NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION
MUDR. Rudolf Černý CSc
Dept.of Neurology
2
nd
Medical Faculty
Charles University, Prague
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Functional principle of NE
few possibilities are given for the physical
investigation of the nervous system (NS) by
our senses
neurological examination is based on the
functional principle
result:
functional status of the NS
no anatomical information can be inferred
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
NE is a hierarchically build mosaic
of tests - reflexes, chosen so, that
all principal part of NS are checked
NE is a result of clinico-pathological
comparisons, started from mid-
nineteenth century
Charcot school, France
Erb, Friedreich, Germany
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
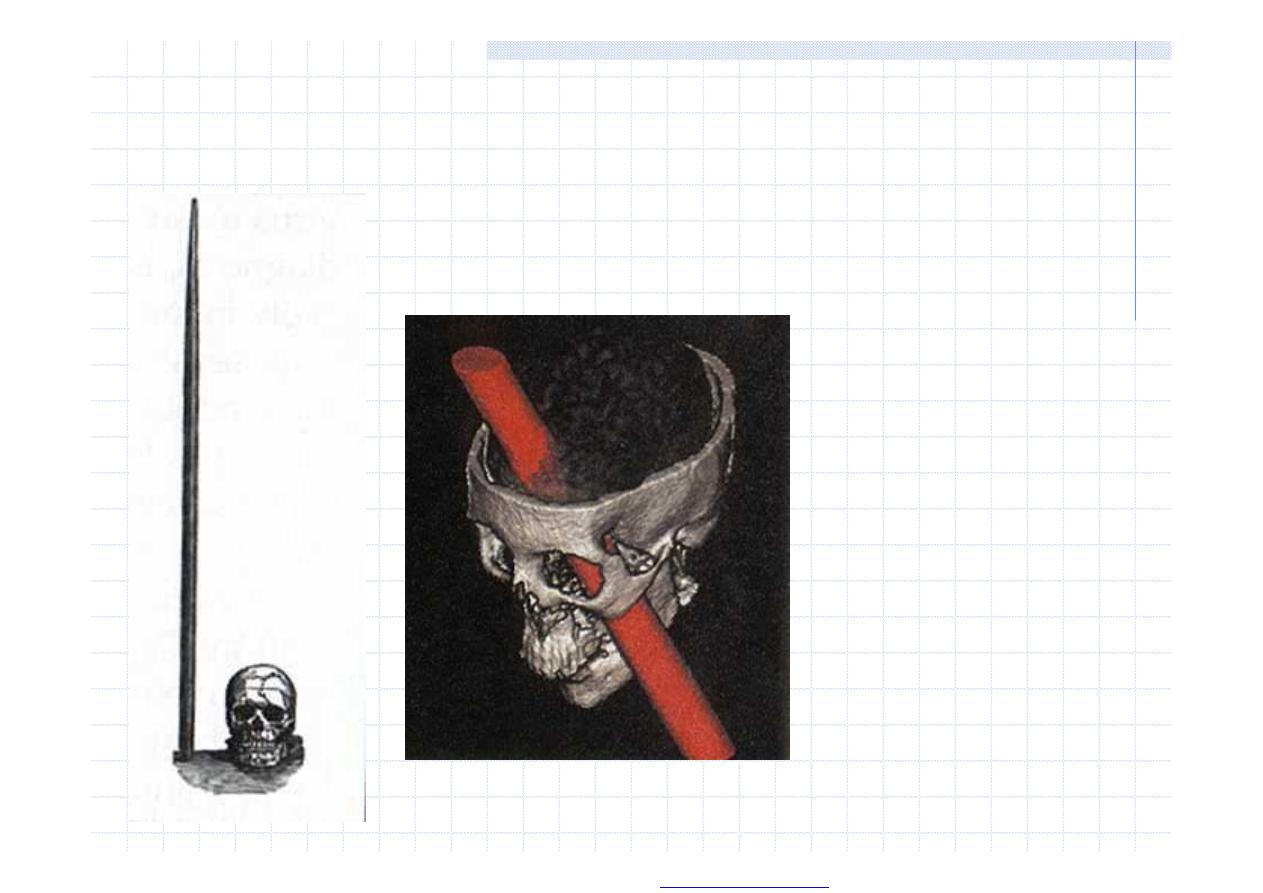
Phineas Gage case, 1868
…his mind was
radically
changed, so
decidedly
that his
friends said
he was “no
longer
Gage”…
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
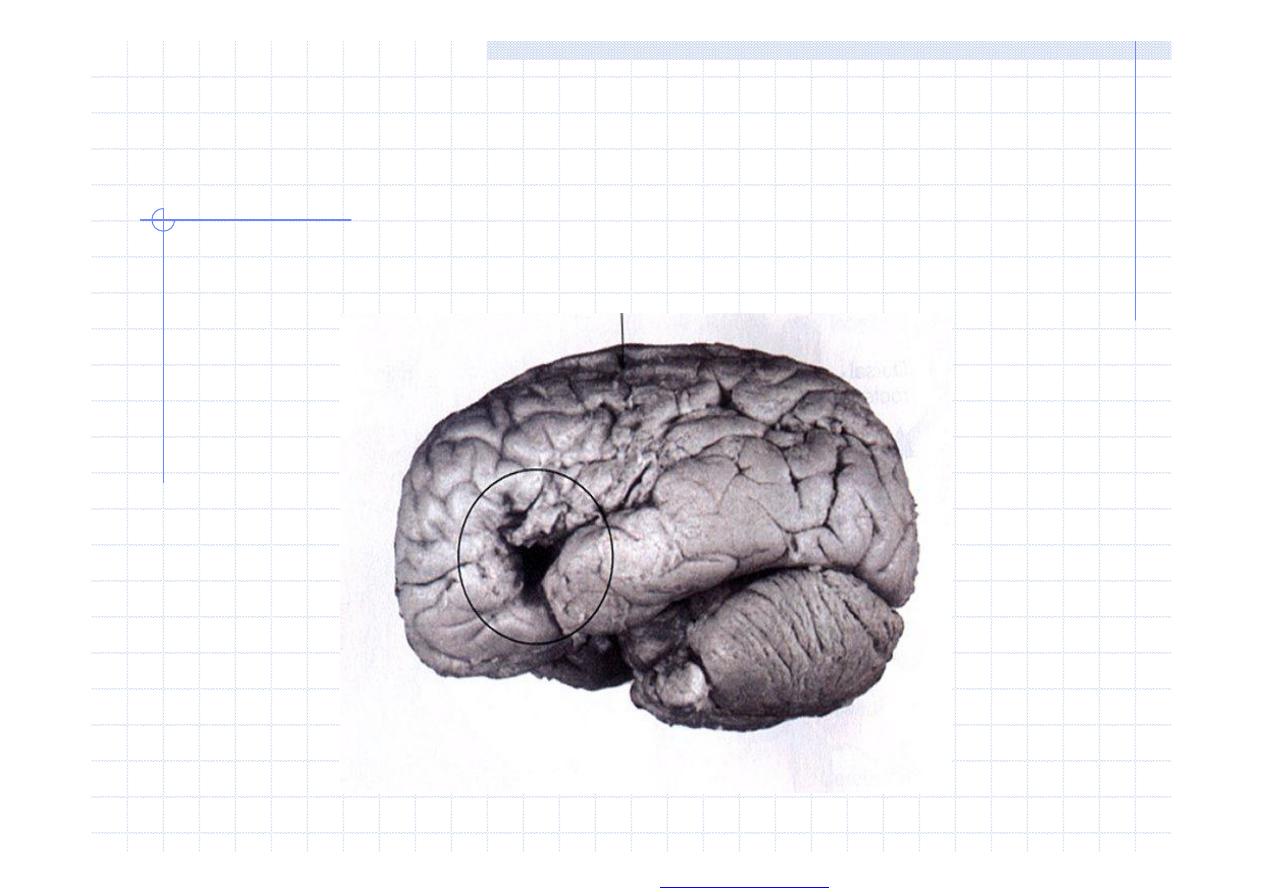
Broca’s aphasia, 1861
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Objective of NE
What is wrong ?
symptoms, semiological diagnosis
Where is the lesion ?
anatomical interpretation, topical diagnosis
What is the cause ?
etiological diagnosis
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Flexibility of NE
NE should be tailored to the clinical
problem
different schemes exists for:
infants
comatose patients
non-cooperating patients
cooperated, conscious adult
abnormal findings are explored in
detail
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Adult, co-operative patient
I.
Mental, intellectual status
II. Cranial nerves
III. Motor function
upper and lower extremity
extrapyramidal, cerebellar signs
IV. Stand and gait
V.Somatosensorial function
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Mental status
Minimental status examination (Folstein, 1976)
Long term memory (name, birthday, place of
living, name of the president, this place)
Short term memory (repetition of three short
words)
Phatic functions
spontaneous speech, repetition of grammatical
particles (no ifs, buts or ands)
calculation (subtracting 7 from 100)
practical skills (knot the tie, dressing, gestures)
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
writing a sentence
copy of a simple picture
detailed neuropsychological and/or
psychiatric examination
Mental status
Minimental status examination (Folstein, 1976)
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (

Cranial nerves
I
olphactory nerve - smell sense
Anosmia = olphactory groove, anterior fossa!
Uncinate fits = olfactory pseudo hallucination - caused by medial temporal pole – tumours!
II
optic nerve = visual field testing
Confrontation of patient´s and investigator´s visual fields
computer perimetry
III, IV, VI oculomotor nerves
lids - symmetry, ptosis ?
globes
misalignment = strabismus
eye movements
primary, secondary and tertiary positions of the eyes are investigated
nystagmus
(direction - horizontal, vertical or rotatory, intensity - I, II, III, amplitude - fine, coarse)
oculomotor palsy (note the direction, which muscle is weak ?)
diplopia (double vision)
pupils
regular, round and symmetric ? = isocoria.
miosis x mydriasis x anisocoria
Photoreaction direct x indirect
Near reaction - convergence and pupilar constriction
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
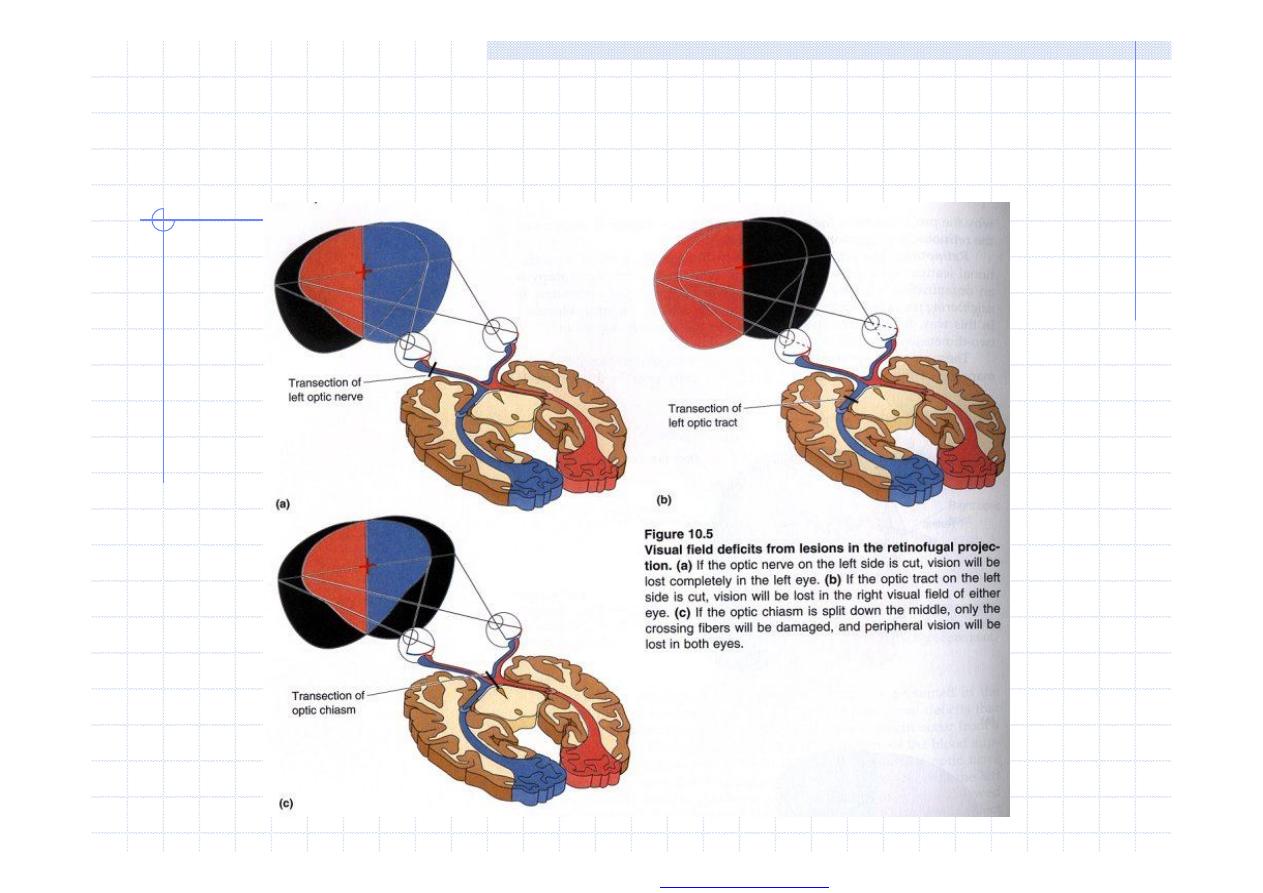
Visual fields
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
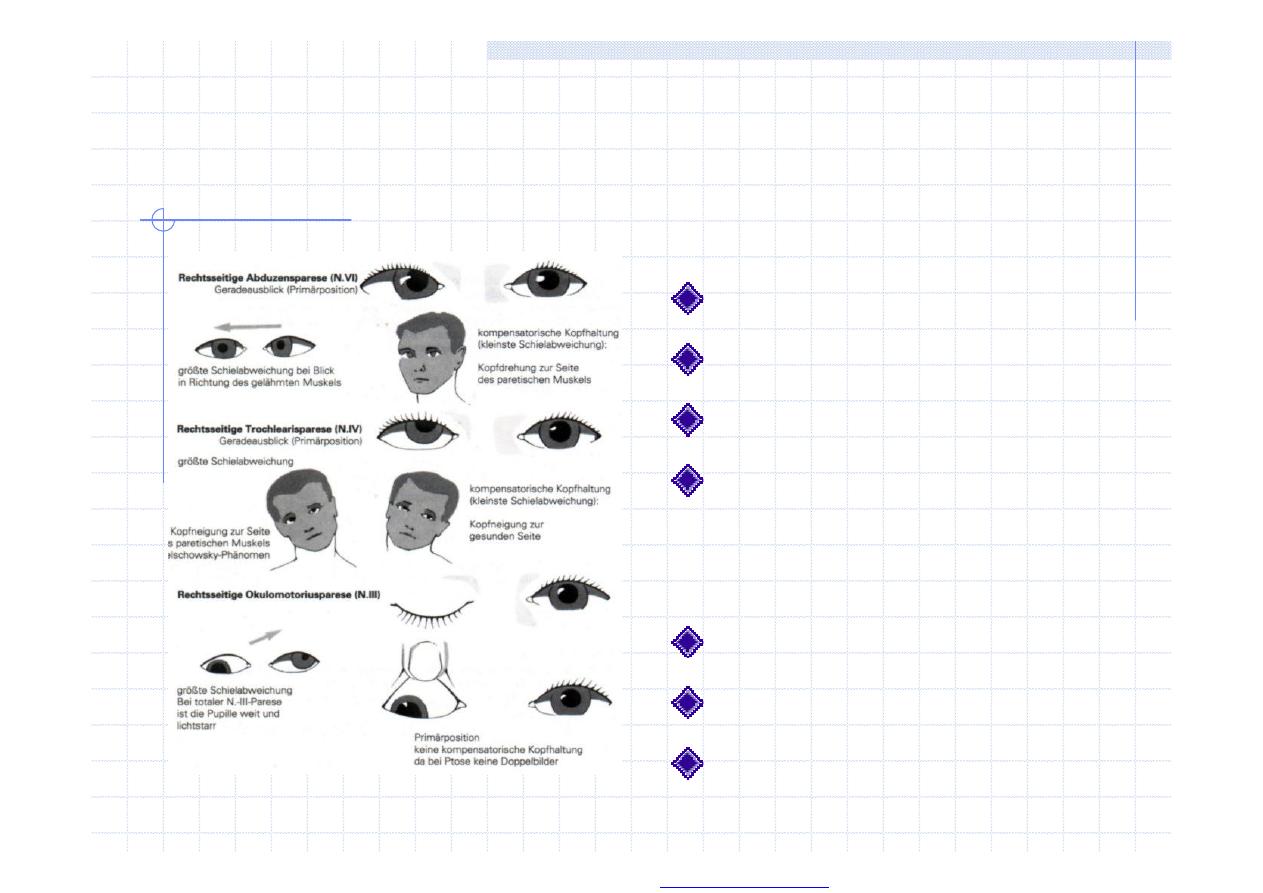
Ocular motor nerves
III, IV, VI
ptosis
position in orbit
active movement in
nine cardinal
positions
nystagmus
diplopia
pupils
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Trigeminal nerve (V-th)
tactile and thermic sensations of the face and
head
Peripheral sensory deficit:
horizontal strips
Central sensory deficit
vertical strips
Motor function
masseter muscle tone
(palpation with clenched teeth)
Reflexes
masseter (trigemino-trigeminal)
corneal (trigemino-facial)
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Facial nerve (VII-th)
mimic muscles, parasympathetic fibres for
parotid gland.
Face symmetry:
forehead, eyelids, nasolabial sulcus, mouth and
platysma muscle on the neck.
Mimic movements
wrinkles, eye closure, mouth corners retraction
Reflexes
Axial = fronto-orbicular, labial and mentolabial
Tetanic sign - Chvostek phenomenon
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Stato-acoustic nerve (VIII-th)
Senses of hearing and balance
Hearing
tuning fork test (Weber, Rinné)
tinnitus
Balance
vertigo, nystagmus description
vestibulospinal phenomena
stand I, II, III, gait I, II, Romberg test, tandem gait
with eyes closed
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (

Glossopharyngeus, Vagus, Accessorius and
Hypoglossus nerves
(IX, X, XI, XII – bulbar nerves)
motor, sensitive and autonomic inervation
mouth, tongue, gastric tract, bronchi
sternocleidomastoideus and trapezius muscles
tongue
atrophy, fasciculations, deviates to the paretic side
tactile sensations and taste on the posterior part of tongue,
pharynx, soft palate.
soft palate
dysphagia and dysarthria
fluid aspiration, uvula retraction away from the paretic
palate
Gag Reflex
missing in bulbar syndrome
enhanced in pseudobulbar syndrome
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Examination of the extremities :
Range of movements
active (paresis - neurology) X passive (skelet, joint or
ligaments - orthopaedics)
strength, muscle tone
paretic pyramidal signs (Mingazzini, Dufour)
irritative pyramidal signs (Babinski, Juster)
myotatic reflexes (spinal cord segment responses)
cerebellar syndrome
taxis, diadochokinesis, muscle atonia, intention tremor
extrapyramidal syndrome
elementary postural reflexes
rigidity, bradykinesia, static tremor
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
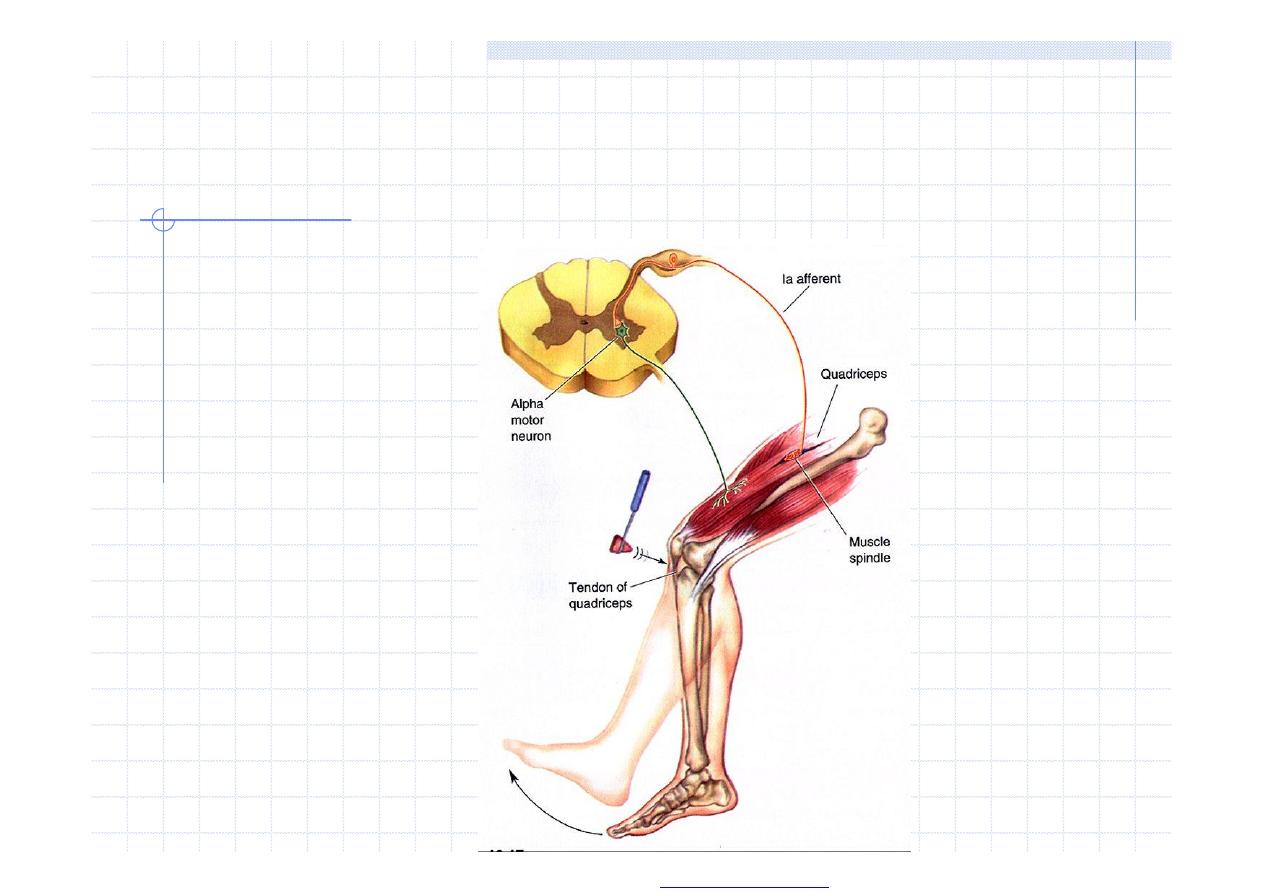
Stretch reflex
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
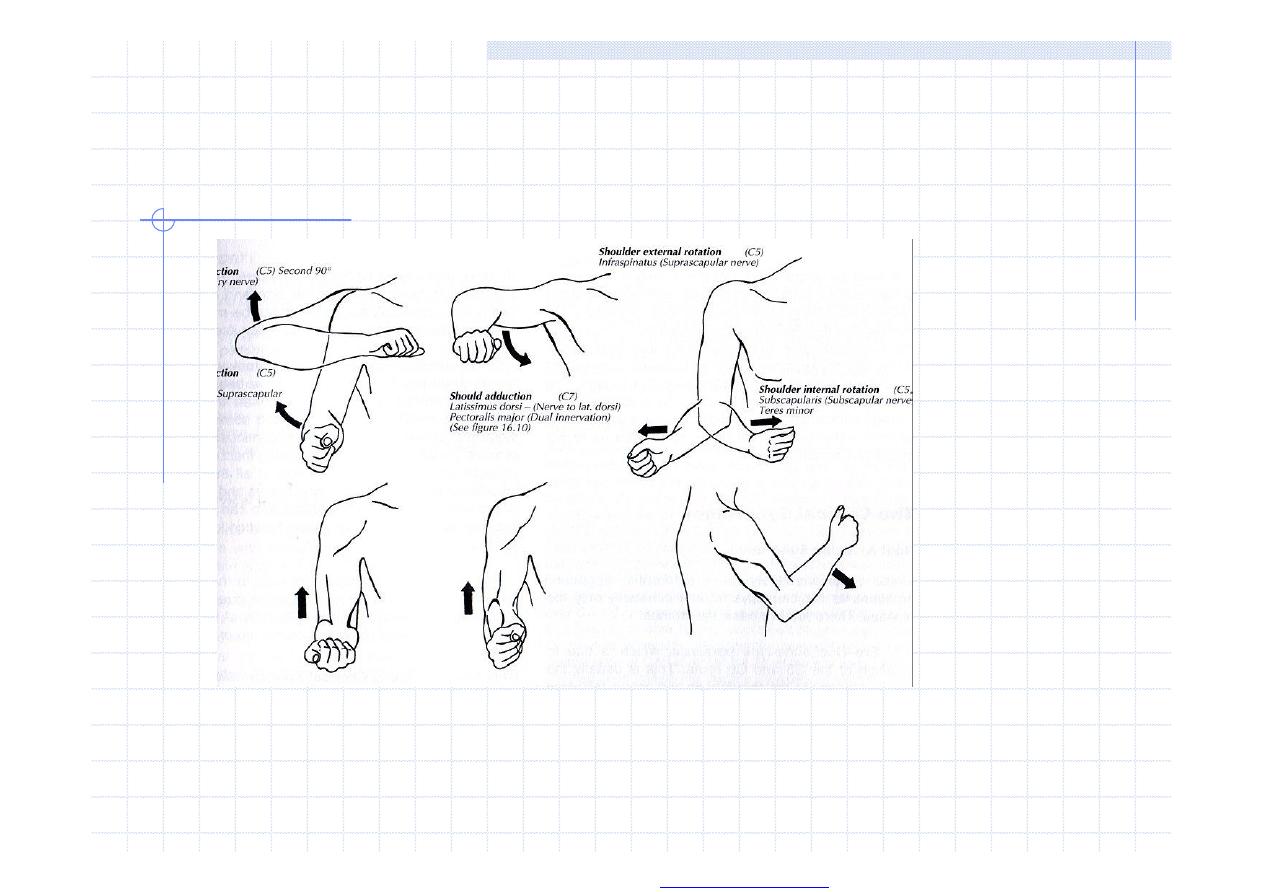
Upper extremity
Paretic signs
Mingazzini, Dufour, Barré, Hanzal, retardation
Spastic signs
Juster, Marie-Foix, Hoffman-Tromner, prefrontal paraxial
signs
Myotatic reflexes
biceps C5, styloradial C6, triceps C7, carpal, mediopalmar,
finger flexors C8
Rigidity
Elementar postural reflexes in biceps muscle
Cerebellar signs
finger-nose, diadochokinesis, turning of the hands, Stewart
Holmes
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Strength - UE
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (

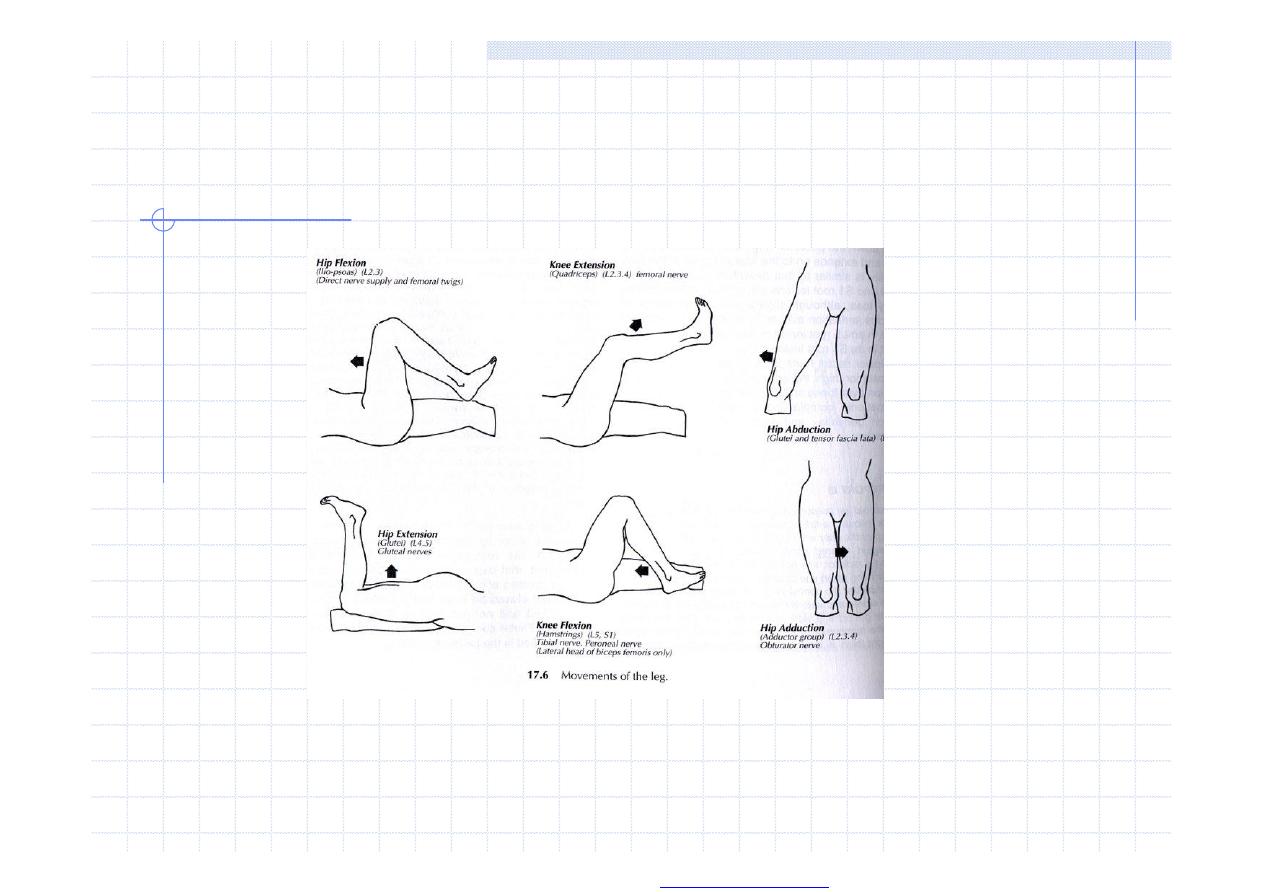
Lower extremity
Paretic signs
Mingazzini, Barré
Spastic signs
extensor plantar response = Babinski, Roche, Oppenheim,
Chadock, Siccard, Strumpell
flexor response = Rossollimo I,II, Žukovskij-Kornilov, Mendel-
Bechtěrev)
Raise leg testing
Lassegue, Kernigue signs
Myotatic reflexes
patellar L2/4, Achilles tendon and medioplantar L5/S2
segments
Cerebellar signs
heel to knee
asynergia - sitting up without help of arms
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Strength - LE
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
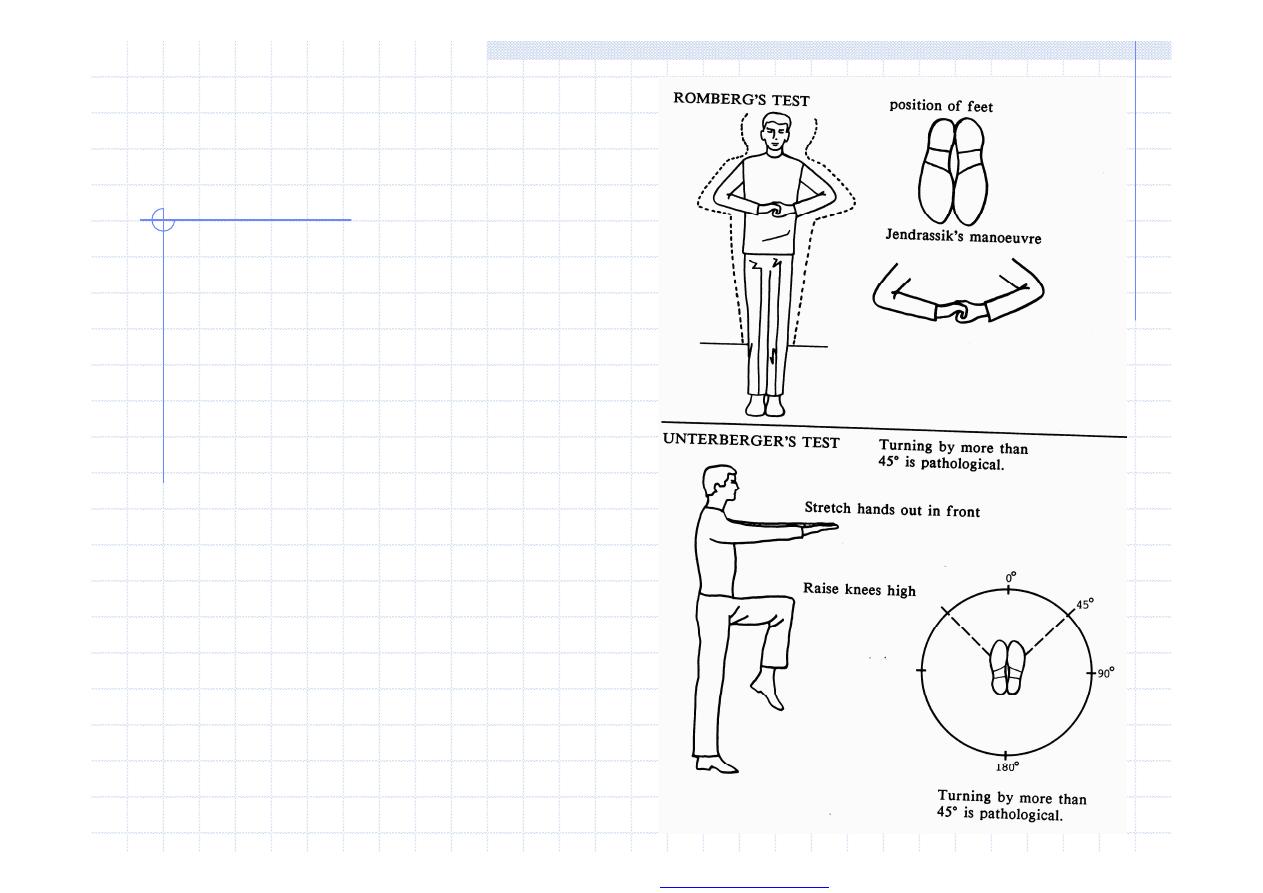
Stand and Gait
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (

Somatosensorial examination
Modalities
touch and proprioception (lemniscal, dorsal column)
pain and thermic sensation (spinothalamic tract)
vibration sense by tuning fork (dorsal column)
Distribution
spinal cord
horizontal “border” - horizontall
brainstem or supratentorial
verticall hemihypoesthesia
radicular
dermatomes
polyneuropathic
glove - stocking
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
Conclusion – neurological status
Symptomatologic diagnosis
list of pathologic signs
Topical, syndromological diagnosis
Specific sets of symptoms
Aetiological diagnosis
Relates the topical diagnosis to a specific disease
pattern.
Knowledge of clinical neurology is indispensable
Based on:
disease history
auxiliary examinations
You created this PDF from an application that is not licensed to print to novaPDF printer (
