بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Injuries to the male urethra
By
Dr.Zaid Saadeldin khudher
MBChB,FIBMS,FEBU
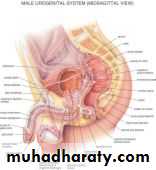
Anatomy
Rupture of the bulbar urethra
History of a blow to the perineum usually due to a fall a stride a projecting object
Clinical Features :The triad of signs is retention of urine , perineal hematoma & bleeding from the ext. urinary meatus
Preliminary assesment & treatment
Analgesic DrugsDiscourage patient from passing urine& if bladder is full perform percutaneous suprapubic cystostomy((this will reduce the likelyhood of urinary extravasation &allow appropriate investigations to establish the full extent of urethral injury))
Kit for percutaneous suprapubic drainage of the bladder.
Treatment of rupture bulbar urethra
Its controversial ,the main warry is that injudicious catheterisation will convert partial into complete transection of the urethramore information obtained by ascending urethrogram or flexible cystoscopy to asses the inj.
If complete tear of the urethra then leave suprapubic catheter until repair
Treatment..(cont.)
Some surgeons advocate early open repair of urethra with excision + spatulation + end to end anastamosis of the urethraOther surgeons wait longer
Complications
Subcutaneous extravasation of urine in complete rupture if the patient attempt to pass urine.stricture is common sequel whether there is partial or complete tear
infection
Rupture of the Membranous Urethra
Intrapelvic rupture of membranous urethra occurs near the apex of the prostate
Clinical Features
Two types of fracture pelvis .. 1.hemipelvic displacement 2.butterfly fractureabout 10-15%of cases of fractured pelvis have associated urethral inj.
There is often multiple trauma with inj to head thorax & abdomen
Clinical features (cont.)
The type of ureth. inj. can often be deduced from the plain radiographThere may be associated inj. to the bladder with either intra or extra peritoneal rupture
Intraperitoneal rupture associated with peritonitis
Clinical features (cont.)
Extra peritoneal rupture of the bladder cause symptoms like rupture memb.urethraif the prostate is displaced it may be impossible to reach or appear to be very high on DRE
Treatment :
ABC..to keep patient a livethe ureth. Inj.can be managed in the short term by inserting a suprapubic cath.
Intraperit. rupture of UB=exploration &repair of UB
Extraperit. rupture ofUB=repair +suprapubic cath.+retroperit. drain
Complications:
1.Urethral stricture2.Urinary incontinence: if the ext. urethral sphincter is destroyed continence will depend upon competence of bladder neck mechanism
3.Impotence..this is the result of damage to the nerve supply of penis
4. Extravasation of urine
Renal Transplantation
One of the early Boston recipients of a kidney transplant from an identical twin, shown here with her twin sister and their children.
Types of graft rejection
HyperacuteImmediate graft destruction due to ABO or pre-formed anti-HLA antibodies.
Characterised by intravascular thrombosis
Acute
Occurs during the first 6 months
T-cell dependent, characterised by mononuclear cell infiltration
Usually reversible
Chronic
Occurs after the first 6 monthsCharacterised by myo-intimal proliferation in graft arteries leading to ischaemia and fibrosis
Patient selection
Renal transplantation is the preferred treatment for many patients with end-stage renal disease because it provides a better quality of life than dialysis.Evaluation of potential recipients for organ transplantation
Determine presence of comorbidityExclude malignancy and systemic sepsis
Evaluate against organ-specific criteria for transplantation
Causes of allograft dysfunction
Early
Primary non-function (irreversible ischaemic damage)
Delayed function (reversible ischaemic injury)
Hyperacute and acute rejection
Arterial or venous thrombosis of the graft vessels
Drug toxicity (e.g. calcineurin toxicity)
Infection (e.g. CMV disease in the graft)
Mechanical obstruction (ureter/common bile duct
Late
Chronic rejectionArterial stenosis
Recurrence of original disease in the graft (glomerulonephritis, hepatitis C)
Mechanical obstruction (ureter,common bile duct)
Immunosuppressive agents
Corticosteroids :Widespread anti-inflammatory effects.
Azathioprine:
Prevents lymphocyte Proliferation.
Ciclosporin:
Blocks IL-2 gene transcription