
1
Forth stage
Surgery
(Urology)
Lec-1
د.محمد فوزي
19/10/2015
Urinary symptoms and investigation
Urinary system :
US is extra peritoneal system composed of two kidneys located in the upper abdomen
protected by thoracic cage, each weighs about 150 g.
Each kidney supplied by main renal artery from aorta, divided into 5 segmental branches and
drained by renal vein to the inferior vena cava
Urinary bladder :
Muscular organ located in the pelvis, acts as urine reservoir during resting time and
discarding urine via urethra during the process of urination by the action of detruser muscles
Contraction .
.
Normal capacity about 350-400 cc
Urinary symptoms:
1-Haematuria
2-pain
3-altered bladder function
4-incontinence
5-nocturnal enuresis
6-associated symptoms
1-Haematuria :
-Macroscopical
-Microscopical
-Terminal
-Total
-Early
-Intermitent
-Persistant

2
2-Pain:
1.Renal pain
2.Ureteric colic
3.Bladder pain
4.Perineal pain
5.Urethral pain
3-Incontinence : involuntary loss of urine
-Continuous incontinence
-Stress incontinence
-Urge incontinence
-Overflow urinary incontinence
Associated symptoms&sign :
1-GIT :
-Autonomic
-Organ relationship
-Peritoneal irritation
2-Mass or swelling
3-Failure to thrive
4-Uremia
urine examination :
1-Dipstick…RBC,,,protein,,,nitrite,,,,screenig
2-GUE
3-Cytological
4-Bacteriological
5-Biochemical :Haemoglobin ;Myoglobin;Bilirubin;Glucose;Electrolyte
and protein
24h urine for calcium; uric acid; oxalate,protein
3
:
INVESTIGATION
1-Renal function test:More than 70% of renal function must be lost before renal failure
becomes evident
2-Blood urea & serum criatinin
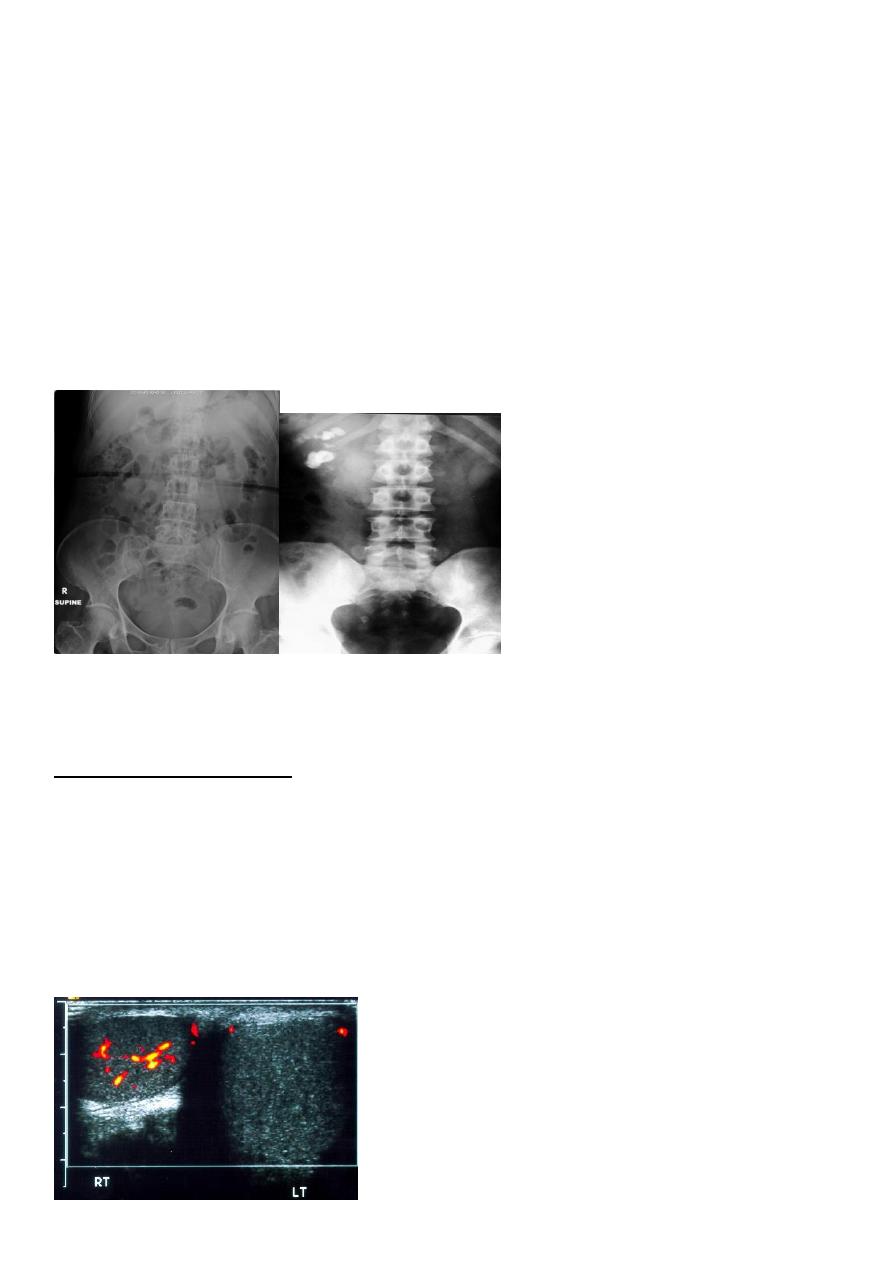
3-radiological:-
KUB (kidney,ureter,bladder):-
A-BonesS
B-Soft tissue
C-Stones
A plain radiograph of the abdomen and pelvis includes the area above both adrenal glands
and extends to 2 cm below the symphysis pubis
KUB: site, skin, sex, stones, psoas shadow, skeleton, and soft tissue shadow
IVU:-
Function Of the collecting system , anatomy of the kidneys , hydronephrosis and
:
filling defect .
.
failure
allergy and renal
C.I.
A-Retrograde ureterpyelography
B-Antegradepyelography
C-Cystography (MCUG)
D-Urethrography
4-Ultrasonography
5-Color Doppler uls

4
6-Transrectalultrasonography
7-CT scan (computed tomography):
-Tumor size , site , invation .
-Lymph node
-Invation of the renal vein & vena cava
-Staging & follow up of testicular tumor
-CT can accurately characterize the nature of tissue in the lesion.
-CT is useful in the preoperative evaluation and staging of tumors.
-CT has replaced IV urography as the primary modality for the assessment of suspected renal
injuries and their complications
-For the evaluation of patients with acute flank pain, unenhanced spiral CT is more sensitive
in detecting calculi than EXU
8-MRI
9-Radioisotop scanning Nuclear imaging :
Tc 99m Diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic Acid 99mTc-DTPA
Mercaptoacetyltriglycine 99mTc-MAG3
Technetium Tc 99m Dimercaptosuccinic Acid 99mTc-DMSA
It gives the split function of each kidney
10-Isotop bone scanning
FOR STAGING KIDNEY&PROSTATE CANCER
11-Urodynamic study
12-Endoscopy : invasive /Urethroscope, cystoscope ureteroscope and
renoscope.Nephroscopy
13-Retrograde ureteropyelography : invasive
14-Cystourethrography :
Contrast-enhanced imaging of the lower urinary tract provides valuable information on the
function and anatomy of the bladder and urethra
15-Angiography :
Currently, CT, MRI, and ultrasonography have supplanted angiography for most diagnostic
indications, providing equivalent and at times greater information with markedly decreased
morbidity and risk
