Arterial Disorders
Introduction:Arterial disease generally includes:
Coronary artery disease or ischemic heart disease
Cerebrovascular disease
Mesenteric ischemia
Renovascular disease
Peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral arterial disease:
What is peripheral arterial disease?Peripheral arterial disease includes:
Chronic arterial occlusionAcute arterial occlusion
Aneurysms
Arterio-venous malformations and fistulas
Chronic Arterial Occlusion
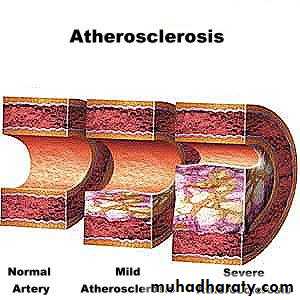
Atherosclerosis:
"Response to injury hypothesis“ by Ross.Risk factors:
SmokingDiabetes mellitus
Dyslipidemia
Hypertension
Obesity
Increase age
Clinical features:
• Intermittent claudication:• Rest pain
• Coldness, numbness, paraesthesia and colour change.
• Ulceration and gangrene;
• Reduced sensation
• Motor weakness
• Absent or diminished pulses
• Arterial bruit
Investigations:
General investigation to diagnose associated disease:• IHD, COPD, DM, renal disease, Lipid abnormalities, and Coagulation abnormalities.
Investigations for arterial mapping:
Doppler ultrasoundDuplex ultrasound
Peripheral angiography
CT angiography and MRA
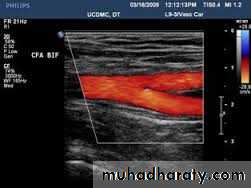
Duplex ultrasound
Treatment:
Stop smokingControl of blood sugar
Reduce blood lipid
Reduce weight
Regular exercise to the limit of claudication
Drugs:
Antiplatelets e.g.; aspirin, clopidogrel, …
Vasodilators e.g.; tolazoline, calcium canal blockers, pentoxifylline,
• I- Conservative Treatment:
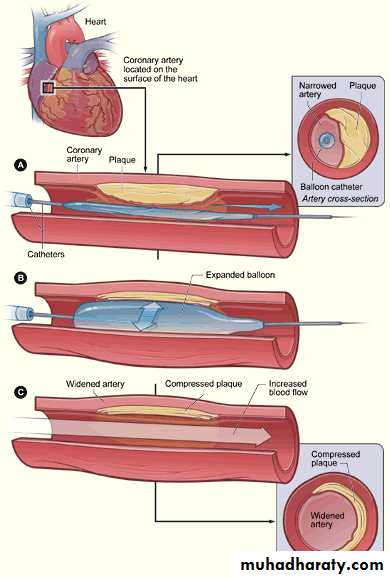
II- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty (PTA)III- Surgical Treatment:
Surgical optoins:• Bypass surgery
• Surgical endarterectomy
• Sympathectomy
• Amputation
Bypass Surgery
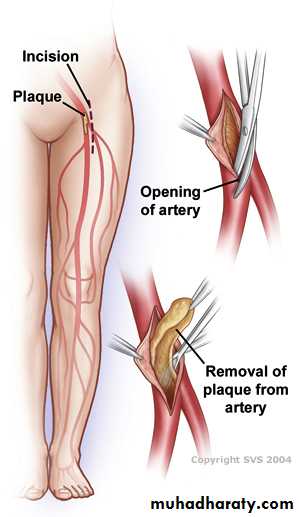
Endarterectomy:
Sympathectomy:
Dorsal Sympathectomy
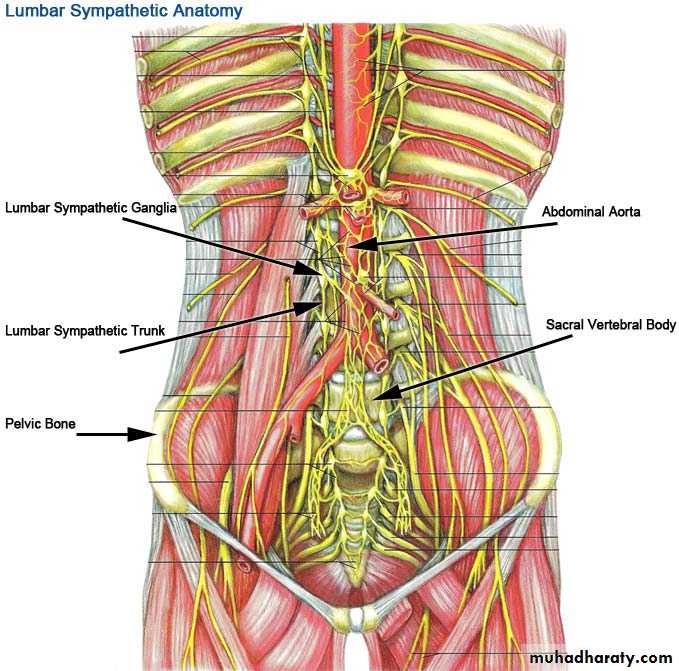
Lumbar SympathectomyAcute Arterial Occlusion
Acute arterial occlusion:Embolism
Thrombosis of an atheromatous plague
Arterial traumaEmbolic Arterial Occlusion
What is an embolus?What is the most common source of an embolus?
What does an embolus cause?
Clinical presentation:Depending on the site of obstruction:
Brain: stroke
Intestine: gangrene of corresponding loop of bowel
Spleen: splenic infarction and left hypochondrial pain
Kidney: loin pain and hematuria
Limbs: (6P)
pain,
pallor,
paresis,
purchasing cold,
pulselessness
paraesthesia
Diagnosis and investigations:
Usually a clinical diagnosisConfirming investigations include:
DopplerDuplex ultrasound
Peripheral angiography
CT angiography or MRA
Treatment:
• Heparin• Relieve pain
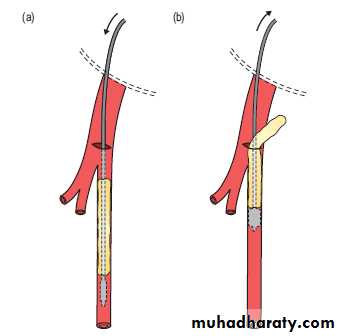
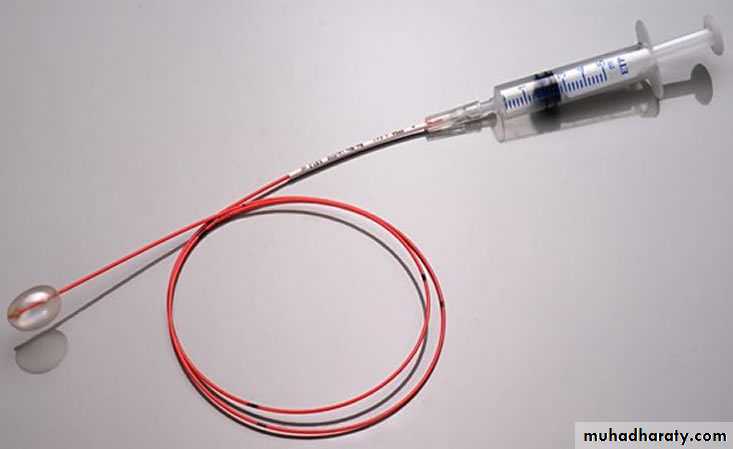
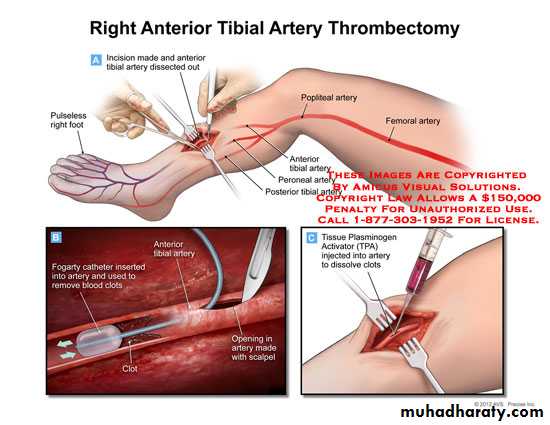
• Emergency embolectomy
Embolectomy catheter
Acute arterial thrombosis:
Sudden occlusion of an already atherosclerosed arteryAcute on chronic ischemia
Similar presentation to emboli but less severe. Why?
Arterial mapping mandatory
Embolectomy may be not enough