
Diagnostic
Approach to Joint
Problems
Dr.Fkhir Yousif
1

2
History
Physical examination
When applicable use rapid screening examination
(see Macleod’s…). If an abnormality is found go on
to a full exam
Blood & urine tests
Imaging
Synovial fluid analysis
Other tests

3
Pain
Stiffness
Joint swelling
Functional impairments
Systemic manifestations
Extraarticular features
Periarticular symptoms

4
Presenting symptoms :
detailed history including:
•
Onset & type
•
Precipitating factors
Pattern of joint involvement
(distribution & sequence)
Systemic manifestations
Associated conditions & review
of systems :
•
Skin
•
Mouth & pharynx
•
GIT
•
Eyes
•
Respiratory system
•
Cardiovascular
•
Systemic symptoms
•
Nervous system
•
Urogenital system
•
Musculoskeletal

5
Record of physical impairment severity :
Careful review of a recent 24 hours activity
Ability of personal care
Daily activities & duties
The need of support (personal assistance, use of crutches, wheel chair,
special toilet …etc)
Effect on sleep
Need for hospitalization or home confinement
Careful record of :
Drug & non drug therapies
Past history including traumas
Social history
Family history

•
Redness
•
Hotness
•
Tenderness
•
Limitation of movement
•
Loss of function
6
7
R.A. / sero-ve spondarthritis / SLE /
… etc
Inflammatory / autoimmune
disorders
“Degenerative joint disease”
(osteoarthritis)
Disc prolapse / meniscus tear …etc
Mechanical disorders
Septic / T.B. / Brucella / gonococcal
… etc
Infective
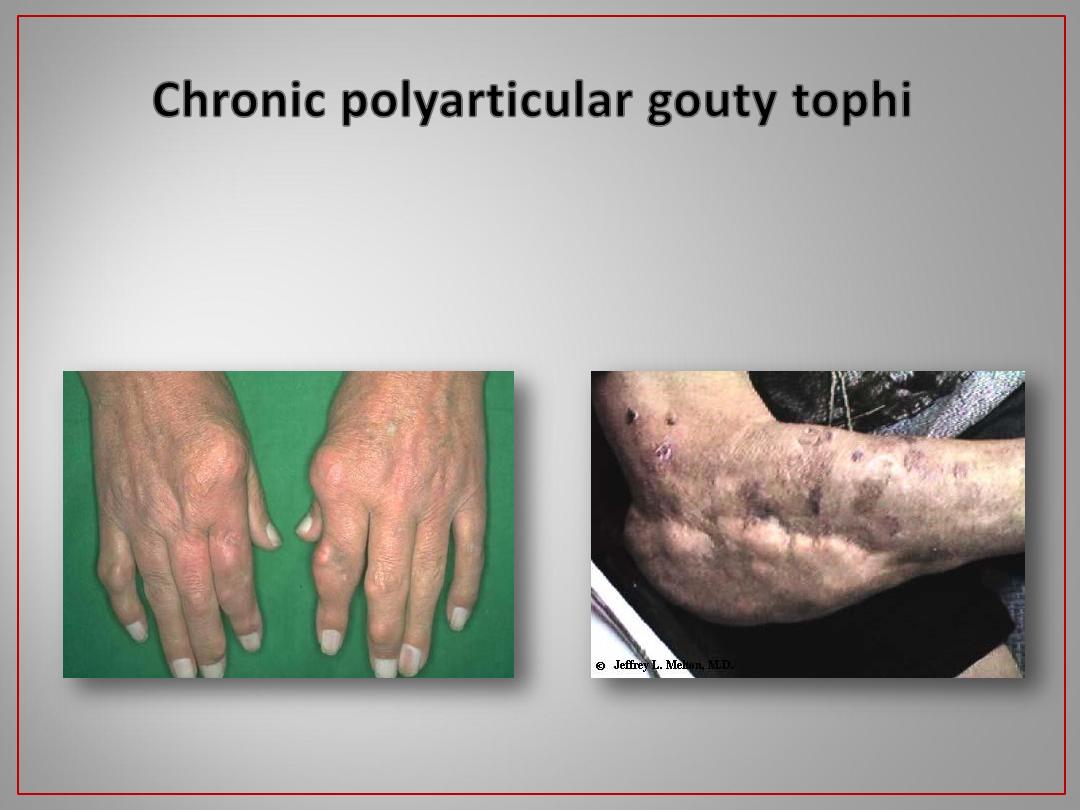
Gout & pseudogout
Crystal induced
Traumatic joint disorders
Tendinitis / bursitis / capsulitis /
epicondylitis / carpal tunnel … etc
Periarthritis
Sickle cell disease / acromegaly /
Systemic diseases related joint
problem
others

8
Polyarthritis : more than 4 joints .
Oligoarthritis : 2-4 joints .
Monoarthritis : one joint .
Chronic polyarthritis : more than 2 months .
Acute , recent … within 2 or “few” months .
“Early” R.A : ? Few months to 2 years .
Migratory arthritis :
Typical non additive.
Additive.
8

9
Causes :
Acute bacterial arthritis (septic , brucella ….).
Acute gout.
Pseudogout.
Monoarticular onset of chronic inflammtory joint
disease such as reactive arthritis , rheumatoid
arthritis and chronic juvenile arthritis.
Traumatic arthritis.
Hemophilic joint.

10
Rheumatoid arthritis and other immune related
disorders such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis ,
spondylarthropathies , systemic lupus and other
connective tissue diseases .
Generlized osteoarthritis .
Pseudogout .
Sarcoidosis .
11
11
12
12
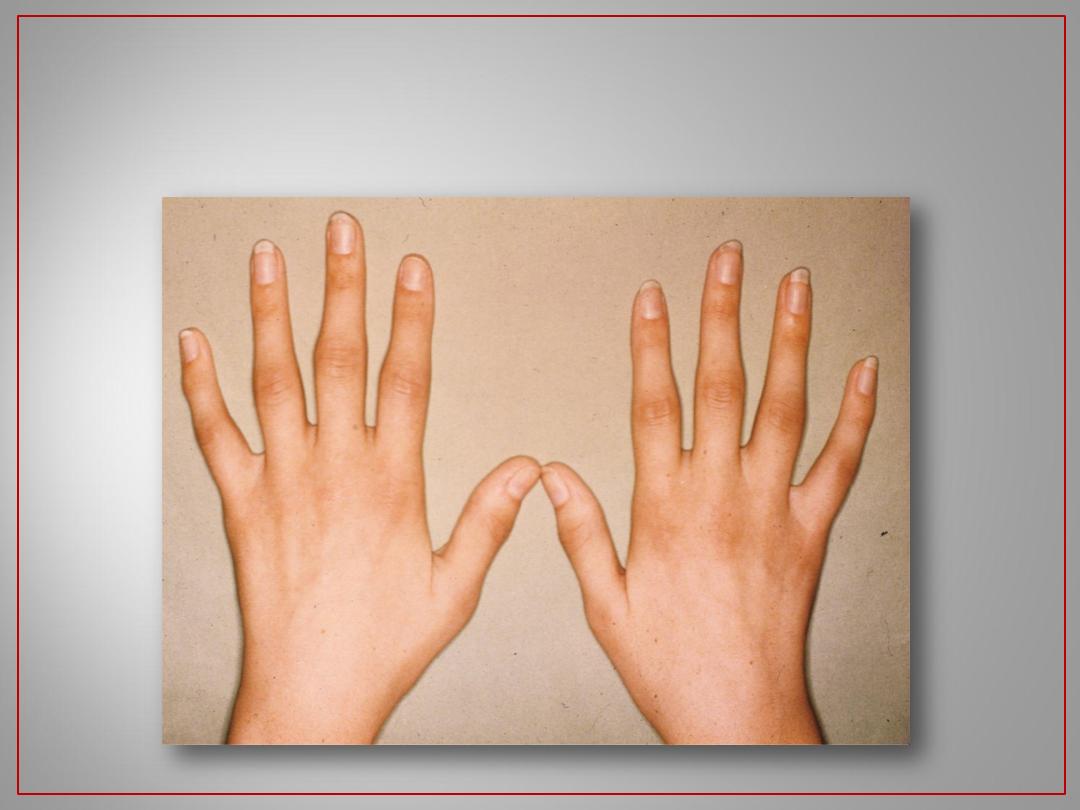
Early RA: First few months of symptoms ,
frequently a challenging diagnosis
13
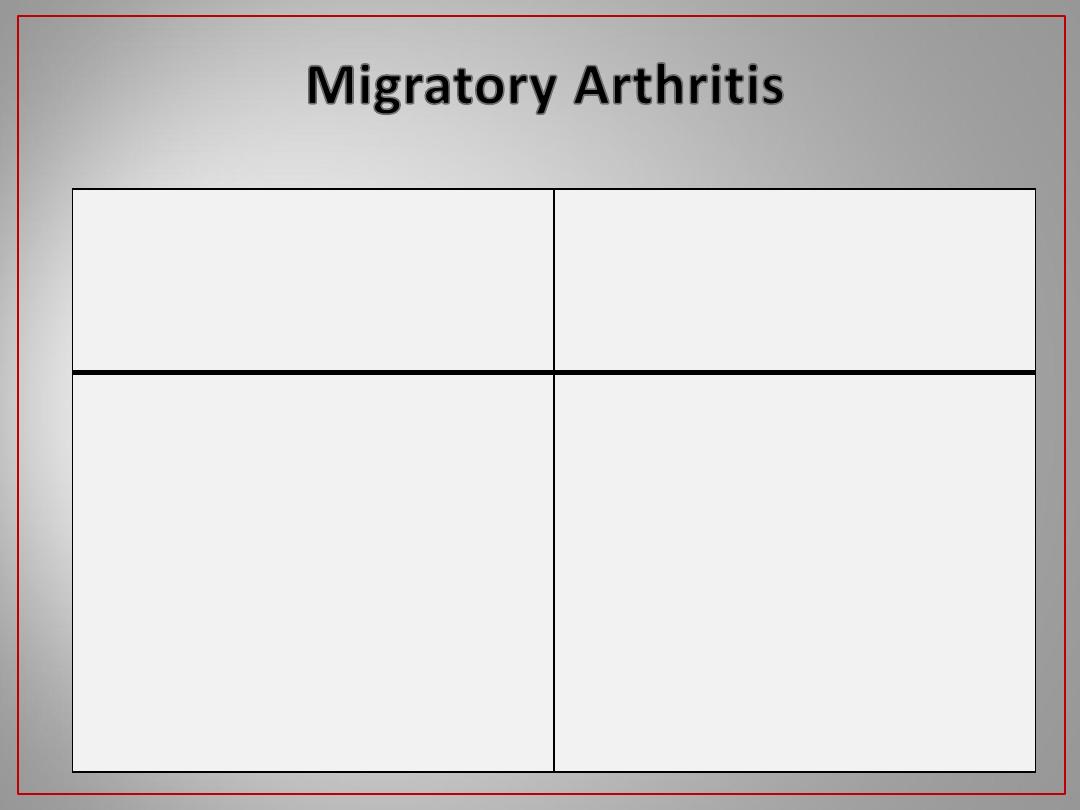
Rheumatic fever
Typical (classical) pattern ;
arthritis does not remain in a
single joint more than 7 days .
Gonococcal arthritis
Viral arthritis
SLE
Idiopathic juvenile arthritis
Poly articular gout
Acute reactive arthritis
others
Migratory element

14
•
Acute Rheumatic Fever :
Typical (classic) migratory pattern , new joints are affected
during decreasing activity of the previously affected joint ,
occurring within 2-3 & up to 5 weeks of streptococcal
pharyngitis . Activity does not remain in a single joint
more than 5-10 days .
Cardiac involvement is common during the acute phase ,
though may be missed . Rheumatic valvular disease may
be found without a past history of arthritis .

15
Reaction to infection :
- Reactive arthritis :
* Diarrhea 1-3 weeks before arthritis .
* Urinary infection .
* Urethritis .
- Rheumatic fever :
* Post streptococcal infection specially pharyngitis / Tonsillitis .
* About a third do not recall pharyngitis .
- ? Some cases of gonococcal arthritis .
- Controversial in many other cases of seronegative spondarthritis .
Reaction to non infective environmental factors :
- U.V. light in SLE .
- Drugs : drugs lupus and serum sickness like illness .
- Hormons .
- Smoking as a risk factor in R.A.
- Diet ,Alcohol , exersion in Gout .
15

16
Red overlying skin :
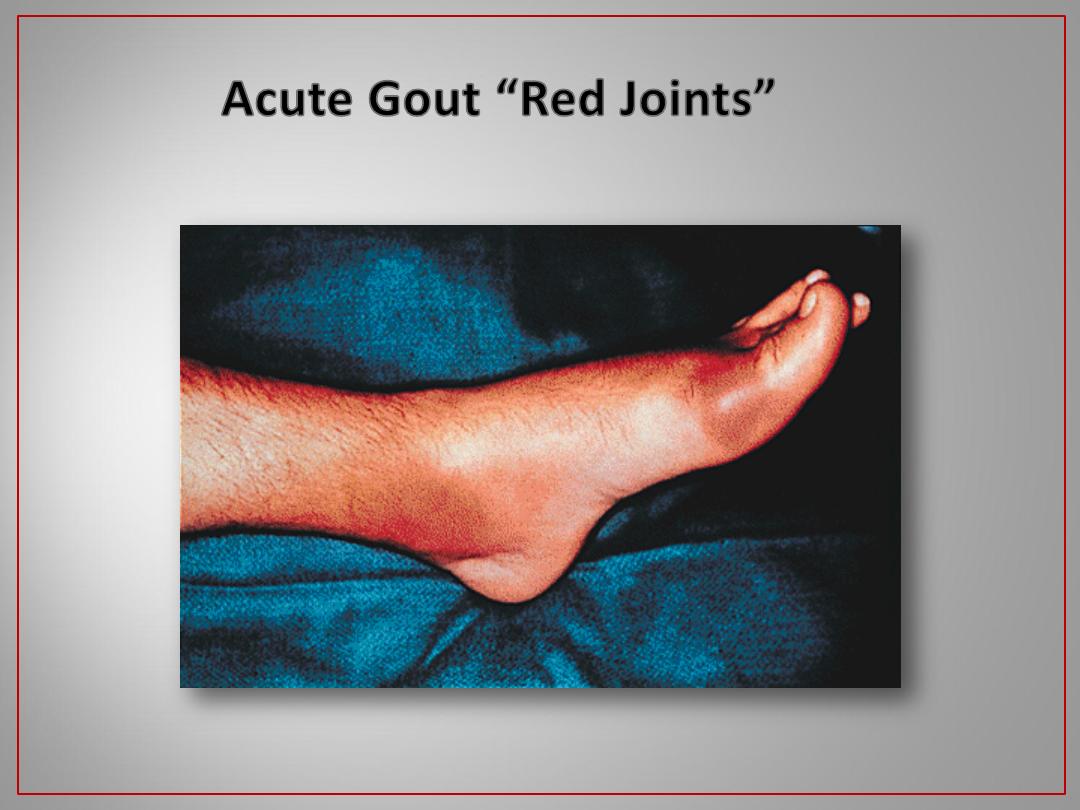
- Acute gout .
- Septic arthritis .
- Skin infection .
- Flare of Heberden’s nodules .
.
16
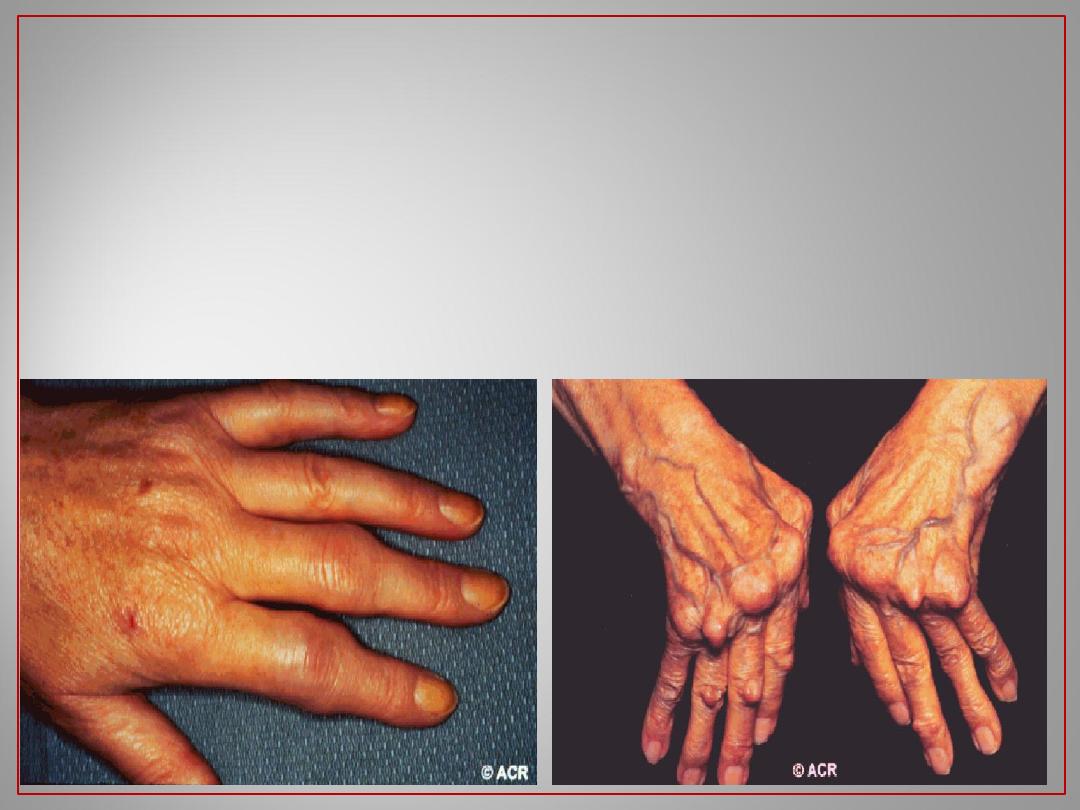
17
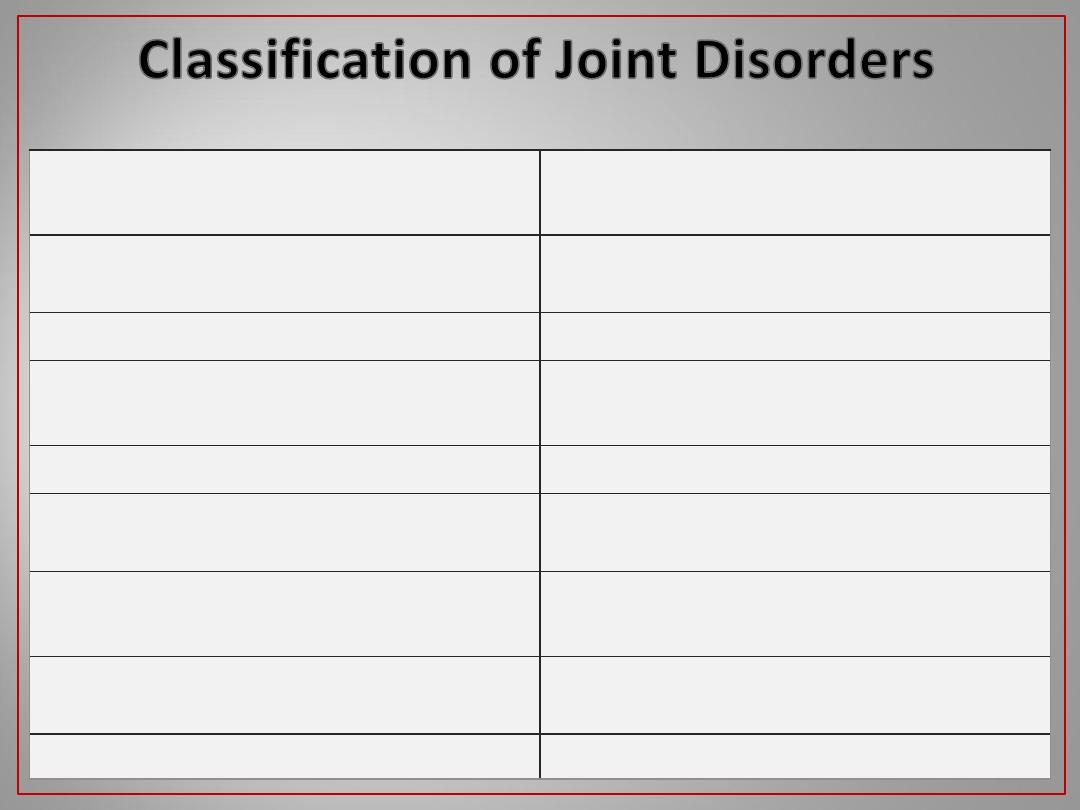
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Hands
5 Months of Disease
5 Years of Disease
a very clear diagnosis
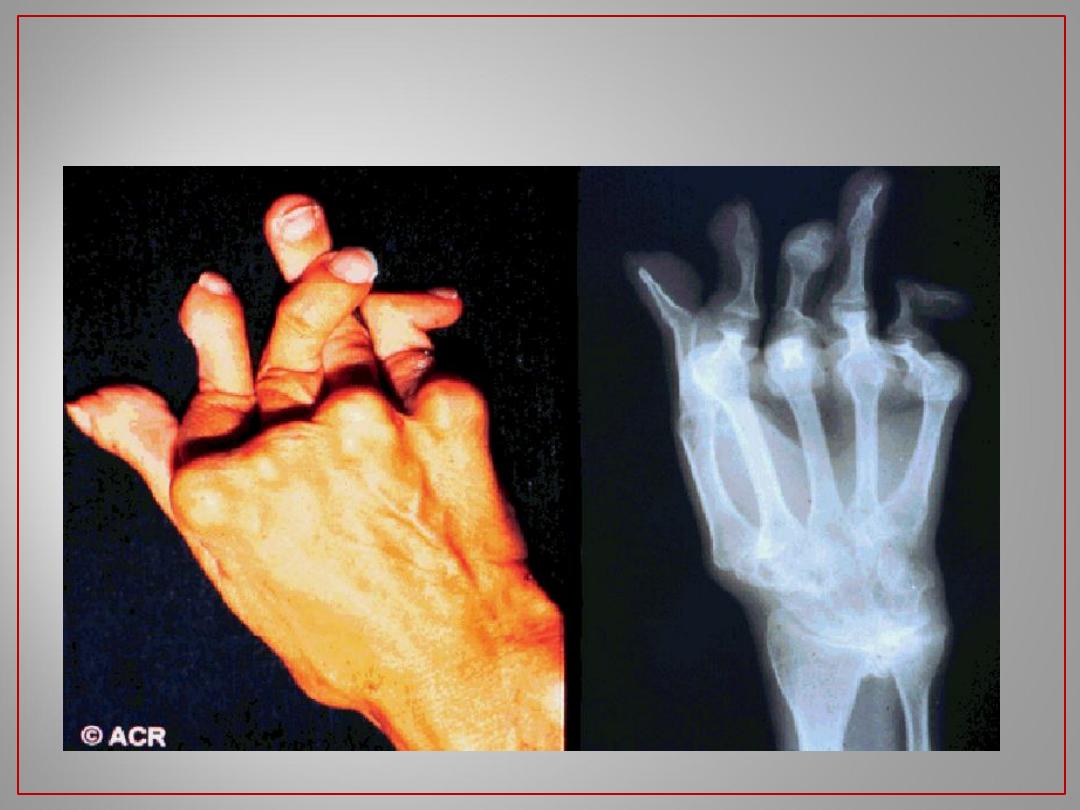
18
18
Rheumatoid Arthritis: 10 Years Later
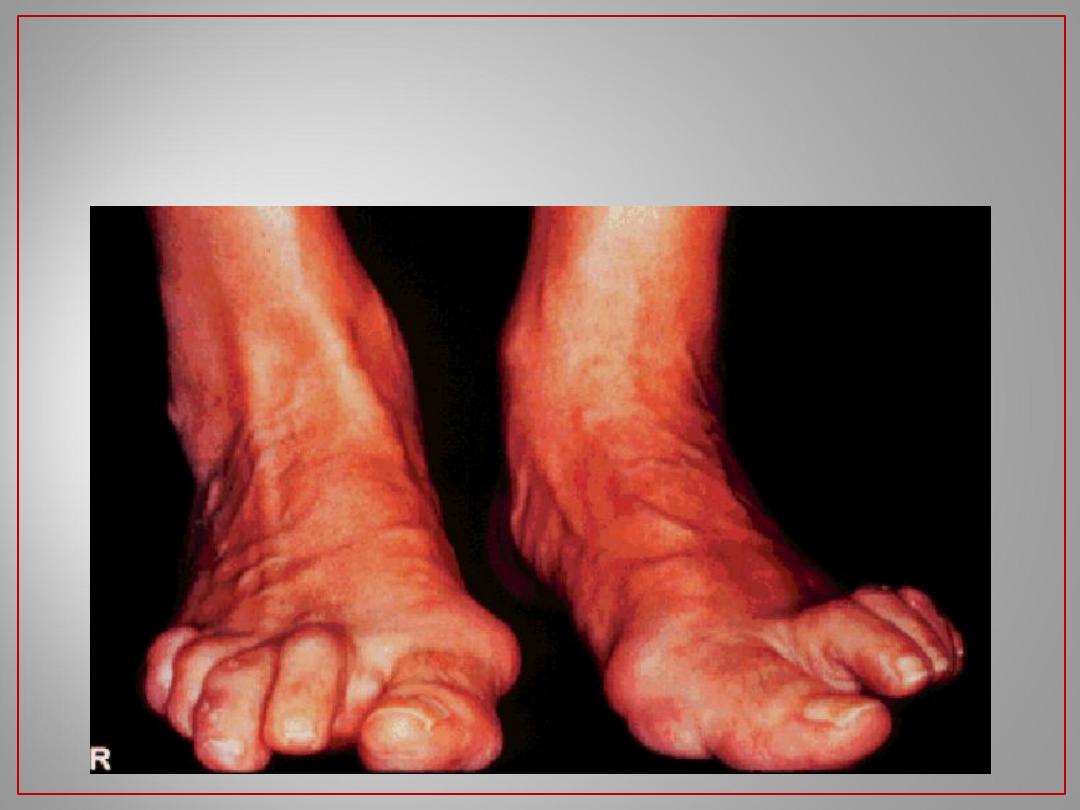
19
19
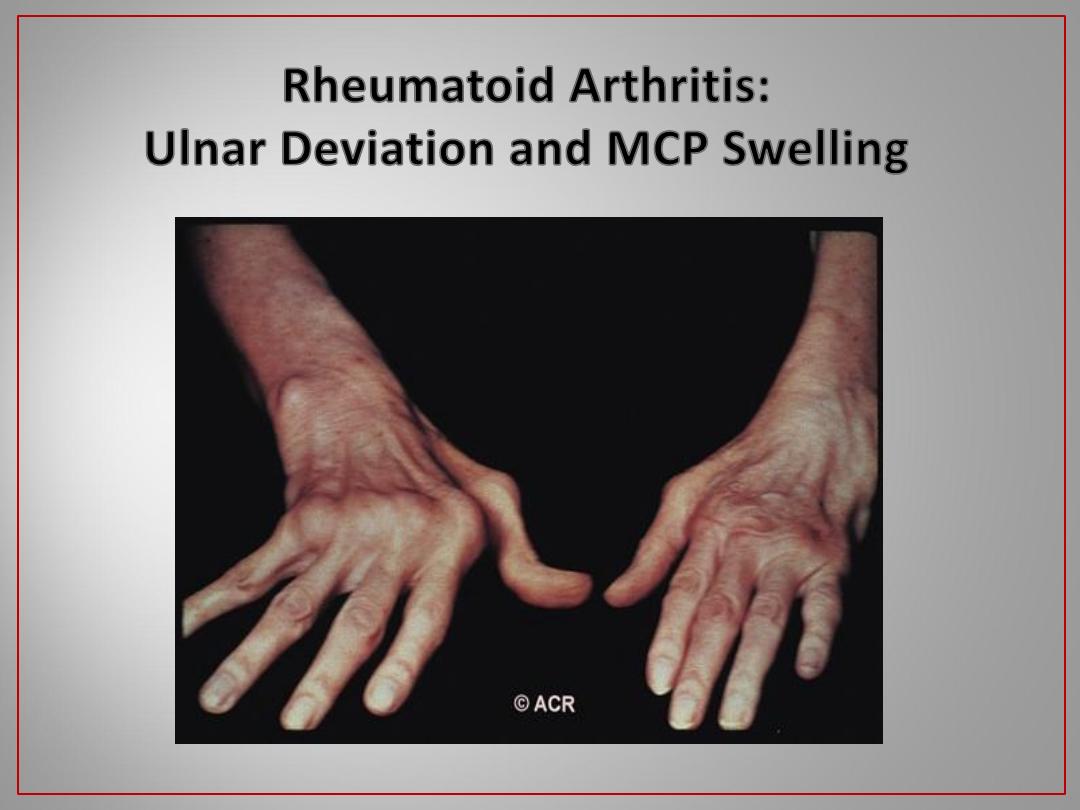
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Feet
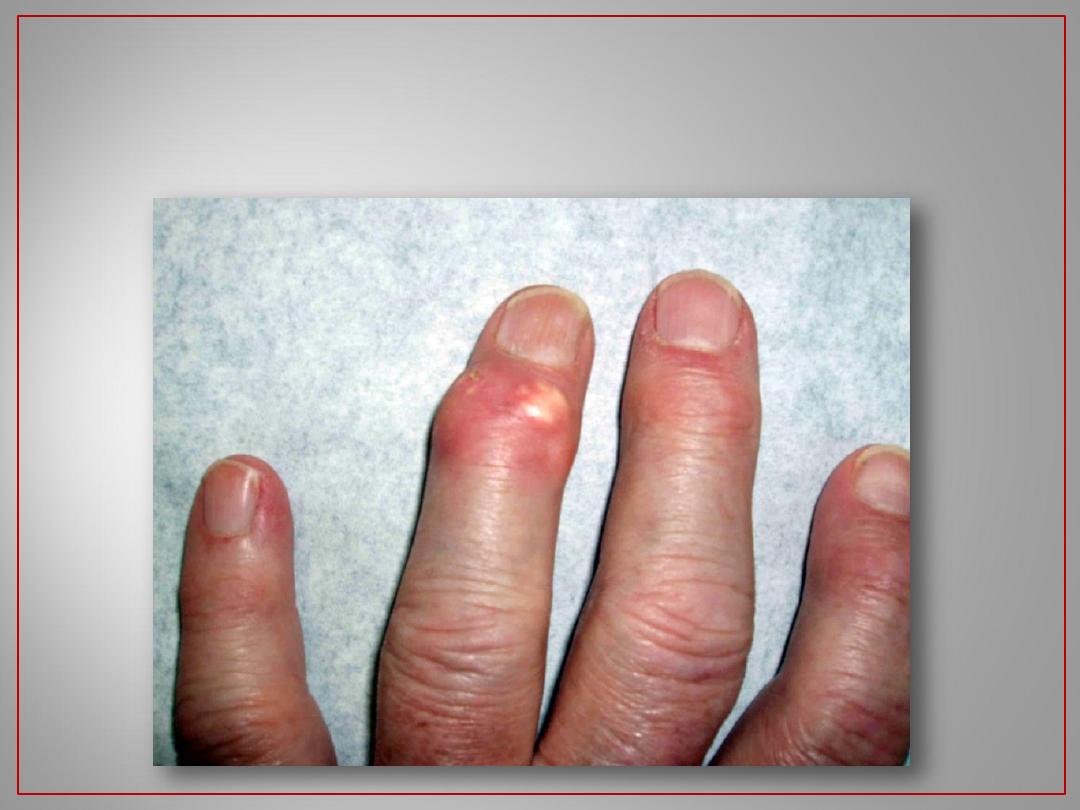
20
20
Gout of the DIPs
21
21
22
22
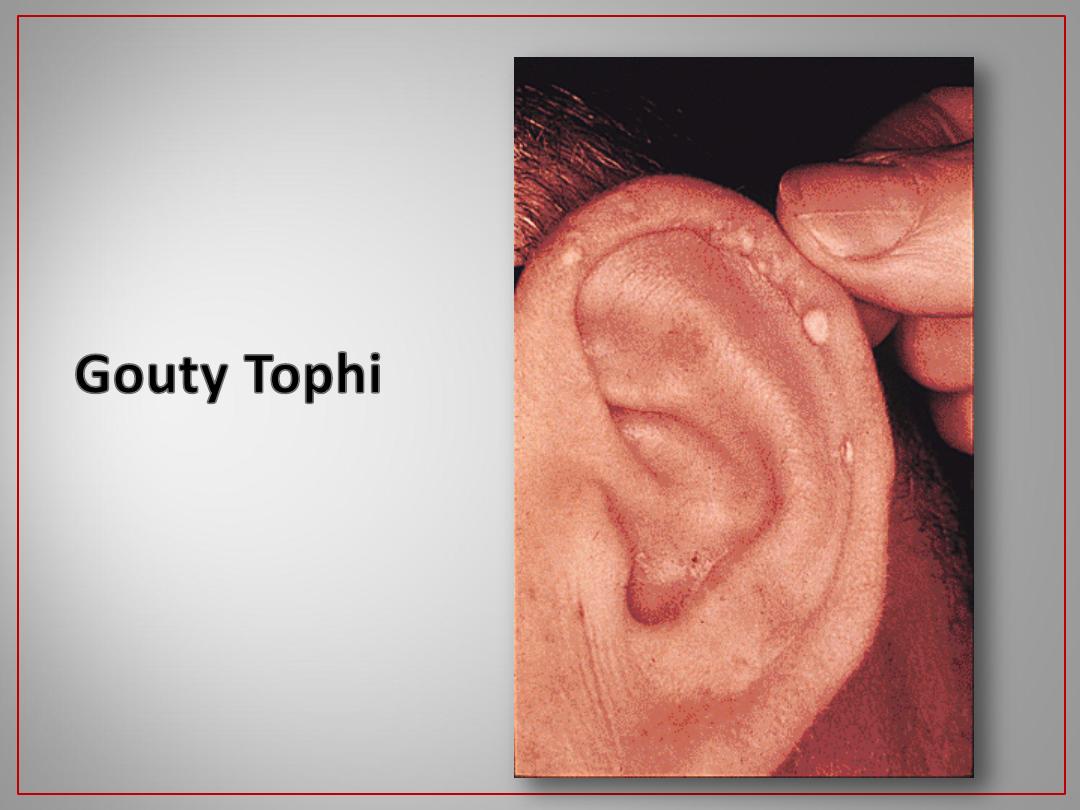
Can occur in various joints, bursa & tendons
23
23
24
Such as fever , weight loss , reduced appetite and general
weakness .
Mild to moderate severity systemic features can occur in
most causes of polyarthritis but not polyarticular O.A.
Severe systemic features :
Arthritis of infective disorders e.g infective endocarditis .
Still’s disease .
SLE .
Acute reactive arthritis .
Bacterial arthritis (about 10-19% polyarthritis) .
24
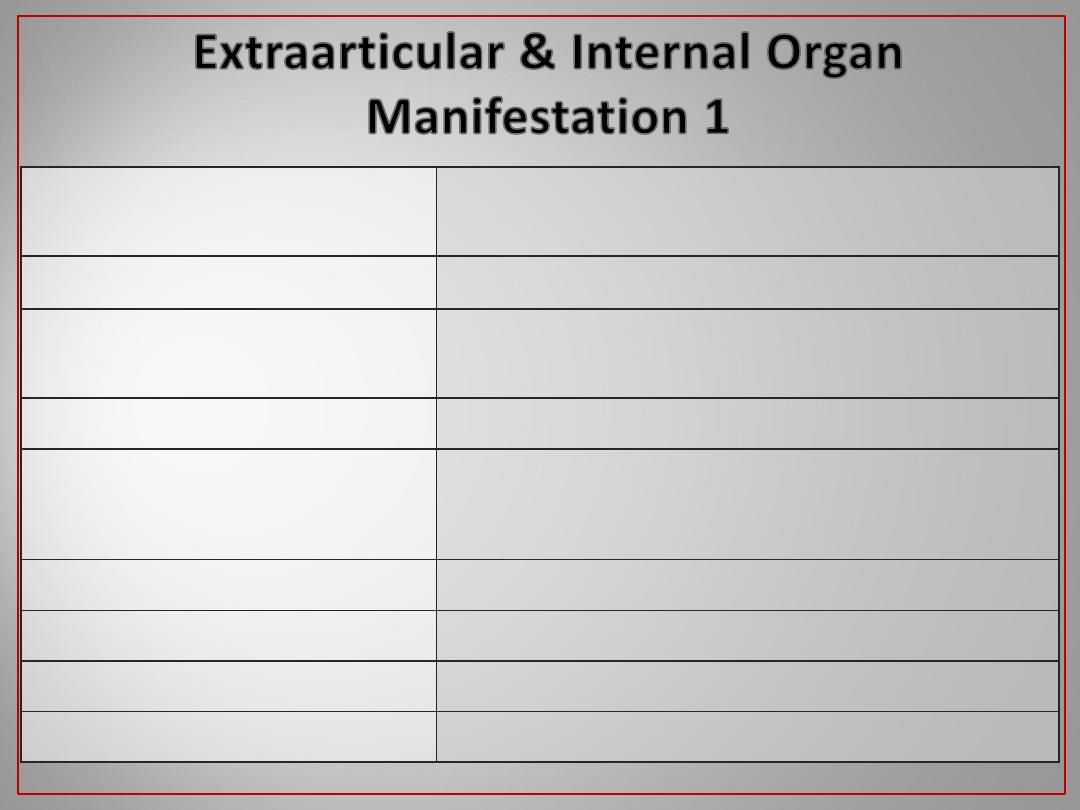
25
SLE, Still’s disease , others vasculitides , Henoch-
schonlein purpura .
Skin rash
Rheumatoid arthritis , acute rheumatic fever .
Subcutaneous nodules
SLE, Behcet’s disease , sarcoidosis , streptococcal
infection , drugs …
Erythema nodosum
SLE , discoid lupus .
Patchy / cicatricial alopacia
SLE , Behcet’s disease , drugs (MTX , Gold …) .
Oral / Pharyngeal ulcers .
Behcet’s disease
Oral + Scrotal &/or penile ulcers
Behcet’s , sero –ve spondarthritis
Anterior uveitis (Iritis)
R.A.
Scleritis / Episcleritis
R.A. Others
Secondary Sjogrens syndrome
25
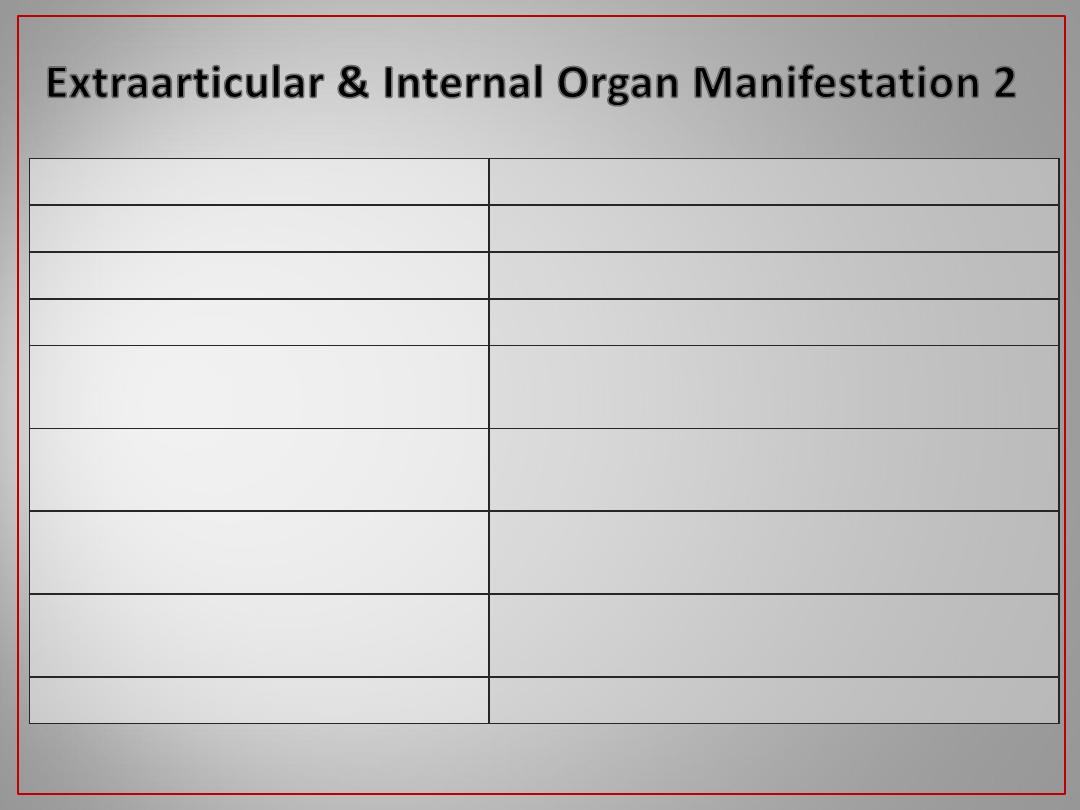
26
SLE , Drugs and others .
Glomerulonephritis
SLE , antiphospholipid syndrome , others .
CNS involvment
R.A. , SLE , systemic sclerosis
Inflammatory lung disease
Systemic sclerosis
Dysphagia
SLE , antiphospholipid syndrome , Behcet’s
disease .
Vascular occlusions
SLE , R.A. and others .
Pleural and/or pericardial
effusions
SLE , R.A. Still’s disease ankylosing
spondylitis , acute rheumatic fever .
Cardiac involvment
Seronegative spondarthritis , R.A. and
others .
Various enthesopathies and
periarthropathies
SLE , antiphospholipid syndrome
Excessive fetal loss
26

27
Typical clinical pattern
e.g. carpal tunnel
syndrome, plantar fasciitis & tennis elbow
Good general health
Tenderness
outside joint margin
Swelling
is absent or outside the joint
Examples
: flexor tendinitis , plantar fasciitis,
subdeltoid bursitis, elbow epicondylitis. It
may affect more than one site
