
1
4th stage
Medicine
Lec-12
د. ظاهر1/1/2016
Investigations in Respiratory Diseases And the Lung Function Tests
Imaging
:
The Plain chest radiograph:
1-Pneumonia, Bronchogenic carcinoma, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, and Pleural Effusion can
be detected very easily by Plain radiograph.
2-Lateral Film provides additional information about the nature and position of the lung
lesion.
3-Follow up chest radiograph is very useful for monitoring the progress of the disease and
the advantage of the therapeutic regimen.
Computed Tomography (CT):
o Computed Tomography of the chest is very sensitive and accurate in determining the
position, the size, and the consistency (calcification or cavitation) of any mass lesion.
o Pre-operative assessment of mediastinal spread in patients with lung cancer.
o High-resolution CT is very useful in diagnosis of interstitial fibrosis, bronchiectasis and
pulmonary embolism.
Ventilation-perfusion
o
133
Xe gas is inhaled (ventilation scan) .
o
99m
Tc-labelled albumin are injected I.V (perfusion scan);
o Pulmonary embolism we will detect filling-defect in the perfusion scan and doesn't
match the ventilation scan .
o Asthma and COPD will show a matched Ventilation-perfusion defect.
Positron emission tomography (PET)
whole-body PET[
18_
fluorodeoxyglucose(FDG)] very useful in staging lung cancer.
Pulmonary angiography for the positive detection of pulmonary embolism.
Endoscopic Examination and others
o Laryngoscopy
o Direct or indirect examination.
o Bronchoscopy
o Mediastinoscopy
o Pleural aspiration and biopsy
o Skin tests; Tuberclin test and skin hypersensitivity tests
o Immunological and serological tests

2
Other tests
o Counter-immunoelectrophoresis of Sputum, blood or urine (e.g. for pneumococcal
antigen).
o Blood for antibody titres for specific organisms(Mycoplasma,legionella,chlamedia or
viruses).Preciptating antibodies for fungi e.g Aspergillus.
o Microbiological investigations.
o Histopathological investigations
Pulmonary Function Testing
Purpose of Pulmonary Function Testing is to know
1-How much air volume can be moved in and out of the lungs
2-How fast the air in the lungs can be moved in and out
3-How stiff are the lungs and chest wall - a question about compliance
4-The diffusion characteristics of the membrane through which the gas moves (determined
by special tests)
5-How the lungs respond to chest physical therapy procedures
Pulmonary Function Tests are used for:
o Screening for the presence of obstructive and restrictive diseases
o Evaluating the patient prior to surgery in patients:
a. Older than 60-65 years of age
b. known to have pulmonary disease
c. obese (pathologically obese)
d. have a history of smoking, cough or wheezing
e. will be under anesthesia for a lengthy period of time
f. undergoing an abdominal or a thoracic operation
Pulmonary function test
Pulmonary Volumes
1-Tidal volume: The volume of air inspired or expired with each normal breath(0.5 L) for
young man.
2-Inspiratory reserve volume: is the extra vol. of air that can be inspired over & above the
normal tidal volume(3 L).
3-Expir.reseve vol.: is the extra vol. of air that can be expired by forceful expiration after the
end of tidal expiration(1.1 L).
4-Residual vol.: The volume of air remaining in the lungs after forceful expiration(1.2L).
Pulmonary capacities
1-Inspir.capacity(The tidal vol. plus the Inspir. Reserve(3.500 L) A person can breathe
beginning at the end of normal expir.level distending the lung to maximum amount.
2-Functinal residual capacity: Inspiratory reserve volume plus residual volume, The amount
of air that remains in the lungs at the end of expiration(2300 millit).

3
3- Vital capacity: Inspiratory reserve volume plus expiratory reserve volume:The maximum
amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after first filling the lungs to their maximum
extent &then expiring to maximum extent(4.6 L).
4-Total lung capacity: maximum vol.to which the lungs can expands(5.8 L).
Functional residual capacity
The vol. of air that normally remains in the lungs between breaths.
o Residual volume= functional residual capacity Minus the Expiratory reserve volume
o Total lung capacity=Inspiratory capacity plus the functional residual capacity .
Minute respiratory volume
It’s the total amount of new air moved into the respiratory passages each minute.
It’s equal the:
Tidal volume times the Respiratory rate(12 X 0.5).
Minute respiratory volume averages(6liter/minute) and can increase up to 30 times the
normal, Normally a person can stand half to two thirds these values for no longer than 1
minute.
A person can live for short time with a minute vol. of as low as 1.5liter/min & respiratory
rate of as low as 2-4 breathes minute
ALVEOLAR VENTILATION
o Normally the volume of the tidal air is enough to fill the respiratory passage ways as
far as the terminal bronchioles.
o Small portion of the inspired air flowing all the way into the alveoli.
o The air move this last distance from the terminal bronchioles into the alveoli by
Diffusion caused by the kinetic motion of molecules.
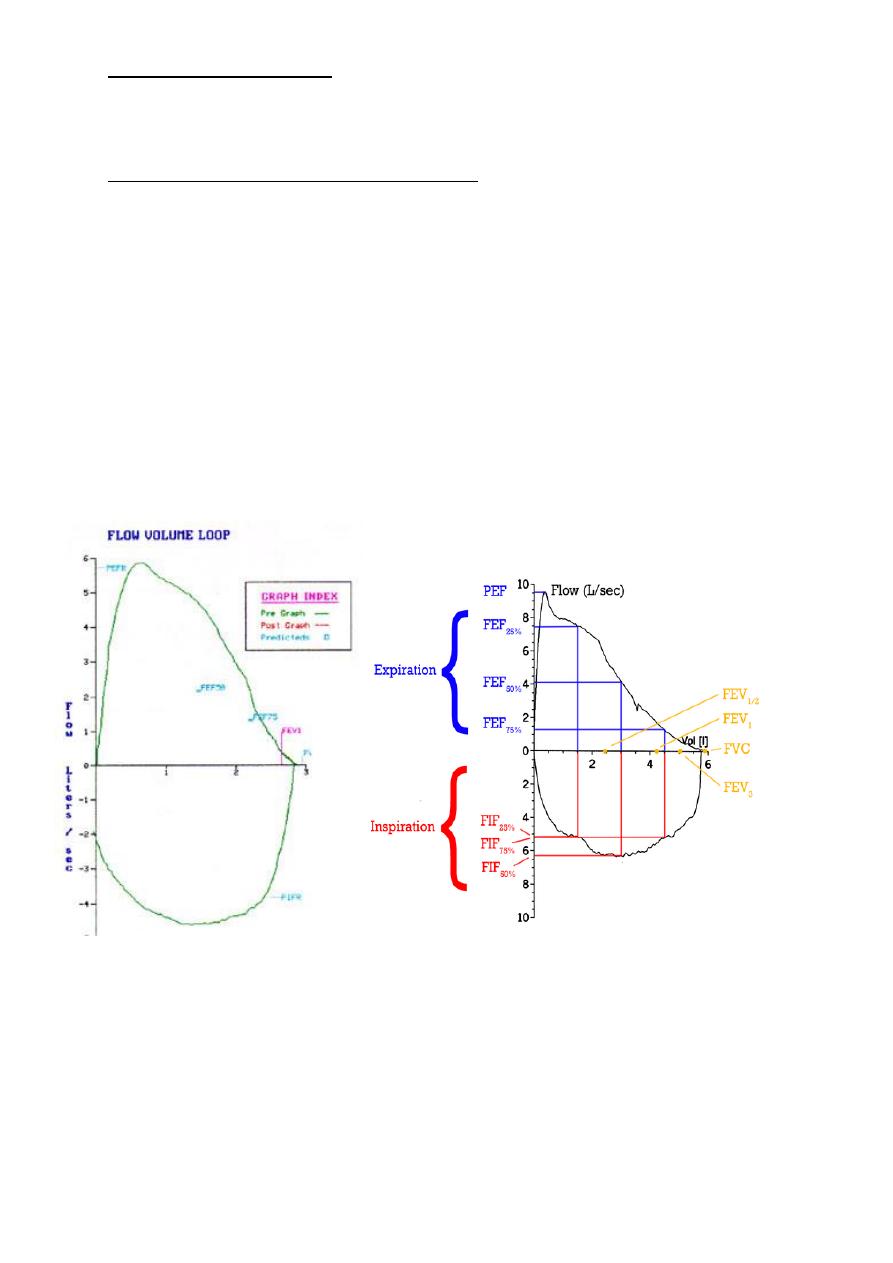
The commonly used Lung function tests
o Forced Vital Capacity FVC: - This is the total amount of air that you can forcibly blow
out after full inspiration, measured in liters.
o Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 Second FEV 1: - The amount of air that you can forcibly
blow out in one second, measured in liters.
o These two tests considered one of the primary indicators for the lung function test.
The commonly used Lung function tests
o FEV 1 / FVC - This is the ratio of FEV 1 and FVC, to determine the amount of the FVC
that can be expelled in one second. In healthy adults this should be approximately 80%.
4
o Peak Expiratory Flow PEF: - The speed of the air moving out of your lungs at the
beginning of the expiration, measured in liters per second.
o Forced Expiratory Flow 25-75% or 25-50% This is the average flow (or speed) of air
coming out of the lung during the middle portion of the expiration
(sometimes referred as the maximal mid-expiratory flow MMEF).
Forced Inspirtory FIF 25-75% or 25-50%: Flow 25%-75% or 25%-50% - This is similar to
FEF 25%-75% or 25%-50% except the measurement is taken during inspiration.
o Forced Expiratory Time FET: - This measures the length of the expiration in seconds.
Flow volume loop
o Normal flow volume loop has a rapid peak expiratory flow rate .
o Gradual decline in flow back to zero.
o The Inspiratory portion of the loop is a deep curve plotted on the negative portion of
the flow axis.
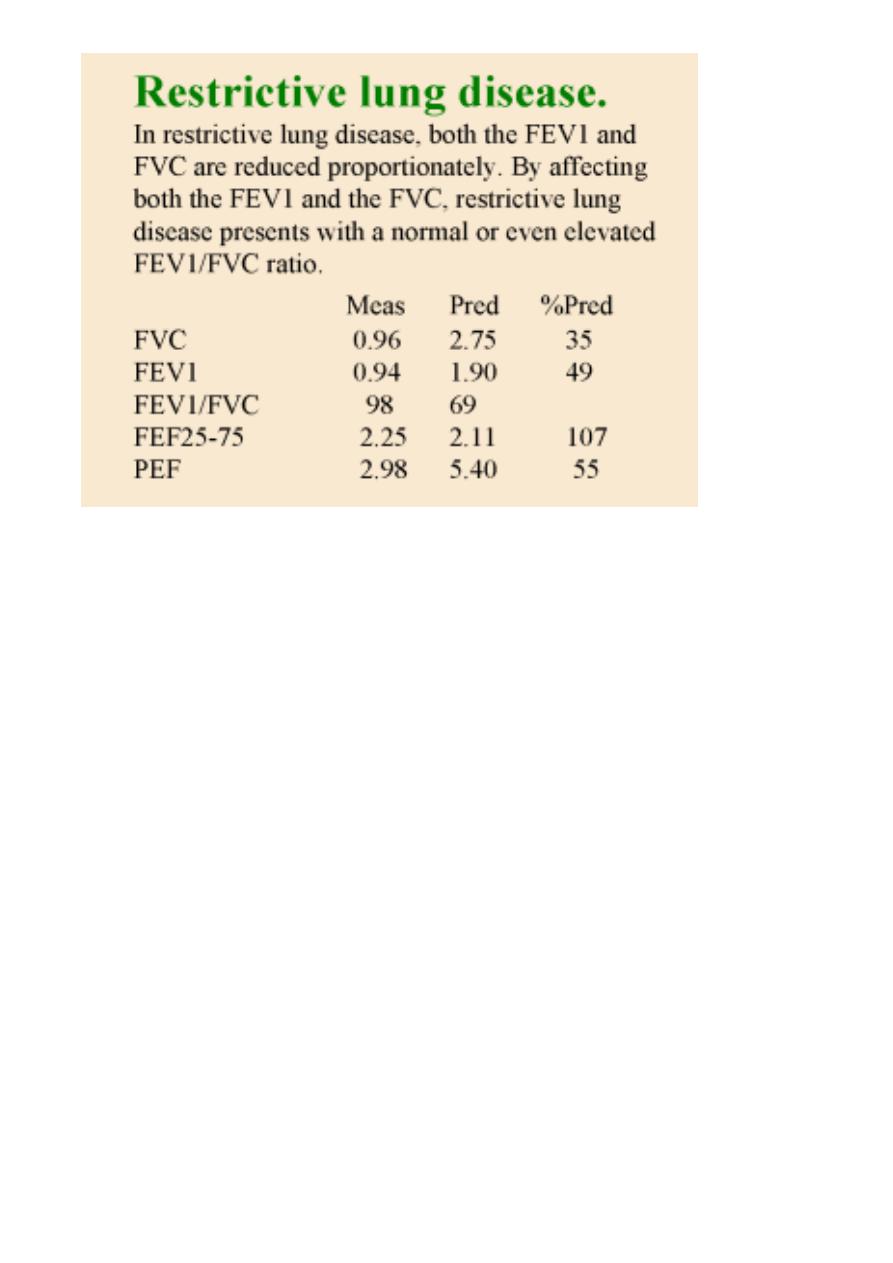
Obstructive Lung Disease
o FEV1 is reduced disproportionately more than the FVC resulting in an FEV1/FVC ratio
less than 70 - 80%.
o This reduced ratio is the primary criteria for diagnosing obstructive lung disease by
spirometry.
o FEV1 > 80% predicted normal
o 65 - 80% mild
o 50 - 65% moderate
o < 50% severe
5
Extrathoracic airway obstruction
o Expiratory flow-volume curve is normal
o Inspiratory flow reaches a low plateau value.
o Typically the FVC and FEV1 are in the normal range .
o The pattern of the expiratory flow-volume curve is normal
o the high pressure in extrathoracic airways distends the airway .
o upper airway obstruction example due to paralysis of the vocal cords.
