Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
1
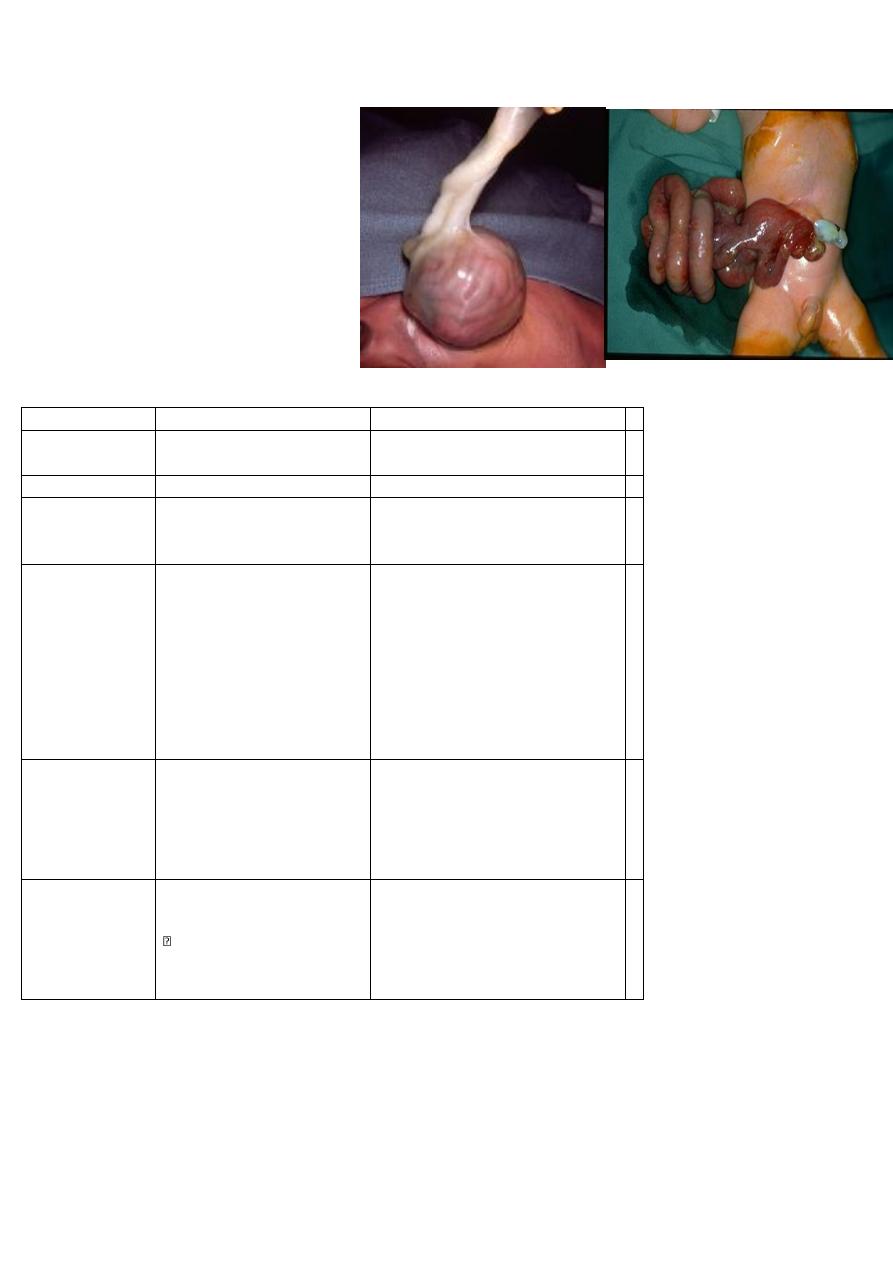
1_ omphalocele and
gastroschisis
differences ? associated
anomaly?
How much fluid you give?
gastochiasis
omphalocele
Item
no covering sac bowel exposed
completely there is
With covering
Covering
Emergency
Not emergency
Urgency to op.
with less congenital anomalie
more
Cong.
Anomalies
associated
In ER: Initial Management
مهم جدا جدا من المحاضرة
Surgical Treatment
; reduce and close the defect,
sometimes we also may use silo
bag to reduce the bowel
gradual
In ER:
Initial Management
مهم جدا جدا من المحاضرة
Non-surgical treatment of
omphalocele(conservative)
“paint” membrane with
betadine-iodine-(induce
fibrosis).
-surgical:silo bag
Mx
to right side of umbilicus
umbilical
site
gastrointestinal problems (25%)
o Including atresia, volvulus, stenosis
Chromosomal abnormalities (50%)
Trisomies 13, 18, 21
Congenital heart disease (50%)
Neural tube defects
Type of cong.
anomalies
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
2
2) Differentiate from hernia hydrocele
D at; hernia as soon as possible.
E. Type of Surgery Herniotomy
Q : what are the differences between Herniotomy and
herniorrphy?
Herniotomy excision of hernial sac
Hernioraghy : strengthen the posterior wall of the
inguinal canal .
Q: in pediatric no herniorrphy why? because of very
short inguinal canal.
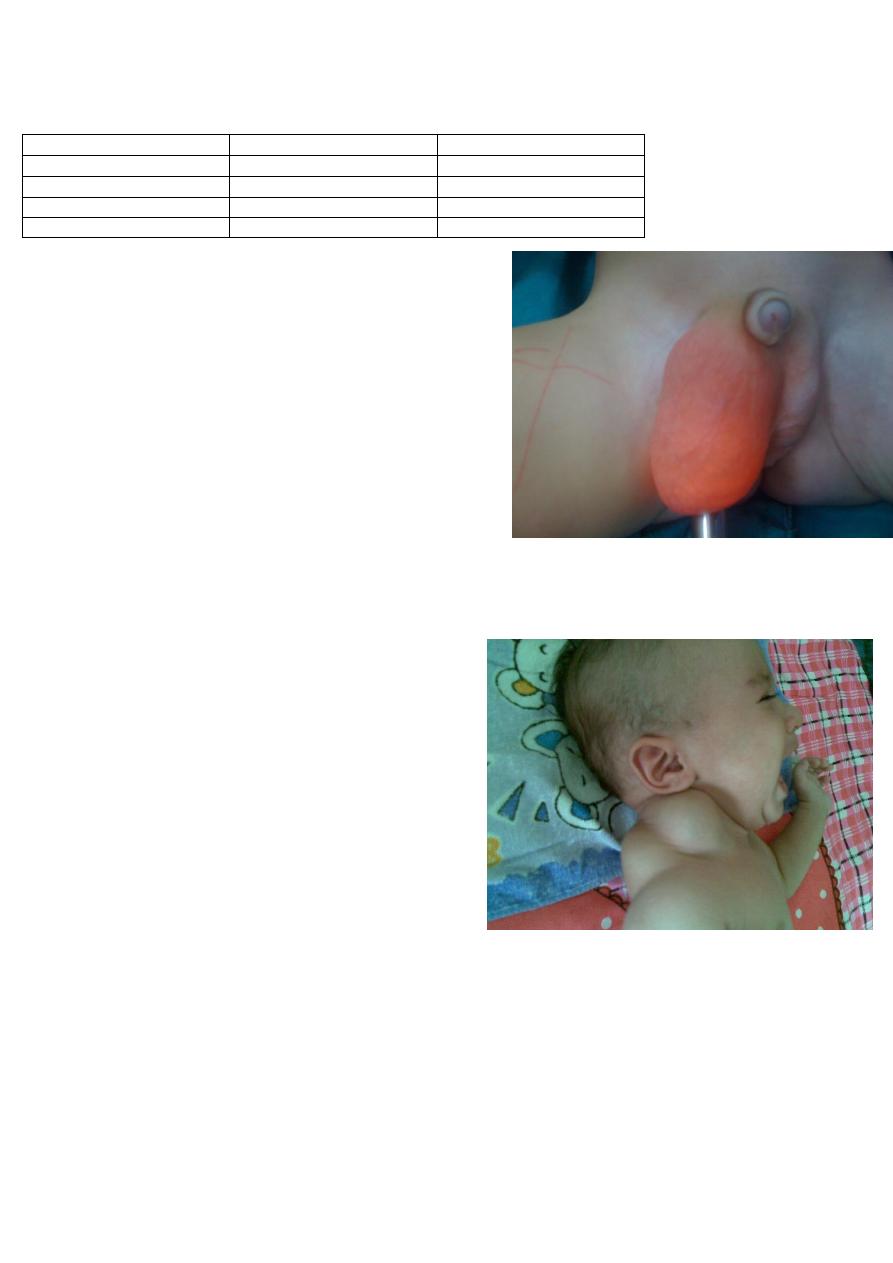
A 3 month old infant born with this congenital abnormality. On examination the mass was
not tender with fluctuation
1. What is the diagnosis ?
2. What is the cause behind it ?
3. What are the modalities of treatment ?
) cystic hyagroma what it is??
It is Lymphatic abnormality causes collection of
Lymphatic on single or multiple sacs .
Treatment; excision
Aspiration and injection sclerotherapy
Most common Site; posterior triangle of neck ,
axillary
Risk of it :nearby structure invasion
hernia
hydrocele
can't
can
Can get above it
+ve
-ve
.
cough impulse
as soon as possible
1 year age
time
Surgery
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
3
4) diaphragmatic hernia
Classify it ?? Congenital and acquired
Congenital 3 types :
1 _ Bochdalek hernia on left.
2 _ Morgagni hernia on central part
3_ hiatus hernia
What is the Presentation.?
Inv. X_ray prove it
Management .
5) Meckel's diverticulum
What is the Role of two?
2% of population.
-
2 type of mucosa (ectopic gastric mucosa+pancreatic tissue).
-
2 feet from iliocecal valve.
-
-2 main type of complication(ulceration+inflamm.)
-2 type of surgery(wedge resection---in inflammation
& resection and reanstomosis—if he'd bleeding
-
-2 inches in length.
What is the Types of diverticula? True & false
DDX :Appendicitis
Inv. Isotope scan& laparoscopy ( diagnostic and therapeutic)
*how the Meckel pt presented to U?(very imp.)
-chronic abd pain + bleeding per rectum or as A.Apendicitis--------open saw the appendix
isnot inflamed so check for the diverculum
-_In meckel's diverticulum there will be sever bleeding marron color.
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
4
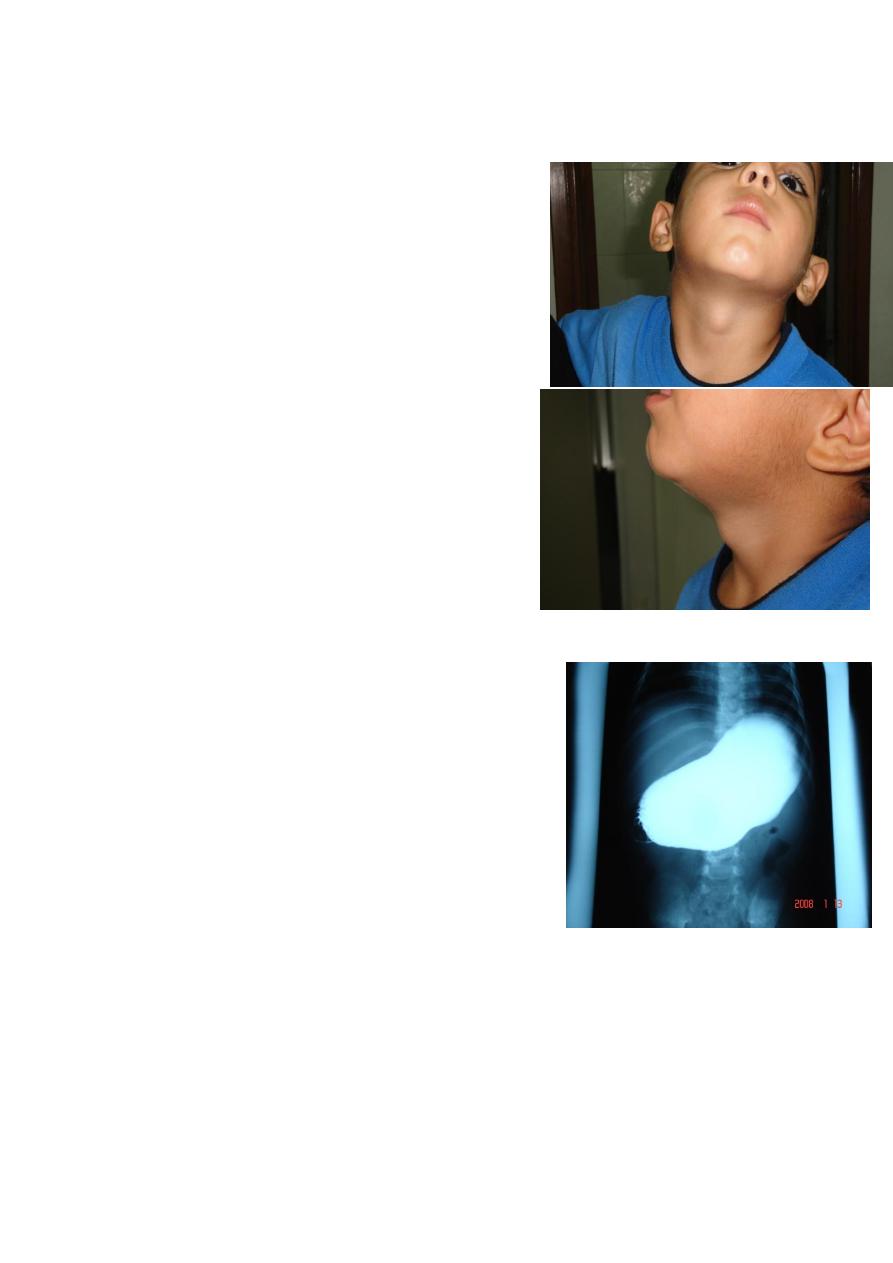
6)thyroglossal cyst
*Ex. Ask the patient to open the mouth and protrude the
tongue, the cyst move up.
*DDX- Lymphoma &Thyroid nodul&
sebaceous cyst &Dermoid
*Complication; infection
Abscees
Pre malignant
*Treatment; removal the cyst with tract & central part of
hyoid bone call sis-trunk operation.
*Content : fluid and ectopic thyroid tissue.
Note :so we must be careful if there is thyroid tissue or
not bz if present remove the thyroid tissue and reimplant
it &give thyroxine for life long(to avoid hypothyroidism)
7) congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis(CHPS)
A 4 week old boy presents with vomiting. The pictures show
the investigation .
1.. What is the investigation shown?
2.What is the diagnosis ?
3. How do you treat ?
*Hx:
جان طبيعي وبدا يزوع بقوة من خشمه مثلحليب مخثر وبس يزوع يرجع
يرضع وجاي يفقد وزن
.
Ex. Olive mass & dehydrated child
Inv. US(width>4mm &length>16mm) , barium meal ,
electrolyte (hypokalemia hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis) bcs of the vomiting.
K+ given by infusion and urin output should be normal,Start with ringer then after full
rehydration we give glucose.
Mang. Give him Ringer then isotonic saline , K ( under ECG control. Risk for cardiac arrest.)
Surgery : ramstedt operation.
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
5
8) intestinal obstruction features?
Causes of delayed passes meconium after 24 hours. or COMMON CAUSES OF NEWBORN
BOWEL OBSTRUCTION(in lect. Is imp.)
A. Could be normal
B. Hirschprung disease.
C. hypothyroidism
D. Premature baby
E. preeclampsia
Inv: 1-imaging:erect abdominal x_ray ( to see air fluid level)
Us
Laboratory inv.
2
-
-preop. Measures (Pre-op: it's imp imp)
1) IV hydration; 120-150 ml/kg per day
2) NG decompression
3) Antibiotics
4)incubator
9 ) esophagealatresia & tracheoesophageal
fistula
Types
A.pure
B. H type
C. With fistula
-Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal
fistula( the most common type)
Presentation (in lec.)
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
6
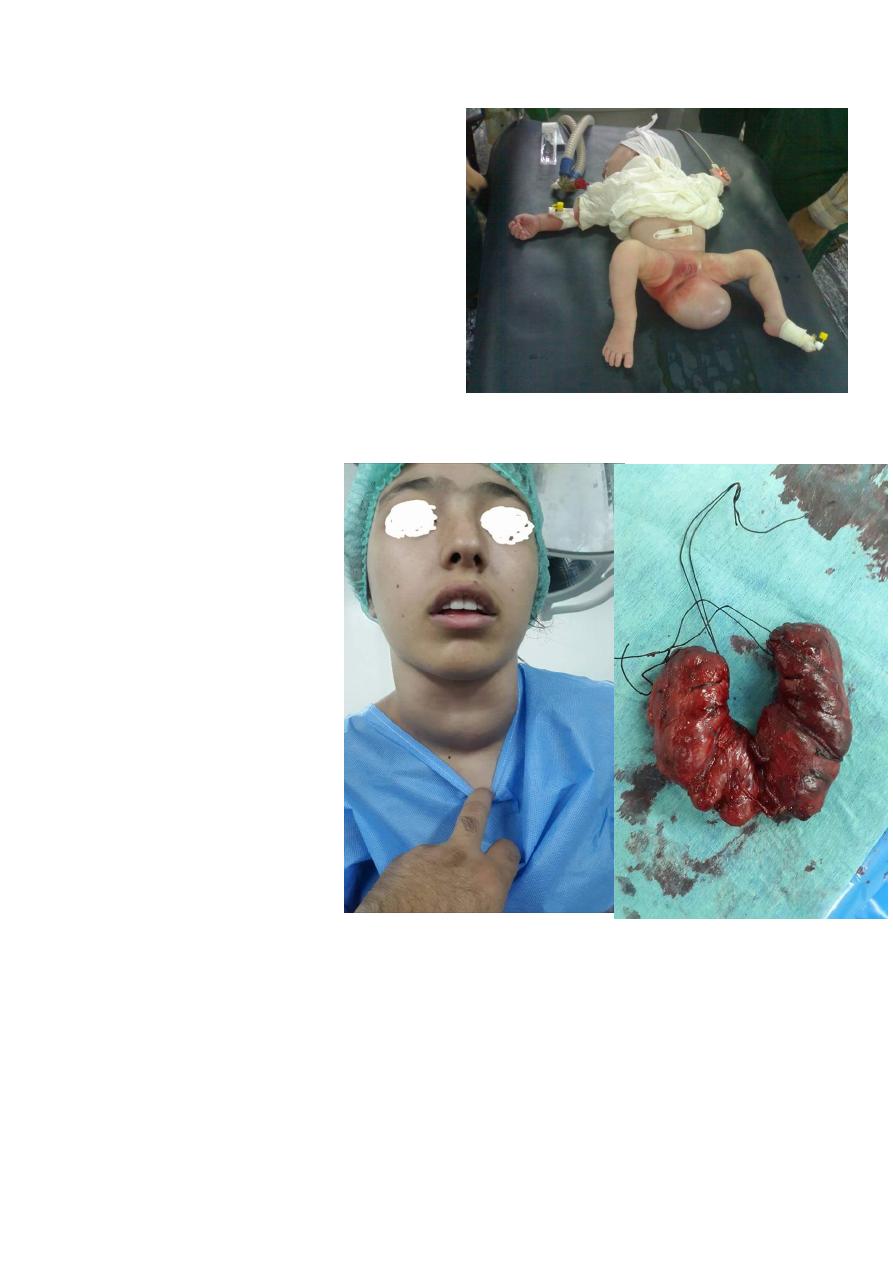
10) Sacrococcygeal teratoma
Surgery at 1wk of life (At 70% of the
sacrococcygeal teratoma convert to
malignancy )
-Tumor marker( alpha fetoprotein) if normal do
the operation with follow up if increased after
surgery that mean there is recurrence & in
surgery should be removed with coccyx
because of the risk of recurrence .
11 ( goiter
Types of thyroid cancer
A. Papillary
B . follicular
C. medullary
D. Lymphoma
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
7
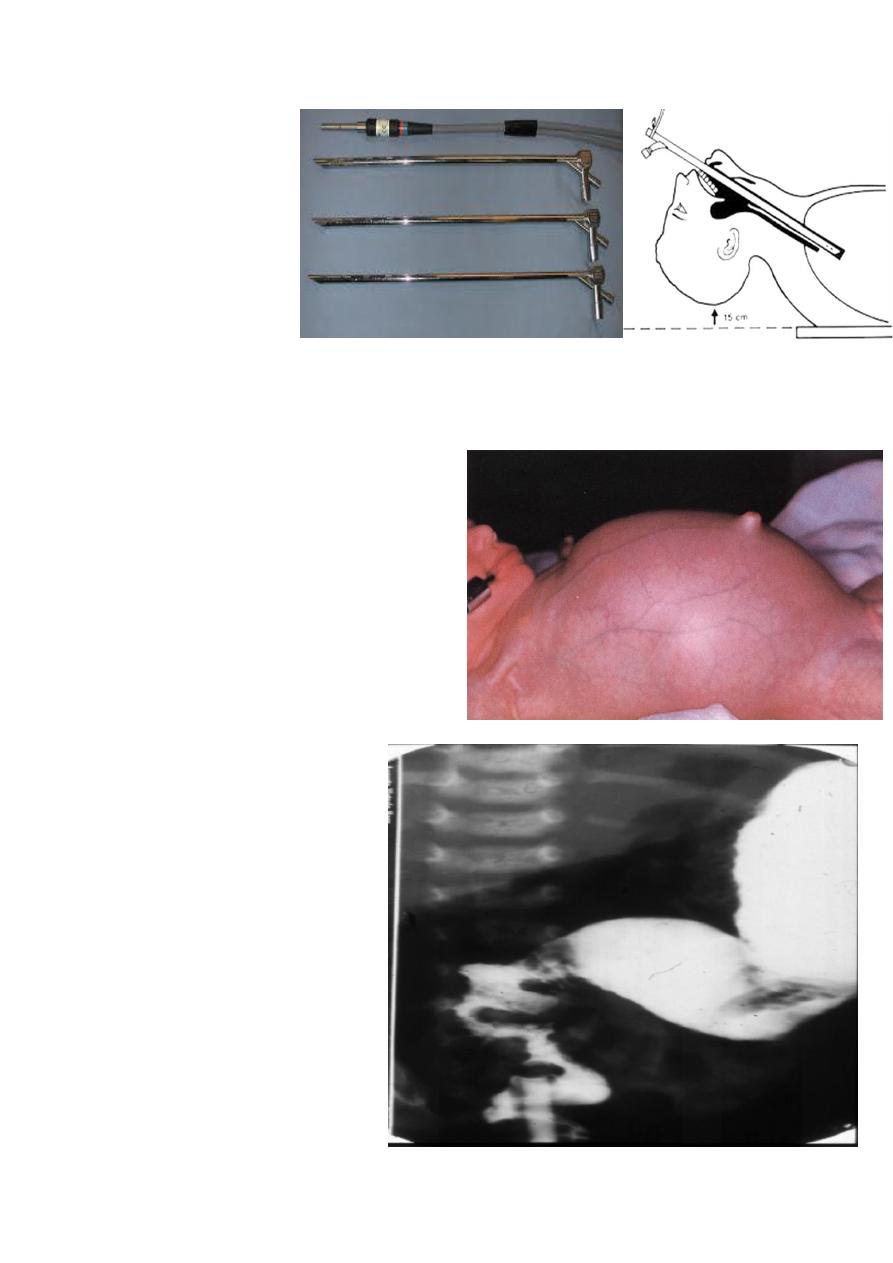
rigid bronchoscopy
(Under GA)
Indication
1-diagnostic &2-
therapeuti
ؤ
)
seminar
st
(in the 1
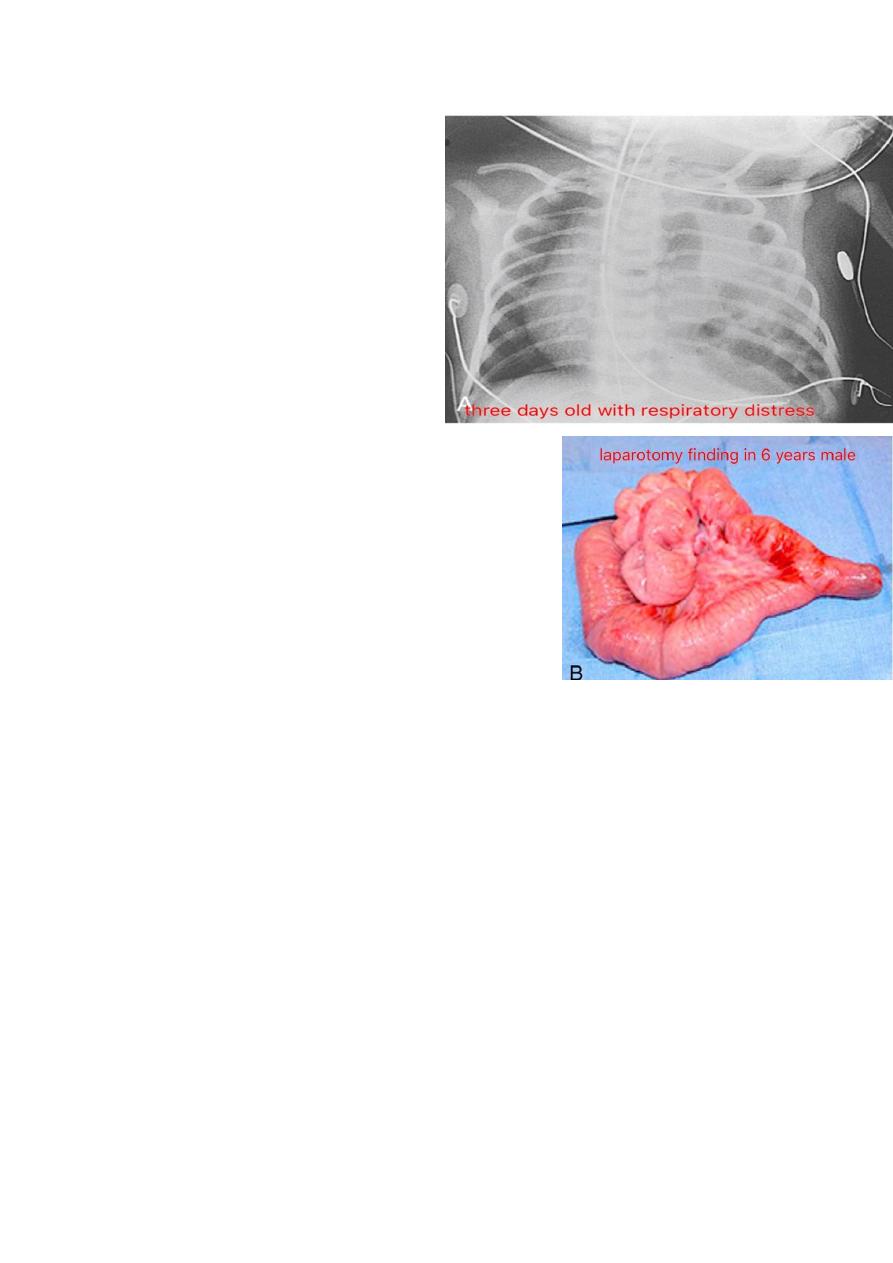
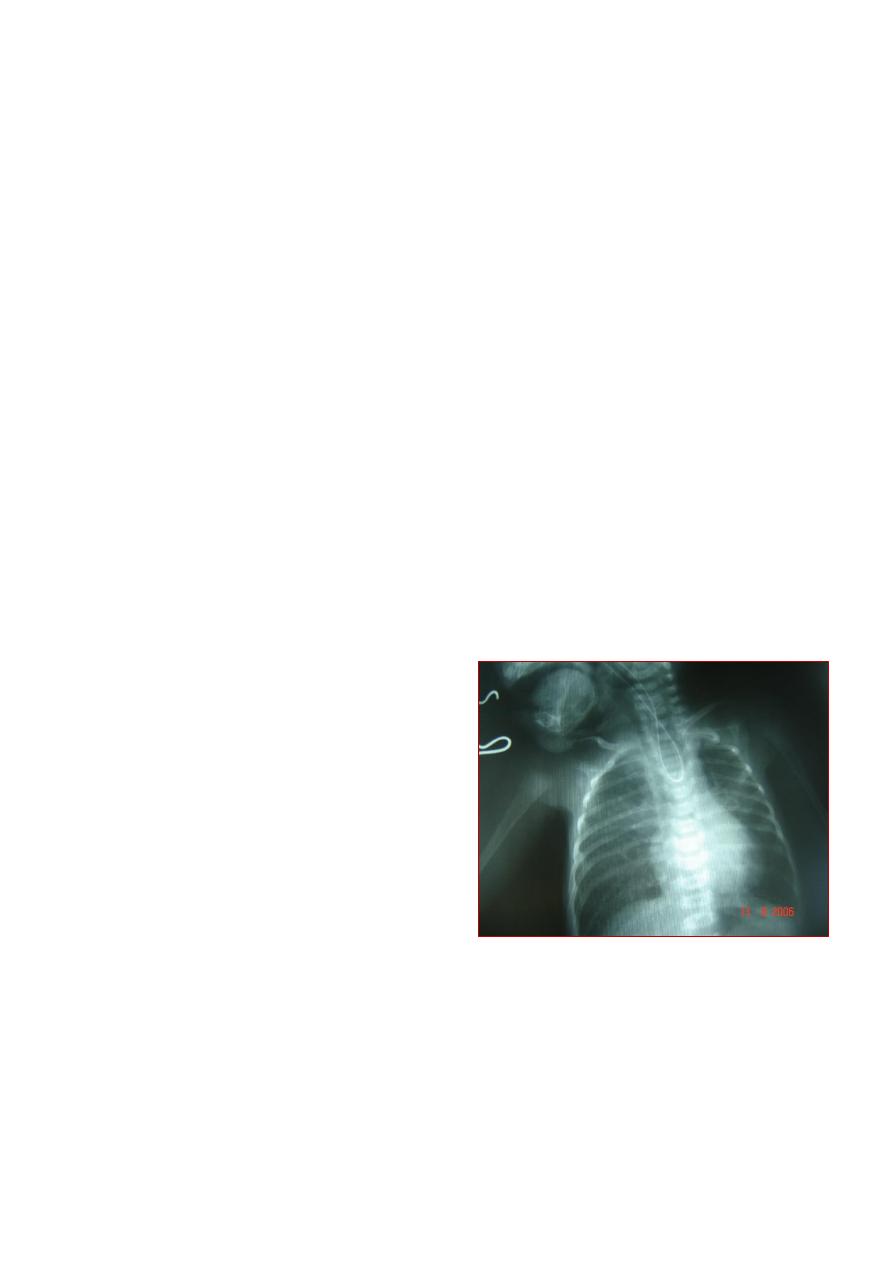
hirschprung disease
)
12
A 2 week old boy presents with history of
constipation, abdominal distension and bilious
vomiting. The pictures show the operative
findings and radiographic investigation done
for him.
1. What is the diagnosis?
2. What is the underlying pathology for this
condition?
3.Describe the findings in all slides.
4. What other investigations used to reach the
diagnosis?
5. What are the steps of management for this
condition?
Session dr.osama Thursday, August 03, 2016
Seminar 2
8
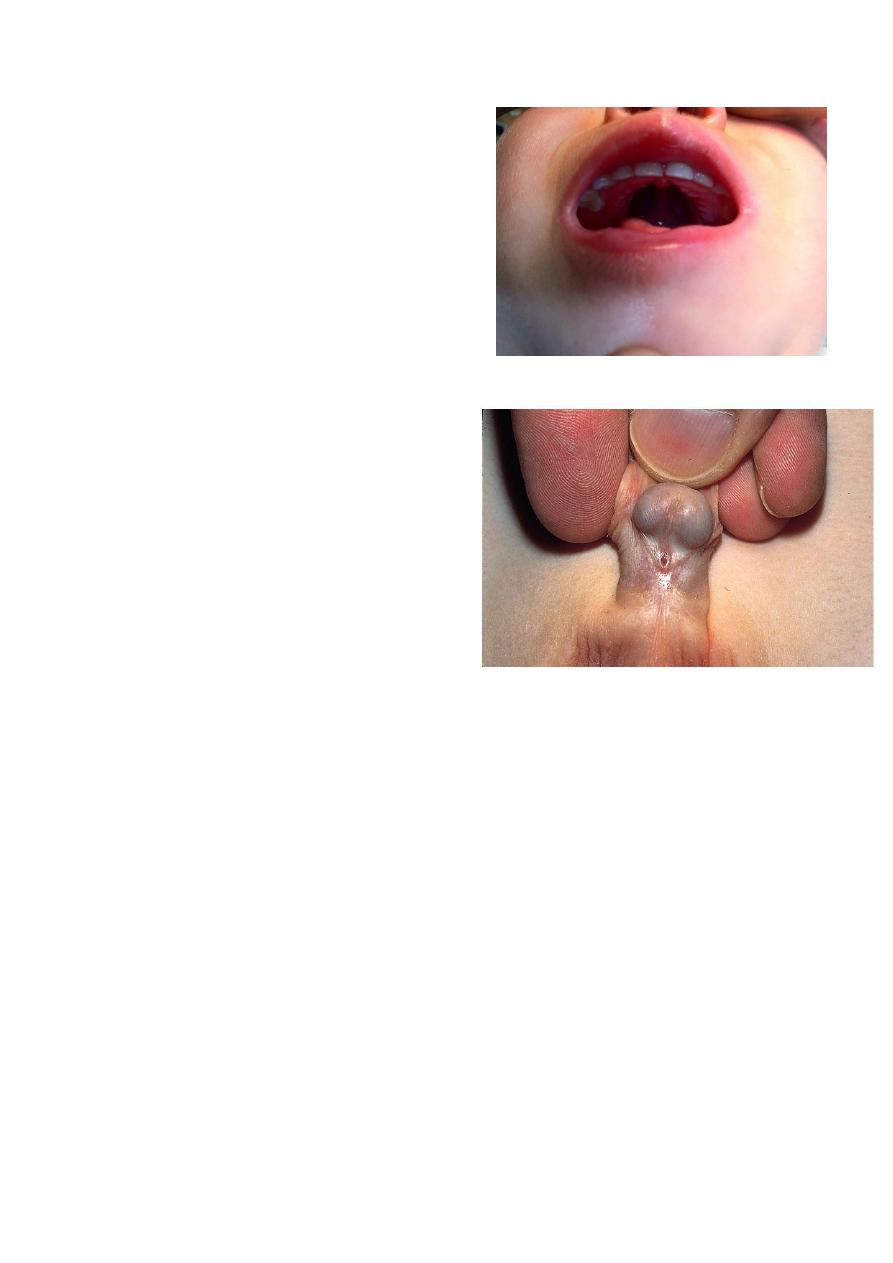
15) cleft palate
-time of Surgery at 3 months .
16) ambiguous genitalia ( hypospadias with
undescended testis)
-check for sex (chromosomal analysis)
-testesterone is high so genetalia developed if
do laproscopy U'll find uterus & ovaries for her
or him
*Intrauterine op. for cleft palate is advanced and done in high centeres –Adv.----nor scar
after birth.
Done by :Group A Active
