
د.هالة عبد الغني الراوي
المرحلة الرابعة
2015-2016
Objectives:
-Clinical assessment of occiput posterior position during labor
-compactions include deep transverse arrest
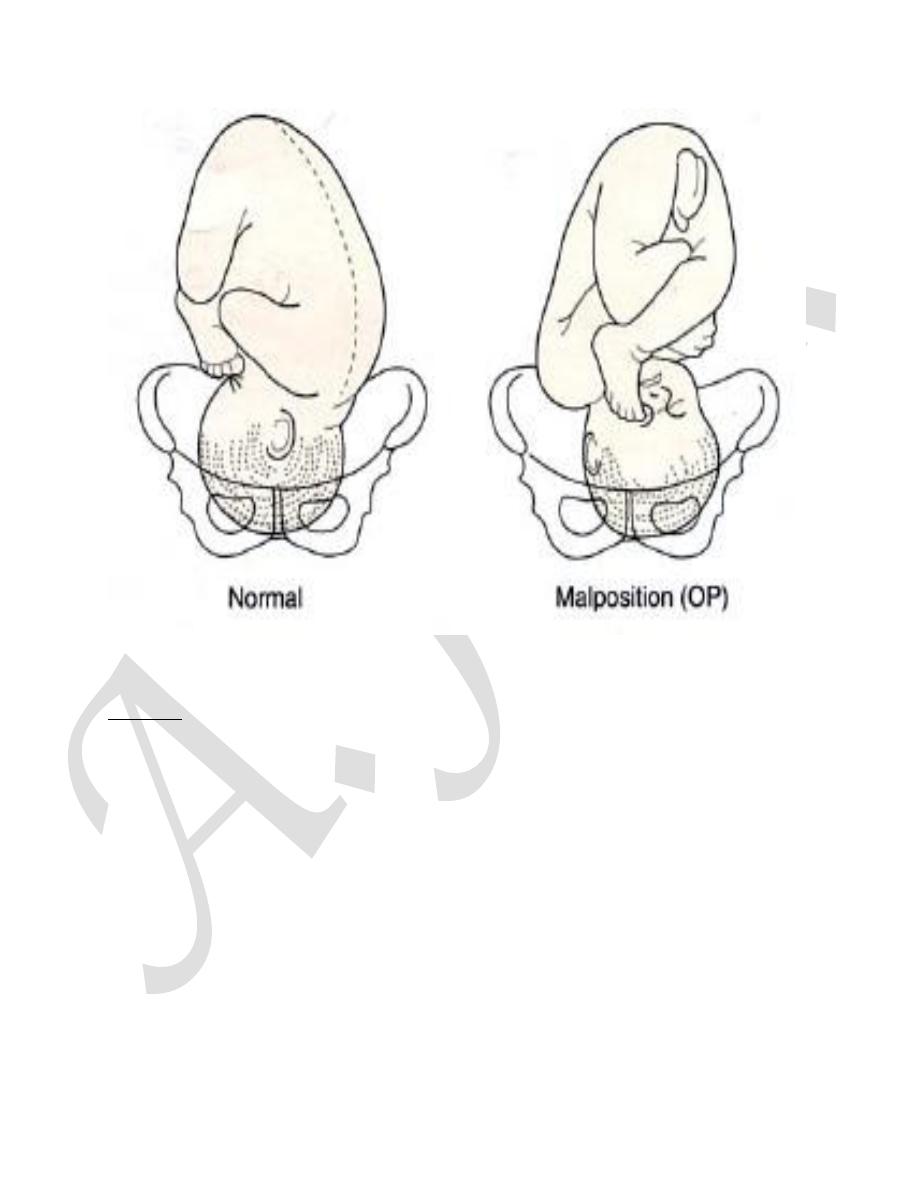
Malposition of the fetal head
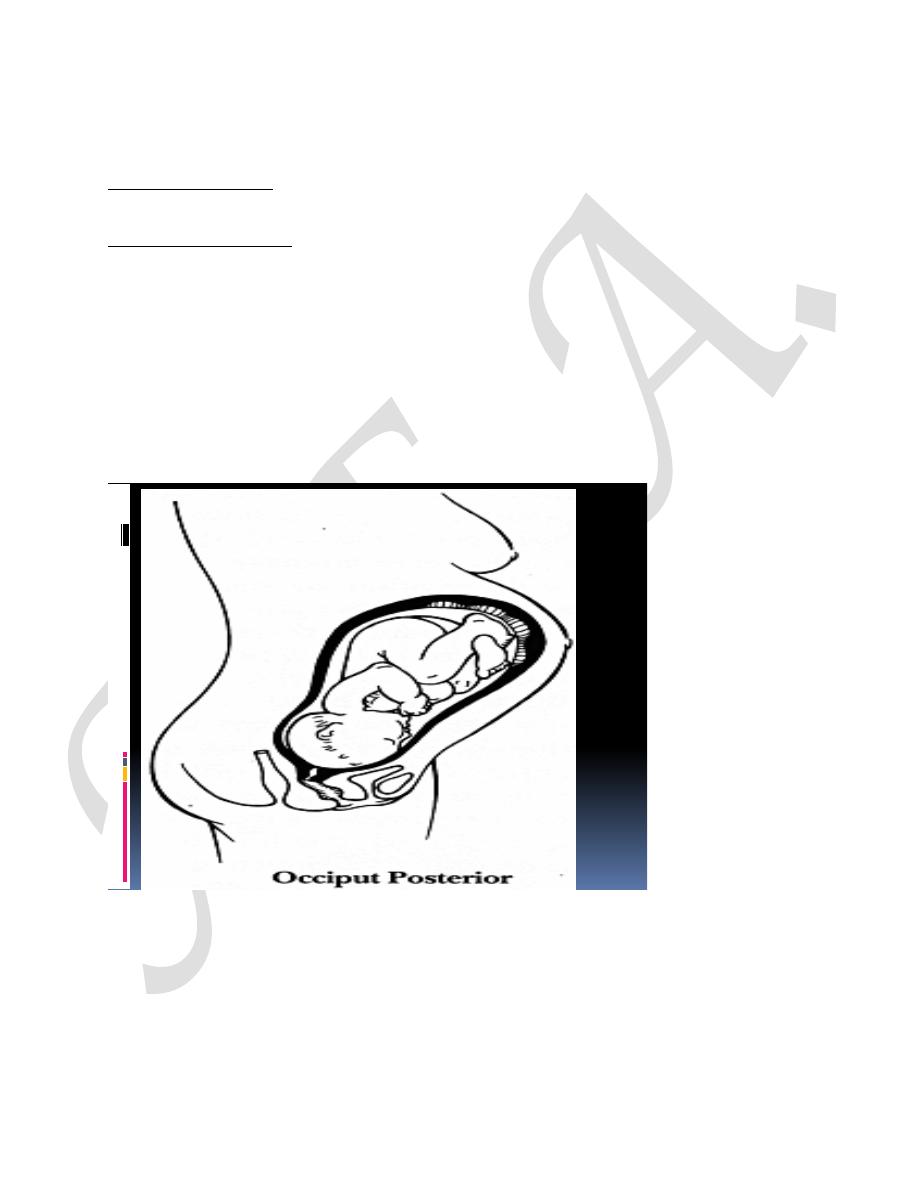
occipito-posterior position of the fetal head :
mean the head inters the pelvis in one of the oblique diameters and
the occiput is directed posteriorly.
There are two positions:
Right occipito-posterior position ROP (the occiput directed to the
right sacro-iliac joint.
Or left occipito-posterior position LOP( the occiput directed to the
left sacro-iliac joint).
The ROP is more common
Occur in 13% of vertex presentations.
The presenting part is the vertex and the denominator is the occipit.
Causes:
1.pendulous abdomen.
2.anthropoid pelvic brim: this favors direct O.P. or direct O.A.
3.anderiod pelvis.
4. a flat sacrum with a poorly flexed head leads to further
deflexion and O.P.
5. the placenta on the anterior uterine wall.
6.idiopathic.
Diagnosis of O.P:
During pregnancy:
It can be a cause of non engagement of the fetal head before the onset
of labour( in primigravida) .
Abdominal examination
1.There is flattening of the lower abdomen.
2.The limbs are easily felt anteriorly.
3.Difficulty in defining the back which felt far in the flank.
4.Difficulty to hear the fetal heart sound which is heard in one of the
flanks.

Vaginal examination:
Early in labour:
Early rupture of membranes is common.
High presenting part.
Established labour
The position can be determined from the direction of the anterior
fontanelle, which can be easily felt behind the pubis
The degree of flexion of the head can be determined from the
fontanelles also.
1.If only the anterior fontanelle can be felt the head is poorly flexed.
2.If both the anterior and posterior fontanelles can be felt the head is
less poorly flexed.
3.If only the posterior fontanelle felt the head is well flexed.
A well flexed head is more likely to rotate anteriorly.
Mechanism of labour:
The mechanism of labour depends on whether the head is well flexed
or incompletely flexed .
1.The well flexed head:
•If the head is well flexed,
•The occiput will be at lower level than the sinciput
•It will hit the pelvic floor first.
•undergoing long anterior rotation through three-eighths of a circle
to lie behind the symphysis pubis.
The occiput has thus rotated through the angle of 135 degree to bring
the occiput to the symphysis pubis. The mechanism is thereafter t

2.When the head is incompletely flexed:
•If the head is incompletely flexed the occipito-frontal diameter which
measure 11.5 cm has to pass through the pelvis instead of the sub-
occipito-bregmatic diameter which measure 9.5 cm.
•It is this that explain why some cases of occipito-posterior position has
difficult and prolonged labour.
With incomplete flexion the sinciput will meet the pelvic floor first
and rotate anteriorly to lie behind the symphysis
•While the occiput rotate backward by one-eighth of the circle to lie
in the hallow of the sacrum.
This is known as SHORT ROTATION (45 degree) and gives the persistent
O.P or direct O.P position.
•The head may now be born with the face towards the posterior
surface of the symphysis pubis (face to pubis).
•The root of the nose is pressed against the bone.
•The vertex is born by flexion and followed by the occiput.
•Then the head extends, so the face and chin emerging from under
the pubic arch.
•The vulval orifice is stretched by the occipito-frontal instead of the
sub-occipito-frontal diameter with a difference in size of 1.5 cm. and a
severe perineal tears may result.

3. Deep transverse arrest:
In some cases the head becomes arrested with its long axis in the
transverse diameter of the pelvis.
•The degree of extension being such, that neither the occiput nor the
forehead is sufficiently in advance to influence rotation.
This is called deep transverse arrest of the head.
It result from either:
Incomplete forward rotation of the occipito-posterior position.
The majority are the result of failure of the head which inter the
pelvis in occipito-transverse position to rotate anteriorly.
The course of labour in occipito-posterior position:
Prolongation of the 1
st
and 2
nd
stage of labour are common.
Ineffective uterine contraction is common because the poorly
flexed head fails to press down upon the cervix.
In 70% of cases there will be spontaneous rotation of the occiput to
the anterior position.
In about 10% there the occiput undergoes short back ward rotation
and delivered in direct occipito-posterior position (face-to-pubes).
In the remainder deep transverse arrest of the head.
Management of the first stage of labour:
The 1
st
stage is managed as in a normal case.
Nothing can be done to correct the Malposition or to influence the
rotation of the head at this stage.
A partogram is done to monitor the :
1.Uterine contraction (frequency, duration and strength ).
2.Fetal heart.

3.Dilatation of the cervix.
If progressive cervical dilatation does not occur augmentation with
an oxytocin drip may be tried.
If still no progress obtained in a few hours caesarian section (C/S) is
performed.
Also if there is fetal distress C/S is done..
Management of the 2
nd
stage of labour:
1.In most cases (70% ) provided that the uterine contractions are
strong and the woman is able to make good expulsive efforts the
occiput rotates forward and normal delivery takes place.
2.In other cases (10% ) the baby may be delivered face-to-pubes with
out difficulty but there is a great risk of a perineal tear. Large
episiotomy may be required.
3.In about 20% of cases there is failure of the presenting part to rotate
and descend and such cases delivered by C/S or rotation can be
enhanced by assistance .
The first step in assisting delivery is rotation of the fetal head
This can be performed by:
1.Manual rotation.
2. Forceps delivery Kjelland’s forceps.
These two procedures needs an experts to perform them other wise it
may result in excessive fetal and maternal morbidity and complications.
3.Vacuum extractor.
Nowadays C/S is done in these conditions to reduce fetal and
maternal complications
Retention of urine is common in such labours and catheterization may
be required.
The mother may feel an urge to bear down before the second stage is
reached, probably due to pressure on the sacrum and rectum.

Premature expulsive efforts can delay progress by causing oedema of
the cervix.
An epidural is again helpful in this situation
Deep transverse arrest:
Means arrest of labour when the fetal head has descended to the
level of the ischial spines and the sagittal suture lies in the transverse
diameter of the pelvis.
The occiput lies on one side of the pelvis and the sinciput on the
other side and the head is badly flexed.
It is only diagnosed during the 2
nd
stage of labour.
If the head is firmly fixed in the transverse position obstructed labour
will occur.
It is commonly caused by an android pelvis
.
So the head will fail to descend to the pelvic floor, where rotation
normally occur.
The diagnosis usually made by vaginal examination during the 2
nd
stage
where the head found to be arrested at the level of the ischial spine
with the sagittal suture in the transverse diameter. both fontanelles are
usually palpable
Management:
When the head is arrested in the transverse position the safest way to
deliver the fetus is by performing C/S.
