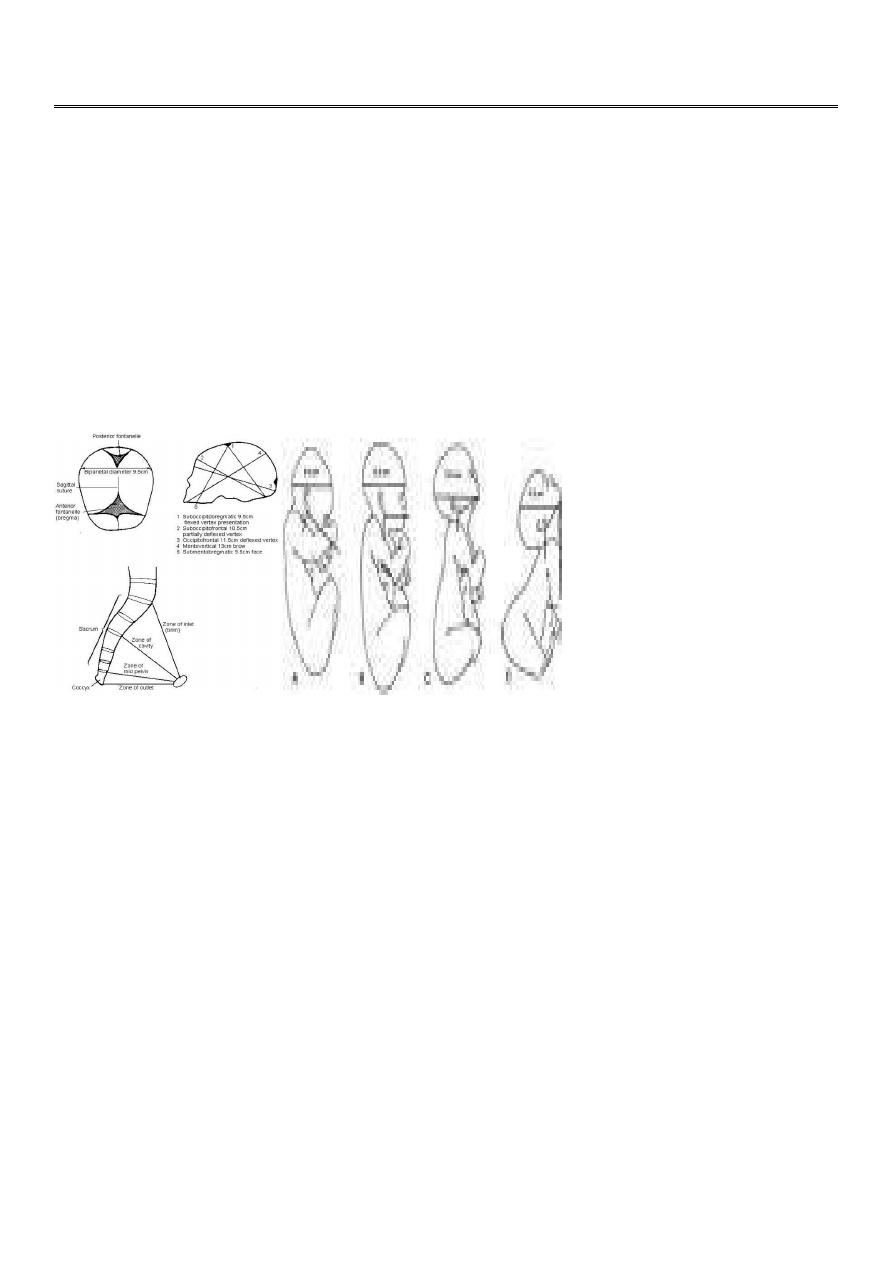
1
Forth stage
Obstetric
Lec-3
.د
ا
سماء
1/1/2016
Malposition of Fetus
Vertex;
The area of the skull between the anterior and posterior fontanelles, and the parietal
eminenceTop of the skull
Occiput
;
Back of the fetal head behind the posterior fontanelle
Sinciput;
That part of the fetal head in front of the anterior fontanelle.-foreheador brow
Malposition:
Position: The relationship of a defined area on the presenting part (Denominator) to the
mother’s pelvis .
Occiputoposterior Position:
A cephalic presentation of the fetus with its occiputturned toward the turn right (ROP) or to
Left (LOP) sacroiliac joint of the mother
Diagnosis:
-Diagnosis during pregnancy is of no importance, except that OP is a cause of:
1. non-engagement of the head before the onset of labor.
2. Early rupture of the membranes because of poorly engaged ,poorly flexed head during
labor.

2
-Abdominal examination:
Slight flattening of the lower abdomen
Limbs are easily felt anteriorly
Difficult to define the back or to feel the fetal heart.
Slow descend of the head during labor because of wider diameter of the poorly flexed
head.
-Vaginal examination:
High presenting part,
Early rupture of the membranes
Easy to feel the anterior fontanelle behind the pubis (poorly flexed head).
Both anterior and posterior fontanelle felt (less poorly flexed head).
Only posterior fontanelle felt posteriorly in well flexed head.
-Diagnosis should be made early in labor because it will be difficult later on because of the
formation of caput succedaneum late in labor .This is frequently happened and present with
delay in the second stage.
-Fingers may be passed above the caput to feel the sutures, or the free margin of an ear.
-US in labor may be of help.
Course of labor in Occiputoposterior position:
70% spontaneous rotation to OA
10% short rotation to OP delivery as face to pubis.
Remainder assisted rotation will be required.
-In the great majority of labors in the OP position is the same as in OT or OA, except that the
occiput has to rotate through 135 degrees, instead of 90 and 45 degrees respectively .This
occurs if there is:
Effective uterine contraction.
Adequate flexion of the head.
Average size fetus.
Mechanism of labor in OP:
It depends on the head whether well flexed or incompletely flexed.
The well flexed head
Occiput in advance meeting the resistance of pelvicfloor, slides on the gutter of the
levator ani muscule with rotation through 3/8 of circle, reaching the free space under
the pubic arch. Delivery of the head is by extension (as in ROA)

3
There is no delay in labor as the head enter the pelvis with The subocciputobregmatic
diameter(9.5)
((Delivery as OA after spontaneous rotation))
Incompletely flexed head
1. If there is large head or small pelvis:
When the head is pushed during labor theBPD is hindered if the pelvis is small or the
head is largeforehead descend more easily than the occiput and enter the pelvis
incompletely.
The larger occiputofrontal diameter(11.5)diameter present to the birth canal.
Neither the occiput nor the sinciput insufficiently in advance to influence
rotationspontaneously and alternative mechanism isused for rotation and delivery.
Difficult and prolonged labor
((No progress of labor without intervention))
2. If there is small head or adequate pelvis:
the forehead meets the resistance of the pelvic floor, will rotates (1/8 of circle) to the
front of the subpubic area and the occiput to the hollow of the sacrum.
Delivery is by face to pubis, the occiput delivered by flexion about the nose ,followed
by delivery of the forehead and the face and chin.
Large occiputofrontal diameter may result into wide perineal tear
((Delivered as face to pubis))
Incomplete forward rotation from occiputoposterior position with arrest of the head in the
occiputo transverse position described as deep transverse arrest of the head and calls for
assistance. ((Assisted delivery to OT))
Management of the first stage of labour
1. Nothing should be done to affect rotation of the head during the first stage of labour.
2. Management is like normal labor with monitoring of the contraction, dilatation, fetal
heart rate.
3. Continuous epidural pain relief, allow time for spontaneous rotation.
4. Augmentation of contraction.
5. C.S. is indicated in case of no progress of first stage for few hours ,or fetal distress.
Management of the 2nd stage of labor
1. Careful vaginal examination to diagnose the second stage (rectal discomfort with
desire to bear down)
2. Finding suggest that spontaneous rotation may not occur like:
deflexion .
large caput succedaneum.

4
moulding .
3. Indication for interference are:
failure of descend
fetal distress
maternal distress
Assisting delivery in OP:
Assistance is by rotation of the head to OA to present a smaller more favorable diameter to
the birth canal. Rotation can be performed:
1. manual rotation and forceps delivery (kielland’s forceps)
2. vacuum extractor.
Arrest at the pelvic outlet:
When the fetal scalp is easily visible at the vulval outlet. further progress is prevented by
the muscles of the pelvic floor .
Adequate episiotomy.
Careful traction of the head by obstetric forceps in OP,or by vaccum.
Trial of forceps
In case of
large head with 2/5 palpable with marked caput &moulding.
Outlet contraction (prominent ischial spines).
Head is not descend with contraction.
Trial of forceps in the operating theater with scrubbed staff and ready for C.S. if there is :
1. difficulty in applying the blades
2. too much force needed to deliver the baby
We should resort to C.S. without delay and Without risk to the mother and the baby.
Occipito transverse position OT
In which the head enter the pelvis in the occipitotransverse position. Subsequently will rotate
to:
ociipito–anterior position in majority of cases.
Occipitoposterior position in minority of cases.
In a small percent of cases,the head fails to rotate and persist in an OT
Rotation occurs because the head flexes as the leading part of vertex meets the resistance of
the pelvic floor and then rotates to adjust to the shape of the gynaecoid pelvis
Causes:
Cephalopelvis disproportion.
Platypelloid or android pelvis.
Relaxed pelvic floor due to multiparity and epidural anasthesia.

5
Diagnosis
:
Easy early labour( may be difficult when labour is obstructed.(moulding ,caput))
Deep transverse arrest of the head: describe arrest of descend of the head for a
period of 1 hour .
Arrest occurs because of deflexion that accompanies the persistant OT resulting in
the larger occipitofrontaldiameter(11cm)becoming the presenting diameter.
Commonly occurs with the vertex at the +1,+2 station.
Management:
During second stage :
Midpelvis is compromised --> C.S.
Normal pelvis+ average size pelvis+inadequate uterine contraction --> oxytocin
stimulation of labour.
Manual rotation,forceps delivery with kielland’s forceps if normal pelvis ,average size
baby and the head at +1,+2 station (head occupy the hallow of the sacrum.)
