Forth stage
HYPERTHYROIDISMLec-1
د.فاخر
1/1/2014
Hypothyroidism is failure of the thyroid gland to produce adequate amounts of hormones(T3-T4). It is either:*Primary
*Secondary – decreased secretion of TSH from pituitary
*Tertiary – decreased TRH from hypothalamus
Cretinism: congenital hypothyroidism
The prevalence of primary hypothyroidism is 1:100, but increases to 5:100 if patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (normal T4, raised TSH) are included. The female:male ratio is approximately 6:1
Causes
Autoimmune*Hashimoto's thyroiditis
*Spontaneous atrophic hypothyroidism with TSH receptor-blocking antibodies
Iatrogenic
Radioactive iodine
Ablation: Thyroidectomy
Drugs: Carbimazole, methimazole, propylthiouracil Amiodarone Lithium
Hashimoto's thyroiditis: increases in incidence with age and affects ∼3.5 per 1000 women and 0.8 per 1000 men each year. Many present with a small or moderately sized diffuse goitre, which is characteristically firm or rubbery in consistency. The goitre may be soft, however, and impossible to differentiate from simple goitre by palpation alone. Around 25% of patients are hypothyroid at presentation.
The nomenclature of autoimmune hypothyroidism can be confusing.
Some authorities reserve the term 'Hashimoto's thyroiditis' for patients with positive thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies and a firm goitre who may or may not be hypothyroid, and use the term 'spontaneous atrophic hypothyroidism' for hypothyroid patients without a goitre in whom TSH receptor-blocking antibodies may be more importantClinical features
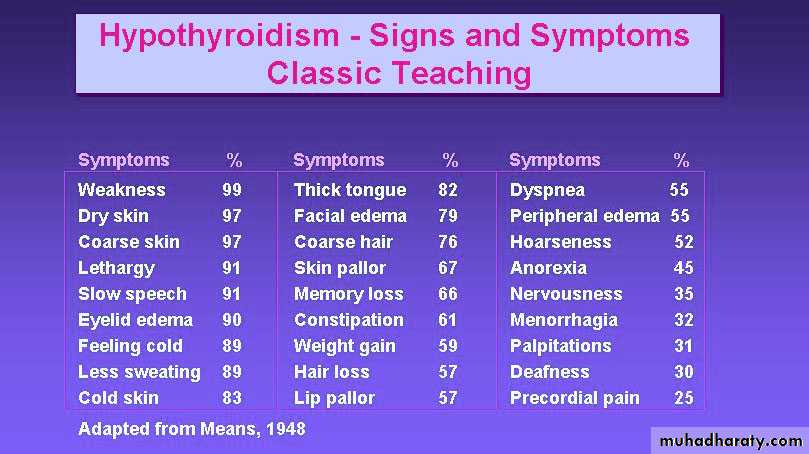
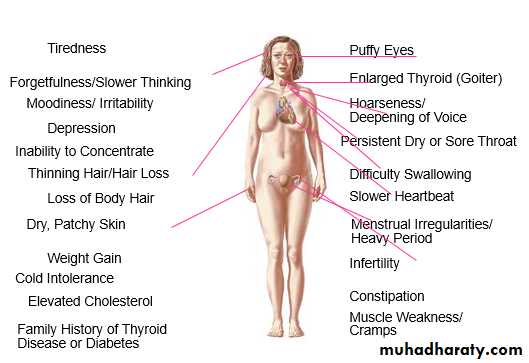
Clinical features depend on the duration and severity of the hypothyroidism. In the patient in whom complete thyroid failure has developed over months or .yearsprolonged hypothyroidism is the infiltration of many body tissues by the ucopolysaccharides, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate, resulting in
1- low-pitched voice
2- poor hearing
3- slurred speech due to a large tongue
4- compression of the median nerve at the wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome).
5- Infiltration of the dermis gives rise to non-pitting oedema (i.e. myxoedema) which is most marked in the skin of the hands, feet and eyelid
6-Periorbital puffiness is often striking and, when combined with facial pallor due to vasoconstriction and anaemias
7- lemon-yellow tint to the skin due to carotenaemia, purplish lips and malar flush
8-middle-aged woman complaining of tiredness, weight gain, depression.
Investigations
In the most common form of hypothyroidism, namely primary hypothyroidism resulting from an intrinsic disorder of the thyroid gland, serum T4 is low and TSH elevatedManagment
Hypothyroidism should be treated with thyroxin it is available in 25 ,50, 100 microgram tablests the dose should be started50 mg then should be increased to 100mg after 3wks ,after another 3wks should raised to 150 mg &should be given single dose .If the patient had ischemic heart disease or elderaly the dose should be reduse to 25 mg daily the response to RX usually appear with 2-3 wk from starting of therapy.early manifestation of response to RX resulting in reduction of body weight &decrease in periorbital oedema &puffiness .the correct dose of thyroxin is that to restor the level of TSH to normal
Myxoedema coma
This is a rare presentation of hypothyroidism in which there is a depressed level of consciousness, usually in an elderly patient who appears myxoedematous.Body temperature may be as low as 25°C, convulsions are not uncommon and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure and protein content are raised. The mortality rate is 50% and survival depends upon early recognition and treatment of hypothyroidism and other factors contributing to the altered consciousness level, e.g. drugs such as phenothiazines, cardiac failure, pneumonia, dilutional hyponatraemia and respiratory failure
Serum TSH should be measured 8 weeks after starting the treatment to check whether the dose needs to be increased and should be measured annually in atients on established treatment to ensure continuing compliance
Treatment is for life, except in mild cases occurring within the first 6 months after radioiodine treatment, pregnancy or partial thyroidectomy and in patients who are hypothyroid secondary to sub acute or silent thyroiditis.
Myxoedema coma is a medical emergency and treatment must begin before biochemical confirmation of the diagnosis. Thyroxine is not usually available for parenteral use so triiodothyronine is given as an intravenous bolus of 20 μg followed by 20 μg 8-hourly until there is sustained clinical improvement. In survivors there is a rise in body temperature within 24 hours and, after 48-72 hours, it is usually possible to substitute oral thyroxine in a dose of 50 μg per day..
Unless it is apparent that the patient has primary hypothyroidism, e.g. thyroidectomy scar or goitre, the thyroid failure should be assumed to be secondary to hypothalamic or pituitary disease and treatment given with hydrocortisone 100 mg i.m. 8-hourly,depending the results of T4, TSH and cortisol concentrations .Other measures include slow rewarming , intravenous fluids, broad-spectrum antibiotics and high-flow oxygen.