Cerebral Oedema and Increased Intracranial Pressure (Intracranial Hypertension)
Cerebral Oedema• Vasogenic Oedema
• Cytotoxic Oedema
• Osmotic Cerebral Oedema
• Hydrostatic Cerebral Oedema
Vasogenic Oedema
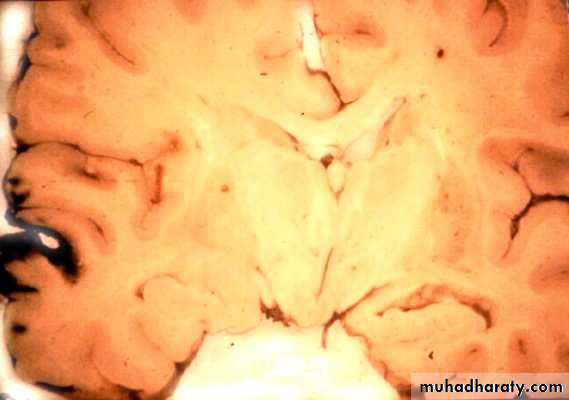
is the most common form of brain oedema encountered in clinical practice.This type is due to increased permeability of cerebral capillaries with resultant accumulation of plasma or its filtrate to enter the extracellular space of the brain. This type is seen commonly in trauma, primary and metastatic tumours and focal inflammation like brain abscess.
Cytotoxic Oedema
Derangement of cellular metabolism which result in inadequate functioning of the sodium and potassium pump leading to cellular retention of sodium and water and cell swelling.This type is seen in various intoxications (e.g., dinitrophenol), Reye’s syndrome and sever hypothermia.
Osmotic Cerebral Oedema
Accumulation of excess water in the brain in response to an unfavorable osmotic gradient operating across the intact Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).This type is seen in :
1. Pathologic ingestion of water.
2. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone.
3. Sever haemodialysis of the uraemic patient.
Hydrostatic Cerebral Oedema
Occurs in acute hypertension in which the elevated pressure is directly transmitted to the cerebral capillaries.
Increased Intracranial Pressure (Intracranial Hypertension)
• The adult skull :• Brain.
• Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF).
• Blood.
Increased Intracranial Pressure (Intracranial Hypertension)
The normal supine intracranial pressure is 5-15 mmHg (60-180 mmH2O).An increase in the volume of any one of the contents of the skull will result in an increase in the intracranial pressure (ICP).
The brains ability to compensate for raised ICP is rapidly exhausted.
Raised ICP is dangerous to the brain.
(Intracranial Hypertension)
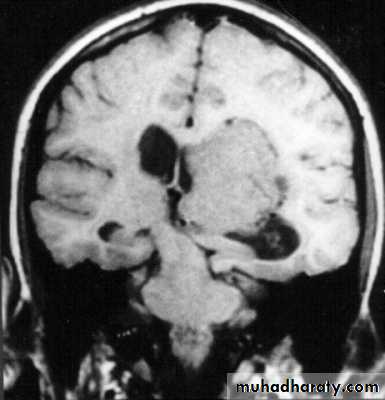
Etiology:1. Localized masses like:
a. Haematomas: epidural, subdural, and intracerebral.
b. Neoplasms: gliomas, meningiomas, and metastases.
c. Abscesses (brain abscesses).
d. Focal oedema due to traumas, infection, and tumours.
(Intracranial Hypertension)
2. Obstruction to CSF pathways: as seen in:
a. Obstructive hydrocephalus.
b. Communicating hydrocephalus.
3. Obstruction to major venous sinuses as a result of:
a. Depressed skull fracture over major venous sinuses.
b. Thromboembolic disease from contraceptive pills.
(Intracranial Hypertension)
4. Diffuse brain oedema or swelling: due to encephalitis, meningitis, diffuse head injury, subarachnoid haemorrhage, Reye's syndrome, water intoxication from fluid overload.5. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is a disease most commonly found in adult female patients (also called pseudotumour cerebri).
6. Systemic hypertension can cause breakdown of the blood brain barrier and causes hypertensive encephalopathy.
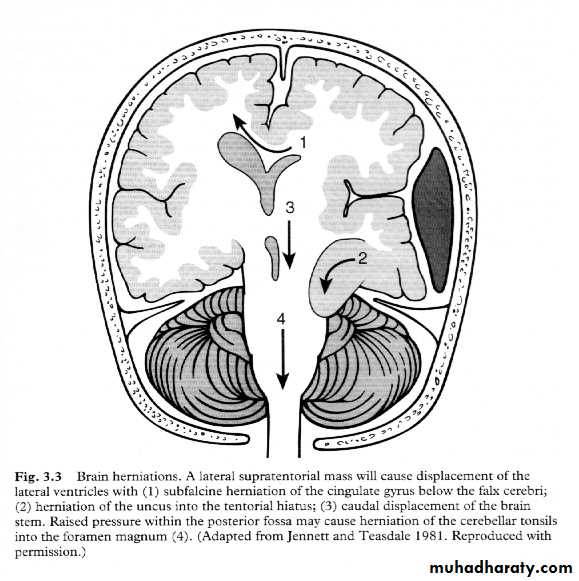
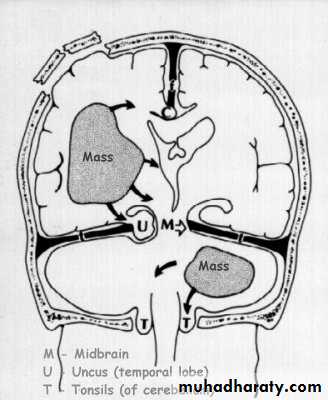
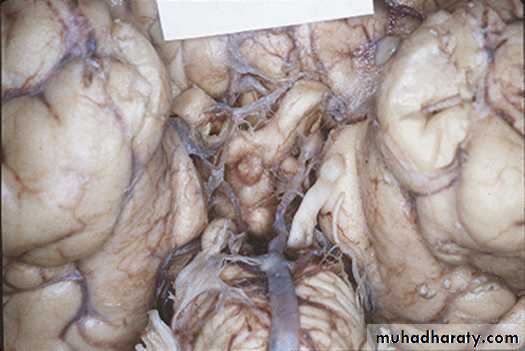
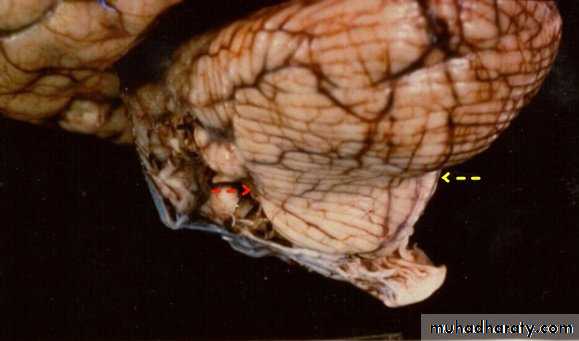
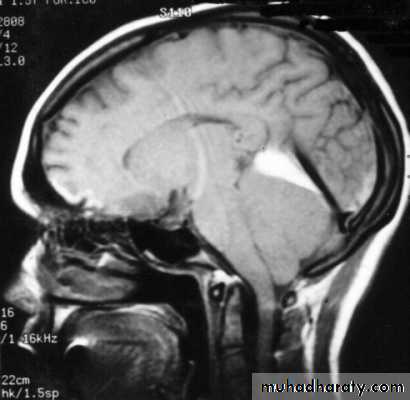
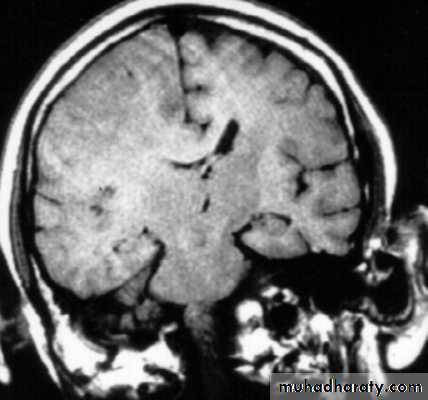
7. Cerebral Herniation
a. Subfalcine Herniationb. Uncal Herniation
c. Tentorial Herniation
d. Tonsillar Herniation
7. Cerebral Herniation
7. Cerebral Herniation
a. Transtentorial Herniation
a. Transtentorial Herniation
b. Foramen magnum herniation
b. Foramen magnum herniation
c. Subfalcine Herniation
c. Subfalcine Herniation
Increased Intracranial Pressure (Intracranial Hypertension)
• Without symptoms and signs.• Headache.
• Nausea and vomiting.
• Drowsiness or altered mental status.
Increased Intracranial Pressure (Intracranial Hypertension)
• 5. Papilloedema• 6. Sixth nerve palsy (False localizing sign).
• 7. At later stages the triad of bradycardia, hypertension and respiratory irregularities.
• 8. In infants: tense bulging fontanelle.
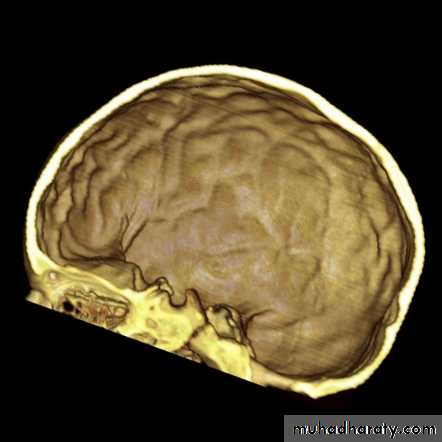
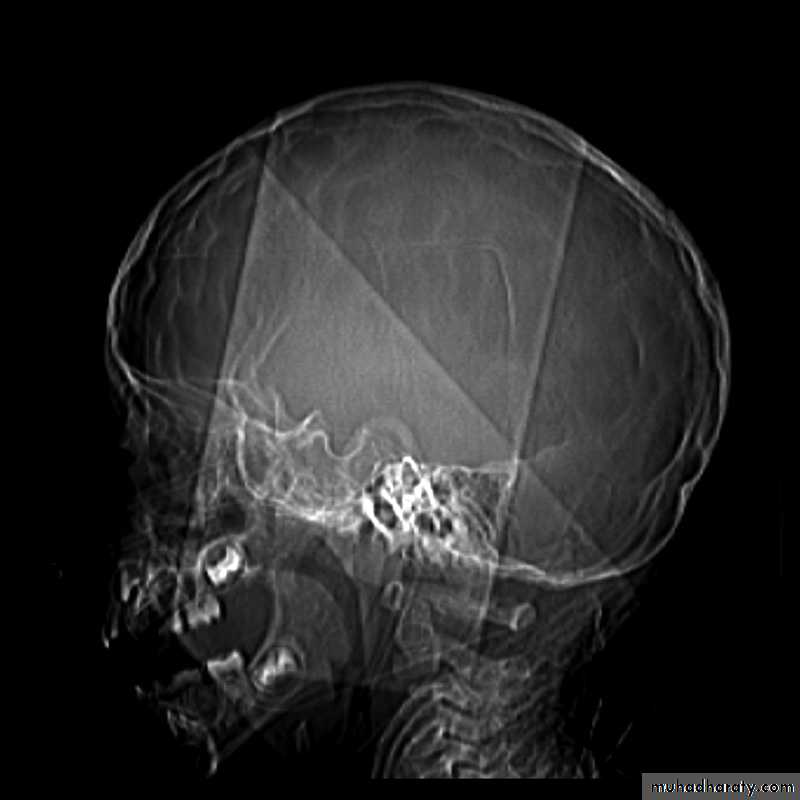
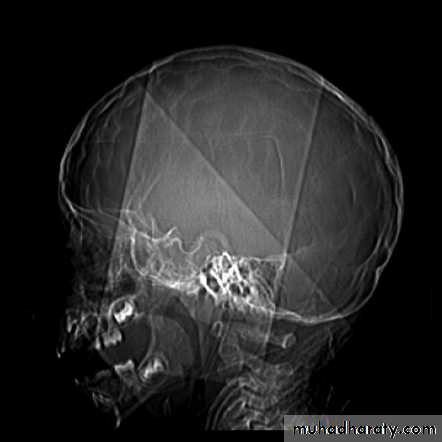
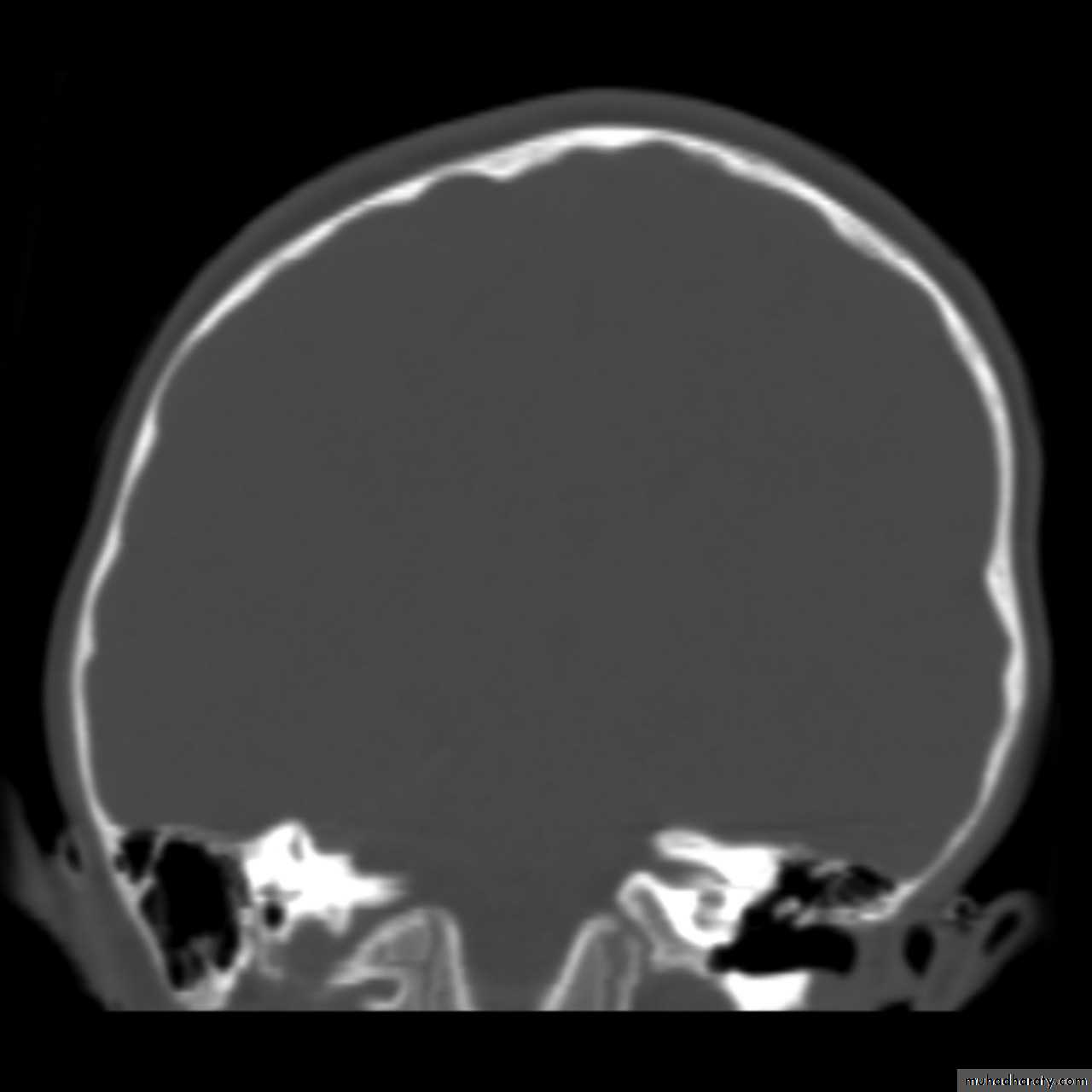
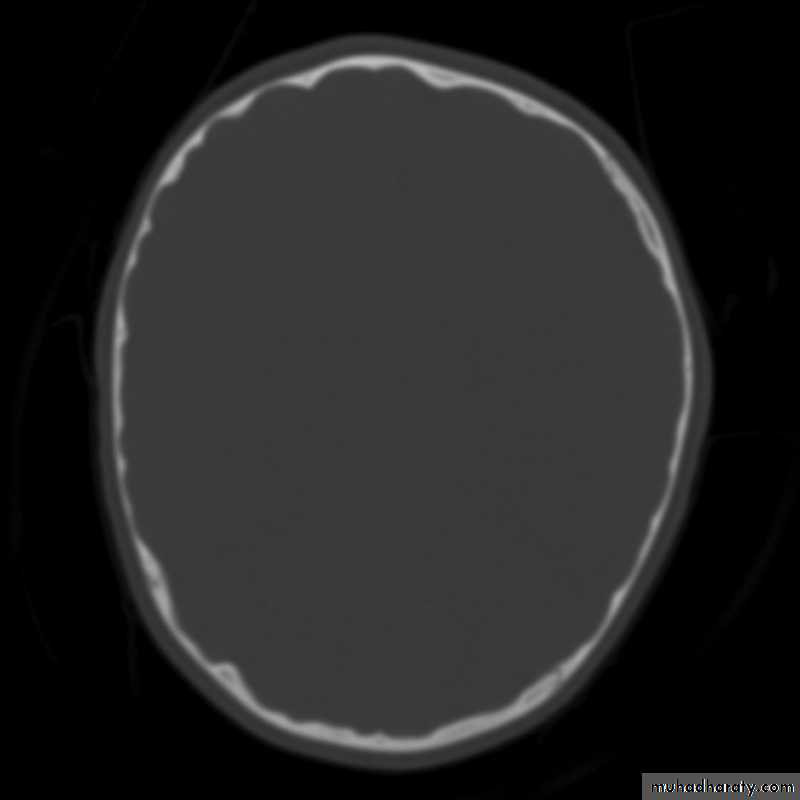
Skull X-ray findings in increased intracranial pressure
• Sutural separation in children.• ‘Copper-beating’ marking of the cranial vault.
• Thinning of dorsum sellae.
• Erosion of the posterior clinoid process.
Copper-beating’ marking
Copper-beating’ marking
Copper-beating’ marking
Copper-beating’ marking
Copper-beating’ marking
Copper-beating’ marking
Treatment of Intracranial Hypertension
• Head position (Head elevation).• Hyperventilation: PCO2 down to (30-34 mmHg).
• Hypertonic solutions including:
• Mannitol, dose of 1g/kg
• Hypertonic saline.
• Furosemide (Loop diuretic): act by
Reducing cerebral oedema.
Reduce CSF production.
Act synergistically with mannitol.
Treatment of Intracranial Hypertension
• 5. Steroids (dexamethasone 4mg, 6-hourly).• Stabilizing the blood brain barrier (BBB).
• Reducing oxygen free radicals.
• 6. Ventricular drainage.
• 7. Barbiturates: reducing cerebral metabolism.
• 8. Hypothermia down to 34°C is a brain protective agent.
• 9. Surgical intervention.
THANKYOU