1
Forth stage
Surgery
Lec-2
د.فراس
1/1/2014
Chronic pancreatitis
It is a chronic inflammatory disease due to repeated bouts of pancreatitis in
which there is irreversible destruction of pancreatic tissue and pancreatic
function.
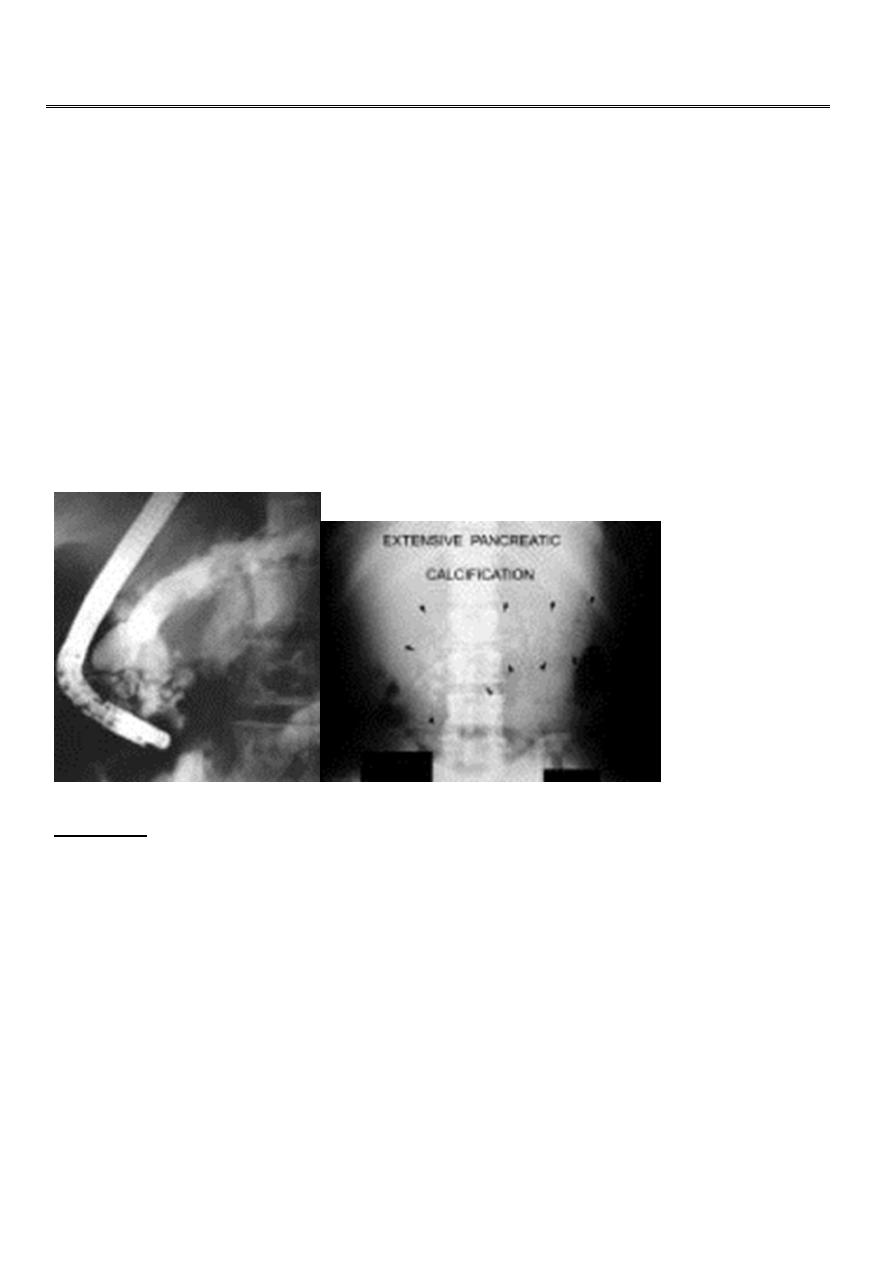
It is characterized by progressive fibrosis and calcification of the pancreas.
Later the pancreas enlarges and become hard.
The duct become distorted, either strictured or dilated containing plugs or
stones.
ERCP Calcification
Etiology:
Alcoholic abuse: 60-70%
Idiopathic 20-30%
Less common causes 10%
Pancreatic duct obstruction
Pancreas divisum
Trauma
Hypercalcemia
Hypertriglyceridemia
hyperparathyroidism
•
Clinical features
1. Pain: is the outstanding symptoms in the majority of patients, it is dull
and gnawing.

2
The site depends on the actual focus of the disease, it may radiate to the
shoulder and back.
Nausea and vomiting are common.
The number of hospital admission and analgesic abuse, give an indicator
to the
severity of the disease.
All the complications of acute pancreatitis can occur, jaundice in 15%
2. Classic triad
Weight loss, steatorrhea, diabetes
Investigations
Serum amylase will rise in the early stages of the disease
Plain X-ray show calcification or stones
MRI, CT scan: will show the outline and the area of damage.
Calcifications seen on CT but not on MRI.
MRCP: will identify the presence of biliary obstruction and the state
of the pancreatic duct.
ERCP : The most accurate test to determine the anatomy
of the
pancreatic duct.
Pure pancreatic juice can be obtained for cytology.
Therapeutic endoscopic papillotomy.
Conservative treatment
Control of pain
Correction of the malabsorption
treatment of diabetes
Avoid alcohol intake
Nutritional and digestive measures
Surgical treatment : indications
1. Persistent uncontrollable pain
2. Relief of biliary or pancr. duct obstruction.
Carcinoma of the Pancreas
Incidence and Aetiology:
It is the sixth most common cancer causing death.
It affects males more than females.
Peak incidence between 65-75 years.
Prognosis is poor. 5 year survival < 5%.
3
Cigarette smoking.
Family history.
Chronic pancreatitis
Hereditary pancreatitis
Pathology:
Adenocarcinoma accounts for 85% of cases, they are solid scirrhous tumors
(1) Cancer of the head (70%)
head proper 2/3
periampullary 1/3
(2) Cancer body and tail (30%)
The growth is infiltrating, hard, and irregular.
Spread
Direct: duodenum
Lymphatic:
Blood:
Peritoneal implantation
Ca Pancreas
Clinical picture
(a) Cancer head : Symptoms:
1. Obstructive jaundice : painless progressive in 75%
2.
pain: steady, dull, epigastric, radiated to the back.
3. Loss of weight, weakness, and anorexia.
4. Steatorrhea, diabetes, malignant ascites, acute pancreatitis, gastric outlet
obstruction.
Signs:
Enlarged liver due to multiple metastasis.
Palpable non tender gall bladder in 60%
Palpable hard epigastric mass
Ascites, secondaries, thrombophlebitis (trousseau’s sign) , and Virchow’s
glands.
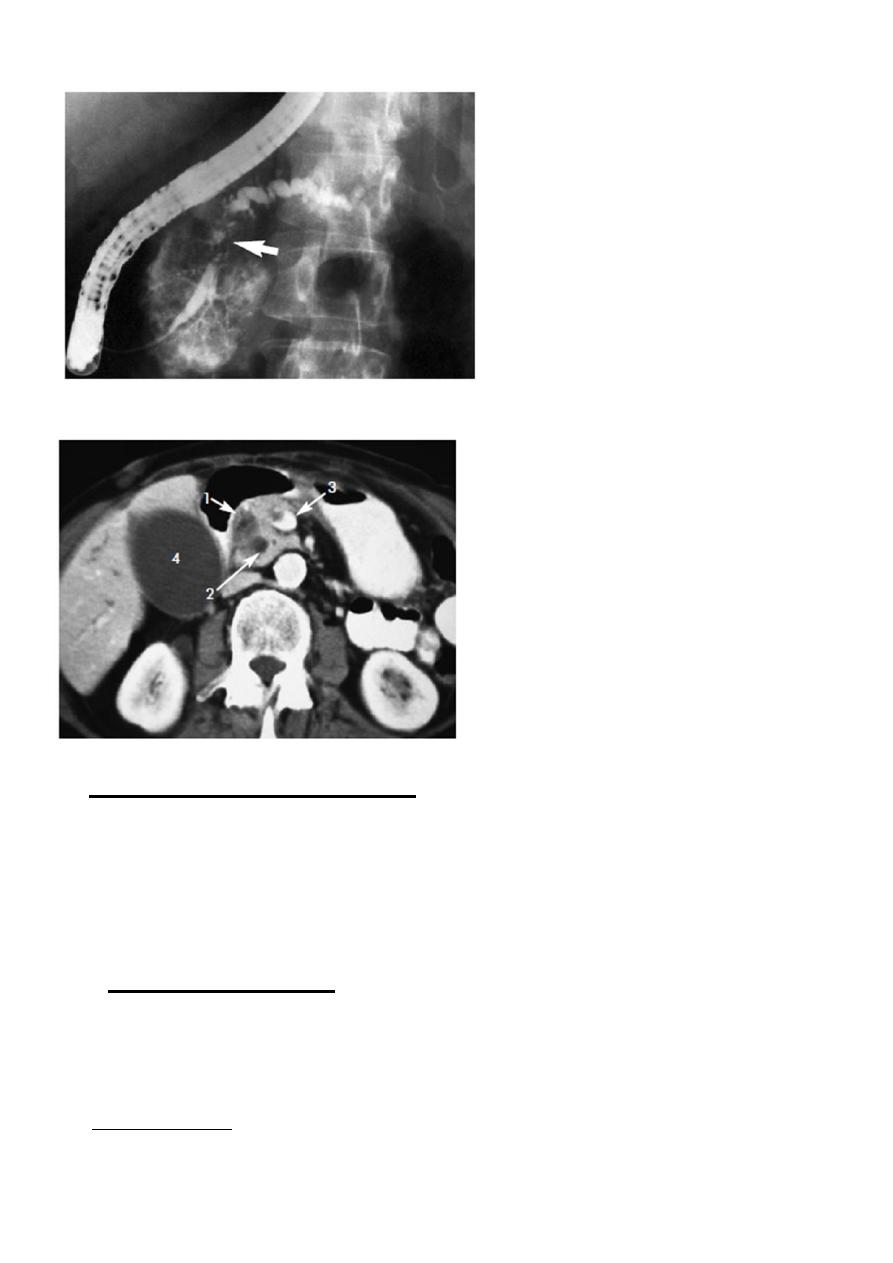
4
ERCP: irregular stricture Ca pancreas
•
CT scan Ca pancreas
(b) Carcinoma of the body and tail:
Intractable pain. The pain is relieved by leaning forward, it is not
related to food.
Loss of weight, weakness, anorexia.
Jaundice in 10% may occur due to LN in porta hepatis.
Sudden onset of diabetes in 25%
Differential diagnosis:
Calcular obstructive jaundice
Chronic pancreatitis
Complications
1. Pancreatic asthenia and cachexia due to
a. steatorrhea

5
b. exhaustion from insomnia due to pain and pruritus.
2. Malignant obstructive jaundice.
3. Duodenal or pyloric obstruction
4. Ascites: from metastasis, portal v. pressure.
5. Edema of the lower limbs
6. Splenic V. thrombosis in 10%
Investigation
Laboratory:
Liver function test
Serum bilirubin level
alkaline phosphatase level
Low prothrombin concentration.
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CA19-9 antigen
Imaging:
Ultrasound: is the first examination to be ordered in obstructive jaundice.
EUS is more useful in the diagnosis and follow up.
CT scan: the preferred test is contrast enhanced CT scan:
It guides for percutaneous FNAC. If the tumor is small (less than 4 cm)
and
confined to the head without evidence of distant metastasis or
vascular invasion should undergo surgery.
MRI:
ERCP:
Barium meal: “ pad sign” which is widening of the C-shaped duodenal
loop.
The reversed 3 sign due to filling defect of the periampullary mass.
Angiography.
laparoscopy
•
Treatment
At the time of presentation 85% of patients are unsuitable for resection because
the disease is advanced.
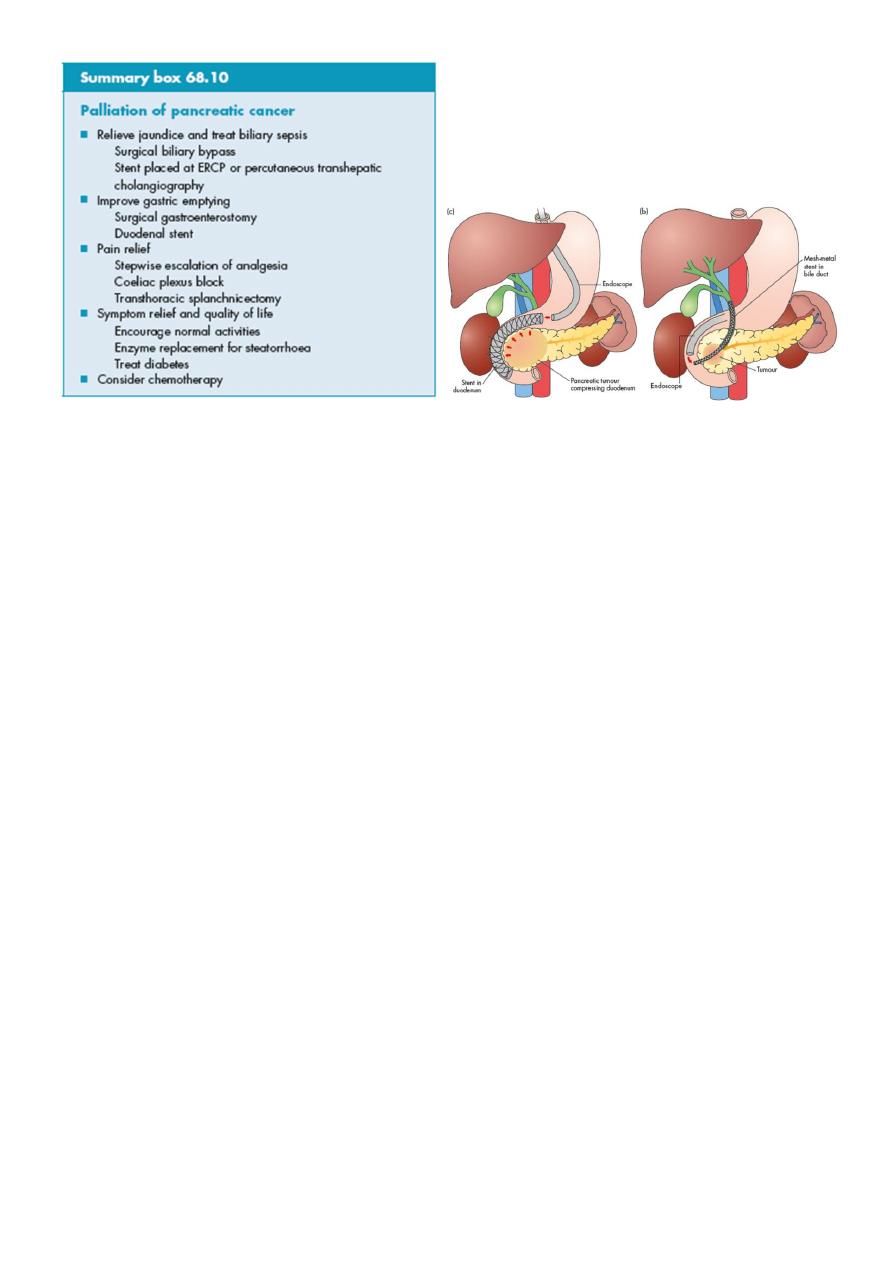
_ potentially curable and fit for surgery : surgery is the best treatment. PPPD
operation.
_ late and unfit patient: drainage procedures by endoscopic stenting or surgical
anastomosis.
Adjuvant therapy: 5-FU, or gemcitabine
6
•
INSULINOMA:
The commonest islet cell tumor. In males less than 40 years old usually
overweight. Usually benign.
Clinical features:
Hypoglycemia less than 45mg/dl
Relieved by glucose
Investigations
Measurement of bd. sugar
Preoperative localization
Treatment:
surgery
