
1
Forth stage
Surgery (Urology)
Lec-3
د.ﻣﺣﻣد اﻟﺷﮭواﻧﻲ
21/10/2015
Hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis
Hydronephrosis
Aseptic dilatation of the pelvi-calyceal system
Obstructive or refluxive .
Unilateral or bilateral .
Whole ureter or part of it may be also dilated,,,hydroureteronephrosis
Mild, moderate or severe
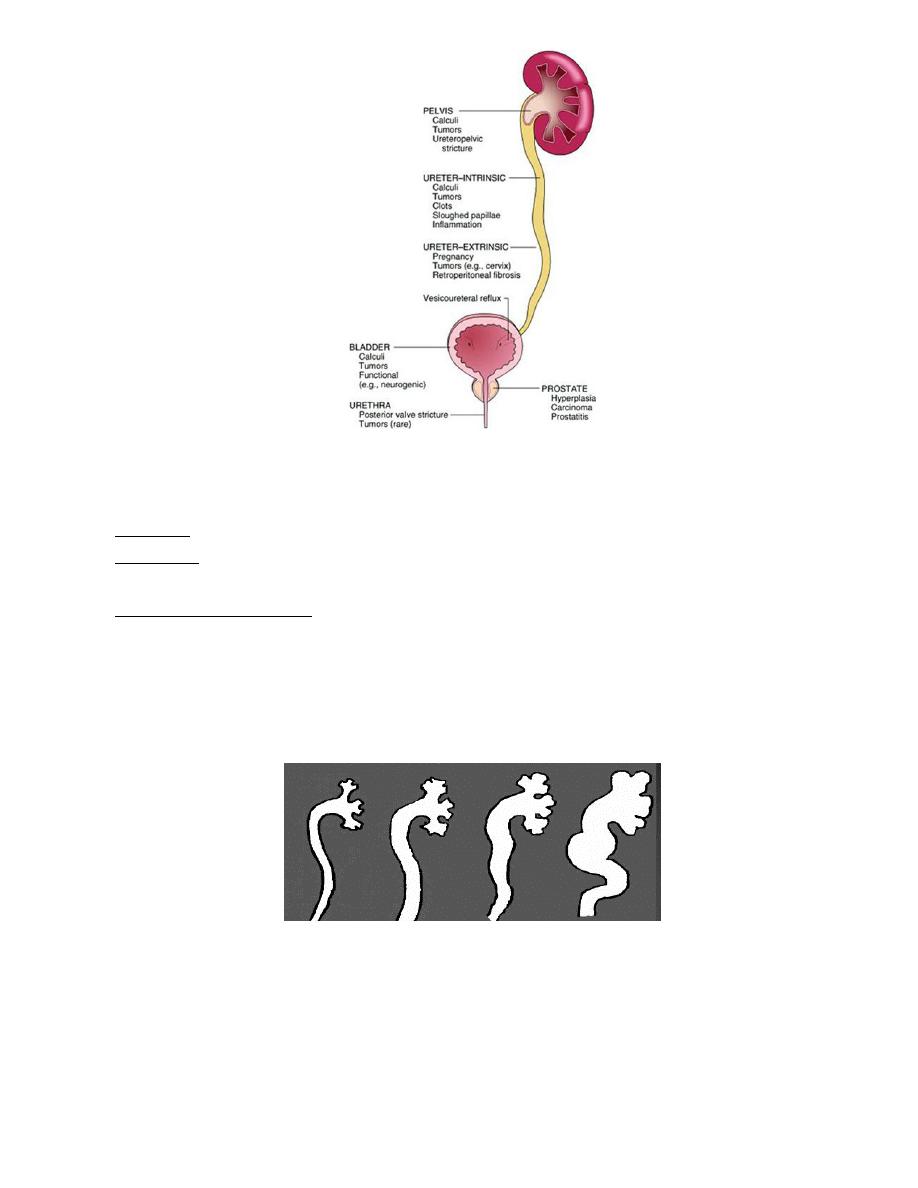
Unilateral hydronephrosis
Extramural
1. tumor of prostate,colon, cervix,rectum,
2. retroperitoneal firosis
3. retrocaval ureter
Mural
1. PUJO
2. ureterocele ,congenital megaureter
3. ureteric sticure
4. neoplasm of ureter
Intramural
1. stone in the ureter or pelvis
2. slught papilla
Bilateral hydronephrosis
Causes:
1. LIKE causes of UNILATERAL WHEN HAPIN BILATERALY
2. Conginital
stricture of external urethral meatus
posterior urethral valve
bladder neck contracture
3. Acquired
BPH, ca prostate,post operative bladder neck scarring
urethral stricture
Neurogenic bladder
2
Other causes of hydronephrosis
VU reflux: due to lower ureteric orifice incompetence, either primary or secondary.
Pregnancy: high level of progesteron causes ureteric smooth muscle relaxation and
hence hydronephrosis.
Residual hydronephrosis (after surgery).
Pathophysiology:
Increased pelvic pressure causes pelvic dilatation, then calyceal dilatation, which results
in a gradual atrophy of the kidney and its function. In severe and long standing cases the
kidney is converted into a sac-like structure with complete loss of its function.
Investigations
1- U/S: non invasive and cheap. Can diagnose Hydronephrosis in utero
2- KUB:Soft tissue shadow
3-IVU: for diagnosis and localize the cause
4- MCU: for diagnosing and grading VU reflux, and posterior urethral valve

3
5- Retrograde pyelography( in non functioning kidney).
6- Whitaker test.
7- Radioisotope renogram.
8-MRI and CT scan
Treatment of hydronephrosis :
Each case treated accordingly
pyonephrosis
Is an infection in a hydronephrotic kidney
Causes
1. Infection of hydronephrosis
2. Follow acute pyelonephritis
3. Complication of renal stone
-Its usually unilateral
Clinical features
Classical triad of symtoms (anaemia,fever and swilling in the loin)
If it is due to infected hydronephrosis ----> high fever,rigor and large swilling
Symtoms of cystitis may be prominent
Investigations
1. GUE…….pyuria
2. CBP……. leucocytosis
3. KUB……..stone
4. ULS………hydronephrosis, stones
5. IVU……….hydronephrosis ; poor functioning kidney
treatment
Surgical emergency !
1. Drainage of the kidney, by :
percutanous nephrostomy
if the pus is thick by ---> formal nephrostomy
2. Parenteral broad specterm antibiotic
3. Nephrectomy ( if affected kidney is non functioning and other kidney is normal)

4
complications
If not treated rapidly :
1. Permenant renal damage
2. septicemia
