Family Planning Food SupplementationFemale EducationLow Birth Weight
Specific ObjectivesAt the end of the lecture you will be able to• Define family planning (FP), its objectives and parameters.
• Draw a line diagram shows the association of FP parameters and maternal ,perinatal, neonatal and infant mortality and morbidity.
• Realize the importance, way of administration and target groups for food supplementation.
• Define food fortification.
• Enumerate most common micro-nutrients used.
• State way of administration with stress of Vit A (target group outcome, prevention of Vit A deficiency.
• 7. Realize the importance of female education in enhancing overall family health.
• 8.Define low birth weight (LBW), small – for-date and preterm newborns.• 9. Enumerate common causes of LBW.
• 10. State importance and incidence of LBW (worldwide and Iraq).
• 11.Suggest a plan for prevention of LBW.
Family Planning
Practice that help couples to attain certain objectives:
To avoid unwanted pregnancy.
To regulate intervals between pregnancies (spacing).
To control time at which birth occurs in relation to age of parents particularly mothers (timing).
To determine the ideal number of children within the family (family size).
Dependant
VariableMortality
Morbidity
family planning parameters
(independent)
Risk to mothers & infants is greatest at the following situations
<18 years of age (too young)
>35 years of age (too old)
After the 4th birth (too many )
Less than 2 years apart (too close)
• Food Supplementation
• Three specific forms of food supplements that have proved to be high cost-effective:• Food supplements directed to target groups
• Pregnant women at risk of delivering LBW
• Extra food supplements(3rd trimester)
• (500 cal+10g PTN /day)
• Extra gain in WT of 1.5 kg
• 300g in BW
• Food fortifications
• A process where by micro-nutrients are added to food to maintain or improve the quality of diet of a community.
• In order to deal with specific nutritional deficiencies & is typically used with conjunction with staple foods.
Iodine added to salt
Vit A capsules or drops every 6mnthsIron changing dietary habits
Iron supplements to pregnant +lactating
food fortification (salt, sugar).
Vitamin A
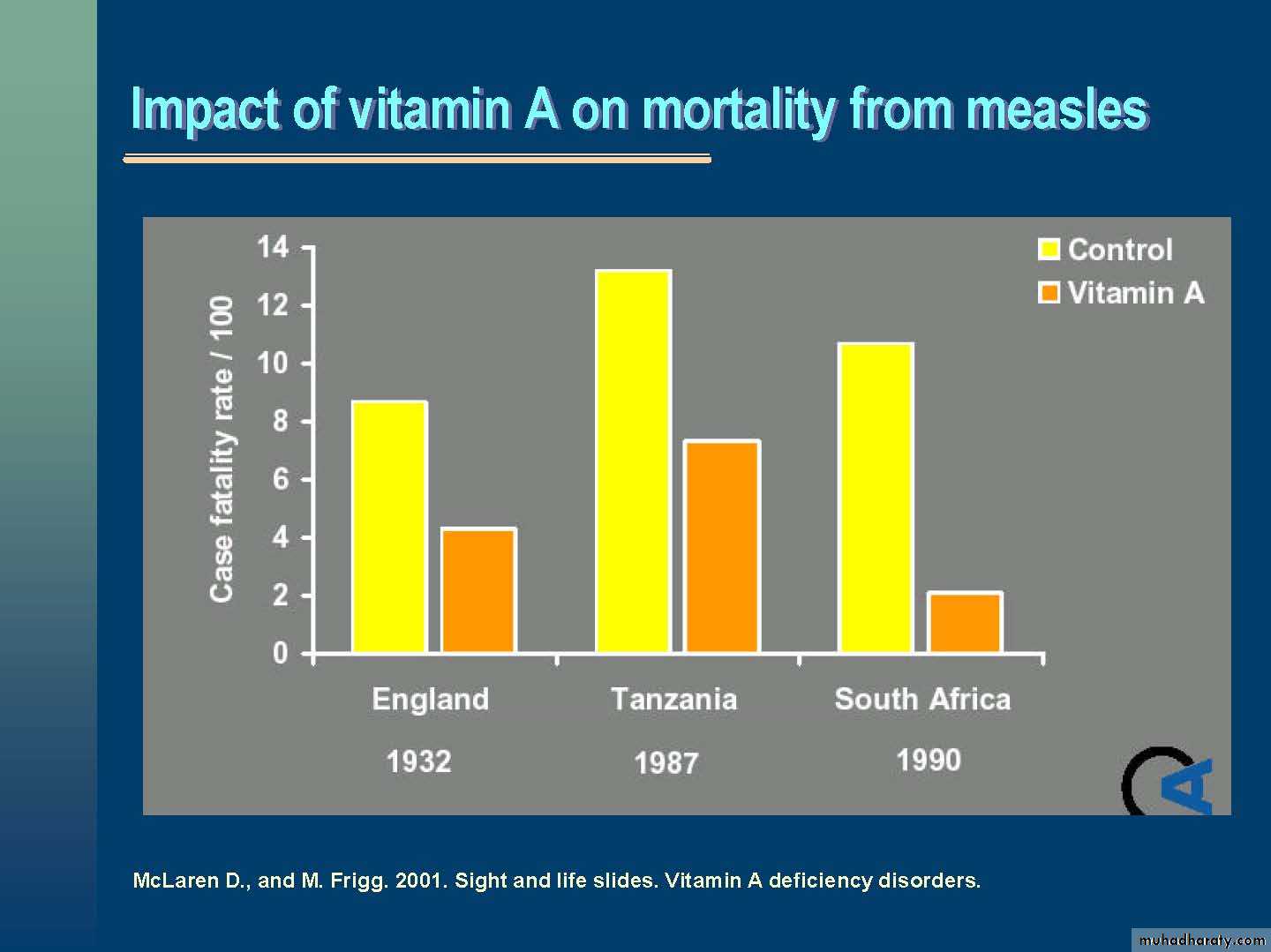
Impact of Vit on child survivalImproving vit A status in children results in global mortality reduction of 23%.
Vit A helps to prevent 1.3-2.5 million deaths annually in children less than 5 years of age.
Vitamin A
Vit A is used in treatment and preventionIndications
Current Xerophthalmia
Measles
Severe malnutrition
Bitot spots
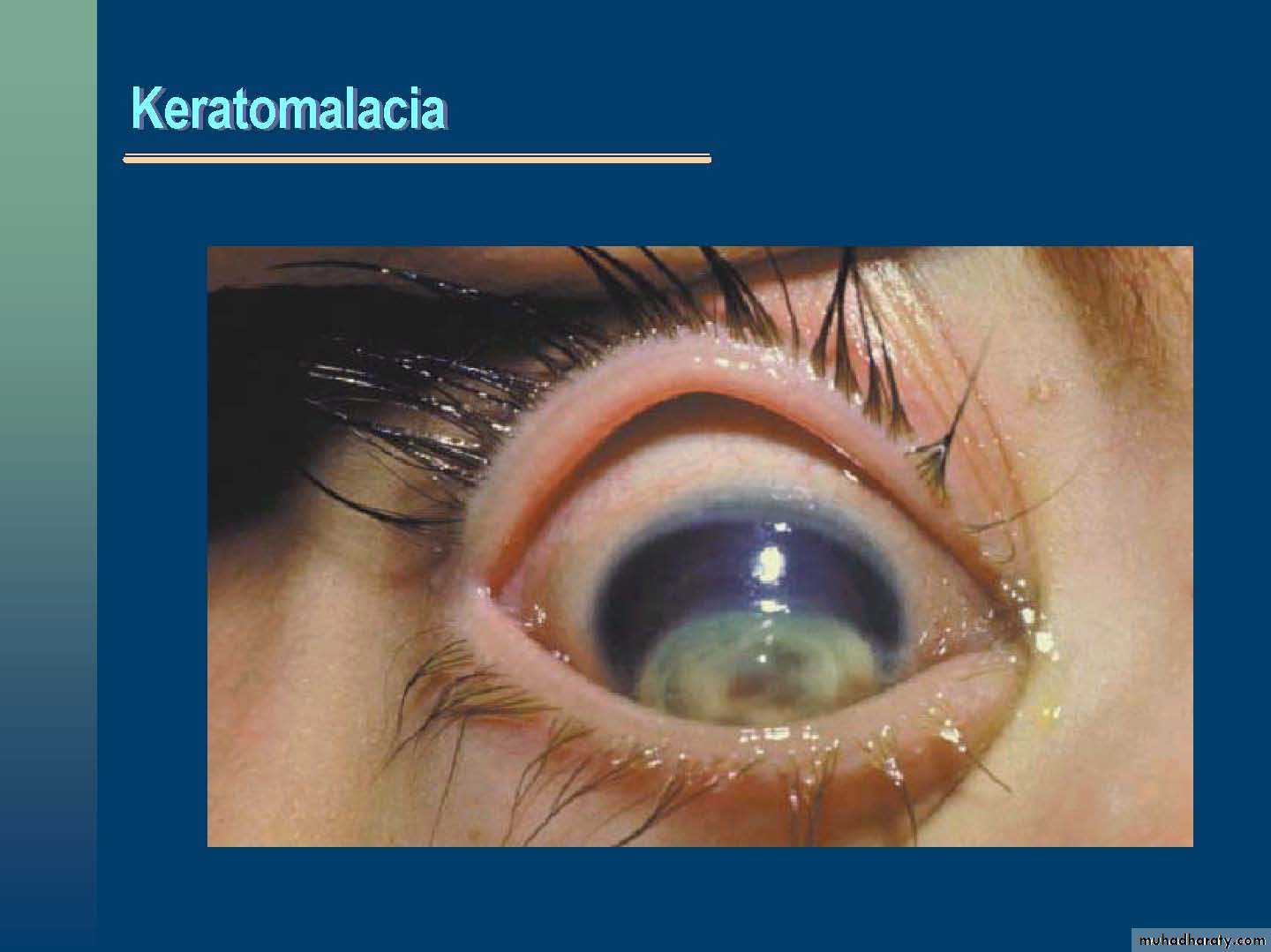
Keratomalacia
Vit A: prevention
Combining the administration of vitamin A supplements with immunization is an important part of this effort together with measles immunization and National immunization days to eradicate polio.Providing high – dose supplementation to new mothers soon after delivery has provided further benefits to young infants through enriched breast milk (200 000 IU) during immunization contact. (only once)
Periodic oral supplementation
Children age 9-12 months, 100.000 IU every 4-6 month.> 12 months, 200.000 IU every 4-6 months.
Optimal interval between doses is (4 – 6 months).
A dose should not be given soon after a previous dose of vitamin A supplement.Interval can be reduced in order to treat clinical vitamin A deficiency and in measles cases.
Food fortification : Vit A fortified sugar
Food diversificationYellow fruits
Carrots
Green leafy vegetable
Liver and oil
Female Education
Act as a powerful independent force in reducing number of infants & children deaths. How?• Schooling enhances women’s ability to provide adequate care.
• Education enhances women status & power within the family.
• Educated mothers can use health services & facilities properly.
Considering low birth weight (LBW) There are two main groups
Those born prematurely
Those with fetal growth retardation
In Iraq…….which is more common?????
Definition….Birth weight (BW) less than 2.5 kg ( up to and including 2499 gm)
Measurements being taken preferably with the first hour of life.
Apart from BW , babies can be classified into 3 groups
Preterm born before 37 wks of gestationTerm… 37-42 completed wks of gestation
Post term… 42 completed wks and overPreterm
Causes ..multifactorial….multiple births, acute infection, hard physical work, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Prevention …
good antenatal care, discouragement of adolescent pregnancy, and treatment of hypertension.
Small for date…
The weight is less than the 10th percentile for the gestational age ..it is the result of intrauterine growth retardation.
Small for date
Maternal causes….malnutrition, severe anemia, heavy physical work during pregnancy, hypertension, toxemia, smoking, malaria, short maternal stature, high parity, short spacing, too young mothers ….etc
Percentage of low BW babies (incidence) =
No. of live birth babies with weight less than 2.5 kgTotal no. of live births
x100
Incidence……world wide is 17%95% in developing countries.
The target reduction in the incidence is to less than 10%Importance o f low BW
Low BW is the most serious challenge in MCH in both developed and developing countries.
Its public health significance may be ascribed to ..
Importance o f low BWHigh incidence.
Its association with mental retardation.
High risk of perinatal and infant mortality.
Human wastage and suffering.
Very high cost of special care.
Its association with socio-economic under development.
Prevention
Direct intervention measuresIdentification of at risk pregnant women and steps should be taken to reduce the risk……use the high risk approach
Some of the direct intervention are as follows:
Prevention
Proper feeding of pregnant women.Treatment of anemia by iron folic acid supplementation.
Supplementary feeding.
Fortification and enrichment of food…..etc.
Controlling infection..e.g. UTIs, malaria, rubella, toxoplasmosis, syphilis.
Early detection and treatment of hypertension, toxemia, and diabetes.
Prevention
Indirect intervention
Family planning.
Avoidance of smoking.Measures aimed to improve health and nutrition of young girls.
Improvement of socio-economic and environmental conditions conditions.
Distribution of health services especially in the under-served areas.
Government support through maternity leaves with full wages and child benefits.
Treatment
Incubatory care.Feeding.
Prevention of infection.
Leading Causes of Death
AtelactasisMalformation
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage secondary to birth trauma or anoxia
Pneumonia and other infections
Conclusion
Family planning, female education and food fortification play an important role in the child health care strategy.
Low birth weight is an important problem. Its public health significance is ascribed to its high icidence and significant association with high infant and childhood mortality and morbidity, which is reflected on the community development as a whole.