Professor Nashwan Q Mahgoob
Department of SurgeryMedical College/University of Mosul
PARATHYROID GLAND
Anatomy
Parathyroid glands are usually
4 in number in 85%, more than
4 in 10% and less than 4 in 5%.
0About 0.6-1 cm in size, 30-50 gram
they are yellowish brown in color.
.
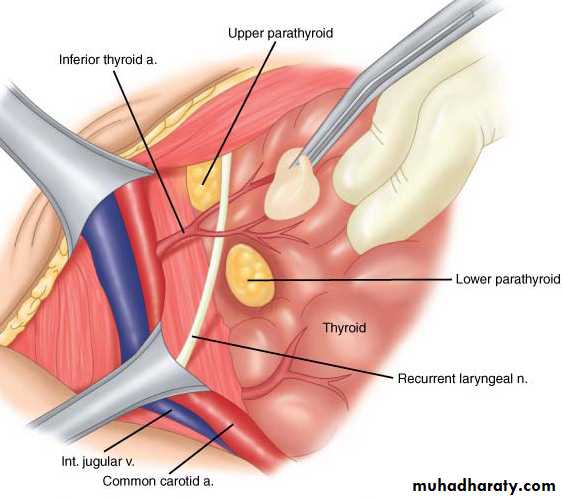
The upper pair derived from IV pharyngeal pouches, they lies just above the inferior thyroid A, posterior to RLN, posterior to thyroid gland.
The lower pair from III pharyngeal pouches, and they are less constant in position, usually at lower pole of thyroid, inferior to inferior thyroid A, anterior to RLN
Arterial supply: by branches from inferior thyroid A,
venous drainage towered thyroid veins.The glandular structures are:
1-Chief cells that produce PARATH H
2-Oxyphil cells.
PTH is released in response to a low
serum calcium or high serum magnesium level.
Calcium is most abundant extracellular cation.
The total serum calcium levels range from (2.1 to 2.6 mmol/L)50% of serum calcium is in ionized form, which is the active component. The remainder is bound to albumin. Function of Calcium : excitation-contraction of muscle tissues, synaptic transmission in the nervous system, coagulation.
Physiology
Function of parath H1- Stimulate ostiolytic activity (mobilization of Ca from bone)
2- Stimulate reabsorbtion of Ca from renal tubule, decrease urine excretion of Ca.
3- Augment Ca absorption from GIT.
4- Increase execration of Ph from renal tubule.
Hypoparathyroidism
Etiology:1-Congenital
1- Digeorge syndrome (absence parath gland and thymus with cardiac defect).
2- Autoimmune polyglanduler syndrome.
2-Acquired
1- Idiopathic: mostly due to autoimmune disease.
2- Inadvertent removal of parathyroid gland during thyroid or parathyroid operation(MOST COMMON).
3- Wilson disease (hemochromatosis) familial disease characterized by deposition of cupper in liver and CNS
Clinical picture
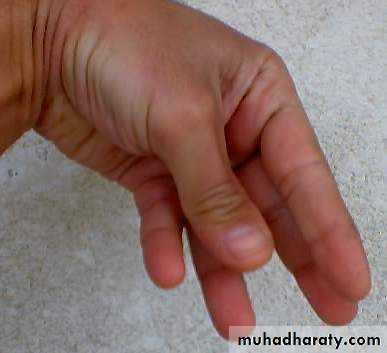
Transient hypoparathyroidism occur in the second post thyroidectomy day, started as circumoral numbness, carpopedal spasm, convulsion like movement, laryngesmus stridulus.Permanent hypoparathyroidism result in repeated carpopedal spasm, anxiety, fatigue, muscle pain mental changes and cataract formation.
Classical signs are trousseas and Chvostek’s signs.
Investigation:
1- ECG: prolonged QT interval.2- serum Ca is low.
3- serum Ph increase.
Treatment for acute or transient attack:
IV calcium gluconate 10%(10 Ml ) in 200 cc glucose water infusion which can be repeated each 8h.
Treatment of permanent type by oral intake of active Vit D3 (1 to 4 ugm), the dose regulated by frequent Ca level checkup.
Hyperparathyroidism
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Elevated PTH. increased serum Ca Due to:
A- sporadic hyperparathyroidism (80%): cause either:
Parathyroid adenoma (85%)
Parathyroid hyperplasia (14%)
Parathyroid carcinoma (<1%)
B-familial: mostly in form of
hyperplasia, usually associated
with other endocrine disease:
1-MEN1(neuro-endocrine tumors
inform of pancreatic and pituitary
adenoma and adrenocortical tumors).
2-MEN2A (parathyroid hyperplasia, medullary thyroid ca, Phiochromcytoma)
Clinical picture
Secondary hyperparathyroidismElevated PTH. Low serum Ca Due to chronic renal failure, malabsorption, rickets.
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Elevated PTH following correction of cause of secondary hyperparathyroidism (renal transplantation)
(kidney stones, painful bones, abdominal groans,
psychic moans, and fatigue overtonesRenal :Colic, haematuria, back pain, polyuria, renal stones, nephrocalcinosis.
Cardiovascular :Hypertension, heart block, palpetation.
Musculoskeletal :Bone pain, pathological fractures, cyst, osteopenia, osteoporosis.
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, nausea, dyspepsia, Polydipsia, weight loss constipation, Peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, cholelithiasis.
Neurological Depression, lethargy, apathy, weakness, psychosis.
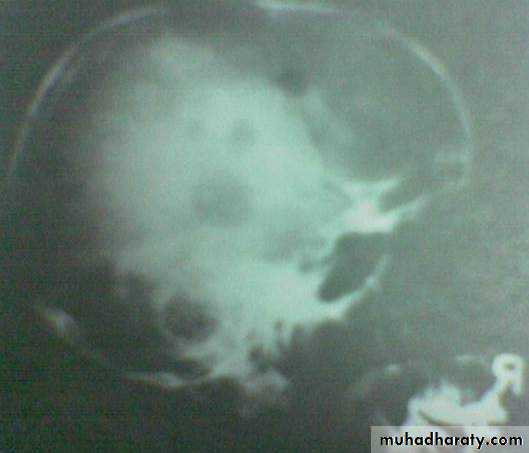
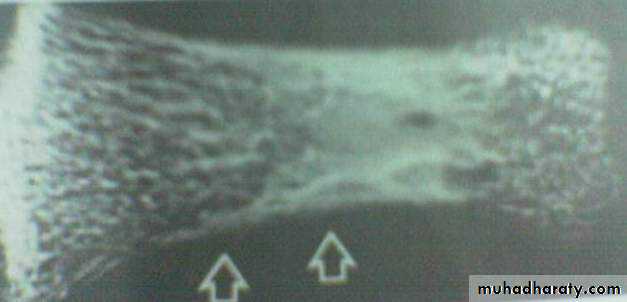
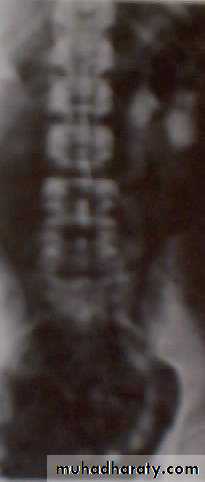
Hyperparathyroidism – image investigation
Multiple bone cyst in the skull
Bone resorbtion in the phalanx
Multiple renal and ureteric stones
- Hyperparathyroidism – chemical investigation1- High scrum Ca (normally 2.6 mmol\L)
2- low serum level of Ph (normally 0.8mmol\L)
3- Increase level of Alkaline phosphatase Enz.
4- Increase urine excretion of Ca (normally 6.2 mmol\L)
5- Increase serum level of chloride.
6- Increase level of Parath H (normally 0.5ugm\L).
Deferential diagnosis of hypercalsaemia:
1-. Hypercalsaemia of malignancy2- Myeloma
3- Immobility
4-Vit D toxicosis.
5- Sarcoidosis
6- Hyperthyroidism
7- Phiochromcytoma
8- Milk alkali syndrome
9- Thiazid therapy.
Medical treatment:1- Adequate hydration2- Avoid food with high calcium concentration.3- Bisphosonate tablet.4- Steroid and estrogen therapy.5- calcium receptor agonist cinacalcet6- Follow up of calcium level.
Indication of surgery
surgery is the only curative option and should be offered to all patients with significant hypercalcaemia it is highly indicated in:
1- Bone involvement.
2- Repeated stone formation.
(3- High level of serum calcium (more than 2.85 m mol/l
2- If all parathyroid glands are enlarged, (parathyroid hyperplasia) ,treatment by subtotal parathyroidectomy or by total parathyroidectomy with autotransplantation.
Every attempt must be made to identify all four glands. Treatment depends upon the number and pathology of abnormal glands.
Surgical management
1- If single adenoma is found and other parathyroid glands are normal, excision of the tumor is enough.3-In malignant tumor, en bloc excision of the tumor and the ipsilateral thyroid lobe. Modified radical neck dissection is recommended in the presence of lymph node metastases.
Complication of surgery1- RLN injury2- permanent hypoparathyroidism3- recurrence of hyperparathyroidism which may result from:missed parathyroid gland, graft dependent recurrence,
parathyromatosis.
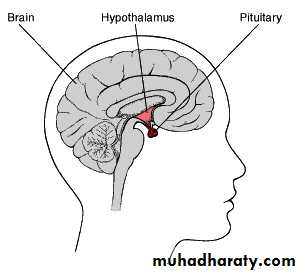
Pituitary gland
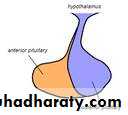
The master endocrine gland, attached by a stalk to the base of the brain.
Its two lobes adenohypophysis and neurohypophysisThe anterior portion, controlled by the hypothalamus it secretes
Prolactine, GH, LH, FSH, ACTH, TSH, and MSH,,
The posterior pituitary secretes
(ADH) and Oxytocin
Function of the hormones:
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), stimulates the secretion of the thyroid hormones; deficiency leads to hypothyroidism.Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), acts on the adrenal cortex to promote the release of cortisol; deficiency leads to adrenal insufficiency.
Prolactin cause milk production in the breasts.
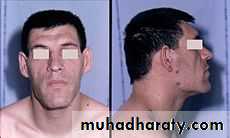
Growth hormone necessary for growth and metabolism throughout life. over secretion cause gigantism if it occurs before growth of the long bones is complete, or acromegaly if it begins during adulthood. Under secretion can lead to dwarfism if experienced during childhood, and decreased endocrine function accompanied by lethargy and loss of sexual capacity in adult.Gonadotrophins LH and FSH, which act on the ovaries and testes.
In female, FSH stimulates growth of the ovarian follicle and LH stimulates production of oestrogen and progesterone from the ovary.In male; FSH stimulates sperm production and LH stimulates testosterone production by the testes.
Deficiency of (LH) and (FSH), in female causes oligo- or amenorrhea and infertility.
In male it results in lose facial, scrotal and trunk hair, decrease muscle mass and anemia.
Both sexes may experience a decrease in libido and increase risk of osteoporosis.
Lack of LH/FSH in children is associated with delayed puberty.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (Vasopressin) plays a role in water balance and maintenance of blood pressure, normal circulating concentrations causing water to be retained by the kidney and higher concentrations causing blood vessels to constrict, thus raising blood pressure. deficiency leads to the syndrome of diabetes insipidus inability to concentrate the urine, leading to polyuria, polydipsia dehydration, as well as hypernatremia.
Oxytocin is important for the birth as stimulator for uterine contraction and for delivery of the milk supply. Deficiency causes few symptoms, as it is only required at the time of childbirth and breastfeeding.
Account for 10–15% of all intracranial tumors.
The majority are benign adenomas.Tumors less than 1cm diameter are microadenomas; larger tumors are macroadenomas. Pituitary tumors may be functional or nonfunctional.
Functional tumors are often diagnosed when quite small size, due to endocrine dysfunction, the most common are Cushing's disease, due to adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion, Forbes-Albright syndrome, due to prolactin secretion, and Acromegaly, due to growth hormone secretion.
Pituitary tumors
Nonfunctional tumors are larger lesions causing mass effects such as visual field deficits due to compression of the optic chiasm or panhypopituitarism due to compression of the gland.
Hemorrhage into a pituitary tumor causes abrupt symptoms of headache, visual disturbance, decreased mental status, and endocrine dysfunction. This is known as pituitary apoplexy.
Investigation
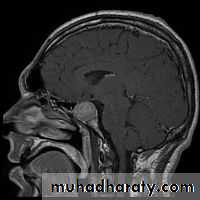
Formal visual field and acuity testing.MRI scan of the pituitary region
Baseline assessment of pituitary function including : Prolactin, fasting serum and urinary free cortisol, GH, FSH, LH and TSH
.
Treatment
The aim is to alleviate mass effect, restore endocrine function and prevent recurrence.Prolactinomas initially treated with dopamine agonists such as cabergoline or bromocryptine.
Growth hormone-secreting tumors may treated with somatostatin analogues such as octreotide.
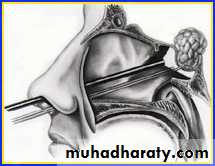
Surgical management of pituitary tumors requires trans-sphenoidal surgery with an operating microscope or endoscope assisted.
Large tumours with suprasellar extension
may need craniotomy.