
1
Forth stage
Surgery (Urology)
Lec-12
د.محمد فوزي
02/20/2015
BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION
(B.O.O.)
It’s urodynamic concept of low flow rates and high intravesical
pressures.
Causes:
1. BPH.
2. CAP.
3. bladder neck stenosis.
4. urethral stricture.
5. neuropathic conditions.
Pathophysiology :
- Boo over time will result in increase in the intravesical voiding
pressure (>80 cm H2O), bladder muscle hypertrophy
(trabiculation, sacculation and diverticulum formation).
- High pressure may transmit to the upper tract causing hydroureter,
hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency.
- Boo results in incomplete bladder evacuation (residual urine)
which predisposes to UTI and stone formation.
- Decrease uro flow rate under 10 ml /sec
Symptomatology (LUTS)
1-Obstructive:
- Hesitancy
- Straining
- Weak stream
- Intermittency.
- Post voiding dribbling.
- Retention of urine.
2
2-Irritative:
- Frequency.,nocturia
- Urgency & urge incontinence.
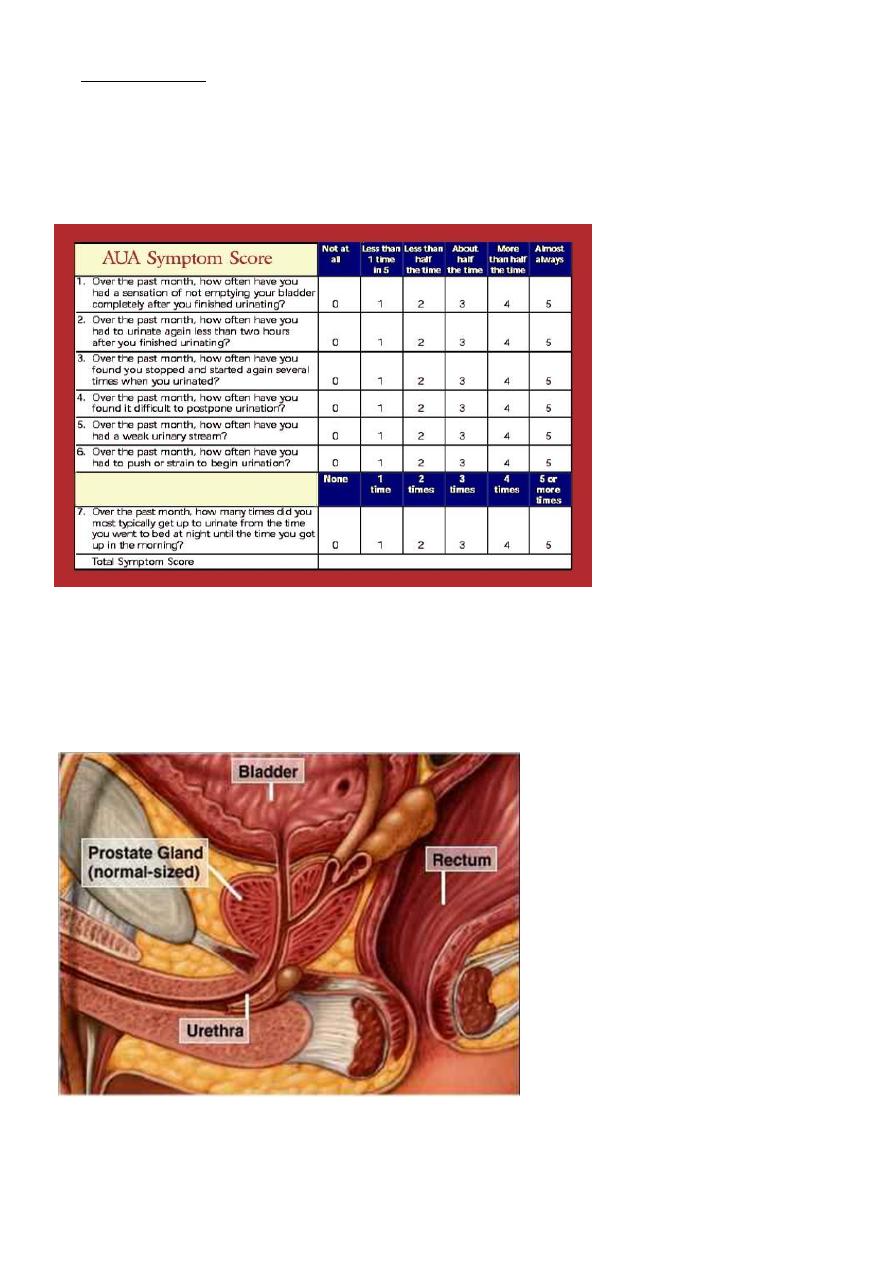
IPSS [international prostatic symptom score]
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Third most common urological pathology , Starts at late 30s & appear
clinically at 60s.
3
Theories:
Hormonal: DHT, growth factor.
Neoplastic: fibromyoadenoma.
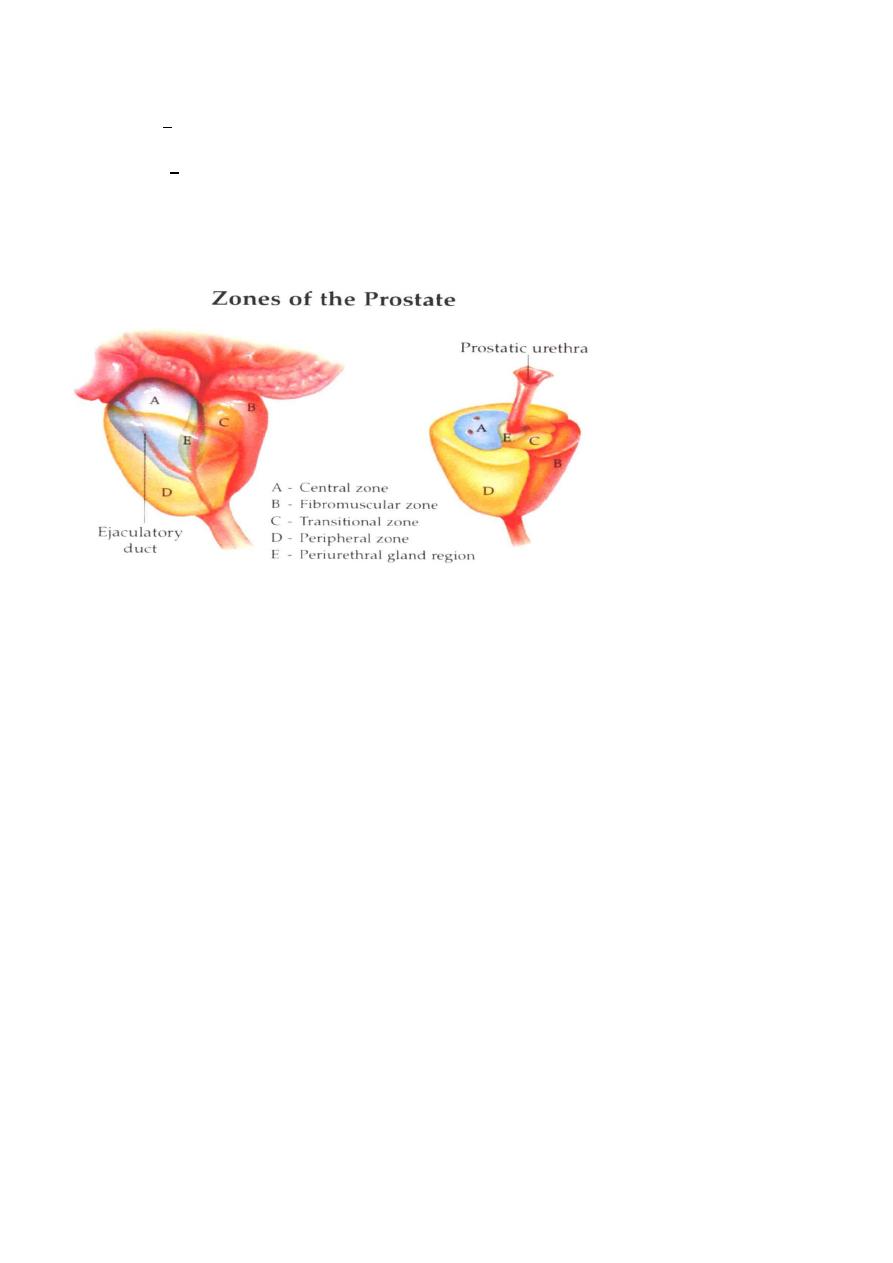
Typically affects submucosal glands at transitional zone.
Symptomatology :
- Boo (irritative and obstructive).
- Symptoms are slowly progressive over years, worsening at
winter time.
- Renal failure.
- Hematuria.
Pain is not afeature of BPH the presence of which may indicate acute
retention,vesical stone,infection,CAprostate
Precipitating causes for retention :
- Severe pain. MI, joint pain.
- Psychological upset.
- Cold exposure.
- Constipation.
- Drugs
- Anticholenergic & diuretic ,decongestant,antihistamin
- Ignoring first desire for urination.
4
Clinically :
- Usually normal.
- Distended bladder.in acute or chronic retention
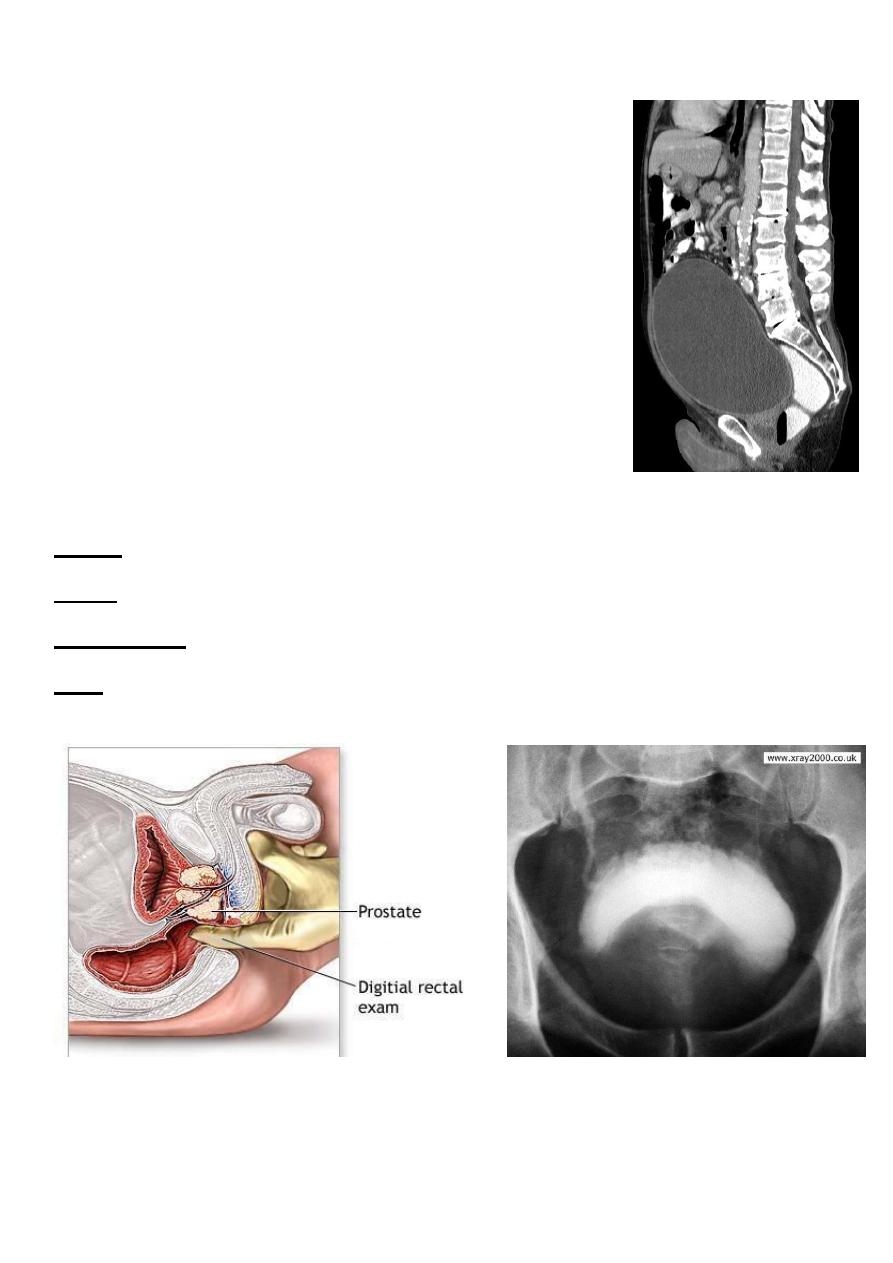
- PR ex: enlarged prostate, smooth, regular,
firm, maintained median sulcus and mobile
rectal mucosa
- Normal anal sphencter tone.
- Normal bulbocovernosus reflex
Investigations :
GUE: normal or UTI
RFT: normal unless there is renal failure
U/S:TRUS: BPH, vesical stone, residual urine and hydronephrosis.
IVU
5
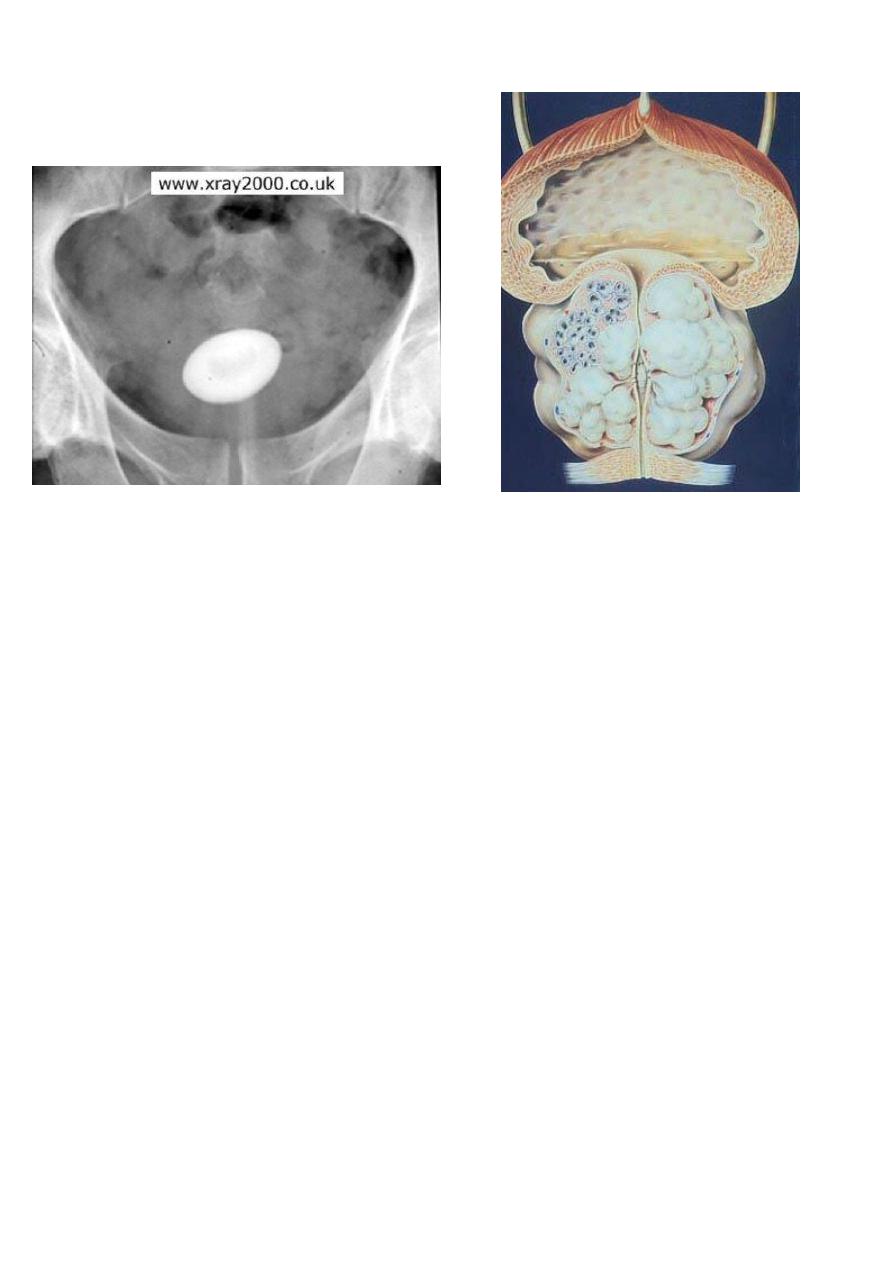
Vesical stone BPH
PSA: (prostate specific Ag)<10 ng/ml.
Cystoscopy: enlarged prostate, trabiculation & stones.
Size of the prostate has no relation with the severity of the symptom but
the degree of urethral compression.
Treatment :
Conservative:
- Avoid ppt factors.
- Treat pains.
- Treat UTI.
- Αlfa blocker: prazocin 1 mg, terrazocin 2mg, doxazocin
2mg.tamsulusin,alfuzosin At night ,
S/E hypotension, 1
st
dose syncope.
- 5 α reductase inhibitors: fenasteride, prosteride 5 mg/day > 6
months.
S/E impotence.
Usually used in large gland

6
Semi surgical:
1. TUMT (trans urethral microwave thermotherapy)
2. HIFU ( high intensity focused u/s)
3. TUIP (Trans urethral incision of prostate)
4. TUNA (Trans urethral needle ablation)
5. Prostatic stents
6. TU baloon dilatation
TUMT TUNA Stent
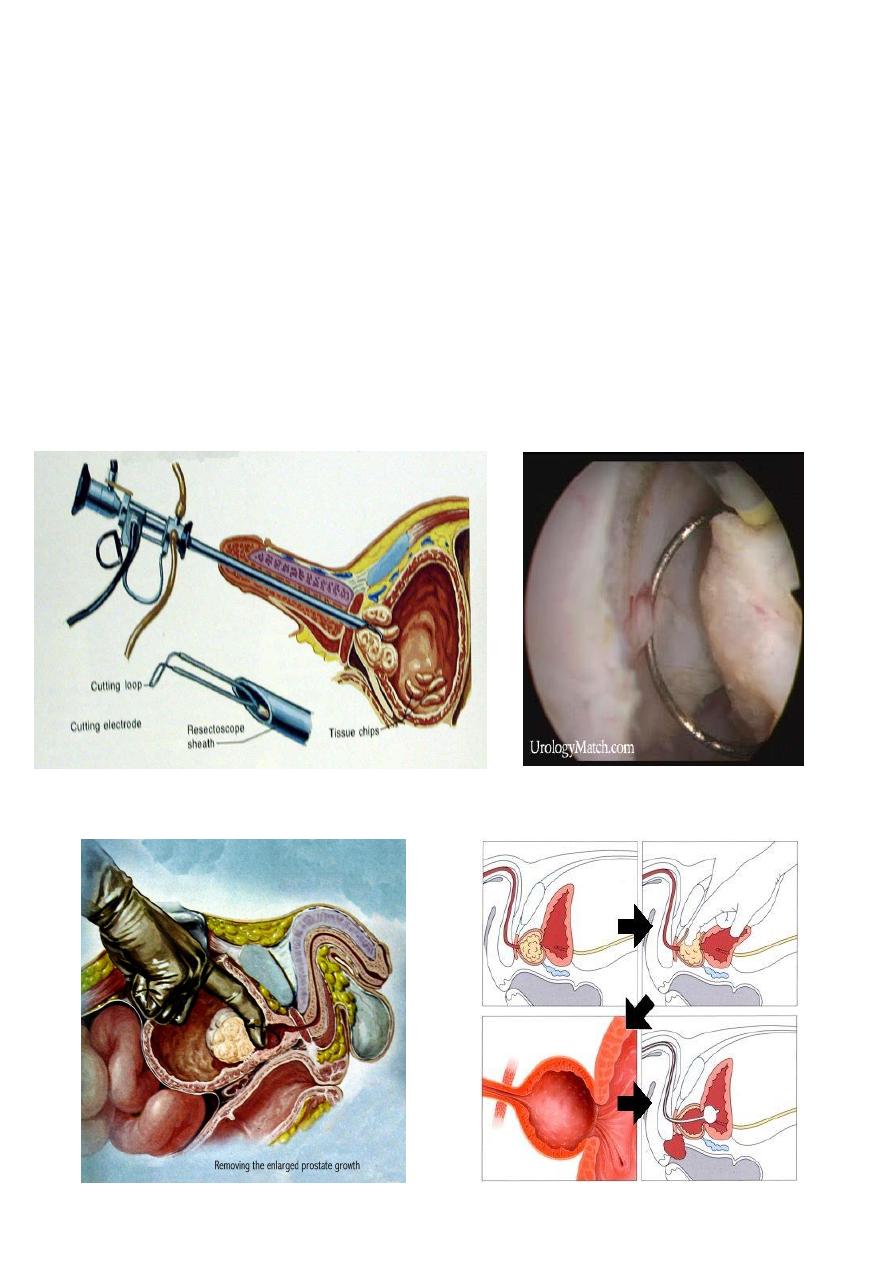
Surgical treatment
Endoscopic:
- TURP
- Laser
Open surgery:
- Trans vesical prostatectomy.
- Rertopubic prostatectomy
Indication of surgery in BPH
1-severe symptoms
2-failure of medical treatment
7
3- complications like :
-acute urinary retention
-chronic retention
-repeated hematuria
-repeated UTI
-vesical stone
-renal impairment due to chronic retention
TURP
Transvesical retropubic
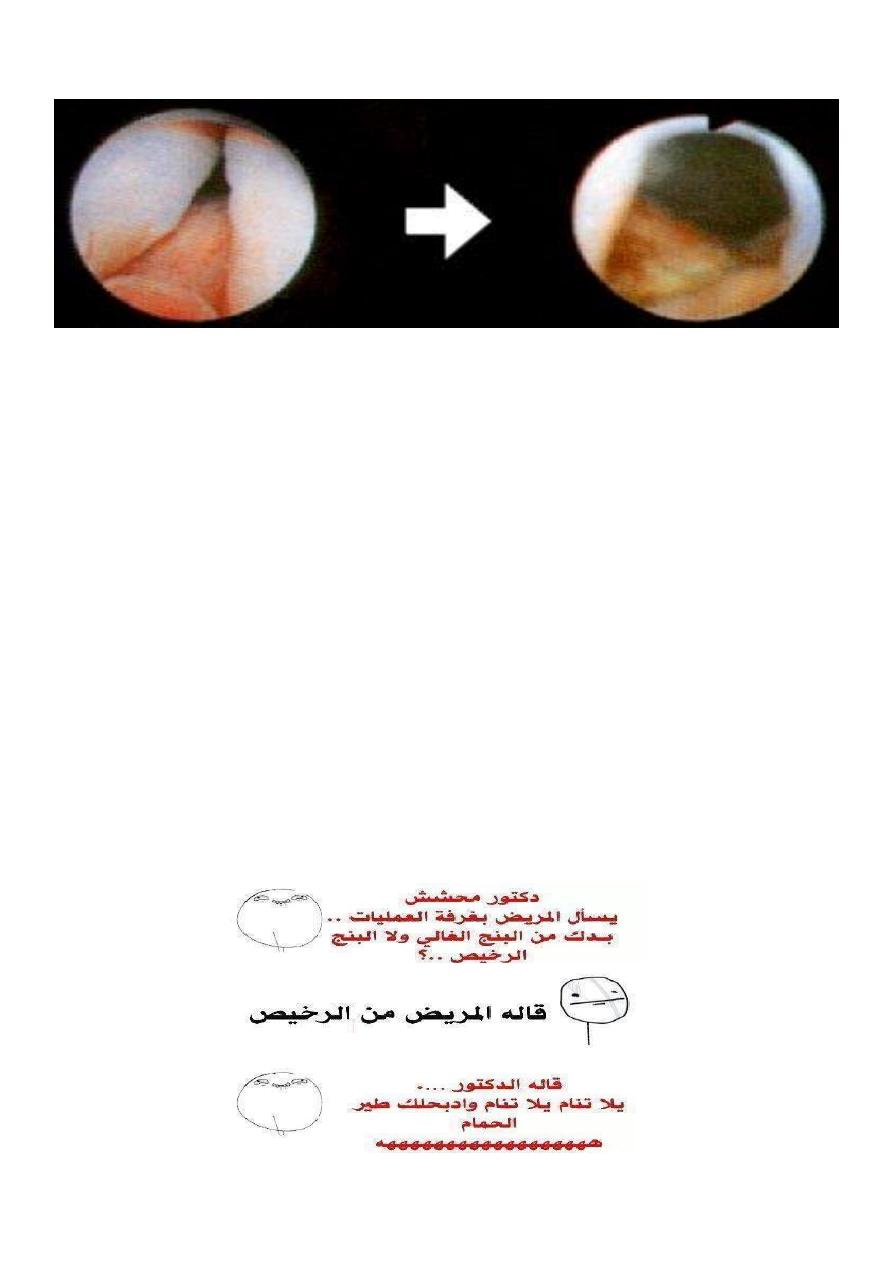
8
Before TURP After TURP
Complications :
Early:
- Bleeding and clot retention.
- TUR syndrom (water intoxication) due to. dilutional hyponatremia.
- Infection.
- Wond infection[in open prostatectomy]
Late:
- Urethral stricture
- Bladder neck contracture
- Retrograde ejaculation.
- Incontinence.
- Impotence.
- Recurrence of BPH. After 5-10 years.
SH.J

9
