1
Forth stage
Surgery
Lec-3
د
.
ليث
الحرباوي
4/18/2016
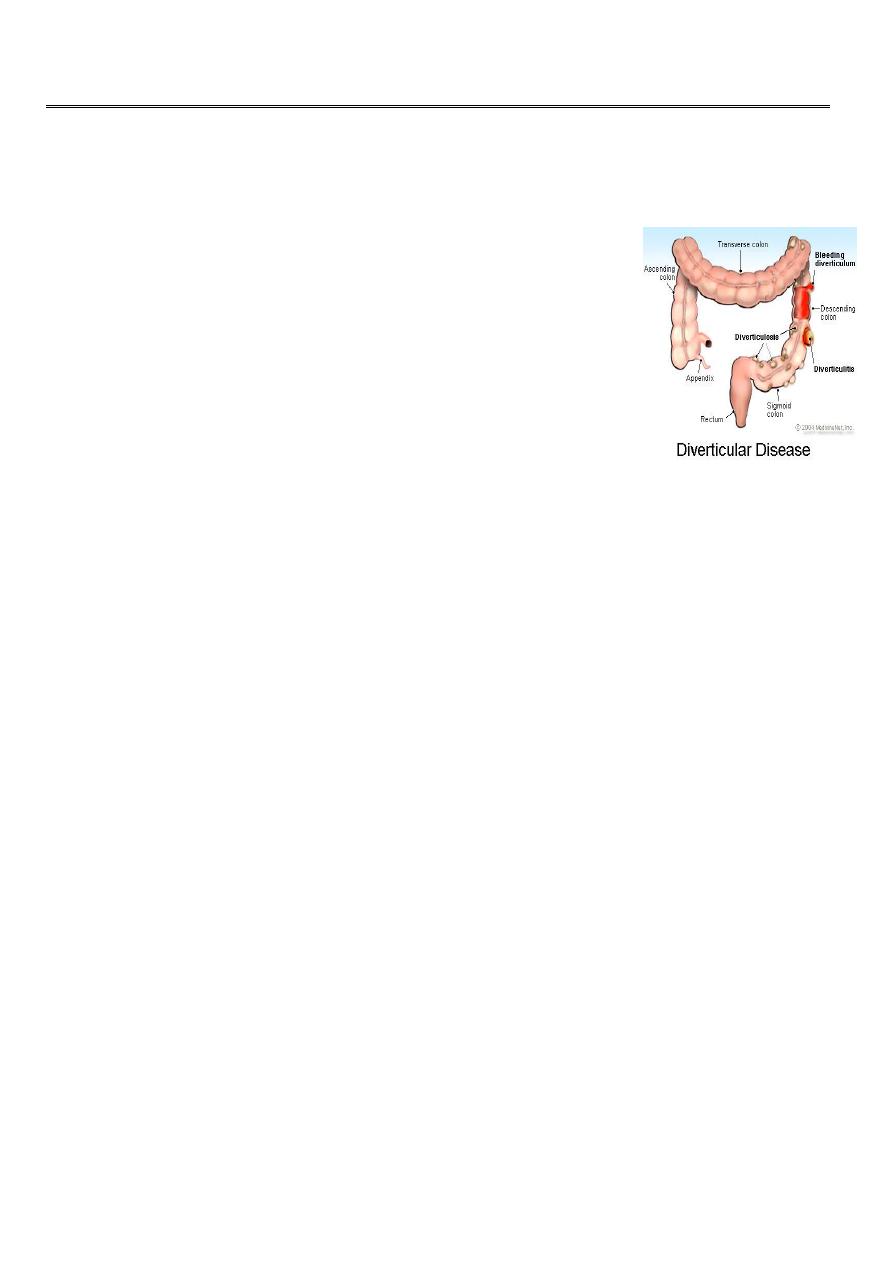
Diverticulitis disease of the large intestine
Found around 75% of over seventy year olds in western
world.Mostly affect sigmoid colon, but can occur in the caecum or
the whole colon ( but not the rectum). Diverticula are most often
asymptomatic( diverticulosis) and found incidentally,but can
present clinically with sepsis or haemorrhage.
• Aetiology: western diet deficient in dietary fibre
Complications of diverticulitis disease:
• 1. Diverticulitis
• 2. Perforations , leading to peri colic abscess, occasionally generalised peritonitis.
• 3. Intestinal obstruction lead to fibrosis can cause stenosis or loops of small bowel
• adhere to inflamed sigmoid.
• 4.Haemorrhage ,diverticulitis may cause haemorrhage.
• 5. Fistula,colovesical,colocutanous,colovajnal,enterocutaneous.
• Classification of contamination:
• The major of sepsis impact on the outcome in acute diverticulitis. The most
commonly used system of classification is: Hinchey
Classification of complicated diverticulitis:
• Grade
• I .Mesenteric or pelvic abscess.
• I l.pelvic abscess.
• I l l.purulent peritonitis
• I v.faecal peritonitis.

2
Radiology:
• Plain chests and abdominal radiograph can demonstrate pneumoperitonium.
• Spiral CT,identifying the bowel wall.
• On identifying of abscess in stable patient ,drainage maybe carried out per
cutaneously.
• Barium enemas and colonoscopy,avoided in acute cases.How can be used after the
attack has settled to exclude a co existing carcinoma.
• Colovesical fistula evaluated with cystoscopy and biopsy in addition.
The differential diagnosis for colovesical fistula includes:
• Cancer
• Radiation injury
• Crohn's disease
• Tuberculosis
• Actinomycosis .
Management
• Conservative
• Nothing by mouth ,rest to the bowel.
• I.v.fluid and antibiotics for gram negative bacilli and anaerobes.
• CT.scan can confirm the diagnosis and assess the complications.
Principles of surgical management:
• Hartman's procedure ,safest option in emergency surgery
• primary anastamosis in selected patients
• elective resection
• colovesical fistula requires resection.
