination essential (no.of opening).
3 opening: suggest vestibular fistula.
2 opening : suggest agenesis.
1 opening : diagnostic for cloacae with common channel(urogenital sinus).
Radiology
Determined:1-relation of rectum to sphincter muscle.
2-associated anomalies.
1-x-ray of the spine and chest (sacral , VATER).
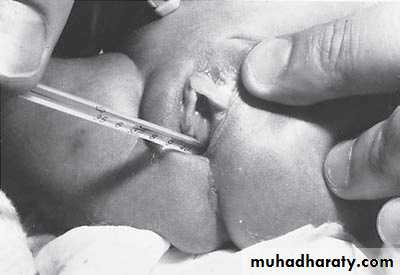
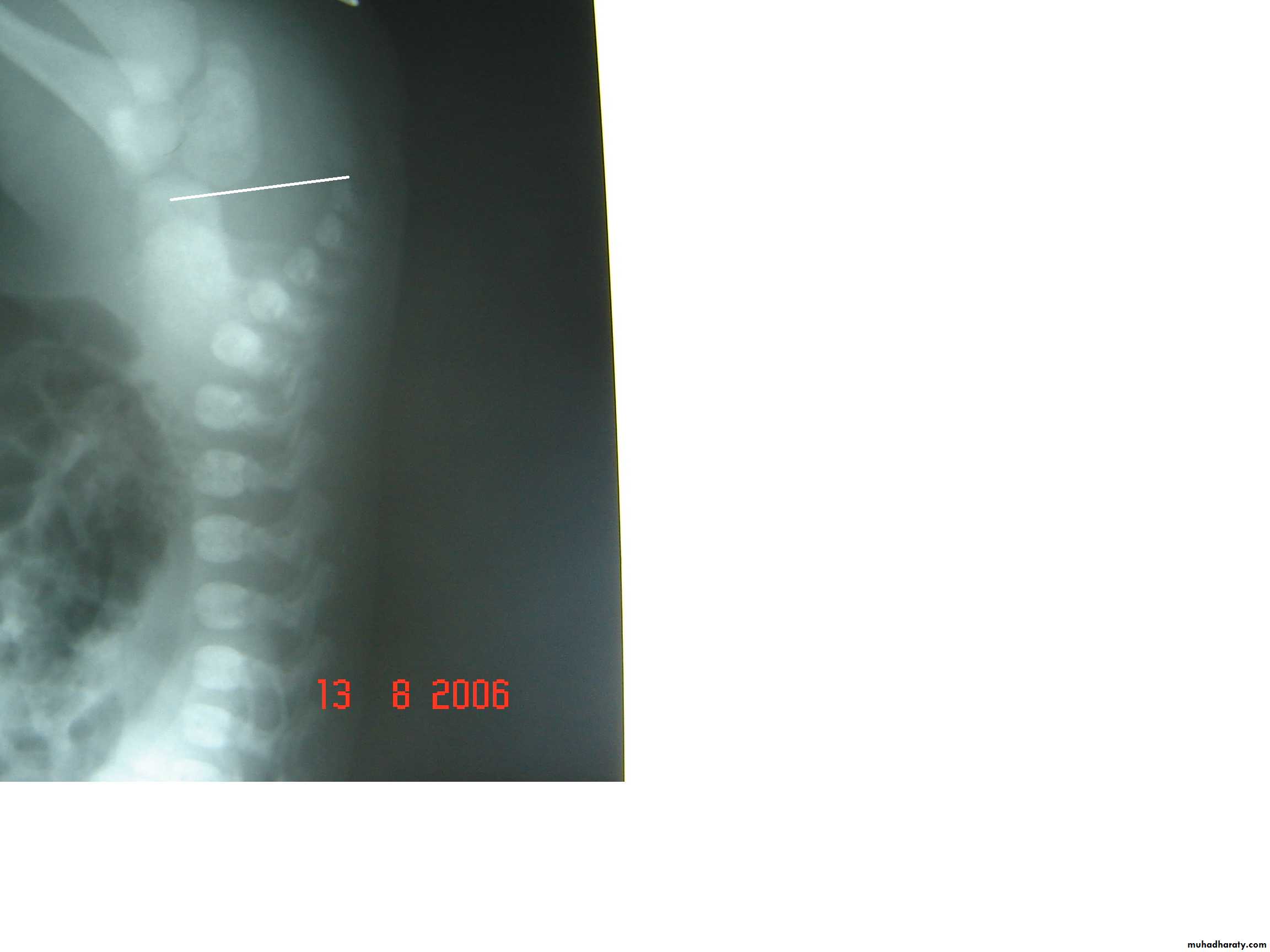
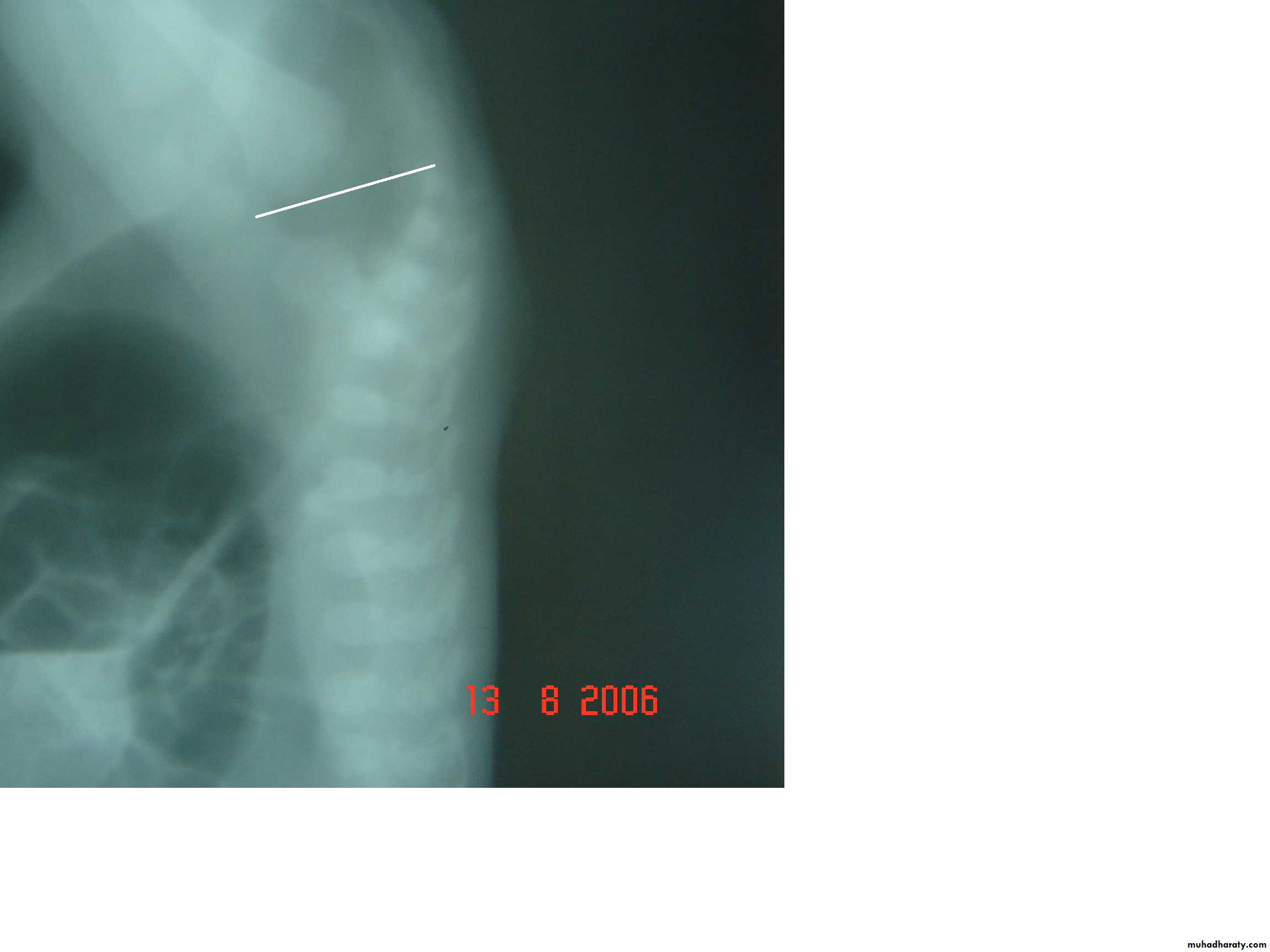
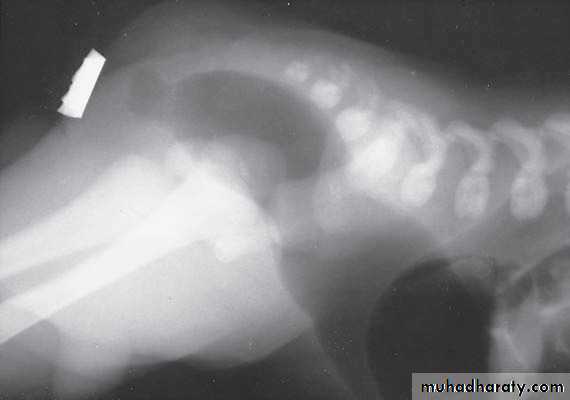
2-Lateral invertogram ( pubococcegeal line) 18-24hr.after birth.
-gas shadow above this line suggest high type.
- gas shadow below suggest low type.
3-lateral decubitus X-ray.
4-M.R.I.
5- ultrasound.
6-Echocardiography.
7- M.C.U.
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS
Satisfactory results=efficient continence.general considerations:
1-perineal fistula=low lesion = good prognosis.
2-meconium in urine (in male) = high type = colostomy.
3-in female=search for fistula=mostly local surgery = good prognosis.
if no fistula = colostomy.
4-sacral anomalies + neurogenic bladder = poor sphincter action = poor prognosis.
Surgical technique
Low lesion:good long term outlook but tendency to constipation
- A perineal anoplasty =cutaneous fistula.
- anal stenosis &imperforate anal membrane=simple incision &dilatation.
-vestibular fistula =transpositioning anoplasty few monthes later.
High lesion:
- Colostomy at birth.
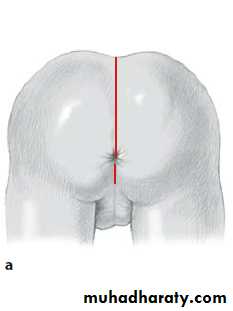
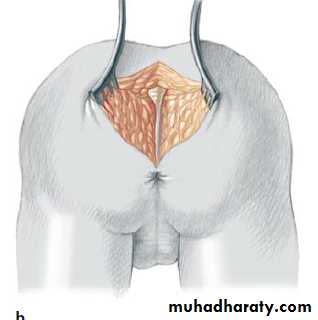
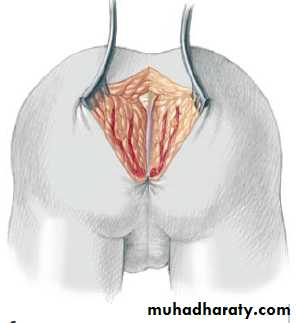
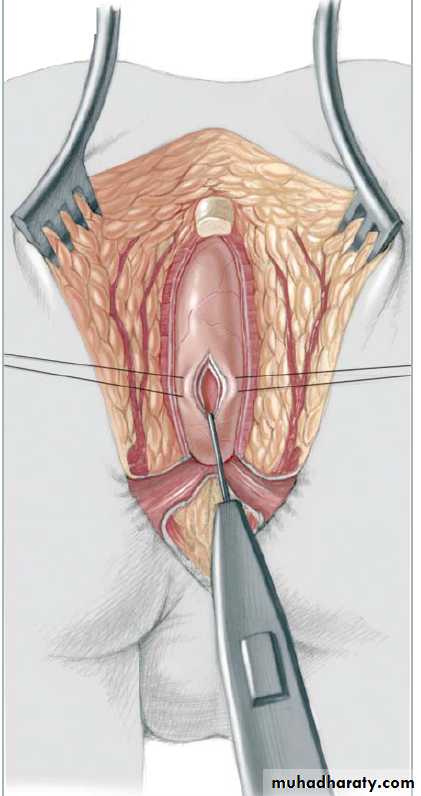
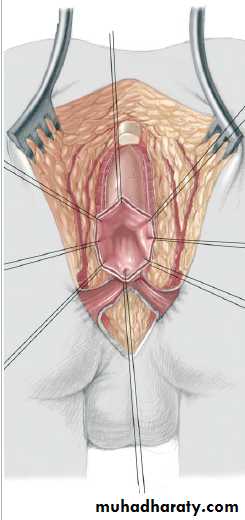
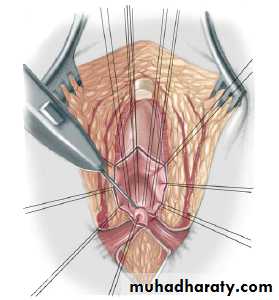
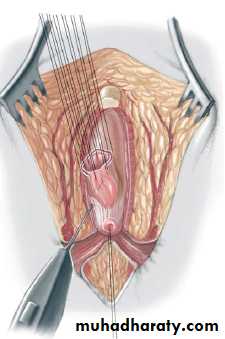
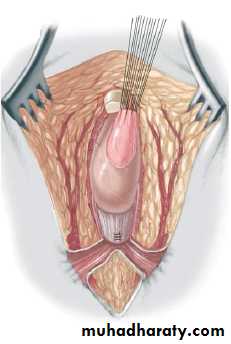
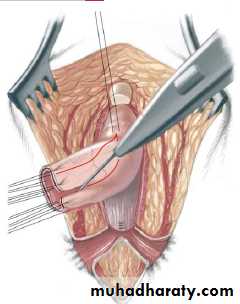
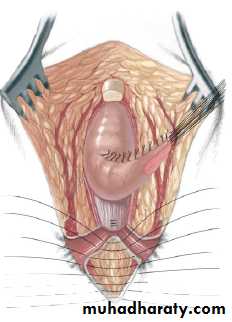
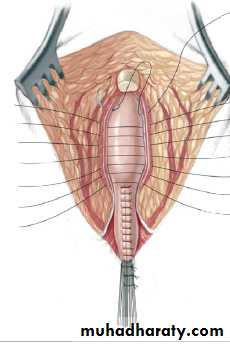
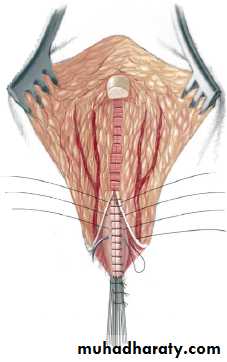
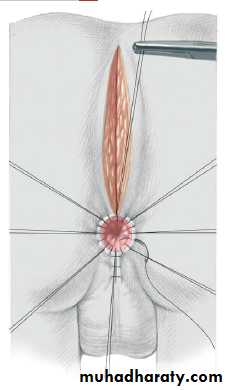
3-4 month later definitive surgery using posterior sagital anorectoplasty(P.S.A.R.P. pullthrogh) Or penna technique.
- Recently laparoscopic pull through using nerve stimulator to identify anal sphincter ,
-the sphincter is not well developed and nerve supply is deficient= continence not good.- 2 months later colostomy closed.
- Regular anal dilatation.
Complications
Early:1-wound infection.
2- colostomy complications.
3-recto urinary fistula .
4- neurogenic bladder.
5- anal stenosis.
6- rectal mucosal prolaps.
Late:
1-constipation.
2-megarectum.
3- soiling (incontinence)