1
Fifth stage
Surgery-Ortho
Lec-11
د. هشام القطان
1/1/2014
Metabolic bone diseases
Bone functions
support
protection
leverage
minerals reservoir
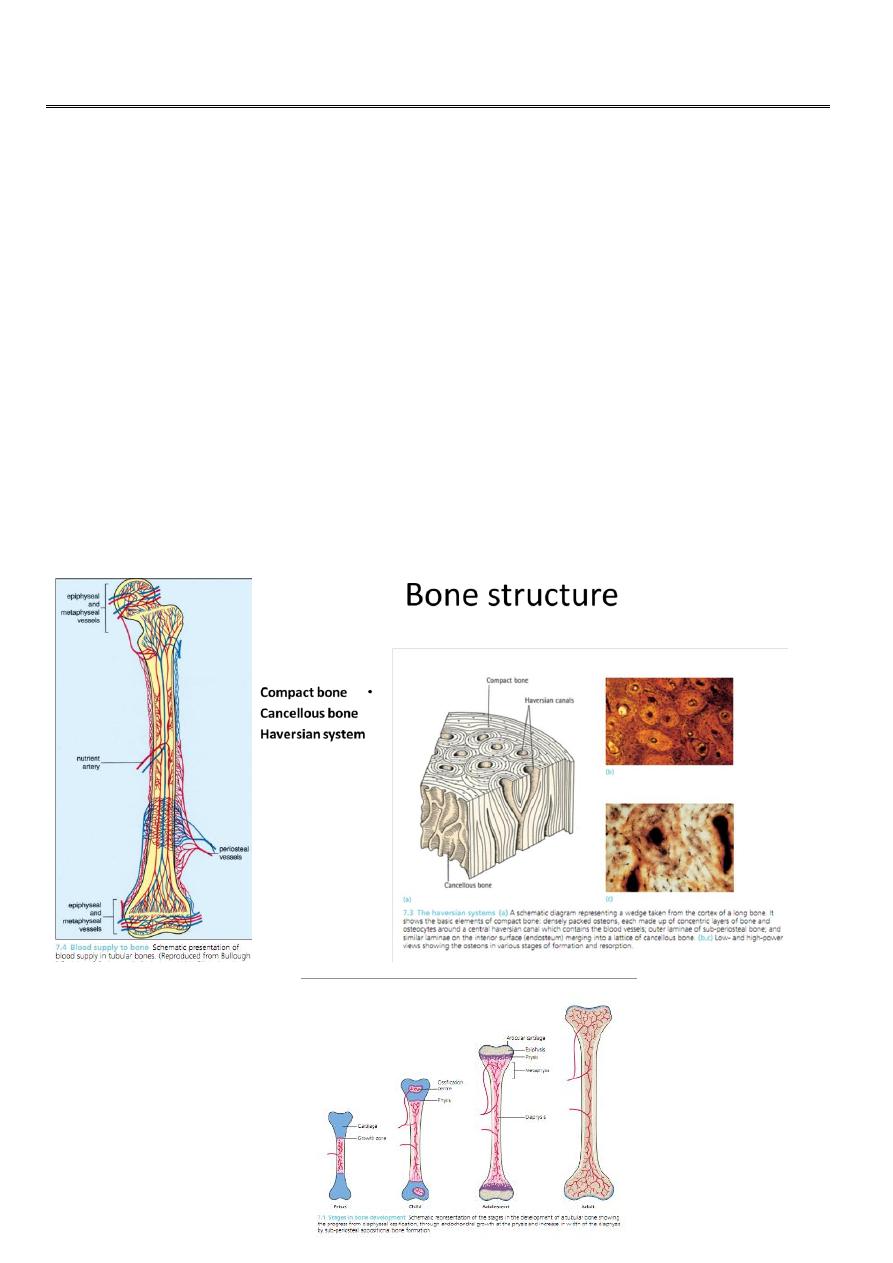
Bone composition
1- the matrix
2- bone mineral
3- bone cells
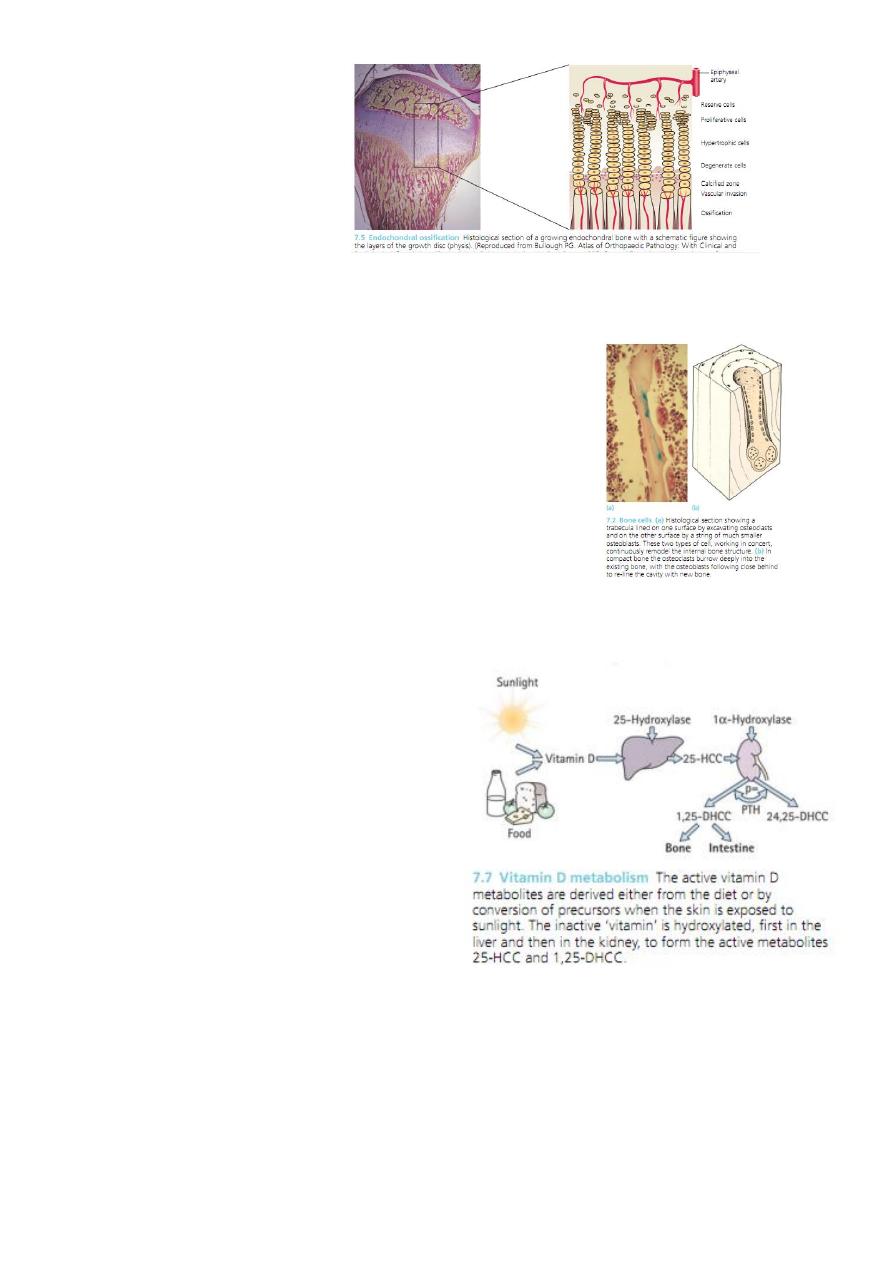
Endochondral ossification
2
Epiphyseal growth plate
Intramembranous ossification
Periosteal new bone formation
Bone formation and resorption.
Bone remodeling
Minerals and Factors affect bone
metabolism
1- calcium.
2- phosphorus.
3- magnesium and fluoride.
4- Vitamin D .
5- Parathyroid hormone.
6- calcitonin.
7- glucocorticoids, gonadal hormone,
thyroxine , growth hormone.
8- mechanical factors.
9- electrical stimulation and other factors.
Factors adversely affecting bone mass
1- Early onset menopause.

3
2- Malnutrition and ill health
3-Lack of Vit D, calcium and phosphate.
4- Chronic illness.
5- High consumption of alcohol.
6- Smoking.
7- Inactivity.
8- Drugs ( corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, anticoagulants, thyroid
hormone, antiepileptics ).
OSTEOPOROSIS
Reduction of normally mineralized bone mass per volume.
It is a clinical disorder characterized by an abnormally low bone mass and defects in bone
structure, render the bone fragile.
A state in which bone is fully mineralized but its structure is abnormally porous and its
strength is less than normal person of that age and sex
It may result from increased bone resorption or
decrease bone formation or both.
Osteopenia: bone which appears to be less dense than normal X-ray.
Any density reduction in DEXA more than 2.5 standard deviation define as osteoporosis.
Between 1-2.5 name osteopenia
1- Osteoporosis is one of the most serious global disease and will increase due to increased
aging.
2- Osteoporosis is a problem in both genders.
3- Osteoporosis may primary or secondary.
Primary osteoporosis may be postmenopausal or senile .
4- Osteoporosis is common cause of fractures especially femoral neck fractures , vertebral
fractures and distal radial fractures .
5- Bone mineral density commonly measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry ( DEXA)

4
Secondary osteoporosis
Malnutrition .
Hypercortisonism ( Cushing’s disease).
Gonadal hormone insufficiency.
Hyperthyroidism and hyperparathyroidism.
Multiple myeloma & carcinomatosis.
Drugs ( steroids, heparin, antiepileptic, cytotoxic, ….).
Alcohol and smoking.
Immobilization.
Chronic disease ( renal failure, TB, rhumatic disaeses... )
Other factors
Treatment of osteoporosis
Hormone therapy.
Bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates is the first-line drugs for treating postmenopausal
women with osteoporosis, Alendronate and risedronate reduce risk of both vertebral
and nonvertebral fractures.
Parathyroid hormone: Teriparatide (PTH 1-34) is reserved for treating women at high
risk for fracture, including those with very low bone mineral density (BMD) with a
previous vertebral fracture. PTH improves BMD and reduces the risk of vertebral and
non-vertebral fractures. Dosage requirements of daily subcutaneous injections may
limit use.
Fluoride, calcium, and vitamin D, calcinotin.
Fracture treatment
Osteomalacia and rickets
inadequate mineralization of bone
Bone tissue throughout the skeleton is abnormally calcified and therefore soften (
Osteomalacia).
Rickets and Osteomalacia is same disease.

5
Osteoporosis and Osteomalacia
common in aging women, prone to pathological fractures, and decreased bone density.
Osteomalacia treatment
Treatment of the cause.
Treatment of pathological fractures.
Hyperparathyroidism
Excessive secretion of PTH.
May be primary , secondary, or tertiary.
PTH- enhance calcium conservation resulting in hypercalcaemia and hypercalciuria and
Hyperphosphouria.
Bone resorption manifest by ostitis fibrosa cystica and subperiosteal resorption.
Clinical features
• 1- features of
• hypercalcaemia.
• 2-polyuria and renal disorders
• 3- bone pain and pathological fractures.
Treatment
• 1- treatment of hypercalcaemia.
• 2- surgery.
6
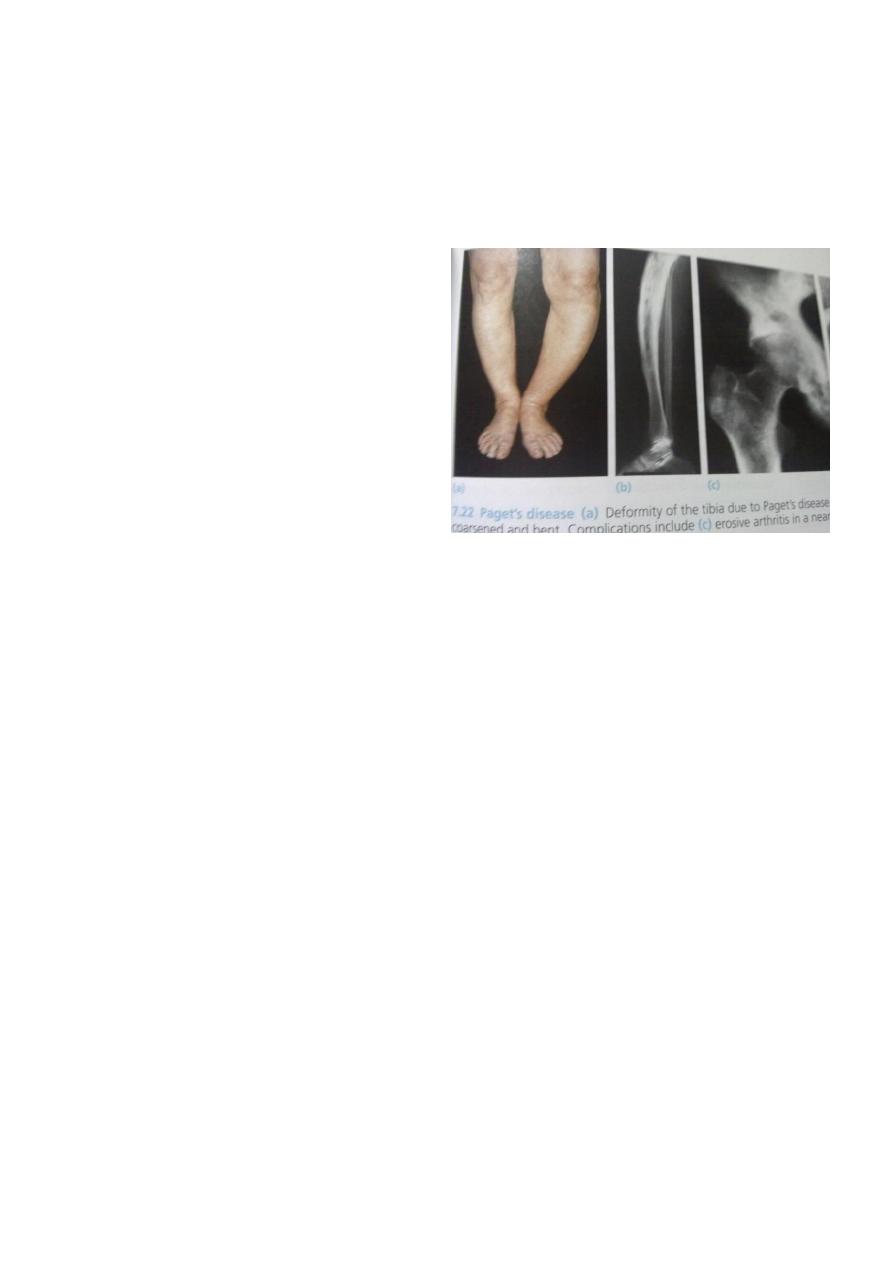
Paget’s disease
This disease characterized by increased bone turnover and enlargement and thickening of
bone, but internal architecture is abnormal and bone is usually brittle.
Complications
1- fractures.
2- osteoarthritis
3- nerve compression and spinal stenosis.
4- bone sarcoma.
5- high cardiac output failure.
6- hypercalcaemia in immobilization.
Treatment
1- calcitonin.
2- Bisphosphonate.
3- surgery
