1
4th stage
Surgery
Lec
Dr.ahmad
4/16/2016
Anal conditions
5
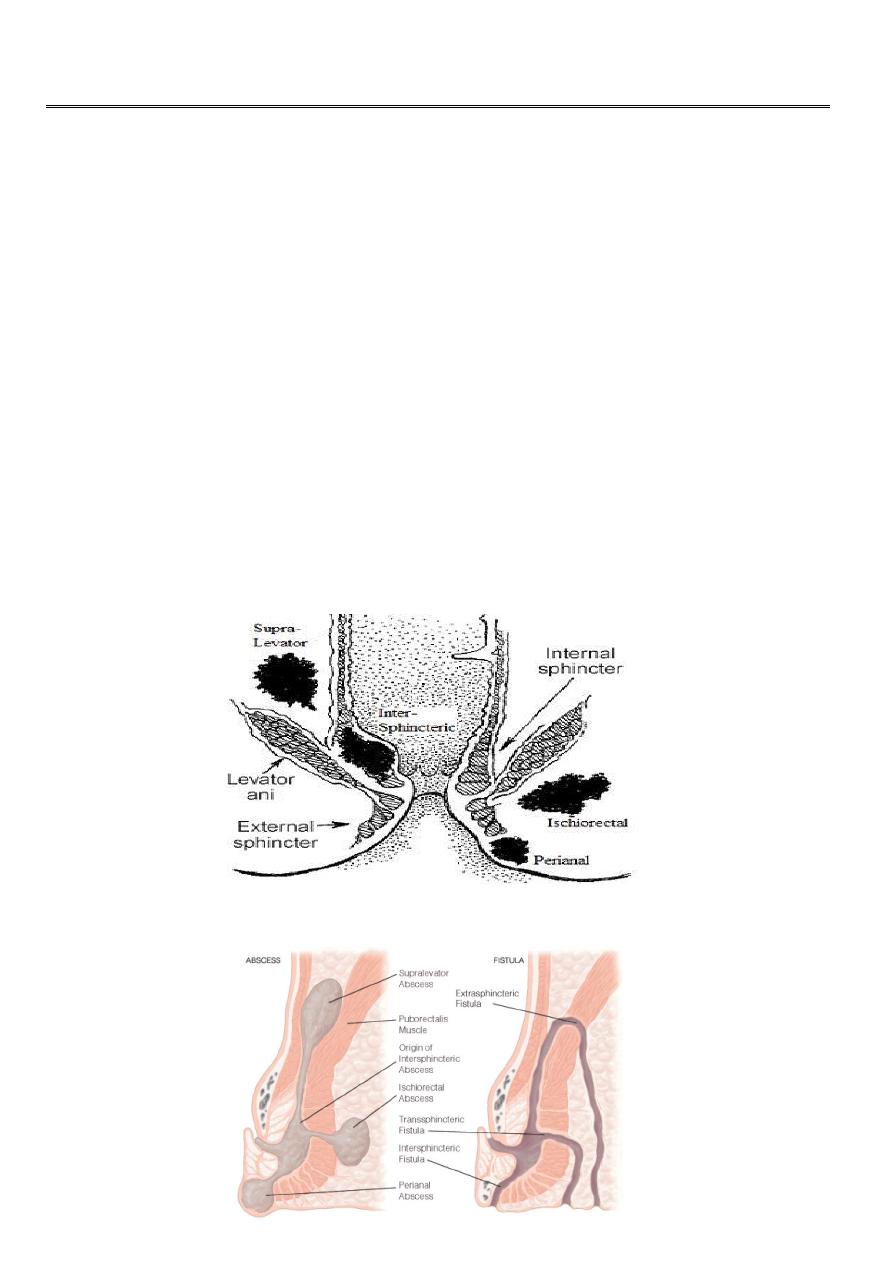
Anorectal Absces:
Acute sepsis in the region of the anus is common.
anorectal sepsis is more common in men than women
Due to infection of anal glands and skin glands.
The anal glands exist in a plane between the internal and external sphincters and
communicate by their ducts to the anal mucosa at the level of dentate line.
Infection of these glands by gram –ve bacilli lead to formation of an intersphincteric
abscess which may spread:-
– Downwards ---perianal abscess.
– Outwards --- ischiorectal abscess.
– Inward ------- submucous abscess.

2
In the majority of these abscesses, there is an inner opening in the anal canal and
drainage of the abscess is usually followed by fistula.
Infection of apocrine glands or hair follicles of the perianal skin [15 – 25%] of cases,
in such cases the causative M.O are staph. and there is no communication with anal
canal .
Secondary anorectal abscess:-
– Inflammatory bowel disease as in Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.
– Specific infection T .B.
– Anorectal carcinoma.
– Infection of perianal haematoma , thrombosed pile, fissure abscess.
Clinical Features:-
1- Perianal abscess 60%:- Is usually due to downward spread of an intersphincteric
abscess or infection of Perianal hematoma, the abscess is subcutaneous near anal verge,
pain and constitunal symptoms marked .
2- Ischiorectal abscess 30% :- Lateral extension of an intersphincteric abscess, fever
with large indurated Swelling in the ischiorectal space, throbbing pain with pitting
edema .If not drained it will spread to other side forming horse shoe abscess, this need
Urgent drainage.
3- Submucous abscess 5%:- The abscess in the sub mucous space above the dentate line,
the patient has Severe pain, fever, but nothing in the anal verge.
Digital examination of the rectum reveals tender boggy swelling.
4- Pelvirectal abscess 5% : this occur secondary to appendicitis, salpingitis --- etc.
Treatment
:-
Incision and drainage under G.A.
Dressing daily.
If fistula present should be treated.
Patient warned that he may develop fistula.
3
ANAL FISTULA:-
A fistula in ano is a track, lined by granulation tissue, which connects deeply in the anal
canal or rectum and superficially on the skin around the anus (to the skin of the perineum or
buttock or rarely, in women, to the vagina). common in men than women.
Aetiology:-
• Most fistulas begin as an anorectal abscess which burst spontaneously or was opened
inadequately.
• Anal fistulae may be found in association with specific conditions, such as Crohn’s
disease, tuberculosis, rectal duplication, and malignancy (which may also very rarely
arise within a longstanding fistula).
• The majority are termed non-specific, idiopathic or crypto glandular.
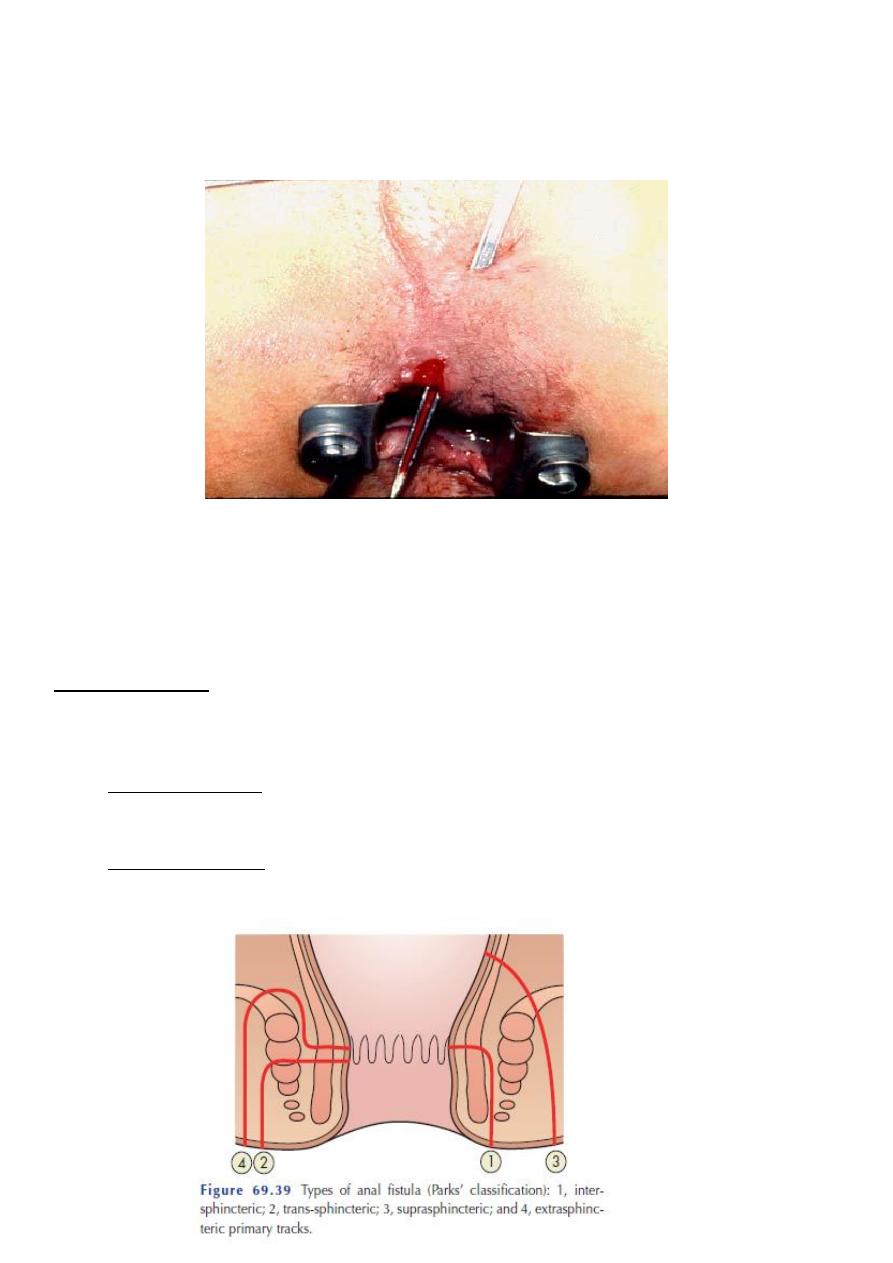
4
A probe must be passed between the opening of the skin’s surface and the interior
opening
The fistula continues to discharge and, because of constant reinfection from the anal
canal or rectum, seldom, if ever, closes permanently without surgical aid
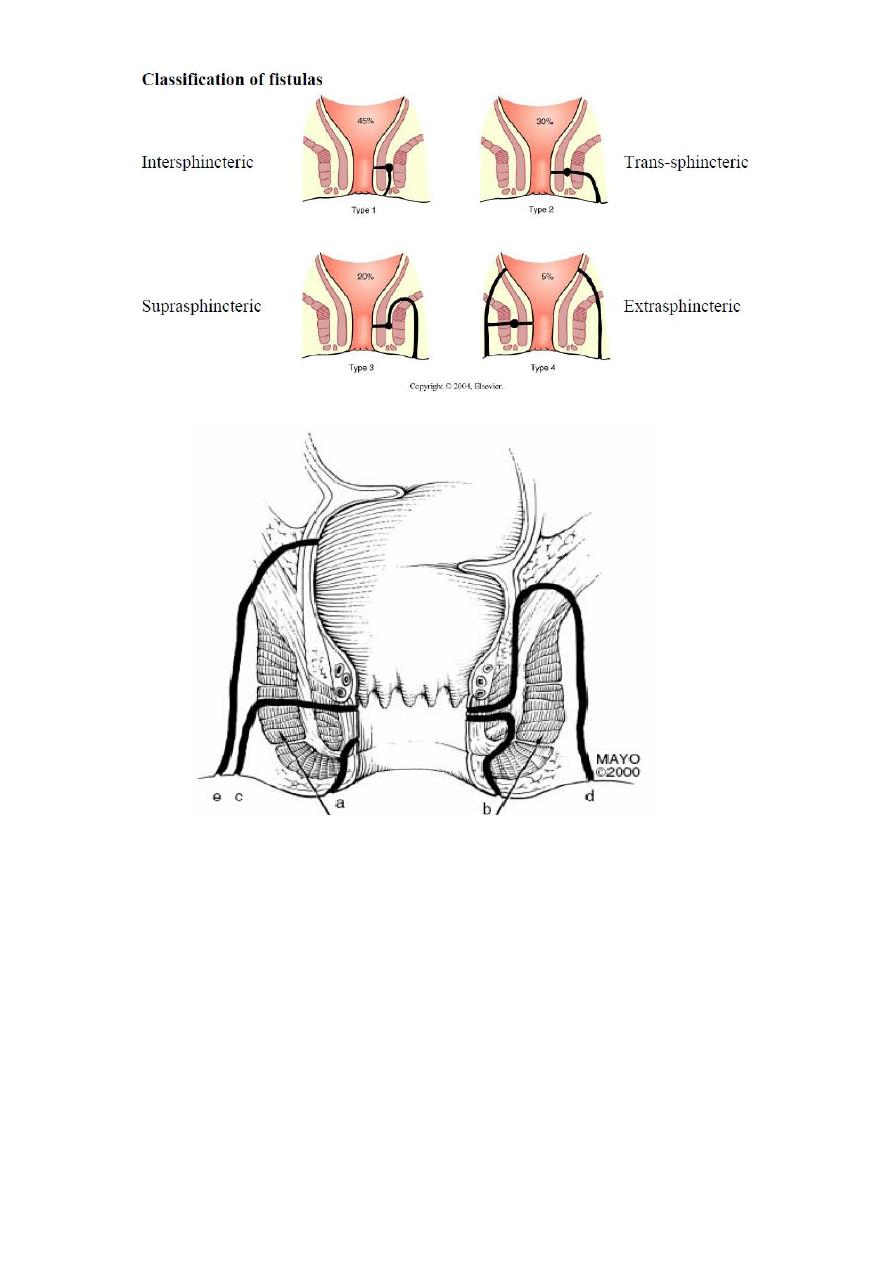
Classification:-
These are divided into two groups, according to weather their internal opening is below or
above the anorectal ring.
• Low-level fistulae
– open into the anal canal below the anorectal ring.
• High-level fistulae
– open into the anal canal at or above the anorectal ring.
5
The importance of deciding a fistula is a low or a high-level type is that:
• A low-level fistula can be open without fear of permanent incontinence (from damage
to the anorectal bundle), while a high-level fistula treated only by ‘staged’ operations,
with the use of a protective colostomy to prevent septic complications and to shorten
healing time between the stages.
• In probing a high fistulous track, great care must be taken not to create an internal
opening into the rectum where none existed previously.
• Such a disaster could convert a relatively straightforward ‘intersphinctenic’ track into
a high ‘pelvirectal’ fistula that might prove very difficult to cure.

6
Clinical picture :
Give history of previous perianal abscess which drain spontaneously, followed by
intermittent or persistent discharge.
the principal symptom is a persistent seropurulent discharge that irritates the skin in
the neighborhood and causes discomfort.
Often the history dates back for years. And as far as the opening is large enough for
the pus to escape, pain is not a symptom, but if the orifice is occluded pain increases
until the discharge erupts.
Attacks of perianal pain occur as recurrent abscesses build up .
Frequently, there is a solitary external opening, usually situated within 3.5—4 cm of
the anus, presenting as a small elevation with granulation tissue pouting from the
mouth of the opening.
Local soreness and pruritus ani .
Sometimes superficial healing occurs, pus accumulates and an abscess reforms and
discharges through the same opening or a new opening.
Thus there may be two or more external openings, usually grouped together on the
right or left of the midline but, occasionally, when both ischiorectal fossas are
involved, an opening is seen on each side, in which case there is often
intercommunication between them .
Goodsall’s rule:-
• Fistulae with an external opening in relation to the anterior half of the anus tend to be
of the direct type.
• Those with an external opening or openings in relation to the posterior half of the
anus, which are much more common, usually have curving tracks, and may be of the
horseshoe variety.
• Note that posteriorly situated fistulae may have multiple external openings which
always connect to a solitary internal orifice, usually midline
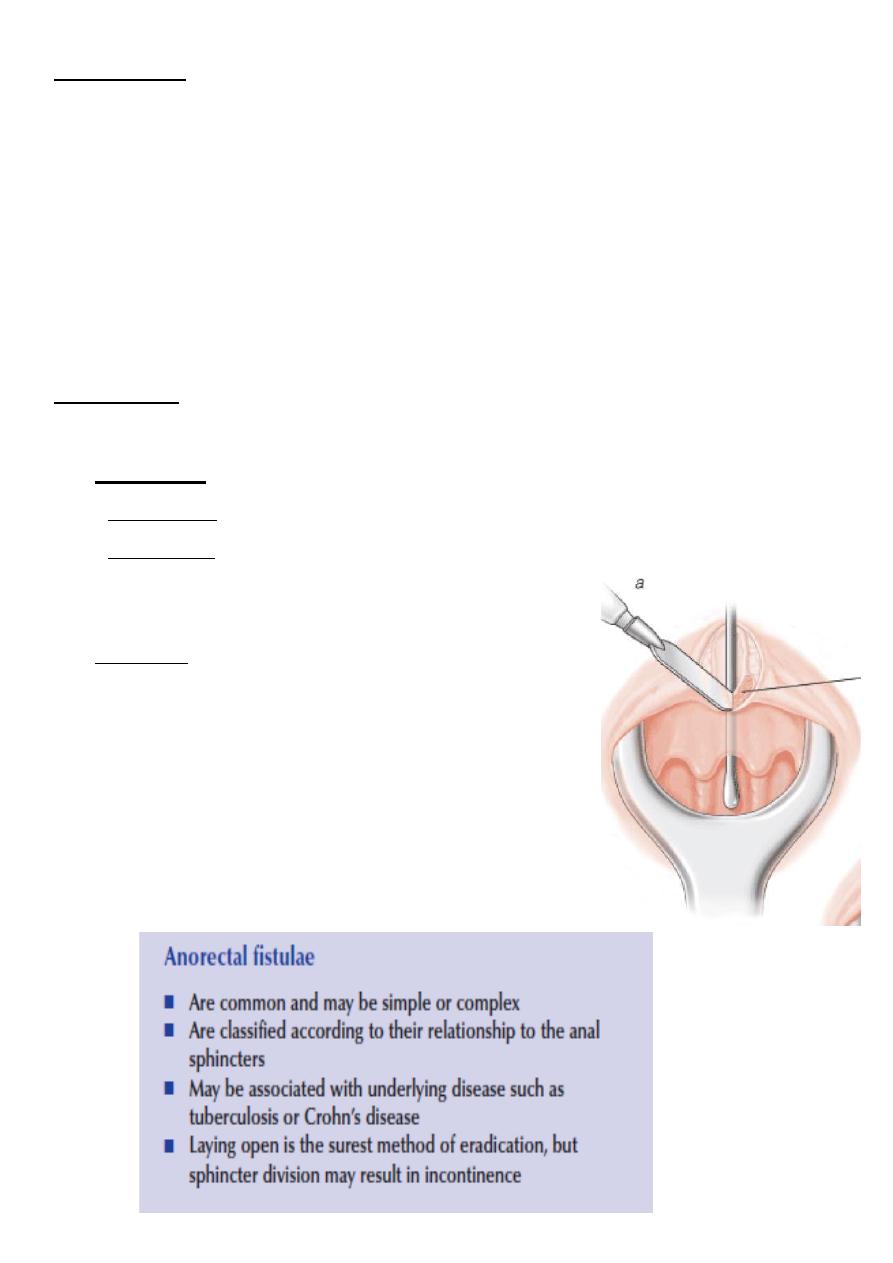
7
Examination
:
Single or multiple external openings next to anal orifices.
• Active fistula granulation tissue with pus.
• Perianal skin show indurations .
• By PR internal opening may be felt.
• Proctoscopy may show the internal opening at the level of dentate line.
• Investigations by colonoscopy, Ba enema if Crhon’s is suspected.
Treatment:-
The goal is to eradicate the fistula while preserving fecal continence.
Low type:-
• Fistulectomy - removal of the whole tract
• Fistulotomy: - tract laid open, tract curetted, edges trimmed, allow the wound to heal
by secondary intension.
High type (through the sphincter).
• Fistulotomy or fistulectomy take care of the sphincter,
divide internal sphincter, sometime part of external.
• High type above the sphincter, treat the cause, multiple
stage excision and colostomy.
