7
Intra partum fetal monitoring
Objectives
The management of first stage of labor has witnessed great changes in the last 50
years. Labor simply is a continuation of normally physiological process through
which all the products of gestations are expelled namely fetus, amniotic fluid and
placenta. Despite labor is a normal physiological phenomena the concept of active
management of has been introduced. Its principles are converting labor from a passive
process into active monitoring of mother and fetus. For the first stage of labor there
are some points which should be followed to reduce or anticipate fetal hypoxia as
early as possible. Those include, evacuation of the bowel, rupture of the amniotic
membrane, mounting of oxytocin infusion, introduction of partogram and giving
analgesia for pain. So in this lecture we will discuss the various most common and
widely used methods of fetal monitoring so fetal hypoxia- acidosis is diagnosed as
early as possible. Below are the most commonly used methods for fetal monitoring
and their interpretations.
Intermittent auscultation of fetal heart rate
Intermittent auscultation for fetal heart sound every 30 minutes is the most commonly
used method for intra partum fetal monitoring. Its mostly suitable for low risk women
and in the absence of mal presentation, mal position of the fetal head. Usually
conducted by a small ultrasound device called Sonicaid. The results are recorded and
plotted on the partogram.
8
Cardiotocography or CTG
Definition
Cardiotocography is usually defined as study the correlation between fetal heart rate
and uterine contractions.
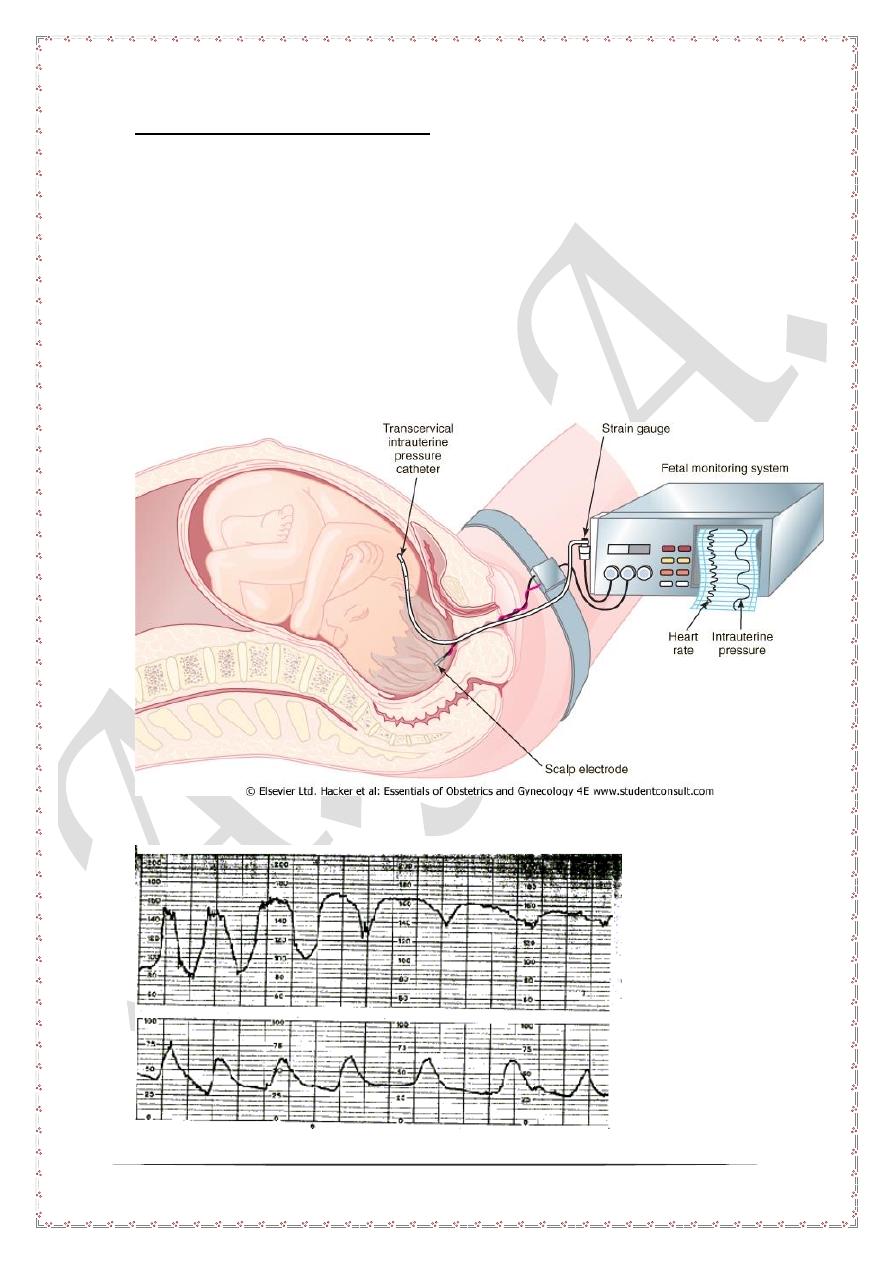
Technique
During labor both uterine contractions and fetal heart sounds can be recorded either
externally or internally. Before the rupture of the amniotic membrane ultra sound
probes are applied to the maternal surface to record both. After rupture of the
amniotic membrane internal probes may be applied to the fetal head scalp to record
fetal ECG in addition other intrauterine probe which measure intrauterine pressure.
The results are plotted on a strip paper called CTG strip, which contains both fetal
heart rate as well as uterine contractions.
9
Interpretation of CTG strip
Simply CTG may show either no fetal heart variation with uterine contraction or even
transient acceleration, in such cases the strip is assuring. However the following
patterns should be look for and recognized.
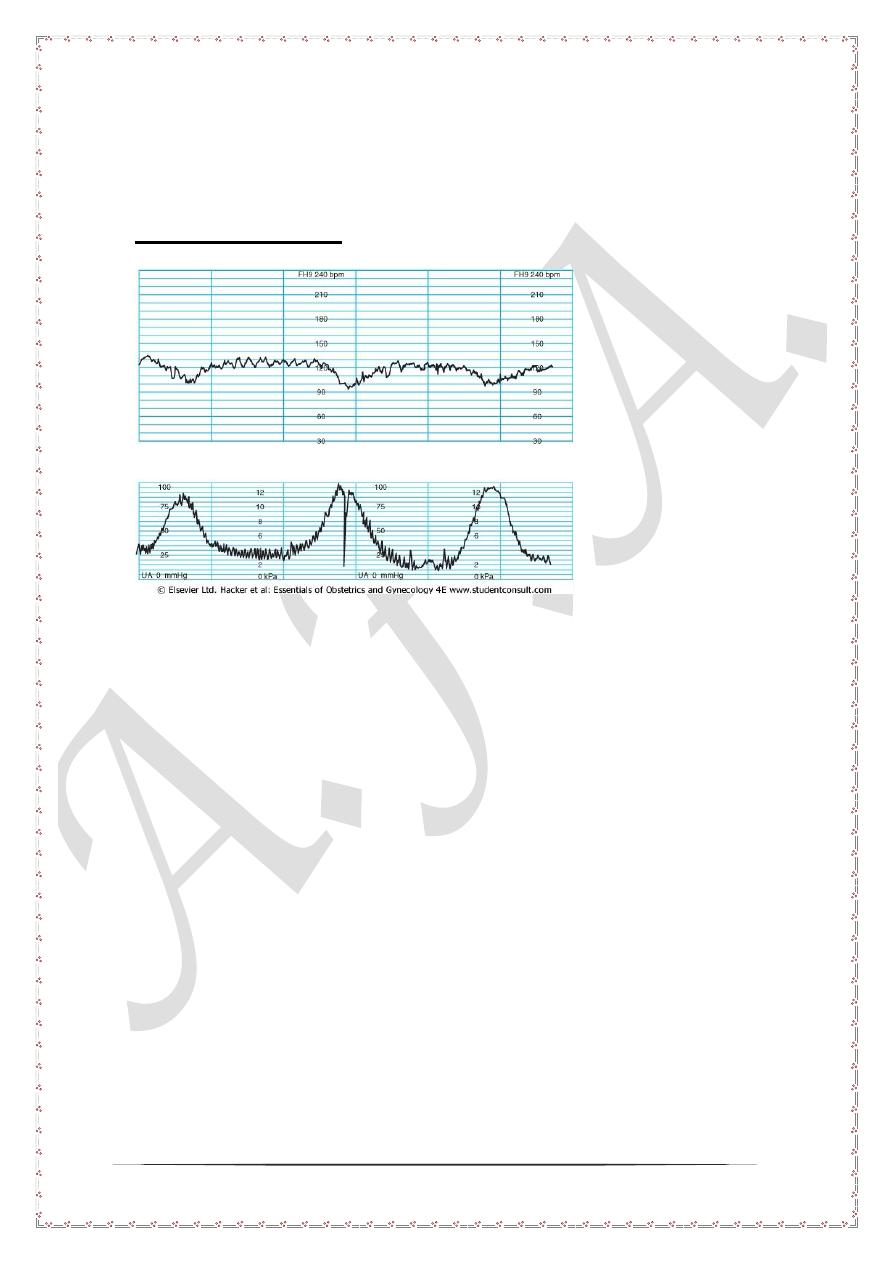
Early deceleration
In early deceleration the fetal heart rate drop bellow 110 beats per minute with uterine
contraction. The nadir of deceleration coincides with nadir of uterine contraction.
However the deceleration returns immediately to normal rate once the uterine
contraction is off. This pattern is called early deceleration and usually associated with
increased intra cranial pressure on the fetal head. This rise is due to compression on
the anterior fontanel mediated by increased intra uterine pressure. This pattern is not
associated with fetal distress or hypoxia. No further action is needed and commonly
seen toward the end of first stage of labor or during the second stage of labor.
10
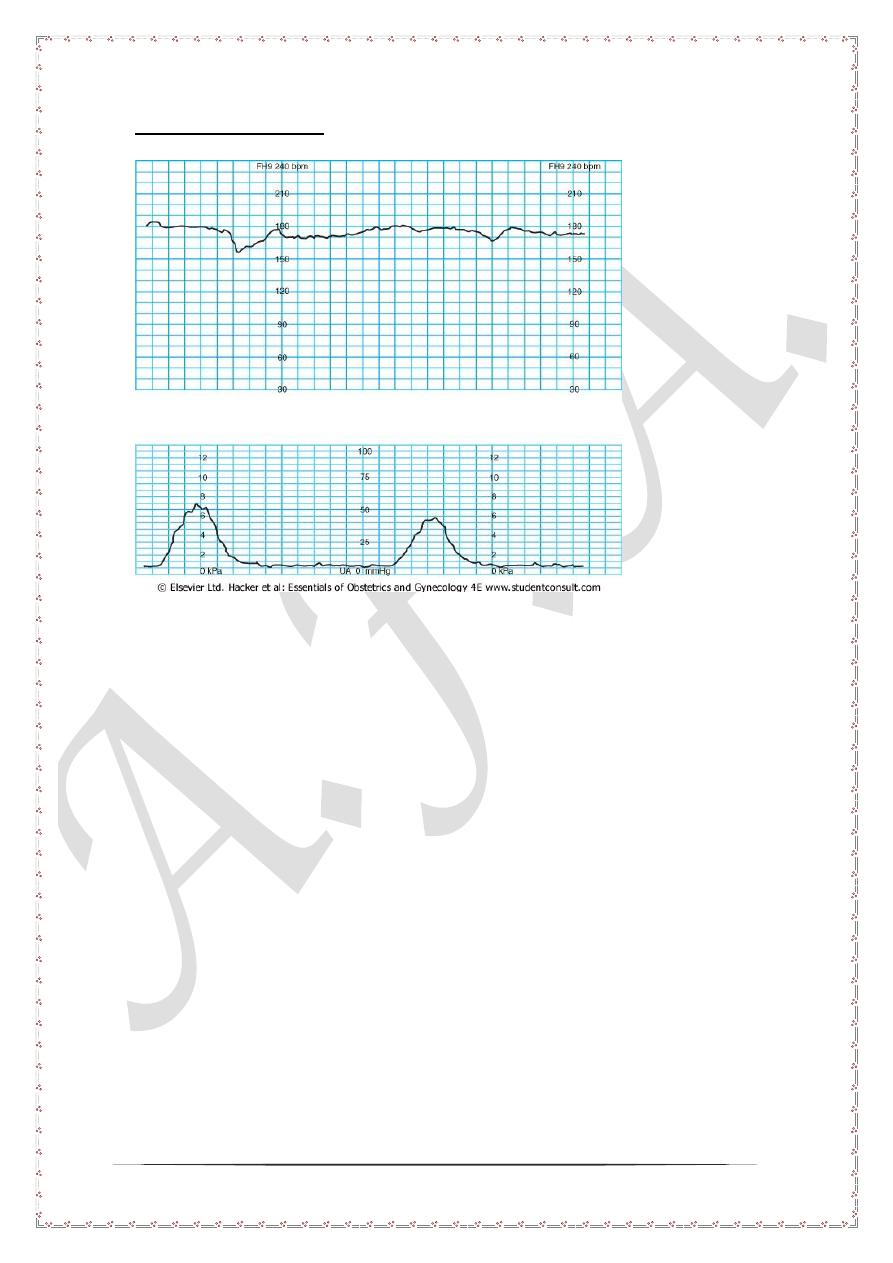
late deceleration
In late deceleration, the drop in fetal heart rate below 110 starts after uterine
contraction and persist after the uterine contraction end. This pattern should be well
recognized and identified as it is the earliest finding associated with fetal distress. The
details will be given shortly after.
11
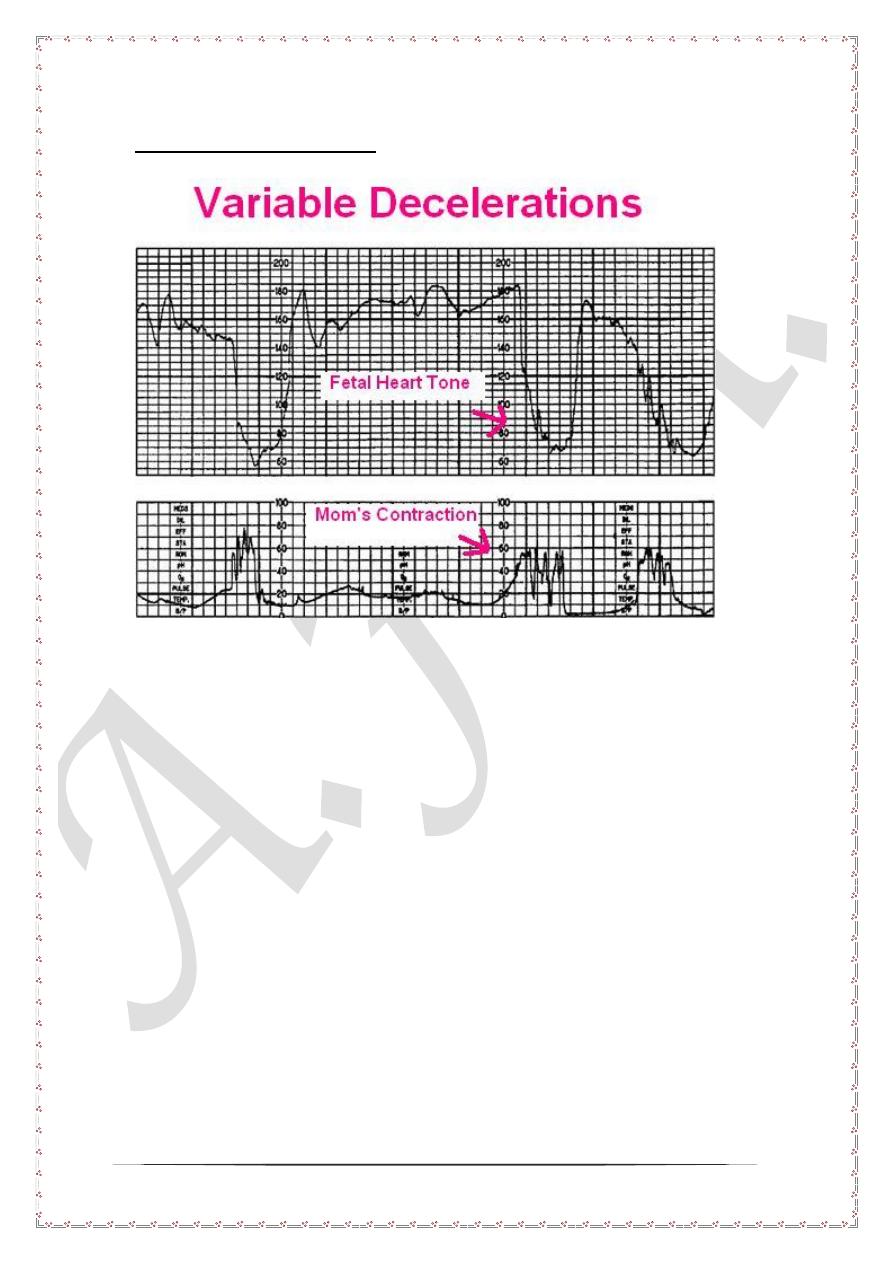
Variable deceleration
Variable deceleration is said to be present when there exist no definite pattern
between uterine contractions and the pattern of fetal heart decelerations. This pattern
is significantly associated with fetal hypoxia and acidosis. Further assessment is
usually mandatory.
Immediate measure for late and variable decelerations
Once late and variable are recognized in the CTG strip the followings should be done
1- Stop ocytocin infusion
2- Turn the patient to either side
3- Oxygen supplementation
4- Infusion of 5 % dextrose to combat any maternal ketosis
5- In some cases tocolytics may be used to stop uterine contraction like
terbutaline or nifidepine.
6- Within these measures the fetal heart rate are usually monitored continuously.
Either we have the deceleration recovers to normal or persist for 15-30
minutes. In such cases fetal blood estimation is mandatory.
12
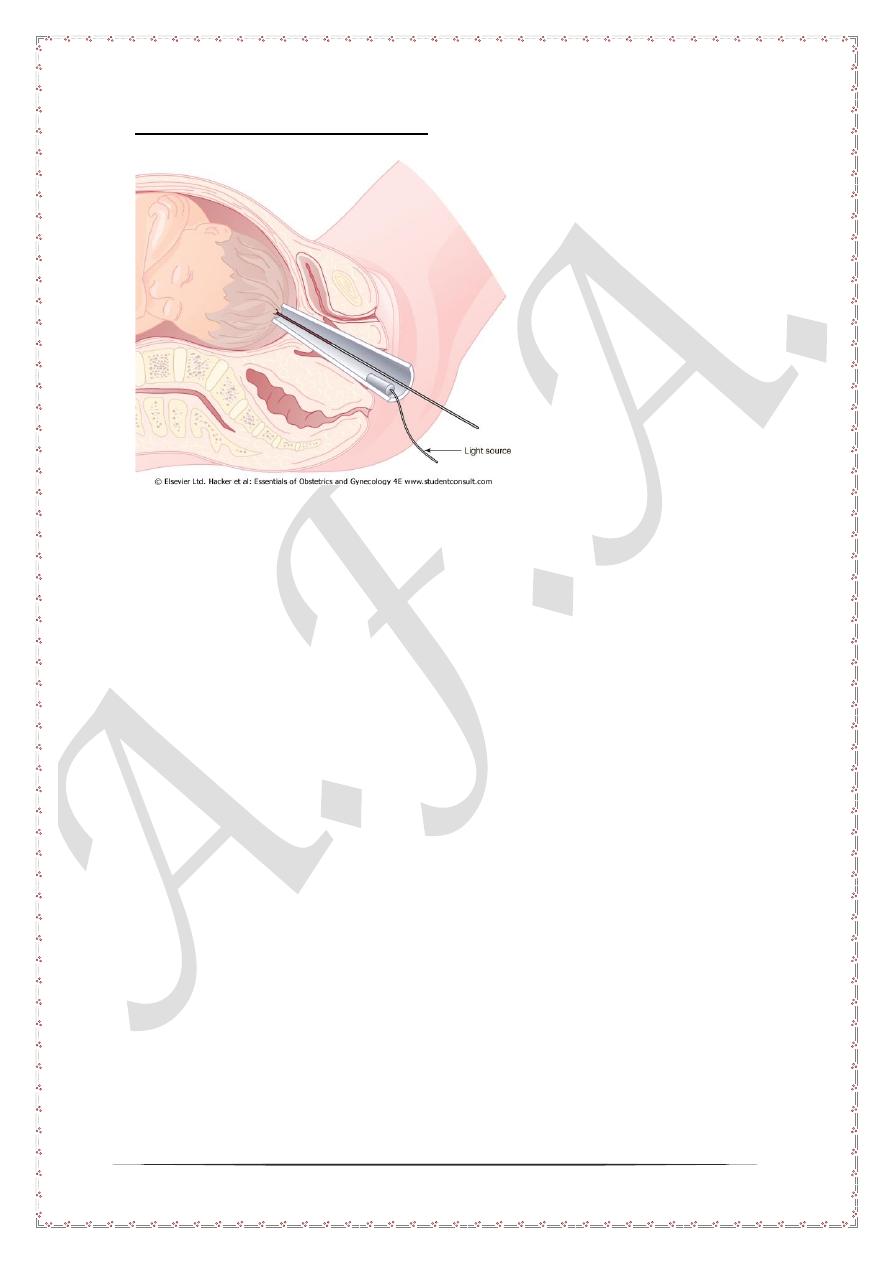
Fetal blood pH estimation
Fetal blood pH estimation is mandatory among infants with late and variable
deceleration. In this technique a special conical speculum is inserted to visualize the
fetal scalp. A drop of fetal blood is obtained by puncturing the fetal scalp. The pH is
estimated by digital pH meter.
Interpretation of fetal blood pH
1- pH> 7.25 repeat after 4 hours during labor
2- pH 7.2- 7.25 repeat every 30 minutes.
3- pH < 7.20 immediate delivery by emergency cesarean section in the first stage
of labor. Otherwise expedite delivery of the fetus in the second stage of labor
by the use of either forceps or vacuum extraction.
