Dr.Manal Madany

It is planned or artificial
initiation of labour before
its spontaneous onset for
the purpose of delivery of
the feto-placental unit.

Induction of labor should be
considered when it is felt that the
benefits of vaginal delivery out
weight the potential maternal &
fetal risk of induction.
These issues should be discussed
with the women prior to initiation
of induction.

1.prolonged pregnancy with
gestational age of at least 10-12 days
beyond the EDD.
2.Pre-labor rupture of membrane
(P.R.O.M.)
is another common indication for IOL
At term (beyond 37 weeks),
good quality evidence supports IOL
approximately 24 hours following
membrane ruptur.

3.Potential fetal compromise
(significant fetal growth restriction,
non-reassuring fetal surveillance).
4.Pre-eclmpsia.
5.Other maternal hypertensive
disease.
6.Deteriorating maternal medical
conditions: (Renal disease,
significant pulmonary disease).

7.Diabetes mellitus.
8.Autoimmune disease e.g. SLE.
8.Rhesus iso- immunization.
9.Twin pregnancy continuing
beyond 38 weeks.
10. Recurrent ante partum
hemorrhage.

Suspected fetal macrosomia, in the
absence of maternal diabetes,
and isolated oligohydramnios at
term are
Not
evidence-based
indications for IOL

11.APH. at term.
12.Placental abruption.
13. Fetal demise.
14. Sometime induction done for
social or geographic reasons
without a medical or obstetrical
indication.

1.IOL may fail
& result in caesarean
section
2.Hyper stimulation of the uterus
may result in fetal asphyxia &the need
for C/S.
3.
IOL in the presence of uterine scare
may result in uterine rupture
.

4. Cord prolapsed
may result
when ARM performed with
presenting part still high.
5.Maternal water intoxication
.

6.Hyperbilirubinaemia resulting
in neonatal jaundice
(following the
use of oxytocin ,not PG.
7.Delivery of preterm infant
due
to incorrect estimated dates

1-Previous myomectomy entering
the uterine cavity.
2-Previous uterine rupture.
3-Fetal transverse lie.
4-Placenta previa.

5.Vasa previa.
6.Invasive cervical cancer.
7.Active genital herpes.
8.Previous classical or inverted T
uterine incision.

Deteriorating maternal condition with
major antepartum haemorrhage, pre-
eclampsia or
cardiac disease
may favour Caesarean
delivery.
Breech presentation
is a relative
contraindication to IOL

Prior
to initiation of induction the following
should be assessed:
Indication
for
induction
/
any
contraindications.
Gestational age.
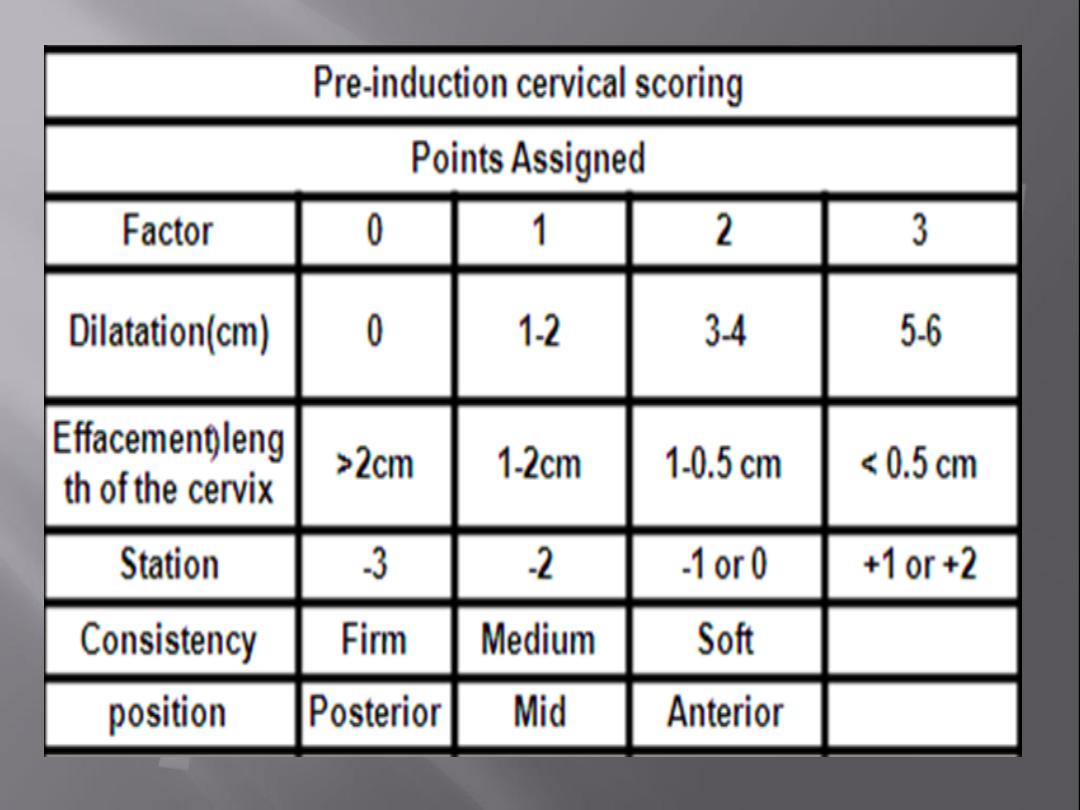
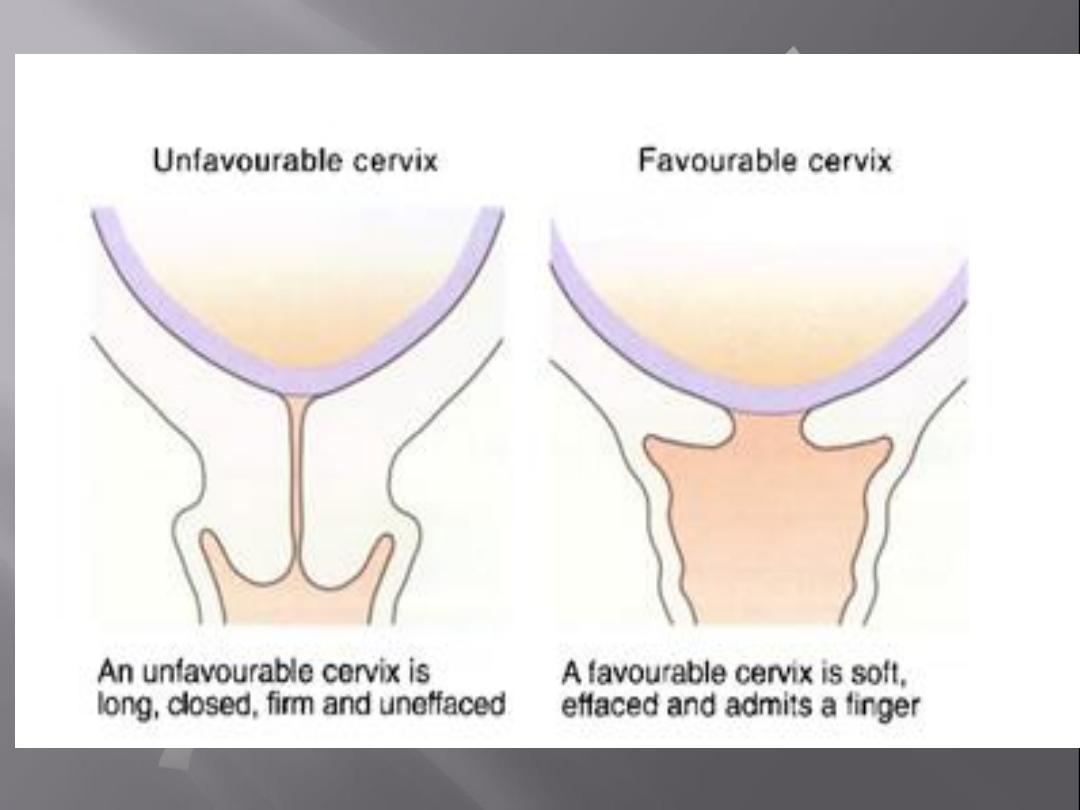
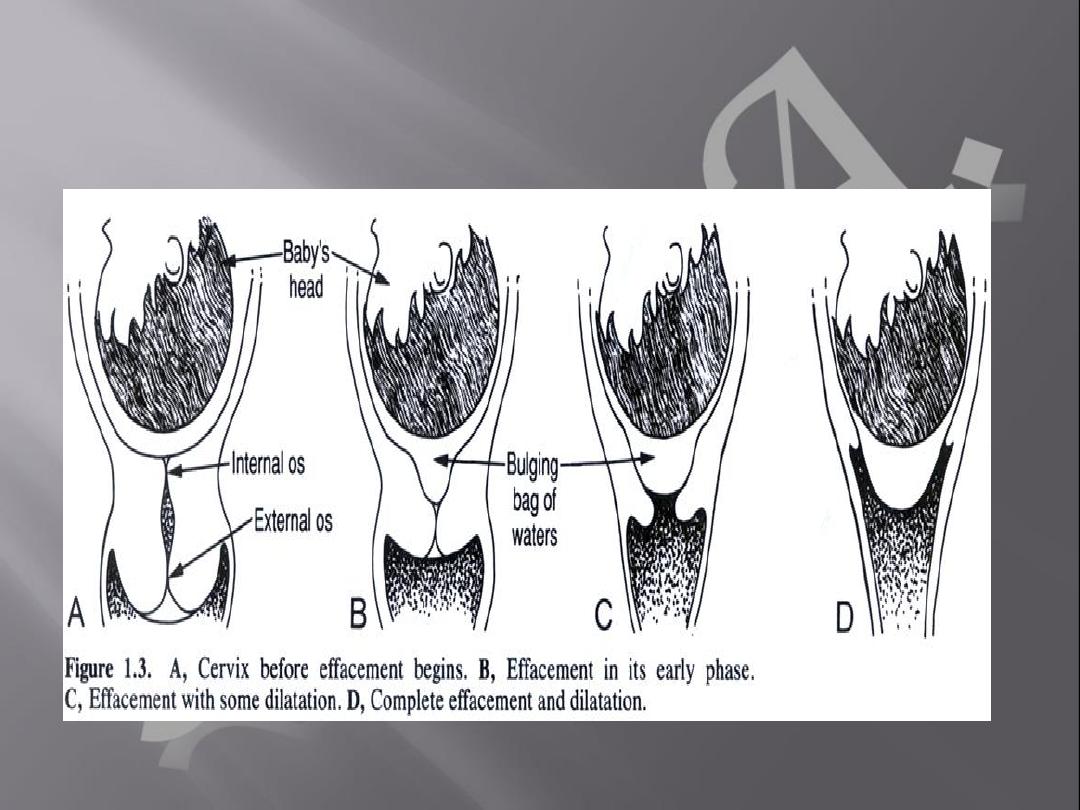
Cervical (cx) favorability (Bishop score
assessment).

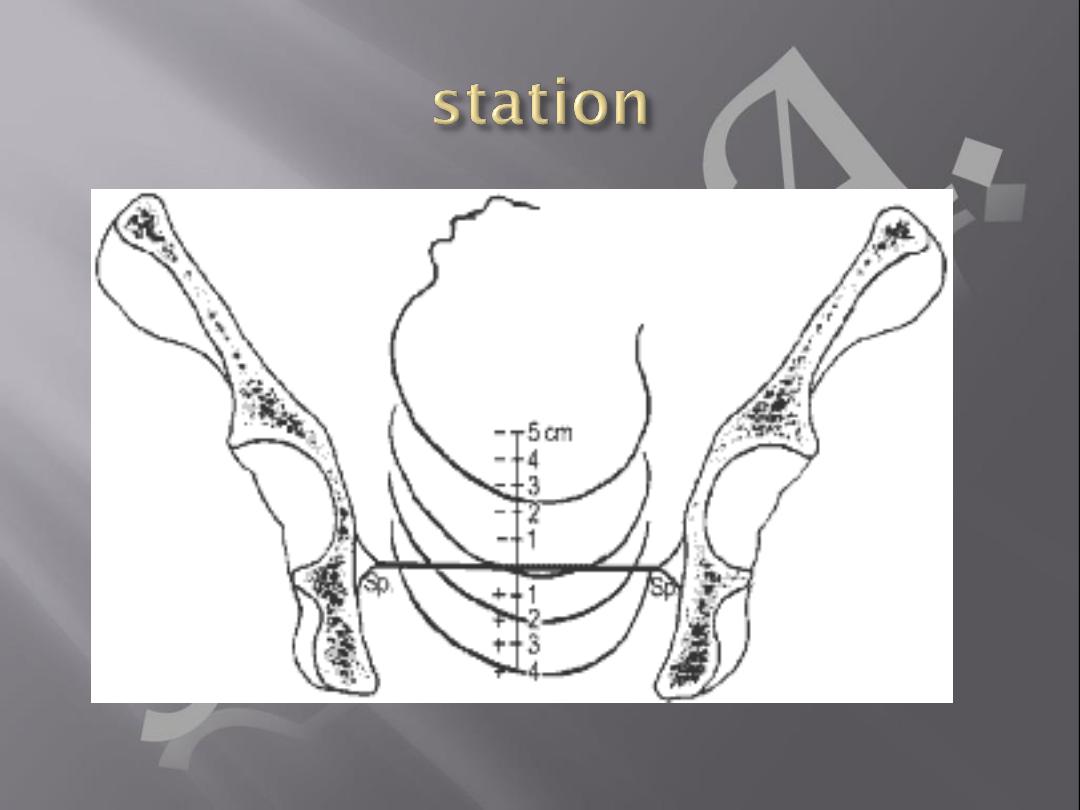
Assessment of pelvis & fetal size /
presentation.
Membrane
status
(intact
or
ruptured).
Fetal wellbeing / fetal heart rate
monitoring
prior
to
labour
induction.

(1)Pharmacological-based
methods
(2)Non-pharmacological
methods

1.Prostaglandins (PGE2)
2.Intravenous oxytocin alone
3.amniotomy with intravenous
oxytocin
4.Misoprostol

Mifepristone
Hyaluronidase
Corticosteroids
Oestrogens
Vaginal nitric oxide donors

It should be administered as a gel, tablet or
controlled release pessary.
The recommended regimens are:
• one cycle of vaginal PGE2 tablets or gel: one
dose, followed by a second dose after 6 hours
if labour is not established (up to a maximum
of two doses)
• one cycle of vaginal PGE2 controlled release
pessary: one dose over 24 hours

(Oral PGE2 , Intravenous
PGE2 Extra-amniotic
PGE2& Intracervical PGE2)
should not be used for
induction of labour.

A common concentration that
is used for oxytocin is 10 IU in
one liter(1000 ml) of balanced
solution (such as normal
saline or Ringer’s lactate)

The combination of intravenous
oxytocin and amniotomy is
commonly used in women
with favourable cervices.

is a synthetic prostaglandin that
can be given orally, vaginally or
sublingually. It is effective in
causing uterine contractions

recommended for the treatment of
(1)missed miscarriages.
(2)incomplete miscarriages
(3)the induction of abortion.
(4)preinduction cervical ripening
.

(5) cervical preparation before
uterine instrumentation.
(6)It also has potential in late
pregnancy for induction of
labour
(7)postpartum haemorrhage
prophylaxis and treatment .

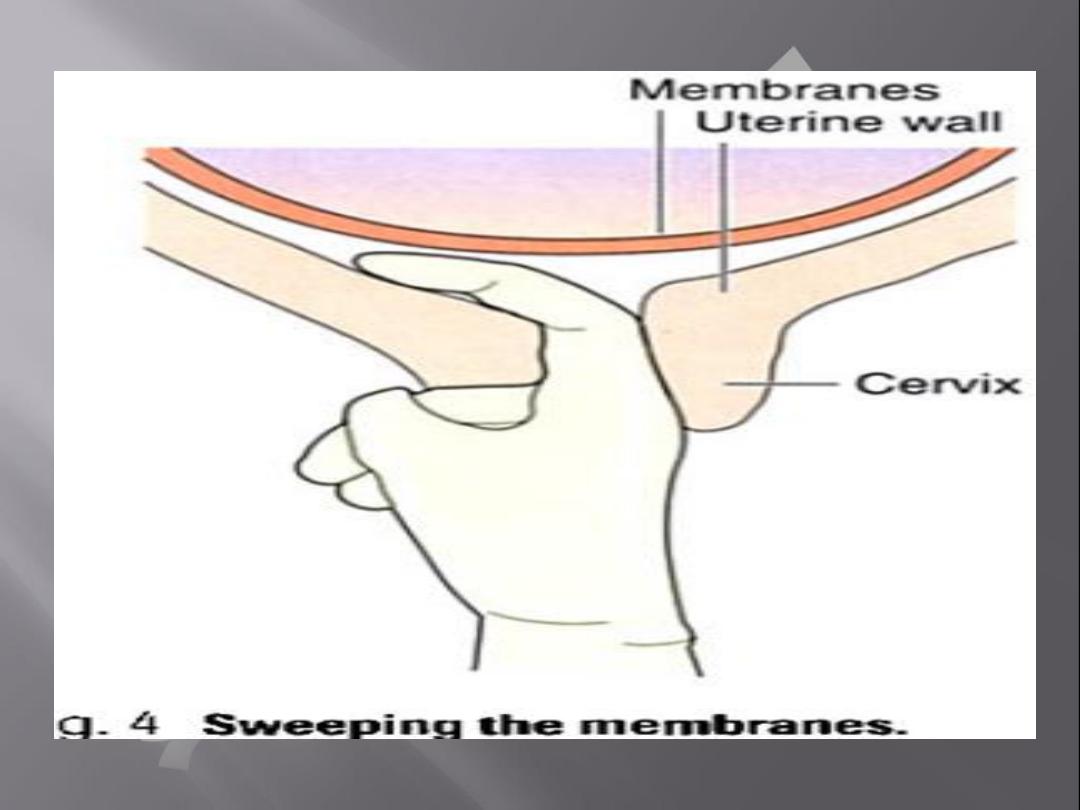
Membrane sweeping
Herbal supplements
Acupuncture
Castor oil, hot baths and
enemas

Sexual intercourse
Breast stimulation
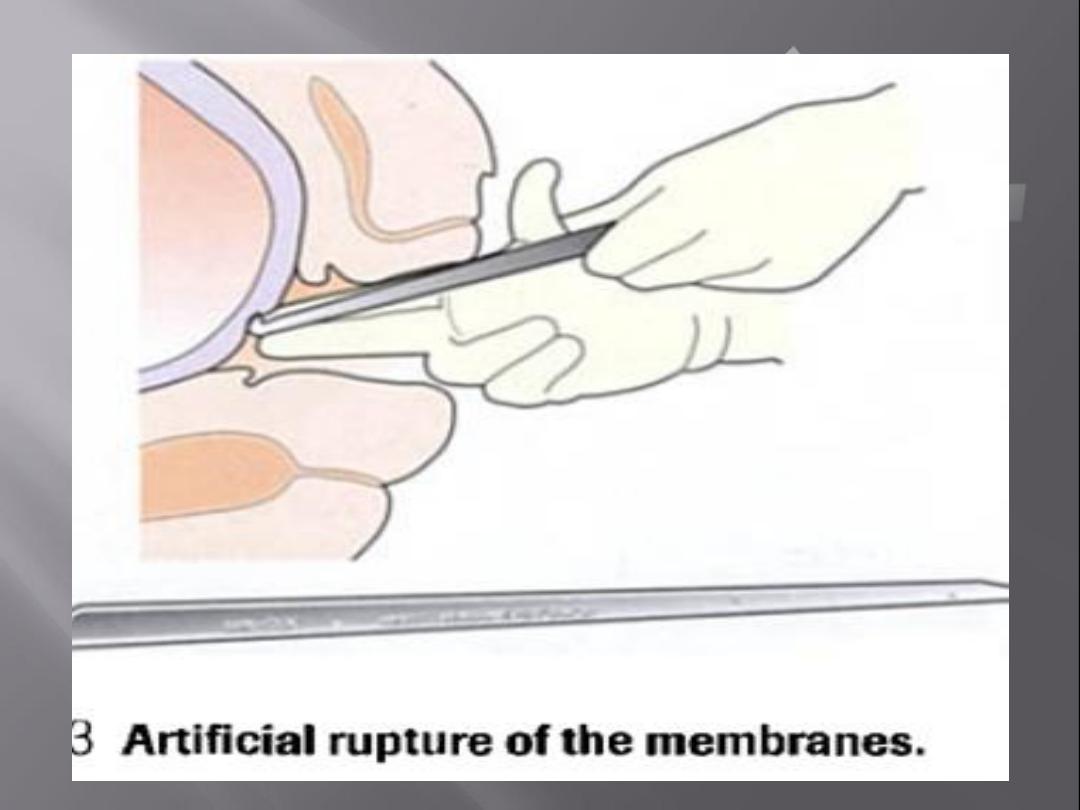
Surgical methods(Amniotomy)
Mechanical methods

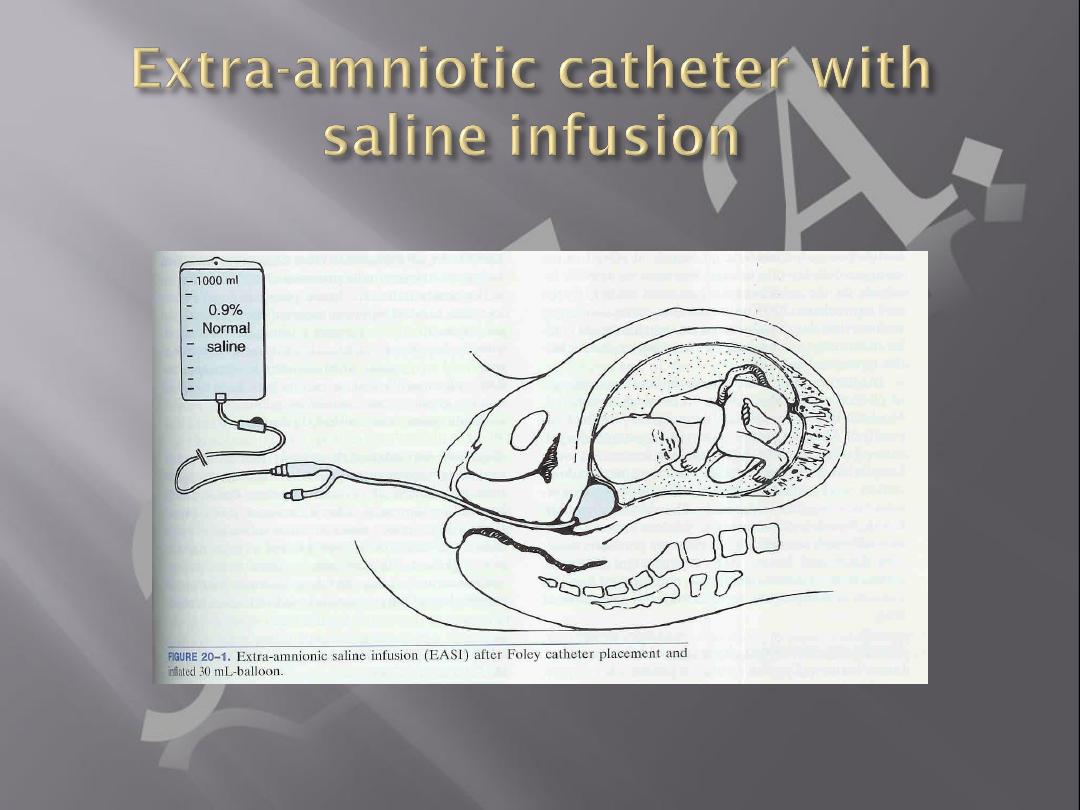
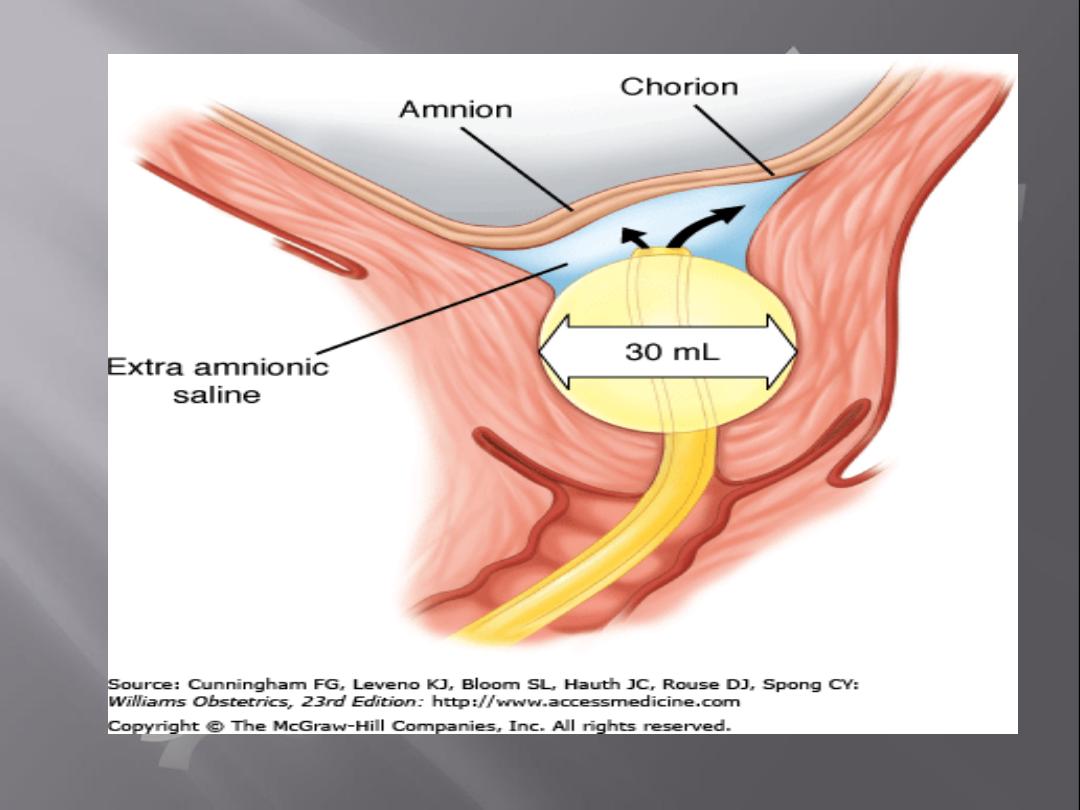
a.Foley catheter (with & without
cervical extra amniotic saline
infusion)
b.Natural dilators (lamineria) and
synthetic dilators.