Randy H. Shih
AutoCAD 2014
Tutorial - First Level:
2D Fundamentals
®
www.SDCpublications.com
Better Textbooks. Lower Prices.
SDC
P U B L I C A T I O N S
Schroff Development Corporation
Multimedia Disc
Video presentations of
selected tutorials
and exercises
AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
1-1
Chapter 1
AutoCAD Fundamentals
♦ Create and Save AutoCAD drawing files
♦ Use the AutoCAD visual reference
commands
♦ Draw, using the LINE and CIRCLE
commands
♦ Use the ERASE command
♦ Define Positions using the Basic Entry
methods
♦ Use the AutoCAD Pan Realtime option

1-2 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
AutoCAD Certified User Examination Objectives Coverage
This table shows the pages on which the objectives of the Certified User Examination are covered in
Chapter 1.
Section 1: Controlling the Display in Drawings
Precision ...........................................................................1-6
Zoom Extent.....................................................................1-7
Drawing LIMITS ............................................................1-6
Status Bar .........................................................................1-10
GRID Display ..................................................................1-10, 1-11
PAN Realtime ..................................................................1-20
Section 2: Creating Basic Drawings
Format ..............................................................................1-5
Units Setup ......................................................................1-5
LINE Command ...............................................................1-8
Coordinates ......................................................................1-8
Interactive Input Method..................................................1-10
SNAP Option ...................................................................1-12
World Space .....................................................................1-15
User Coordinate System ..................................................1-15
World Coordinate System ................................................1-15
UCS Icon Display ............................................................1-16
TTR, Circle ......................................................................1-23
Relative Coordinate .........................................................1-17
Coordinate Systems .........................................................1-17
Cartesian coordinate system ............................................1-17
Absolute Coordinates .......................................................1-17, 1-18
Positions, Defining ...........................................................1-18
LINE, Close Option .........................................................1-19
CIRCLE Command ..........................................................1-23
TTT, Circle ......................................................................1-23
ARC Command ………………………………………... 1-33
Section 3: Manipulating Objects
ERASE Command ..........................................................1-13
Selection Window ............................................................1-14
Cer
tified U
s
er Re
fere
nce
Guide
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-3
Introduction
Learning to use a CAD system is similar to learning a new language. It is necessary to
begin with the basic alphabet and learn how to use it correctly and effectively through
practice. This will require learning some new concepts and skills as well as learning a
different vocabulary. Today, the majority of the Mechanical CAD systems are capable of
creating three-dimensional solid models. Nonetheless, all CAD systems create designs
using basic geometric entities and many of the constructions used in technical designs are
based upon two-dimensional planar geometry. The method and number of operations that
are required to accomplish the basic planar constructions are different from one system to
another.
In order to become effective and efficient in using a CAD system, we must learn to create
geometric entities quickly and accurately. In learning to use a CAD system, lines and
circles are the first two, and perhaps the most important two, geometric entities that one
should master the skills of creating and modifying. Straight lines and circles are used in
almost all technical designs. In examining the different types of planar geometric entities,
the importance of lines and circles becomes obvious. Triangles and polygons are planar
figures bounded by straight lines. Ellipses and splines can be constructed by connecting
arcs with different radii. As one gains some experience in creating lines and circles,
similar procedures can be applied to create other geometric entities. In this chapter, the
different ways of creating lines and circles in AutoCAD
®
2014 are examined.
Starting Up AutoCAD
®
2014
1. Select the AutoCAD 2014 option on the Program menu or select the AutoCAD
2014 icon on the Desktop.
Once the program is loaded into memory, the AutoCAD
®
2014 drawing screen
will appear on the screen.
1-4 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
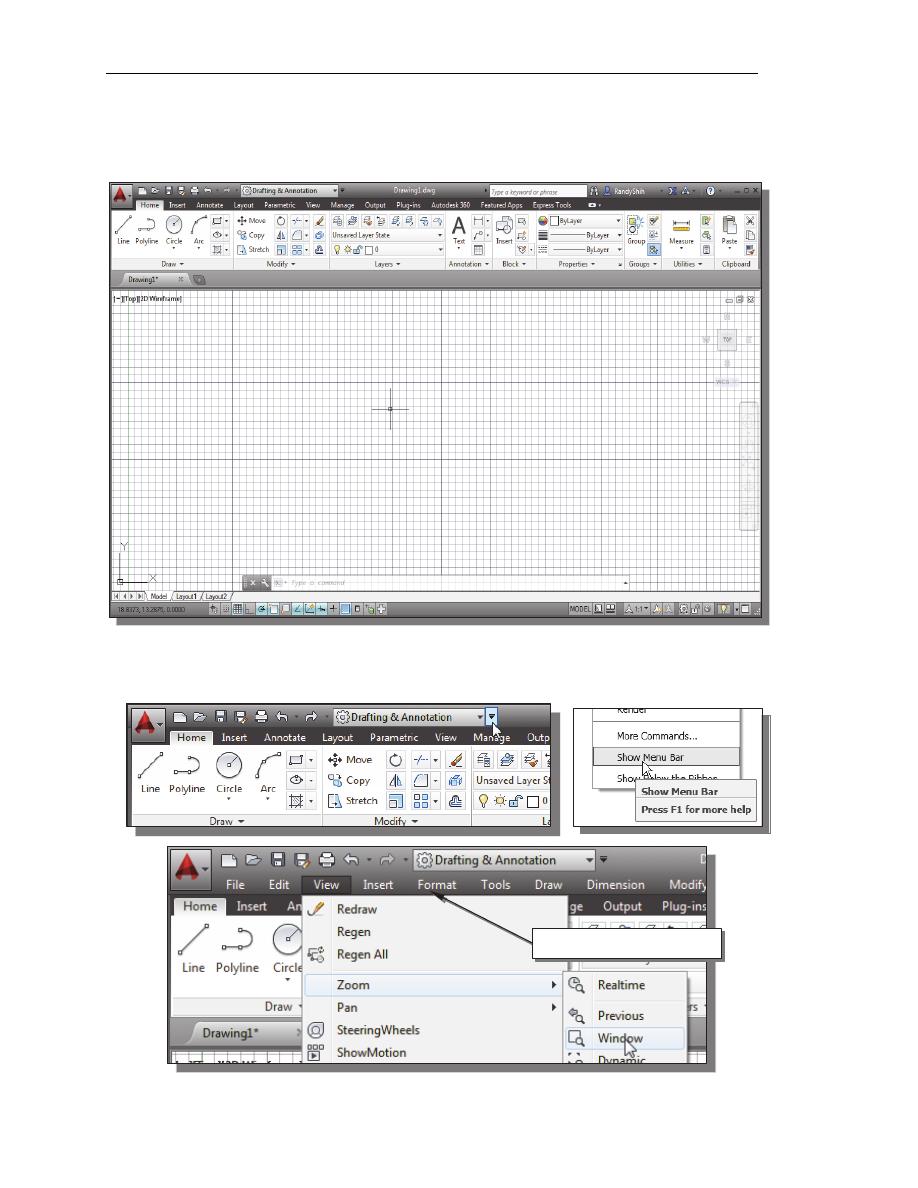
Note that AutoCAD automatically assigns generic names, Drawing X, as new
drawings are created. In our example, AutoCAD opened the graphics window using
the default system units and assigned the drawing name Drawing1.
2. If necessary, click on the down-arrow in the Quick Access bar and select Show
Menu to display the AutoCAD Menu Bar. The Menu Bar provides access to all
AutoCAD commands.
AutoCAD Menu Bar
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-5
Drawing Units Setup
Every object we construct in a CAD system is measured in units. We should
determine the system of units within the CAD system before creating the first
geometric entities.
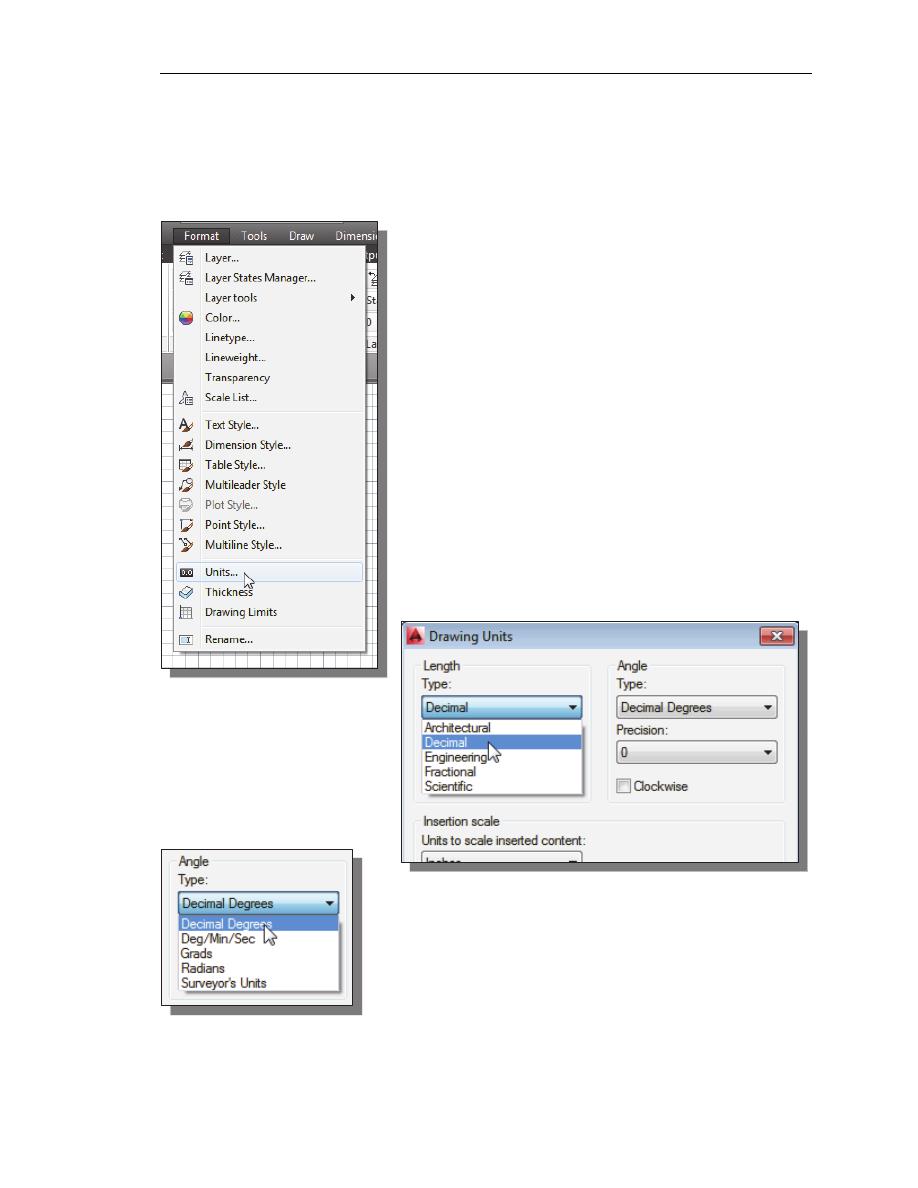
1. In the Menu Bar select:
[Format]
[Units]
• The AutoCAD Menu Bar contains multiple pull-down
menus, where all of the AutoCAD commands can be
accessed. Note that many of the menu items listed in
the pull-down menus can also be accessed through the
Quick Access toolbar and/or Ribbon panels.
2. Click on the Length
Type option to display
the different types of
length units available.
Confirm the Length
Type is set to
Decimal.
3. On your own, examine the other settings that are
available.
4. In the Drawing Units dialog box, set the Length Type to Decimal. This will set
the measurement to the default English units, inches.
1-6 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
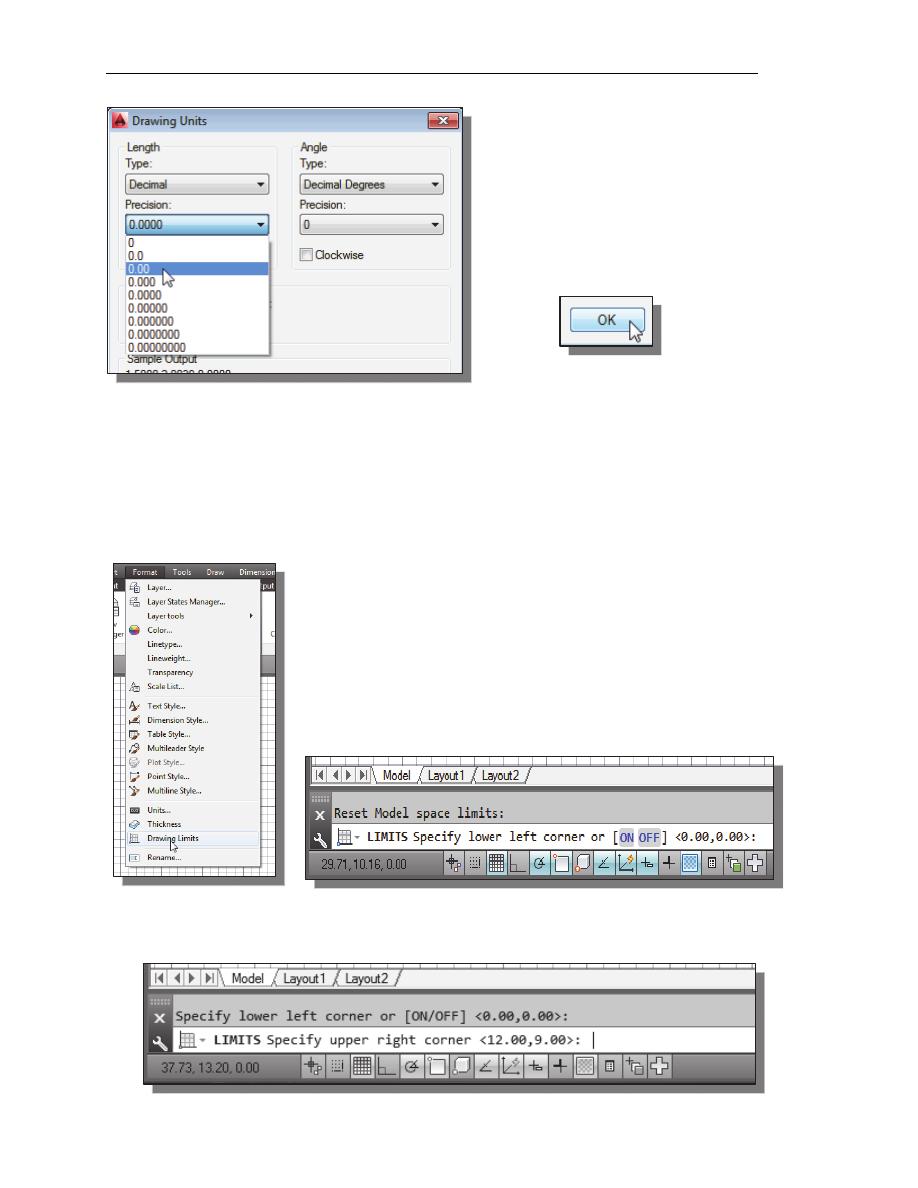
5. Set the Precision to two digits
after the decimal point as shown in
the above figure.
6. Pick OK to exit the Drawing Units
dialog box.
Drawing Area Setup
Next, we will set up the Drawing Limits by entering a command in the
command prompt area. Setting the Drawing Limits controls the extents of the
display of the grid. It also serves as a visual reference that marks the working
area. It can also be used to prevent construction outside the grid limits and as a
plot option that defines an area to be plotted/printed. Note that this setting does
not limit the region for geometry construction.
1. In the Menu Bar select:
[Format]
[Drawing Limits]
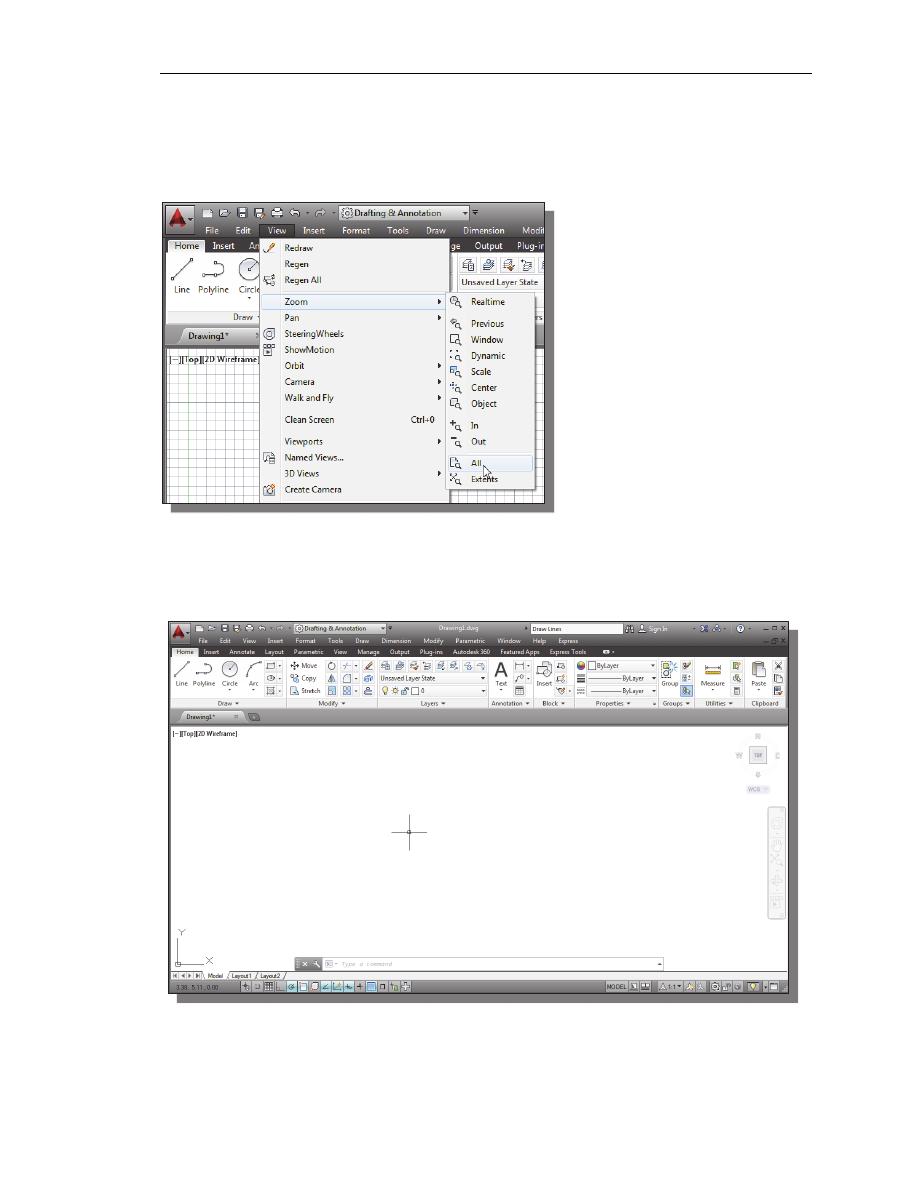
2. In the command prompt area, the message “Reset Model
Space Limits: Specify lower left corner or [On/Off]
<0.00,0.00>:” is displayed. Press the
ENTER
key once to
accept the default coordinates <0.00,0.00>.
3. In the command prompt area, the message “Specify upper right corner
<12.00,9.00>:” is displayed. Press the
ENTER
key again to accept the default
coordinates <12.00,9.00>.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-7
4. On your own, move the graphics cursor near the upper-right comer inside the
drawing area and note that the drawing area is unchanged. (The Drawing Limits
command is used to set the drawing area, but the display will not be adjusted until
a display command is used.)
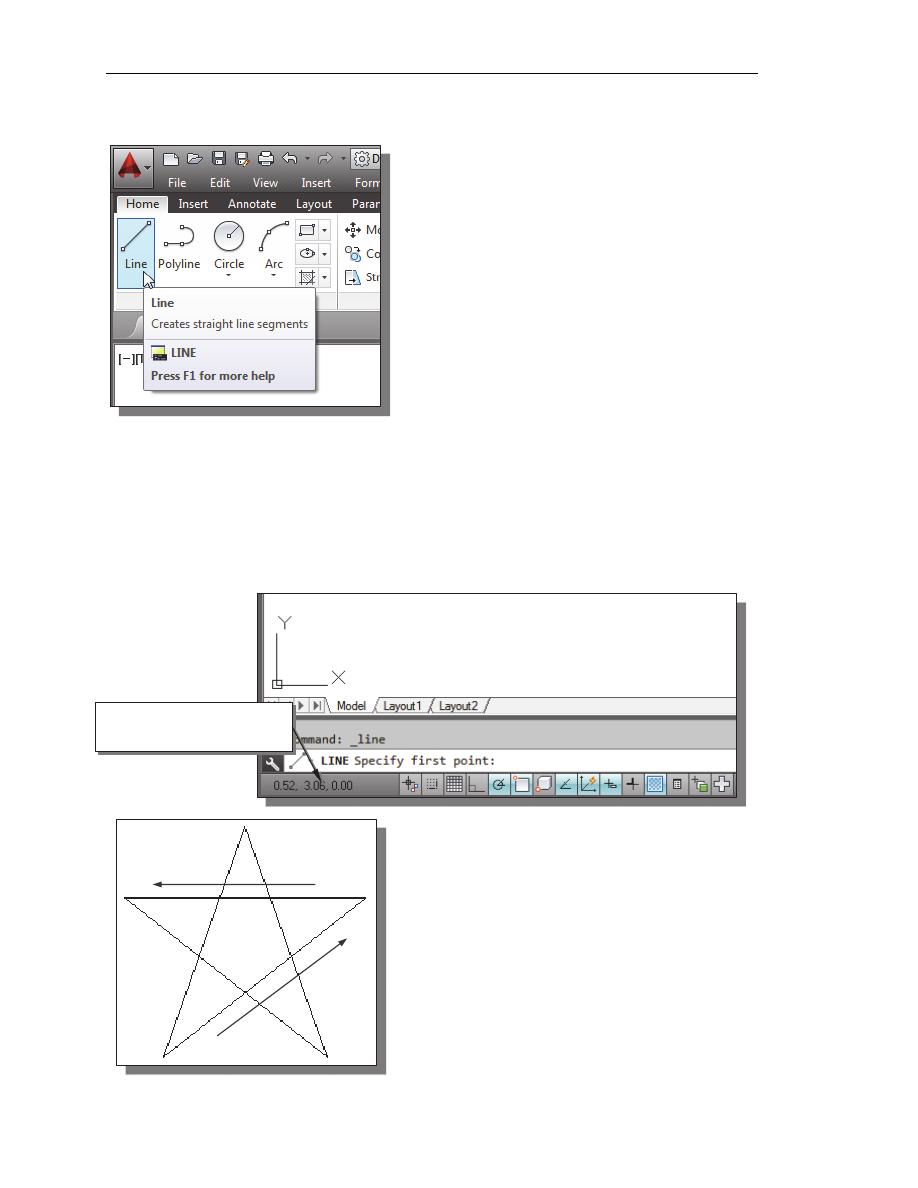
5. Inside the Menu Bar area
select:
[View]
[Zoom] [All]
The Zoom All command will
adjust the display so that all
objects in the drawing are
displayed to be as large as
possible. If no objects are
constructed, the Drawing
Limits are used to adjust the
current viewport.
6. Move the graphics cursor near the upper-right comer inside the drawing area and
note that the display area is updated.
7. Hit the function key [F7] once to turn off the display of the Grid lines.
• Note that function key [F7] is a quick key, which can be used to quickly toggle
on/off the grid display. Also, note the command prompt area can be positioned to
dock below the drawing area or float inside the drawing area as shown.
1-8 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
Drawing Lines with the LINE Command
1. Move the graphics cursor to the first icon in
the Draw panel. This icon is the Line icon.
Note that a brief description of the Line
command appears next to the cursor.
2. Select the icon by clicking once with the left-
mouse-button, which will activate the Line
command.
3. In the command prompt area, near the bottom of the AutoCAD drawing screen,
the message “_line Specify first point:” is displayed. AutoCAD expects us to
identify the starting location of a straight line. Move the graphics cursor inside the
graphics window and watch the display of the coordinates of the graphics cursor
at the bottom of the AutoCAD drawing screen. The three numbers represent the
location of the cursor in the X, Y, and Z directions. We can treat the graphics
window as if it was a piece of paper and we are using the graphics cursor as if it
were a pencil with which to draw.
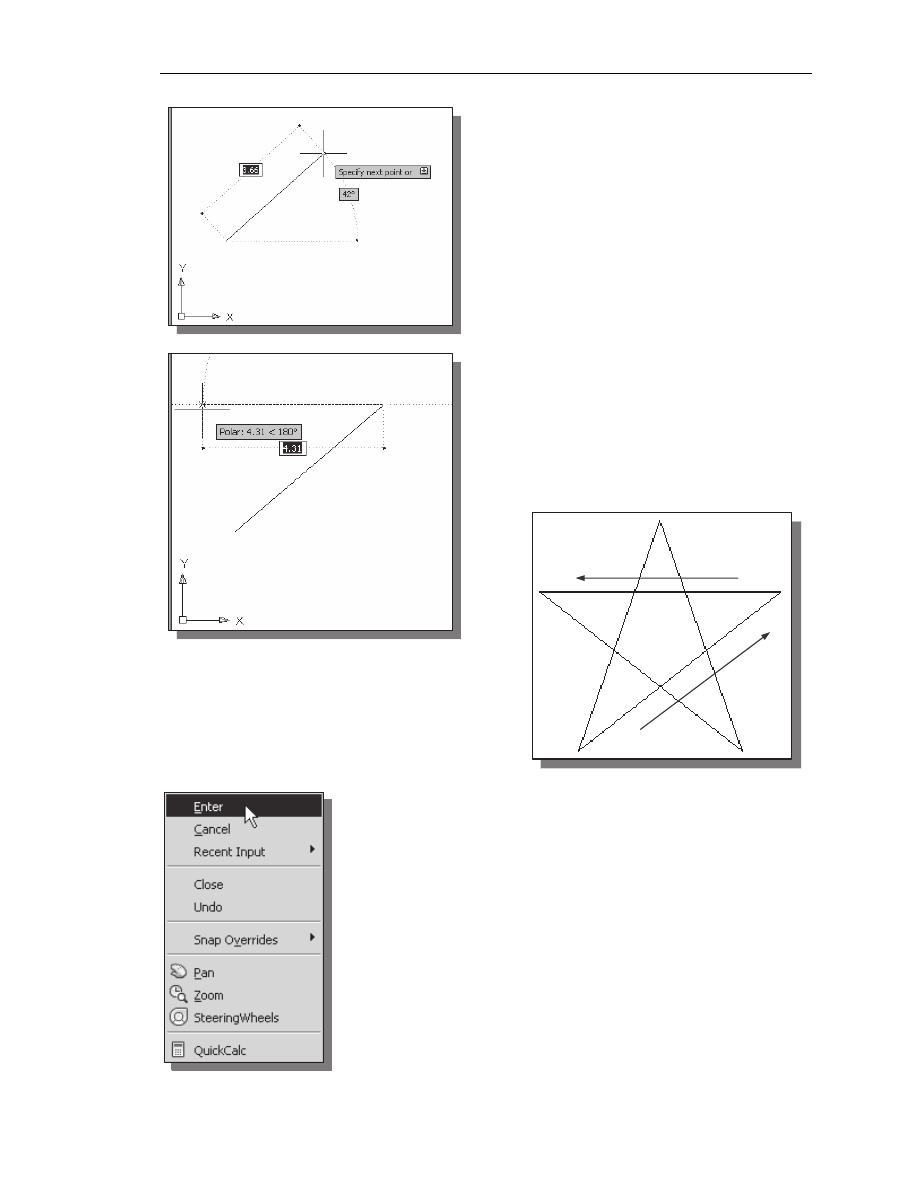
We will create a freehand sketch of a five-
point star using the Line command. Do not be
overly concerned with the actual size or
accuracy of your freehand sketch. This
exercise is to give you a feel for the
AutoCAD
®
2014 user interface.
Coordinates of the graphics
cursor
5
3
2
1
4
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-9
4. We will start at a location about one-third
from the bottom of the graphics window.
Left-click once to position the starting
point of our first line. This will be point 1
of our sketch. Next move the cursor
upward and toward the right side of point
1. Notice the rubber-band line that follows
the graphics cursor in the graphics
window. Left-click again (point 2) and we
have created the first line of our sketch.
5. Move the cursor to the left of point 2 and
create a horizontal line about the same
length as the first line on the screen.
6. Repeat the above steps and complete the
freehand sketch by adding three more
lines (from point 3 to point 4, point 4 to
point 5, and then connect to point 5 back
to point 1).
7. Notice that the Line command remains activated even after
we connected the last segment of the line to the starting
point (point 1) of our sketch. Inside the graphics window,
click once with the right-mouse-button and a popup menu
appears on the screen.
8. Select Enter with the left-mouse-button to end the Line
command. (This is equivalent to hitting the [
ENTER
] key on
the keyboard.)
9. Move the cursor near point 2 and point 3, and estimate the
length of the horizontal line by watching the displayed
coordinates for each point.
5
3
2
1
4
1-10 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
Visual Reference
The method we just used to create the freehand sketch is known as the interactive
method, where we use the cursor to specify locations on the screen. This method is
perhaps the fastest way to specify locations on the screen. However, it is rather difficult
to try to create a line of a specific length by watching the displayed coordinates. It would
be helpful to know what one inch or one meter looks like on the screen while we are
creating entities. AutoCAD
®
2014 provides us with many tools to aid the construction of
our designs. For example, the GRID and SNAP MODE options can be used to get a
visual reference as to the size of objects and learn to restrict the movement of the cursor
to a set increment on the screen.
The GRID and SNAP MODE options can be turned ON or OFF through the Status Bar.
The Status Bar area is located at the bottom left of the AutoCAD drawing screen, next to
the cursor coordinates.
The second button in the Status Bar is the SNAP MODE option and the third button is the
GRID DISPLAY option. Note that the buttons in the Status Bar area serve two functions:
(1) the status of the specific option, and (2) as toggle switches that can be used to turn
these special options ON and OFF. When the corresponding button is highlighted, the
specific option is turned ON. Using the buttons is a quick and easy way to make changes
to these drawing aid options. The buttons in the Status Bar can also be switched on and
off in the middle of another command.
Option Buttons
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-11
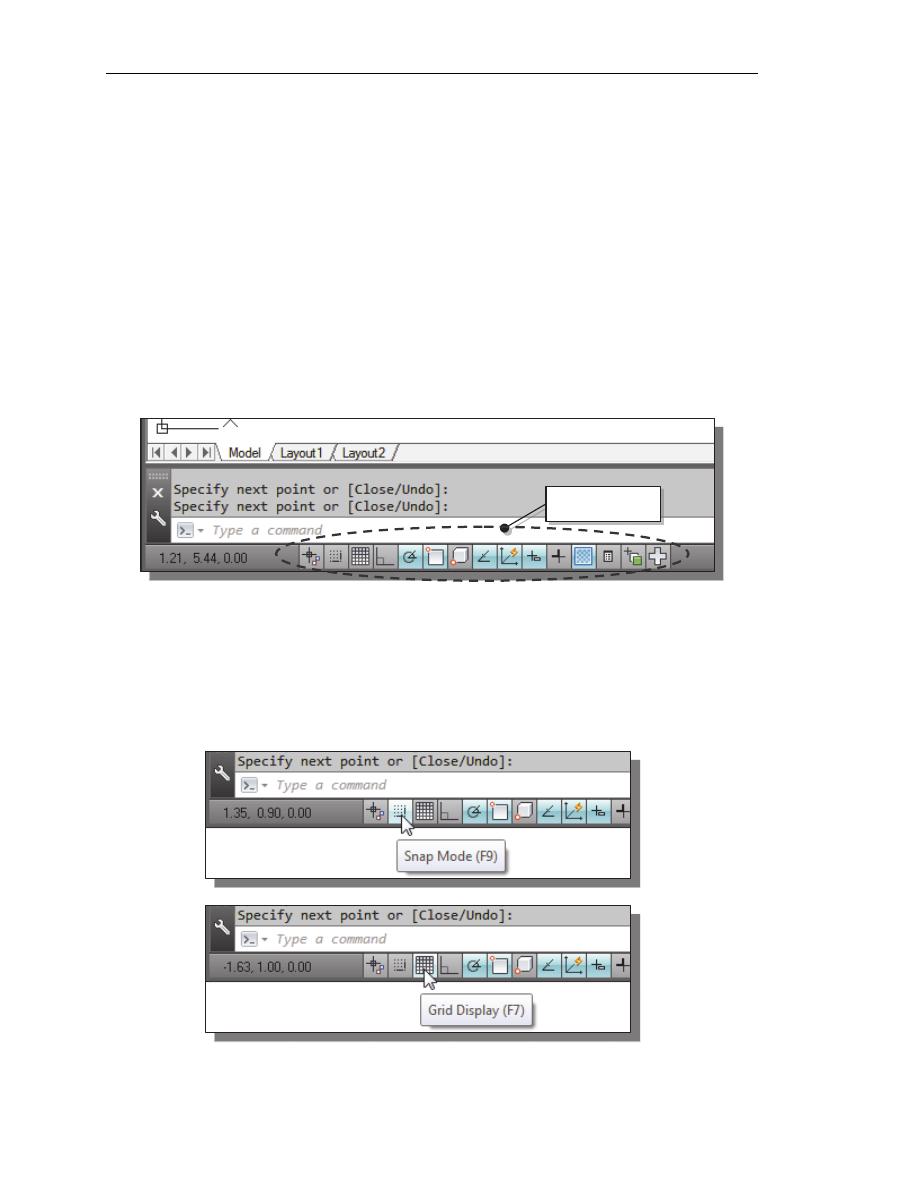
GRID ON
1. Left-click the GRID button in the Status Bar to turn ON the GRID DISPLAY
option. (Notice in the command prompt area, the message “<Grid on>” is also
displayed.)
2. Move the cursor inside the graphics window, and estimate the distance in between
the grid lines by watching the coordinates displayed at the bottom of the screen.
The GRID option creates a pattern of lines that extends over an area on the screen.
Using the grid is similar to placing a sheet of grid paper under a drawing. The grid
helps you align objects and visualize the distance between them. The grid is not
displayed in the plotted drawing. The default grid spacing, which means the distance
in between two lines on the screen, is 0.5 inches. We can see that the sketched
horizontal line in the sketch is about 4.5 inches long.
1-12 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
SNAP MODE ON
1. Left-click the SNAP MODE button in the Status Bar to turn ON the SNAP option.
2. Move the cursor inside the graphics window, and move the cursor diagonally on
the screen. Observe the movement of the cursor and watch the coordinates
display at the bottom of the screen.
The SNAP option controls an invisible rectangular grid that restricts cursor
movement to specified intervals. When SNAP mode is on, the screen cursor and
all input coordinates are snapped to the nearest point on the grid. The default snap
interval is 0.5 inches, and aligned to the grid points on the screen.
3. Click on the Line icon in the Draw toolbar. In the
command prompt area, the message “_line Specify
first point:” is displayed.
4. On your own, create another sketch of the five-point star with the GRID and
SNAP options switched ON.
5. Use the right-mouse-button and select Enter in the popup
menu to end the Line command if you have not done so.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-13
Using the ERASE Command
One of the advantages of using a CAD system is the ability to remove entities without
leaving any marks. We will erase two of the lines using the Erase command.
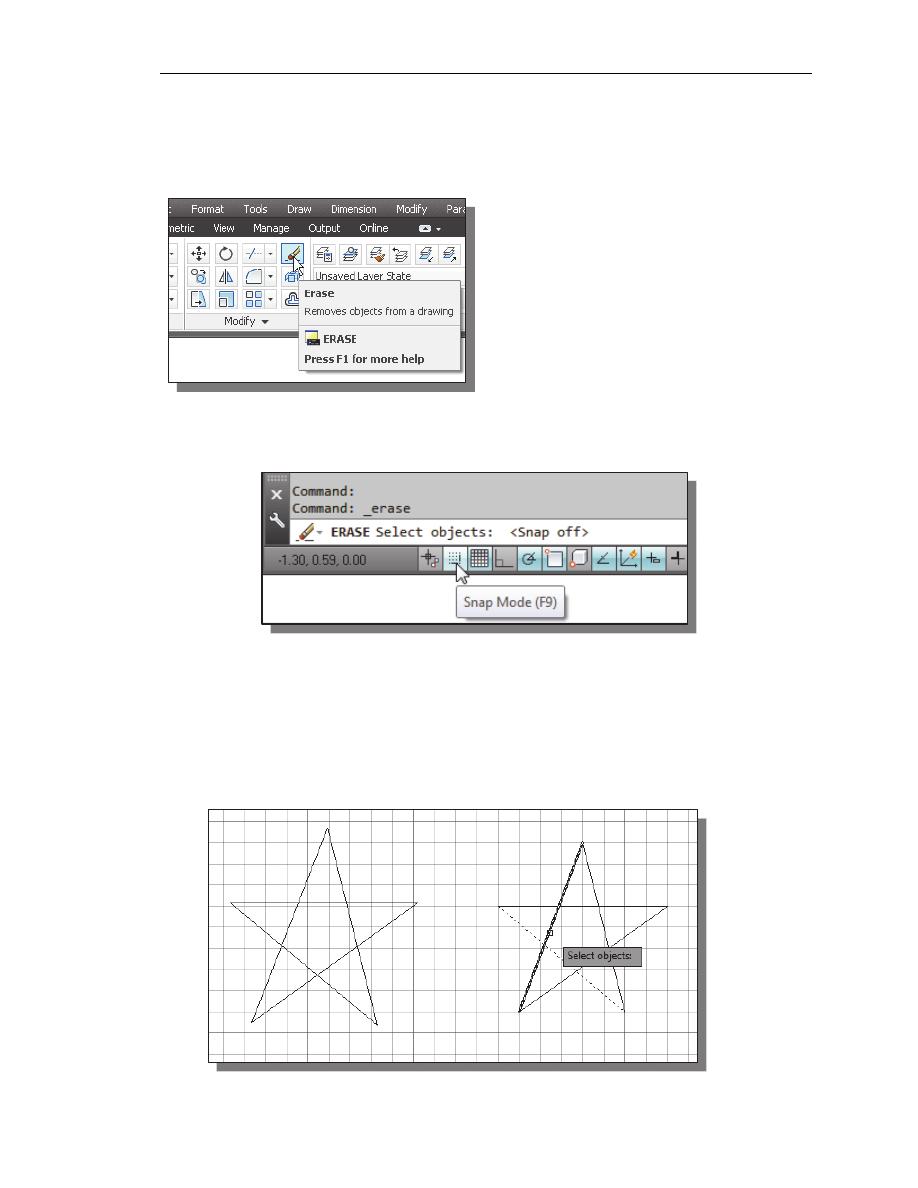
1. Pick Erase in the Modify toolbar. (The
icon is a picture of an eraser at the end
of a pencil.) The message “Select
objects” is displayed in the command
prompt area and AutoCAD awaits us to
select the objects to erase.
2. Left-click the SNAP MODE button on the Status Bar to turn OFF the SNAP
MODE option so that we can more easily move the cursor on top of objects. We
can toggle the Status Bar options ON or OFF in the middle of another command.
3. Select any two lines on the screen; the selected lines are displayed as dashed lines
as shown in the figure below.
To deselect an object from the selection set, hold down the [SHIFT] key and select
the object again.
4. Right-mouse-click once to accept the selections. The selected two lines are
erased.
1-14 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
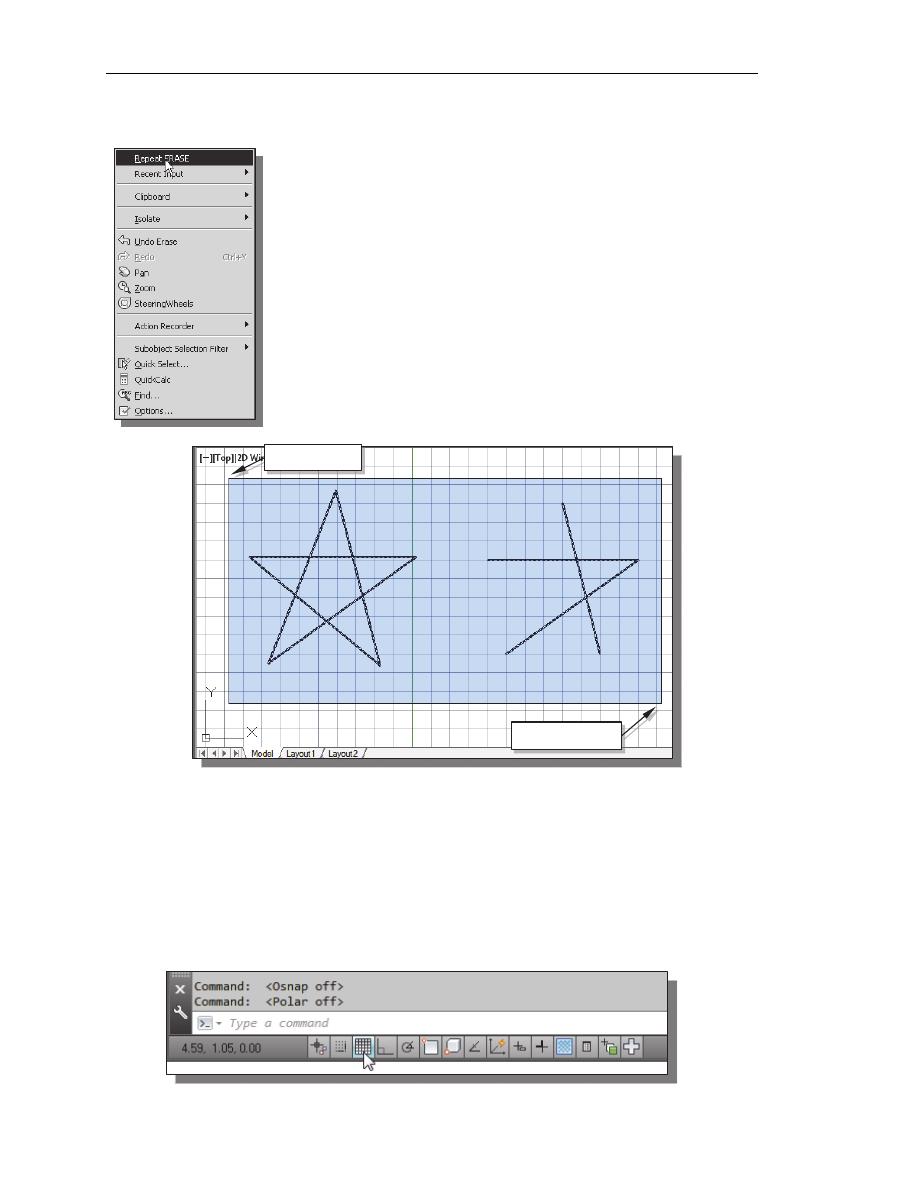
Repeat the Last Command
1.
Inside the graphics window, click once with the right-mouse-
button to bring up the popup option
menu.
2.
Pick Repeat Erase, with the left-mouse-button, in the popup
menu to repeat the last command. Notice the other options
available in the popup menu.
AutoCAD
®
2014 offers many options to accomplish the same
task. Throughout this text, we will emphasize the use of the
AutoCAD Heads-up Design
TM
interface, which means we
focus on the screen, not on the keyboard.
3.
Move the cursor to a location that is above and toward the left
side of the entities on the screen. Left-mouse-click once to
start a corner of a rubber-band window.
4.
Move the cursor toward the right and below the entities, and then left-mouse-click
to enclose all the entities inside the selection window. Notice all entities that are
inside the window are selected.
5.
Inside the graphics window, right-mouse-click once to proceed with erasing
the selected entities.
On your own, create a free-hand sketch of your choice using the Line command.
Experiment with using the different commands we have discussed so far. Reset the
status buttons so that only the
GRID DISPLAY option is turned ON as shown.
Second corner
First corner
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-15
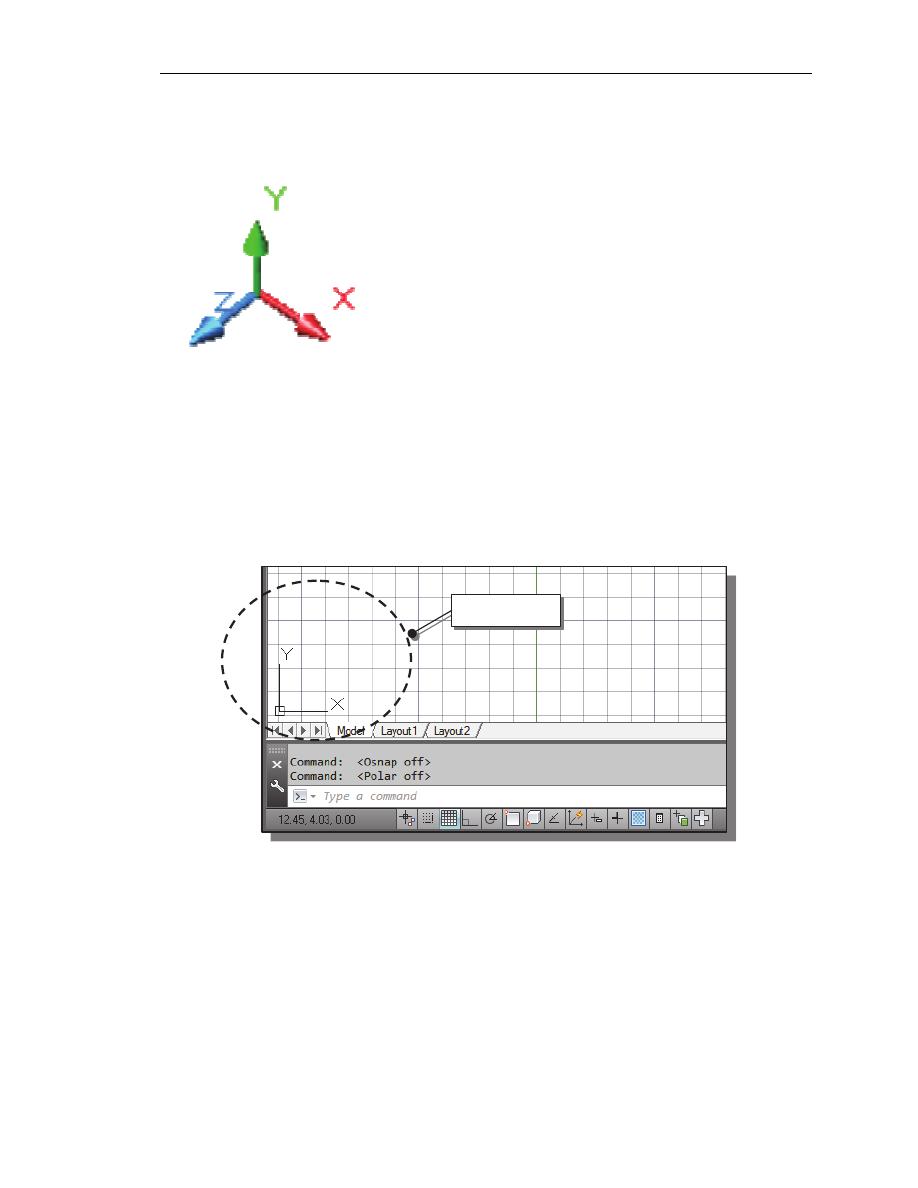
The CAD Database and the User Coordinate System
Designs and drawings created in a CAD system are
usually defined and stored using sets of points in
what is called world space. In most CAD systems,
the world space is defined using a three-dimensional
Cartesian coordinate system. Three mutually
perpendicular axes usually referred to as the X-, Y-,
and Z-axes, define this system. The intersection of
the three coordinate axes forms a point called the
origin. Any point in world space can then be defined
as the distance from the origin in the X-, Y- and Z-
directions. In most CAD systems, the directions of
the arrows shown on the axes identify the positive
sides of the coordinates.
A CAD file, which is the electronic version of the design, contains data that describes the
entities created in the CAD system. Information such as the coordinate values in world
space for all endpoints, center points, etc., along with the descriptions of the types of
entities are all stored in the file. Knowing that AutoCAD stores designs by keeping
coordinate data helps us understand the inputs required to create entities.
The icon near the bottom left corner of the default AutoCAD graphics window shows the
positive X-direction and positive Y-direction of the coordinate system that is active. In
AutoCAD, the coordinate system that is used to create entities is called the user
coordinate system (UCS). By default, the user coordinate system is aligned to the
world coordinate system (WCS). The world coordinate system is a coordinate system
used by AutoCAD as the basis for defining all objects and other coordinate systems
defined by the users. We can think of the origin of the world coordinate system as a
fixed point being used as a reference for all measurements. The default orientation of the
Z-axis can be considered as positive values in front of the monitor and negative values
inside the monitor.
3D
UCS icon
1-16 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
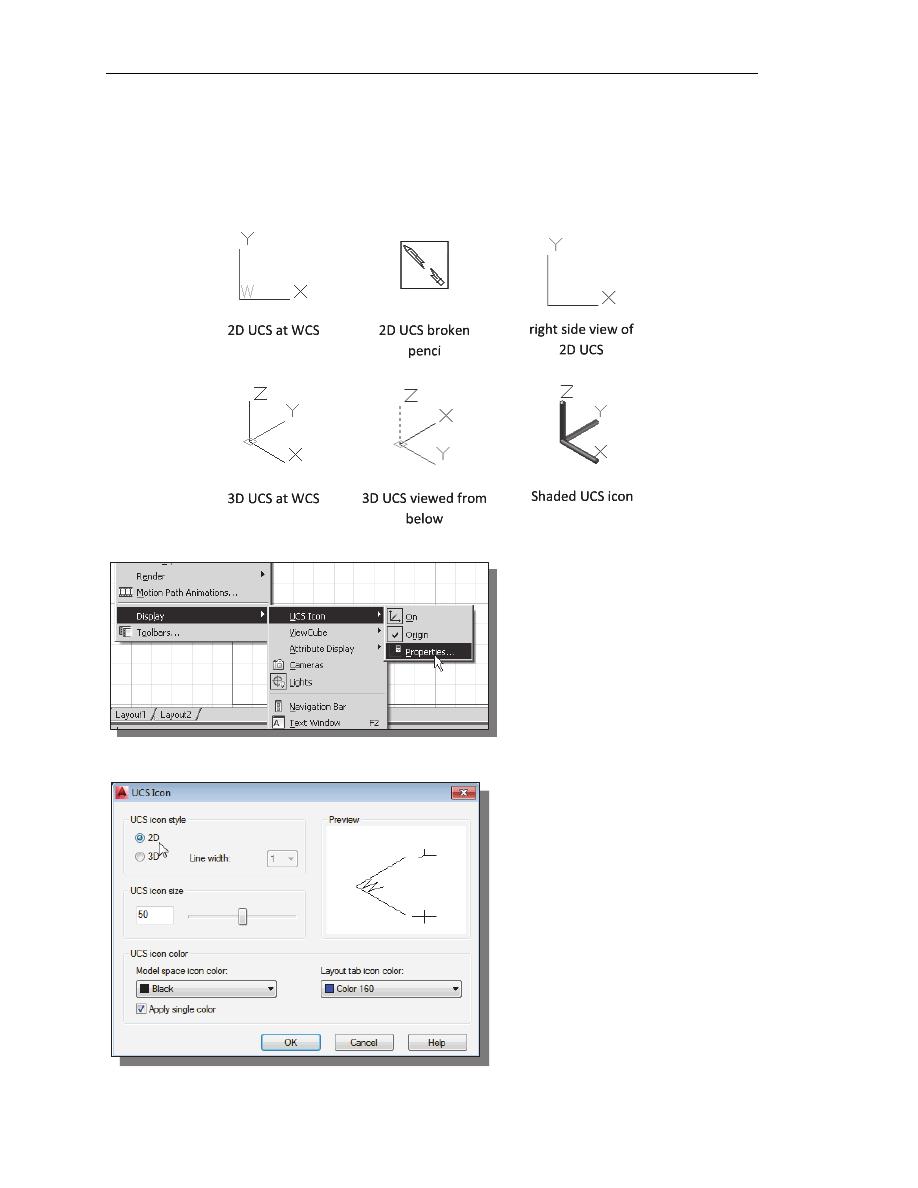
Changing to the 2D UCS Icon Display
In AutoCAD
®
2014, the UCS icon is displayed in various ways to help us
visualize the orientation of the drawing plane.
1. Click on the View pull-down
menu and select
[Display]
[UCS Icon]
[Properties]
2. In the UCS icon style section, switch to the 2D option as shown.
3. Click OK to accept the settings.
Note the W symbol in the UCS
icon indicates that the UCS is
aligned to the world coordinate
system.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-17
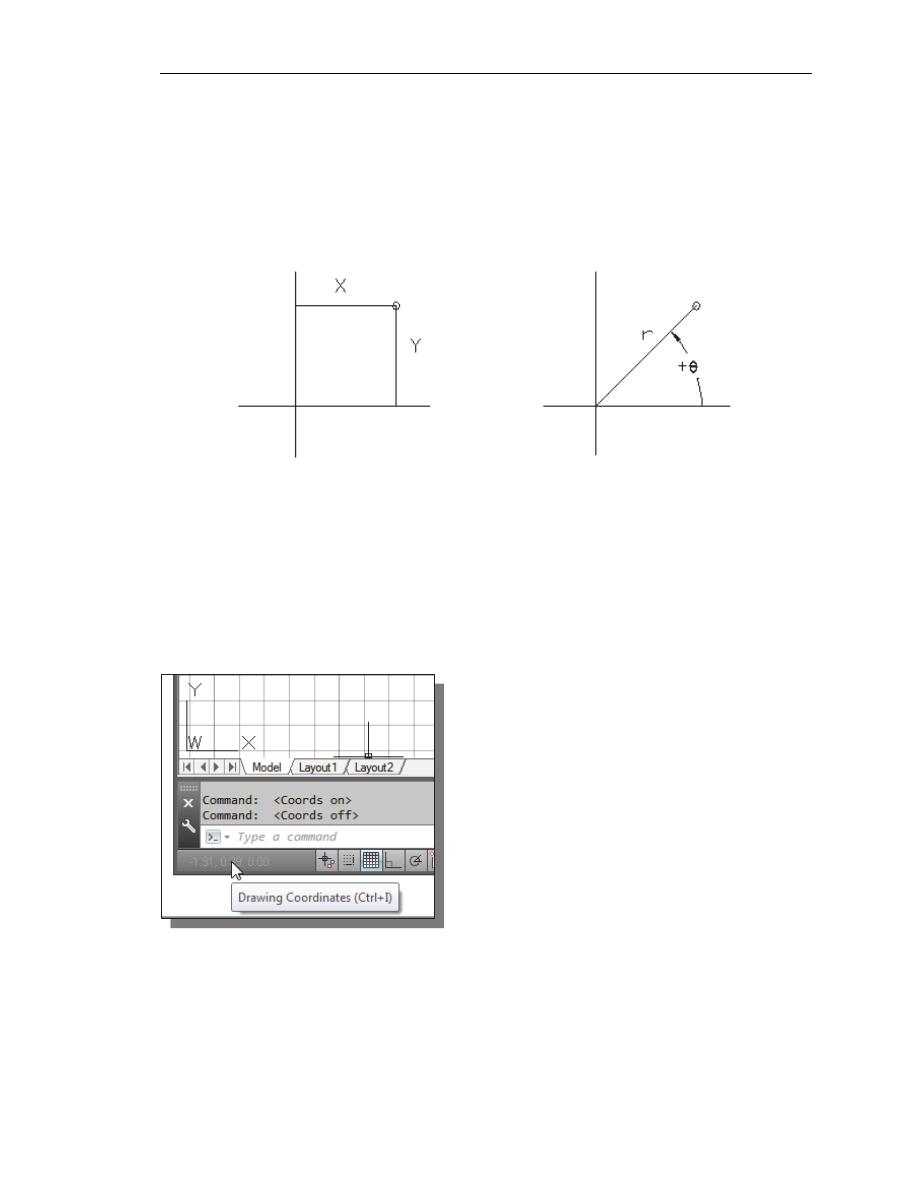
Cartesian and Polar Coordinate Systems
In a two-dimensional space, a point can be represented using different coordinate
systems. The point can be located, using a Cartesian coordinate system, as X and Y units
away from the origin. The same point can also be located using the polar coordinate
system, as r and
θ units away from the origin.
For planar geometry, the polar coordinate system is very useful for certain applications.
In the polar coordinate system, points are defined in terms of a radial distance, r, from the
origin and an angle
θ between the direction of r and the positive X axis. The default
system for measuring angles in AutoCAD
®
2014 defines positive angular values as
counter-clockwise from the positive X-axis.
Absolute and Relative Coordinates
• AutoCAD
®
2014 also allows us to use
absolute and relative coordinates to quickly
construct objects. Absolute coordinate
values are measured from the current
coordinate system's origin point. Relative
coordinate values are specified in relation to
previous coordinates.
Note that the coordinate display area can
also be used as a toggle switch; each left-
mouse-click will toggle the coordinate
display on or off.
In AutoCAD
®
2014, the absolute coordinates and the relative coordinates can be used in
conjunction with the Cartesian and polar coordinate systems. By default, AutoCAD
expects us to enter values in absolute Cartesian coordinates, distances measured from the
current coordinate system's origin point. We can switch to using the relative coordinates
by using the
@
symbol. The
@
symbol is used as the relative coordinates specifier,
which means that we can specify the position of a point in relation to the previous point.
1-18 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
Defining Positions
In AutoCAD, there are five methods for specifying the locations of points when we
create planar geometric entities.
Interactive method: Use the cursor to select on the screen.
Absolute coordinates (Format: X,Y): Type the X and Y coordinates to locate the
point on the current coordinate system relative to the origin.
Relative rectangular coordinates (Format: @X,Y): Type the X and Y
coordinates relative to the last point.
Relative polar coordinates (Format: @Distance<angle): Type a distance and
angle relative to the last point.
Direct Distance entry technique: Specify a second point by first moving the
cursor to indicate direction and then entering a distance.
GRID Style Setup
1. In the Status Bar area, right-mouse-click on
SnapMode and choose [Settings].
2. In the Drafting Settings dialog box, select the Snap and Grid tab if it is not the
page on top.
3. Change Grid Style to Display dotted grid in 2D model Space as shown in
the below figure.
4. Pick OK to exit the Drafting Settings dialog box.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-19
The GuidePlate
We will next create a mechanical design using the different coordinate entry methods.
The rule for creating CAD designs and drawings is that they should be created at full
size using real-world units. The CAD database contains all the definitions of the
geometric entities and the design is considered as a virtual, full-sized object. Only
when a printer or plotter transfers the CAD design to paper is the design scaled to fit
on a sheet. The tedious task of determining a scale factor so that the design will fit on
a sheet of paper is taken care of by the CAD system. This allows the designers and
CAD operators to concentrate their attention on the more important issues – the
design.
1.
Select the Line command icon in the Draw
toolbar. In the command prompt area, near the
bottom of the AutoCAD graphics window, the
message “_line Specify first point:” is displayed.
AutoCAD expects us to identify the starting
location of a straight line.
2.
We will locate the starting point of our design at
the origin of the world coordinate system.
Command: _line Specify first point: 0,0
(Type
0,0 and press the [
ENTER
] key once.)
1-20 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
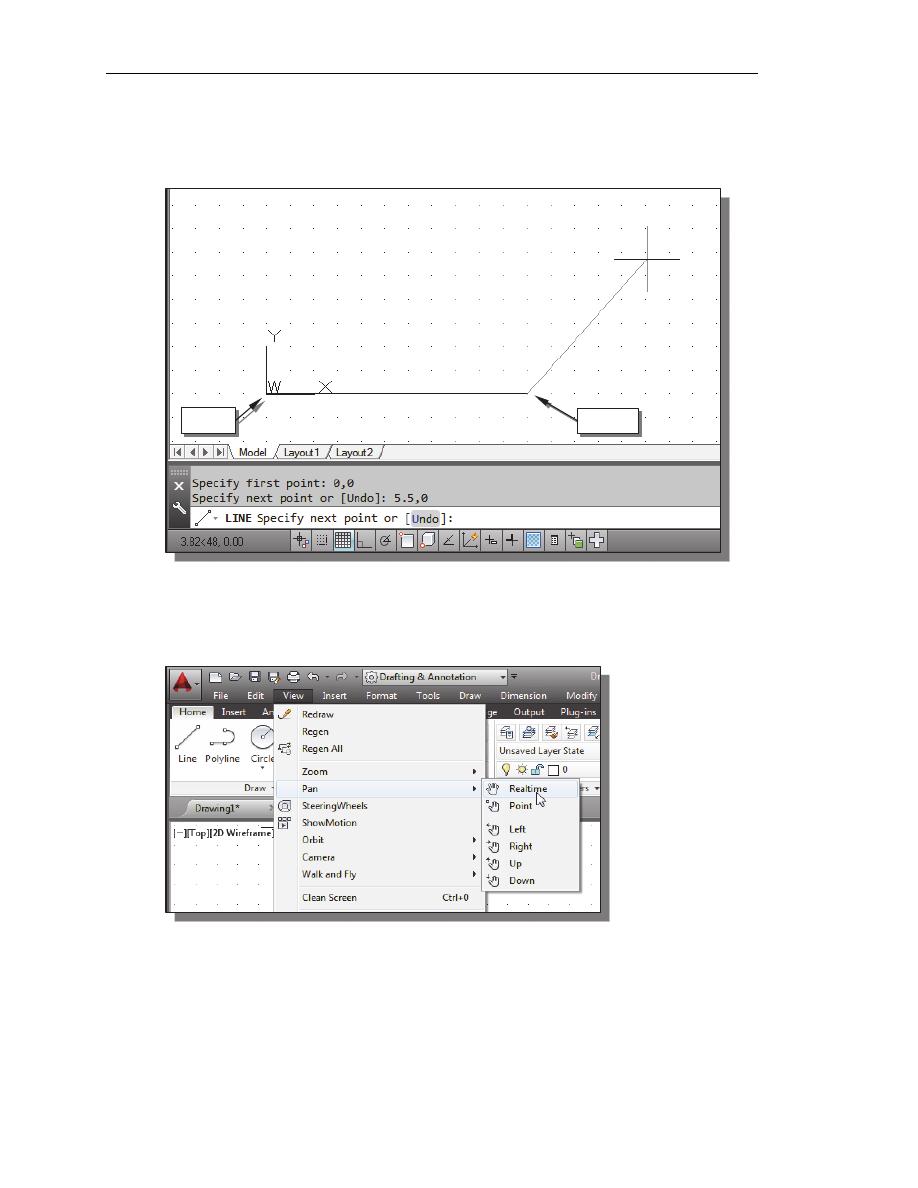
3. We will create a horizontal line by entering the absolute coordinates of the second
point.
Specify next point or [Undo]: 5.5,0
[ENTER]
• Note that the line we created is aligned to the bottom edge of the drawing
window. Let us adjust the view of the line by using the Pan Realtime command.
4. In the Menu Bar area select: [View]
[Pan] [Realtime]
The available Pan commands enable us to move the view to a different position.
The Pan-Realtime function acts as if you are using a video camera.
5. Move the cursor, which appears as a hand inside the graphics window, near the
center of the drawing window, then push down the left-mouse-button and drag
the display toward the right and top side until we can see the sketched line.
(Notice the scroll bars can also be used to adjust viewing of the display.)
(5.5,0)
(0,0)
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-21
6. Press the [
Esc
] key to exit the Pan-Realtime command. Notice that AutoCAD
goes back to the Line command.
7. We will create a vertical line by using the relative rectangular coordinates entry
method, relative to the last point we specified:
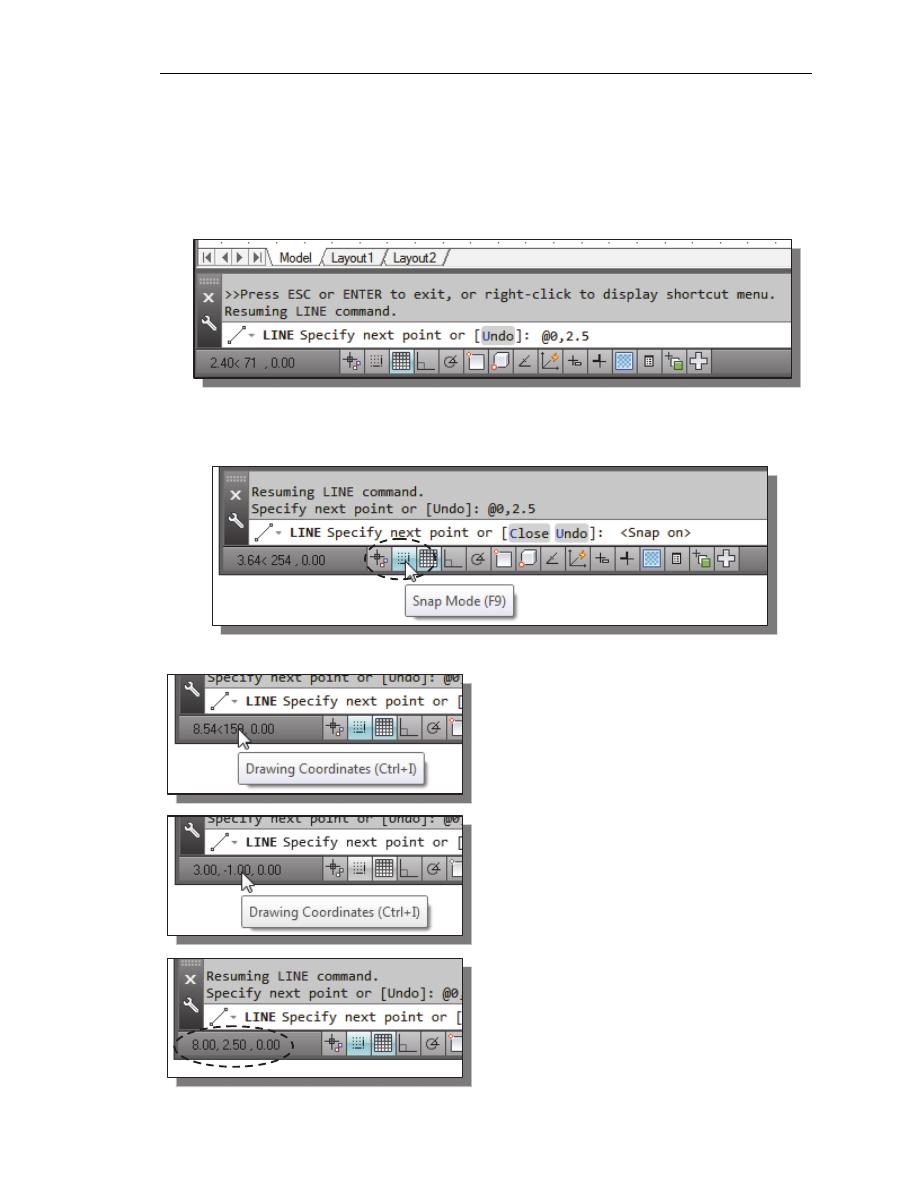
Specify next point or [Close/Undo]: @0,2.5
[ENTER]
8. We can mix any of the entry methods in positioning the locations of the
endpoints. Move the cursor to the Status Bar area, and turn ON the SNAP MODE
option.
Note that the Line command is resumed as the settings are adjusted.
9. Left-click once on the coordinates
display area to switch to a different
coordinate display option. Each click
will change the coordinate display.
10. Note the coordinates display area has
changed to show the length of the new
line and its angle. Left-click once on the
coordinates display area to switch back
to using the world coordinate system.
11. Create the next line by picking the
location, world coordinates (8,2.5), on
the screen.
1-22 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
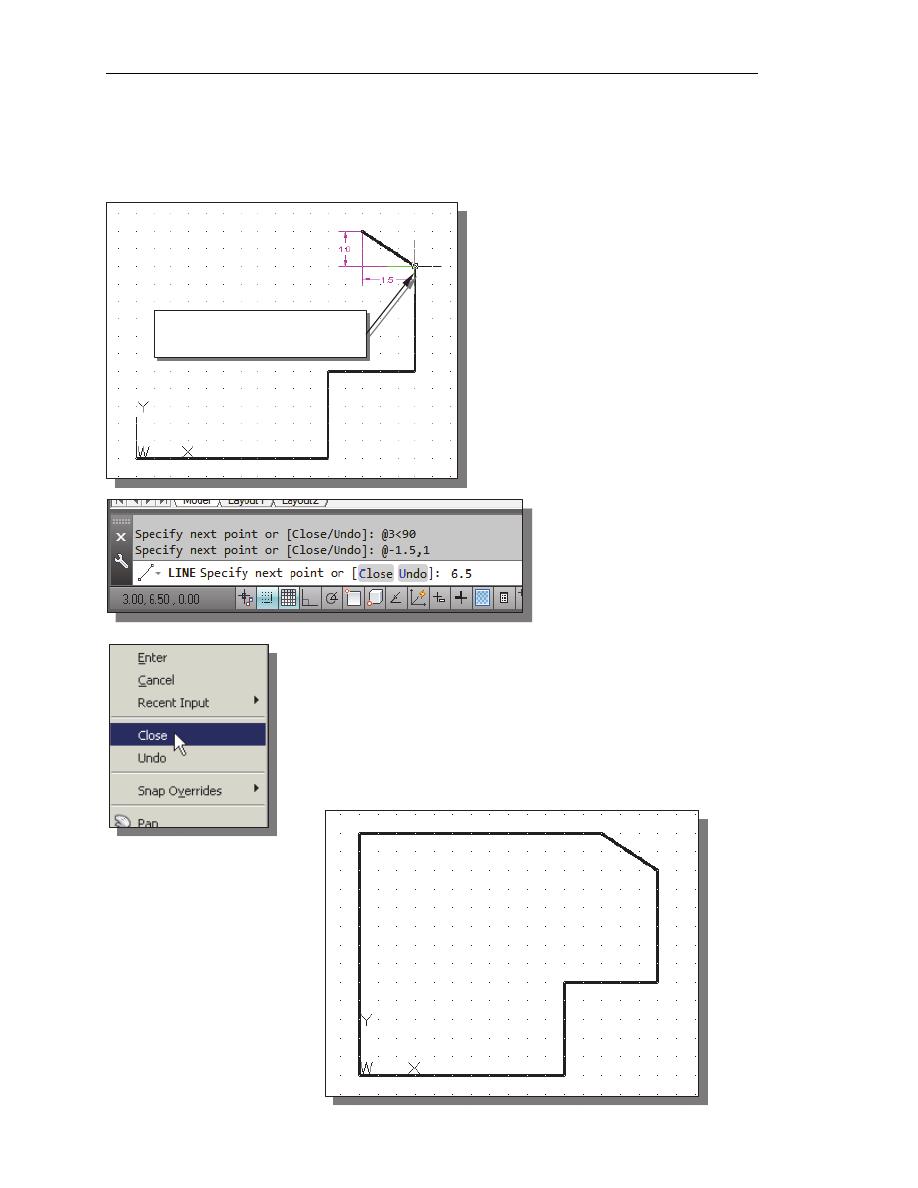
12. We will next use the relative polar coordinates entry method, relative to the last
point we specified:
Specify next point or [Close/Undo]: @3<90
[ENTER]
(Distance is 3 inches with an angle of 90 degrees.)
13. Using the relative rectangular
coordinates entry method to create
the next line, we can imagine a
reference coordinate system
aligned at the previous point.
Coordinates are measured along
the two reference axes.
Specify next point or [Close/Undo]:
@-1.5,1
[ENTER]
(-1.5 and 1 inches are measured
relative to the reference point.)
14. Move the cursor directly
to the left of the last
point and use the direct
distance entry technique
by entering 6.5
[ENTER]
.
15. For the last segment of the sketch, we can use the Close
option to connect back to the starting point. Inside the
graphics window, right-mouse-click and a popup menu
appears on the screen.
16. Select Close with the left-mouse-button to connect back to
the starting point and end the Line command.
Reference Coordinate System
aligned at the previous point
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-23
Creating Circles
• The menus and toolbars in AutoCAD
®
2014 are designed to allow the CAD
operator to quickly activate the desired commands.
1. In the Draw toolbar, click on the little
triangle below the circle icon. Note that the
little triangle indicates additional options are
available.
2. In the option list, select: [Center, Diameter]
Notice the different options available under the circle submenu:
• Center, Radius: Draws a circle based on a center point and a radius.
• Center, Diameter: Draws a circle based on a center point and a diameter.
• 2 Points: Draws a circle based on two endpoints of the diameter.
• 3 Points: Draws a circle based on three points on the circumference.
• TTR–Tangent, Tangent, Radius: Draws a circle with a specified radius
tangent to two objects.
• TTT–Tangent, Tangent, Tangent: Draws a circle tangent to three objects.
1-24 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
3. In the command prompt area, the message “Specify center point for circle or
[3P/2P/Ttr (tan tan radius)]:” is displayed. AutoCAD expects us to identify the
location of a point or enter an option. We can use any of the four coordinate entry
methods to identify the desired location. We will enter the world coordinates
(2.5,3) as the center point for the first circle.
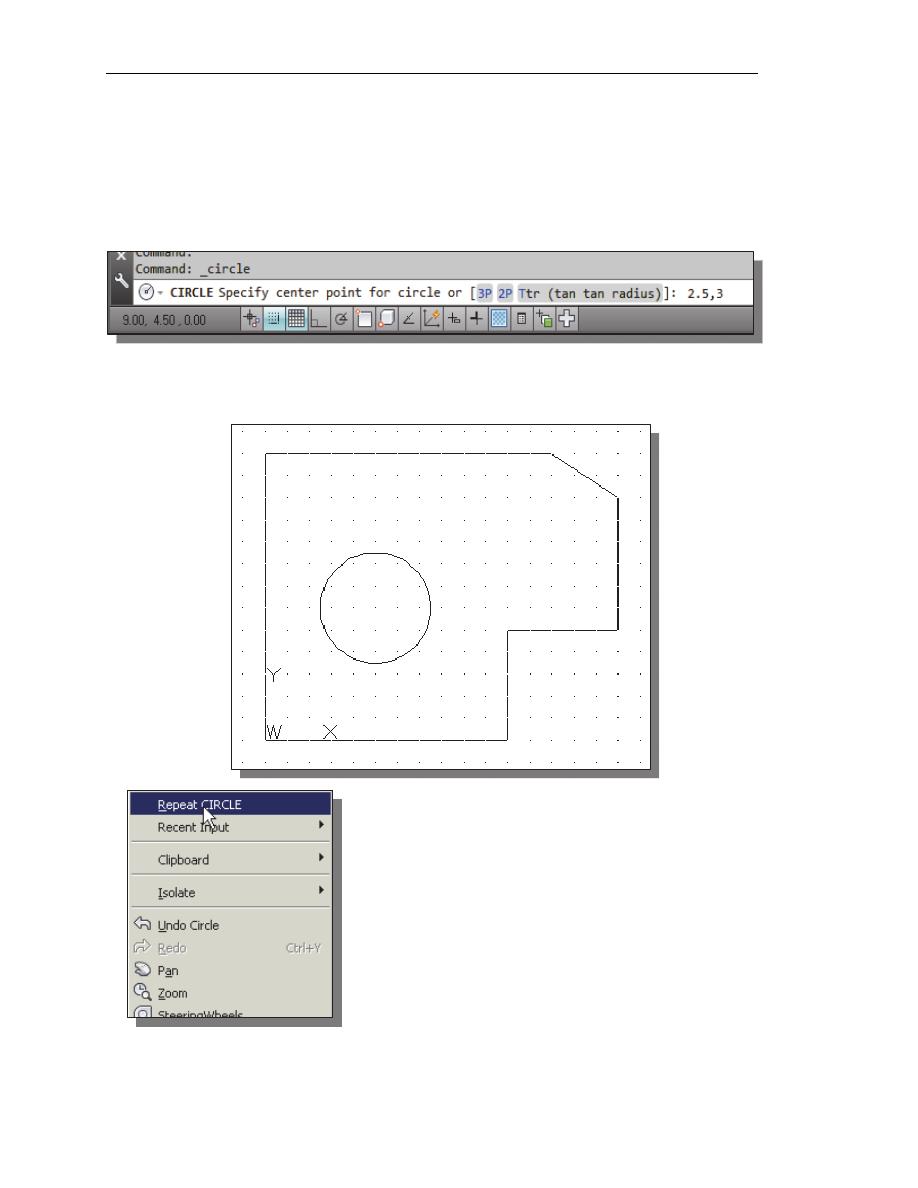
Specify center point for circle or [3P/2P/Ttr (tan tan radius)]: 2.5,3
[ENTER]
4. In the command prompt area, the message “Specify diameter of circle:” is
displayed.
Specify diameter of circle: 2.5
[ENTER]
5. Inside the graphics window, right-mouse-click to
bring up the popup option menu.
6. Pick Repeat CIRCLE with the left-mouse-button
in the popup menu to repeat the last command.
7. Using the relative rectangular coordinates entry
method, relative to the center-point coordinates of
the first circle, we specify the location as (2.5,2).
Specify center point for circle or [3P/2P/Ttr (tan tan radius)]: @2.5,2
[ENTER]
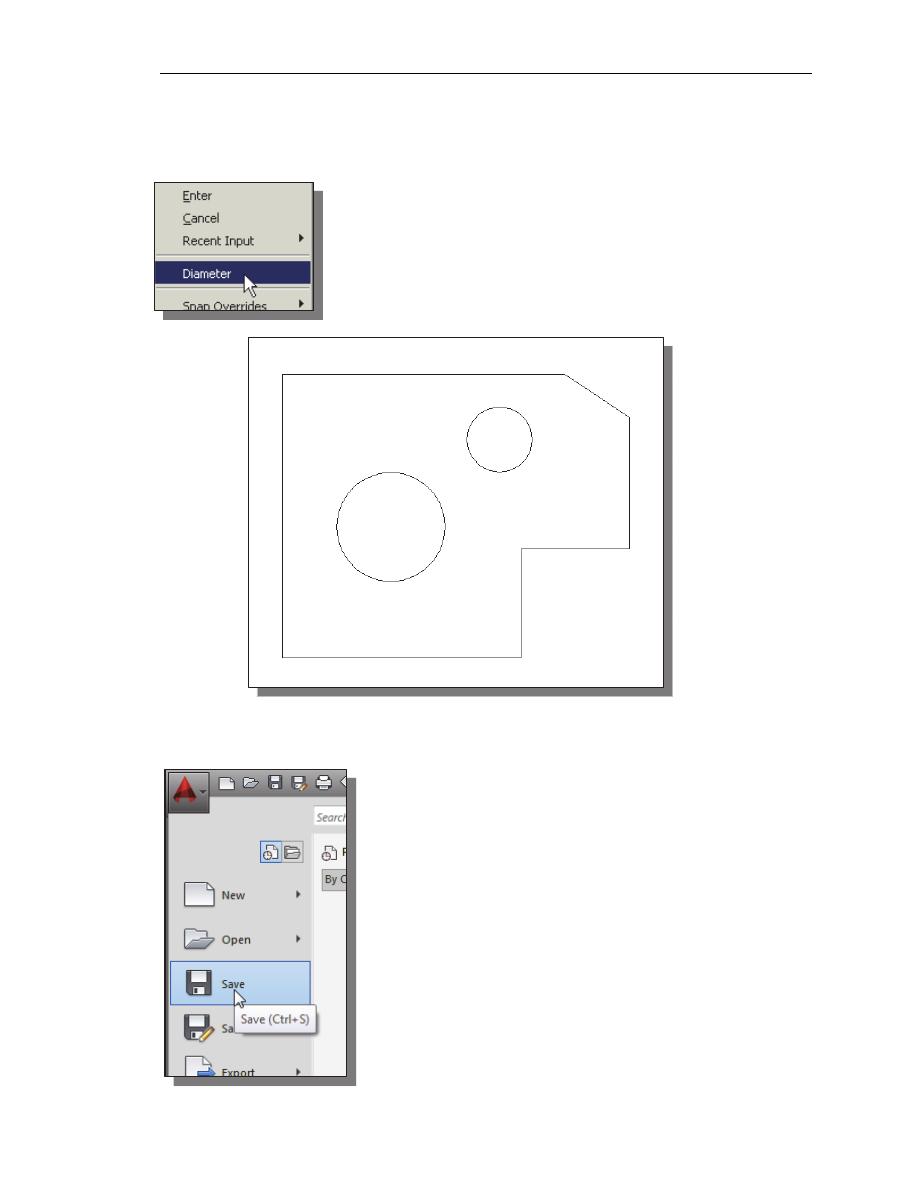
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-25
8. In the command prompt area, the message “Specify Radius of circle: <2.50>” is
displayed. The default option for the Circle command in AutoCAD is to specify
the radius and the last radius used is also displayed in brackets.
9. Inside the graphics window, right-mouse-click to bring up
the popup option menu and select Diameter as shown.
10. In the command prompt area, enter 1.5 as the diameter.
Specify Diameter of circle<2.50>: 1.5
[ENTER]
Saving the CAD Design
1. In the Application Menu, select:
[Application]
[Save]
Note the command can also be activated with quick-
key combination of [
Ctrl
]+[
S
].
1-26 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
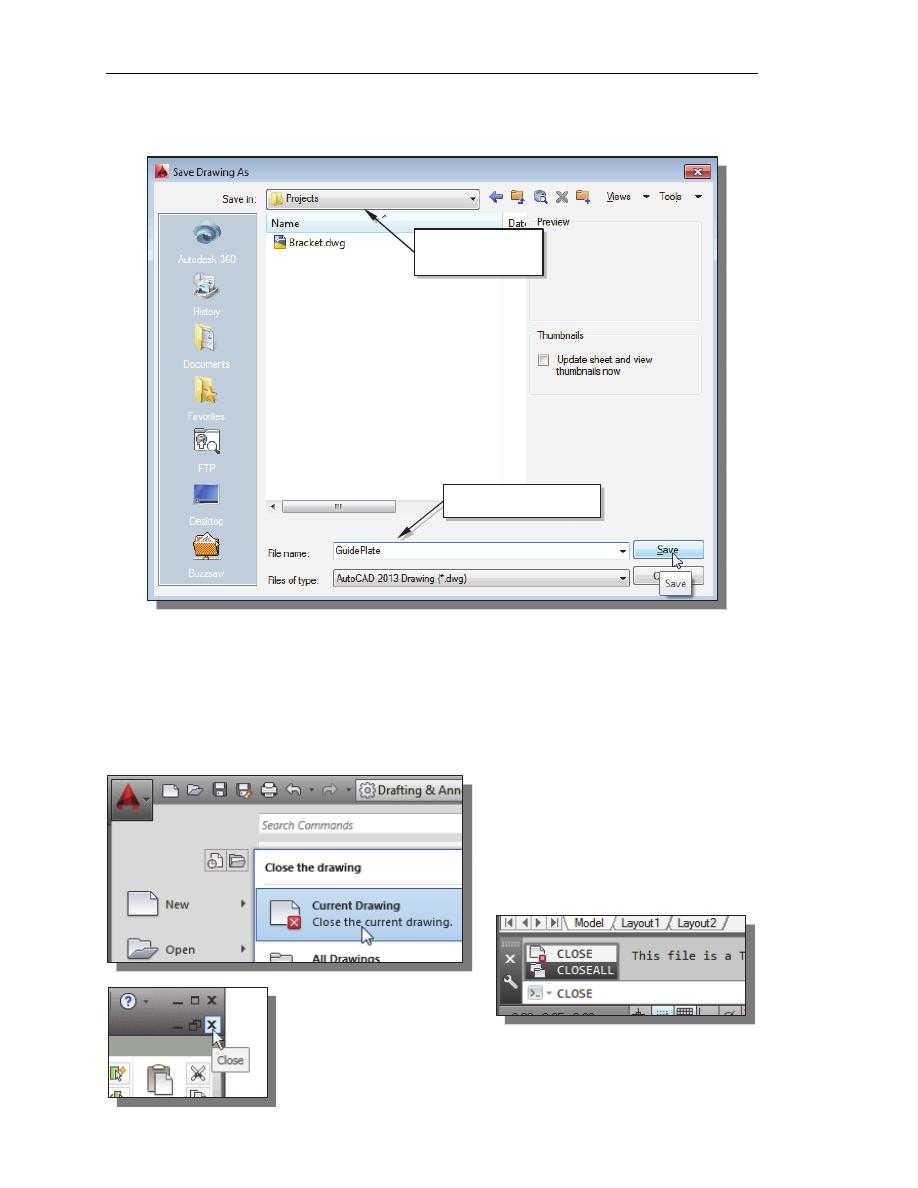
2. In the Save Drawing As dialog box, select the folder in which you want to store
the CAD file and enter GuidePlate in the File name box.
3. Click Save in the Save Drawing As dialog box to accept the selections and save
the file. Note the default file type is DWG, which is the standard AutoCAD
drawing format.
Close the Current Drawing
Several options are available to close the current drawing:
Select [Close] [Current
Drawing] in the Application
Menu Bar as shown.
Enter Close at the command
prompt.
The third option is to click on the [Close] icon, located at
the upper-right-hand corner of the drawing window.
Enter
GuidePlate
Select the folder
to store the file.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-27
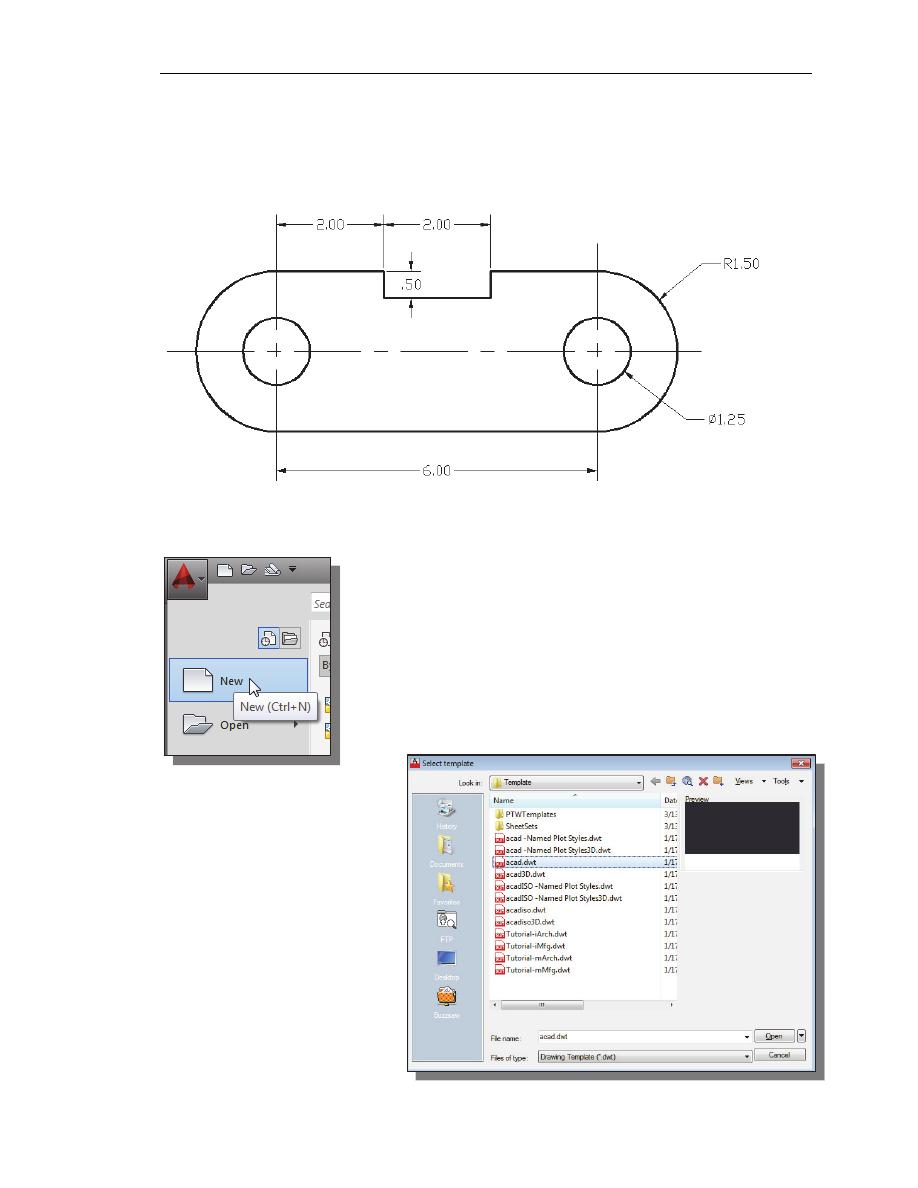
The Spacer Design
We will next create the spacer design using more of AutoCAD’s drawing tools.
Start a New Drawing
1. In the Application Menu, select [New] to start a new
drawing.
2. The Select Template
dialog box appears on
the screen. Accept the
default acad.dwt as the
template to open.
The dwt file type is the
AutoCAD template file
format. An AutoCAD
template file contains pre-
defined settings to reduce
the amount of tedious
repetitions.
1-28 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
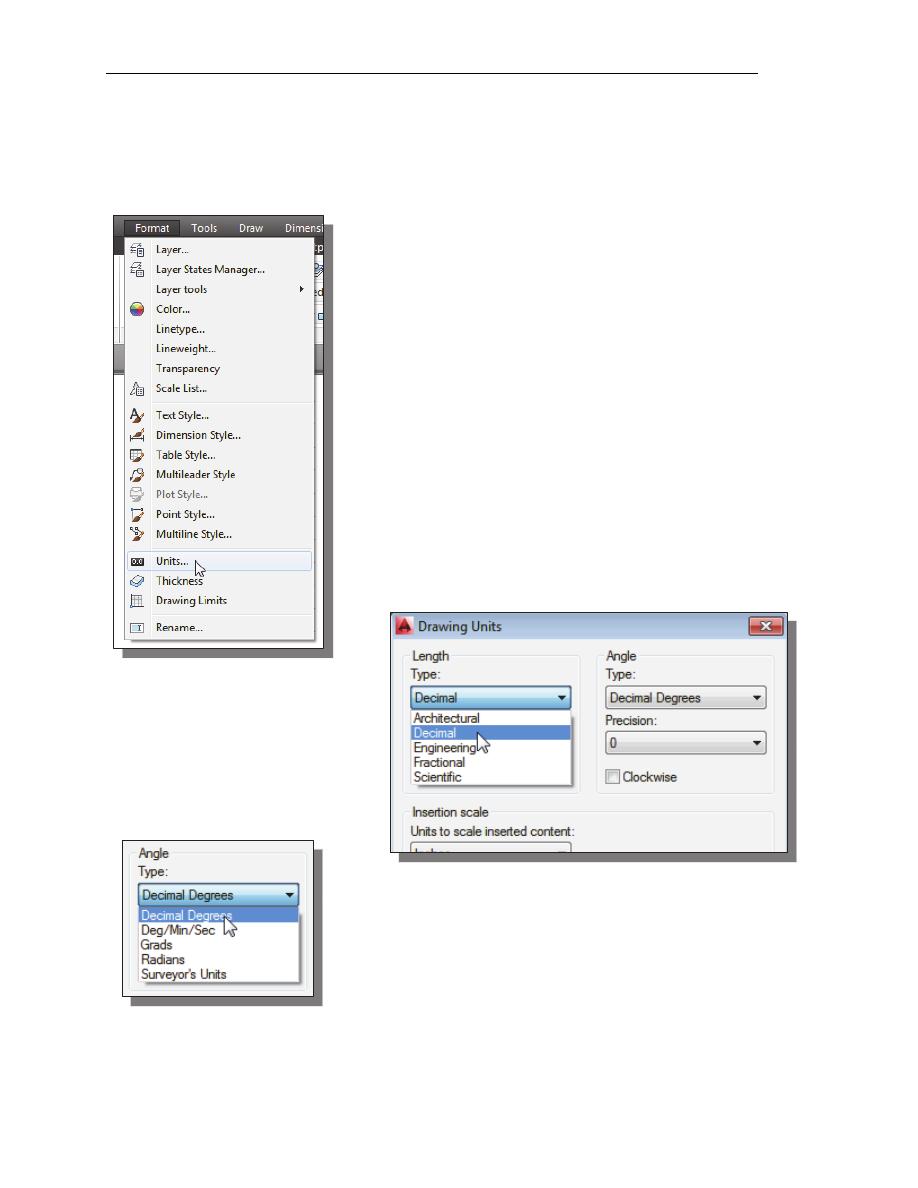
Drawing Units Setup
Every object we construct in a CAD system is measured in units. We should
determine the system of units within the CAD system before creating the first
geometric entities.
1. In the Menu Bar select:
[Format]
[Units]
• The AutoCAD Menu Bar contains multiple pull-down
menus, where all of the AutoCAD commands can be
accessed. Note that many of the menu items listed in
the pull-down menus can also be accessed through the
Quick Access toolbar and/or Ribbon panels.
2. Click on the Length Type
option to display the different
types of length units
available. Confirm the
Length Type is set to
Decimal.
3. On your own, examine the other settings that are
available.
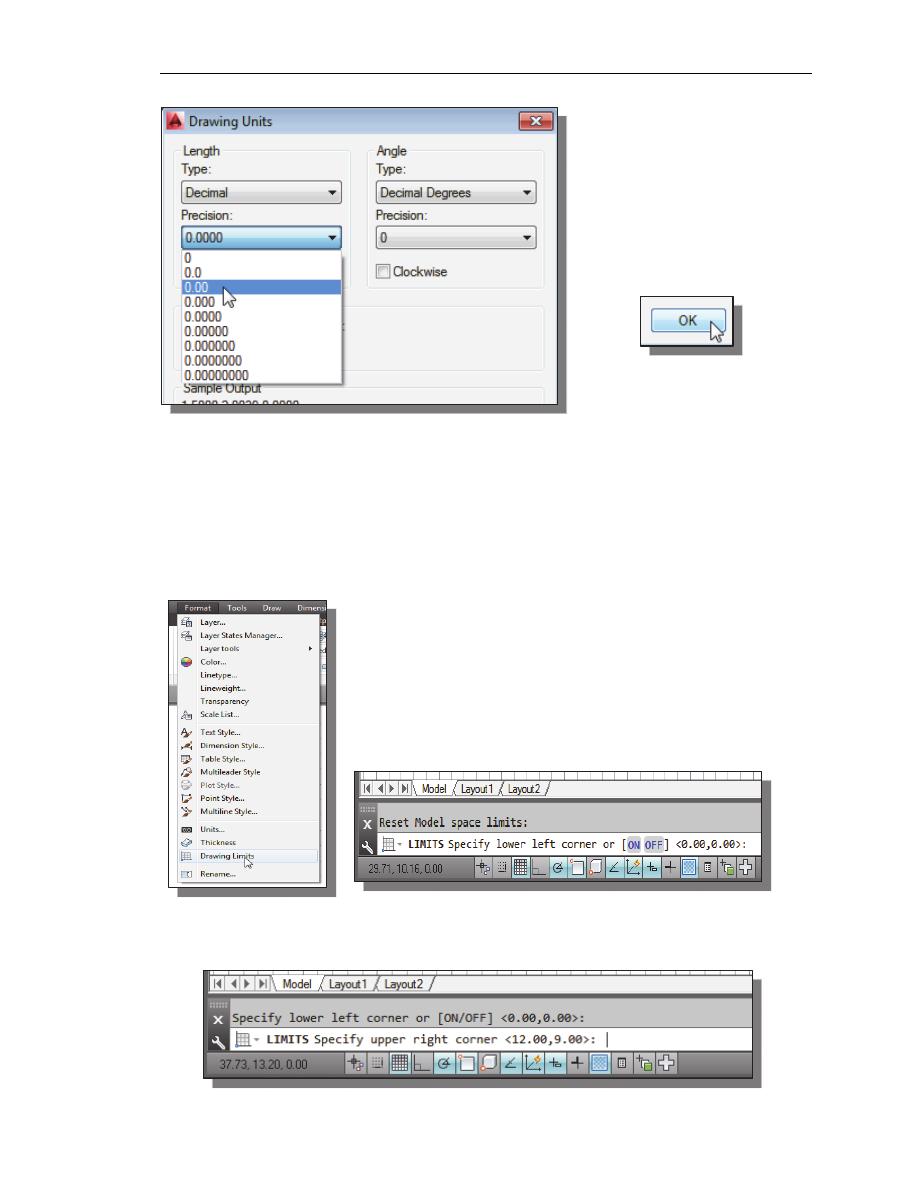
4. In the Drawing Units dialog box, set the Length Type to Decimal. This will set the
measurement to the default English units, inches.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-29
5. Set the Precision to two
digits after the decimal point
as shown in the above figure.
6. Pick OK to exit the Drawing
Units dialog box.
Drawing Area Setup
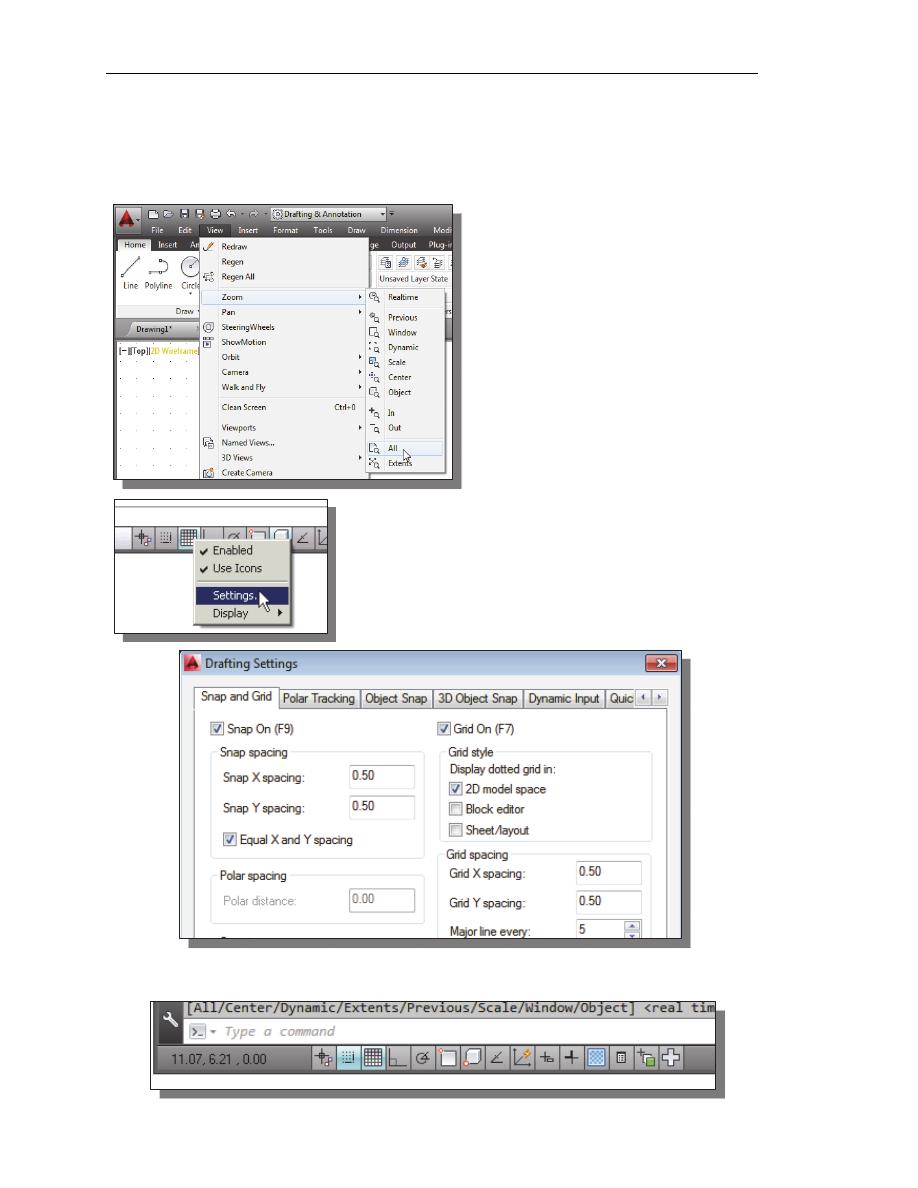
Next, we will set up the Drawing Limits by entering a command in the
command prompt area. Setting the Drawing Limits controls the extents of the
display of the grid. It also serves as a visual reference that marks the working
area. It can also be used to prevent construction outside the grid limits and as a
plot option that defines an area to be plotted/printed. Note that this setting does
not limit the region for geometry construction.
1. In the Menu Bar select:
[Format]
[Drawing Limits]
2. In the command prompt area, the message “Reset Model
Space Limits: Specify lower left corner or [On/Off]
<0.00,0.00>:” is displayed. Press the
ENTER
key once to
accept the default coordinates <0.00,0.00>.
3. In the command prompt area, the message “Specify upper right corner
<12.00,9.00>:” is displayed. Press the
ENTER
key again to accept the default
coordinates <12.00,9.00>.
1-30 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
4. On your own, move the graphics cursor near the upper-right comer inside the
drawing area and note that the drawing area is unchanged. (The Drawing Limits
command is used to set the drawing area, but the display will not be adjusted until
a display command is used.)
5. Inside the Menu Bar area select:
[View]
[Zoom] [All]
The Zoom All command will
adjust the display so that all objects
in the drawing are displayed to be as
large as possible. If no objects are
constructed, the Drawing Limits are
used to adjust the current viewport.
6. Move the graphics cursor near the
upper-right comer inside the
drawing area, and note that the
display area is updated.
7. In the Status Bar area, right-mouse-click on
SnapMode and choose [Settings].
8. In the Drafting Settings dialog box, switch on the
Snap and Grid options as shown.
On your own, exit the Drafting Settings dialog box and reset the status buttons so
that only GRID DISPLAY and SNAP MODE are turned ON as shown.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-31
Using the Line Command
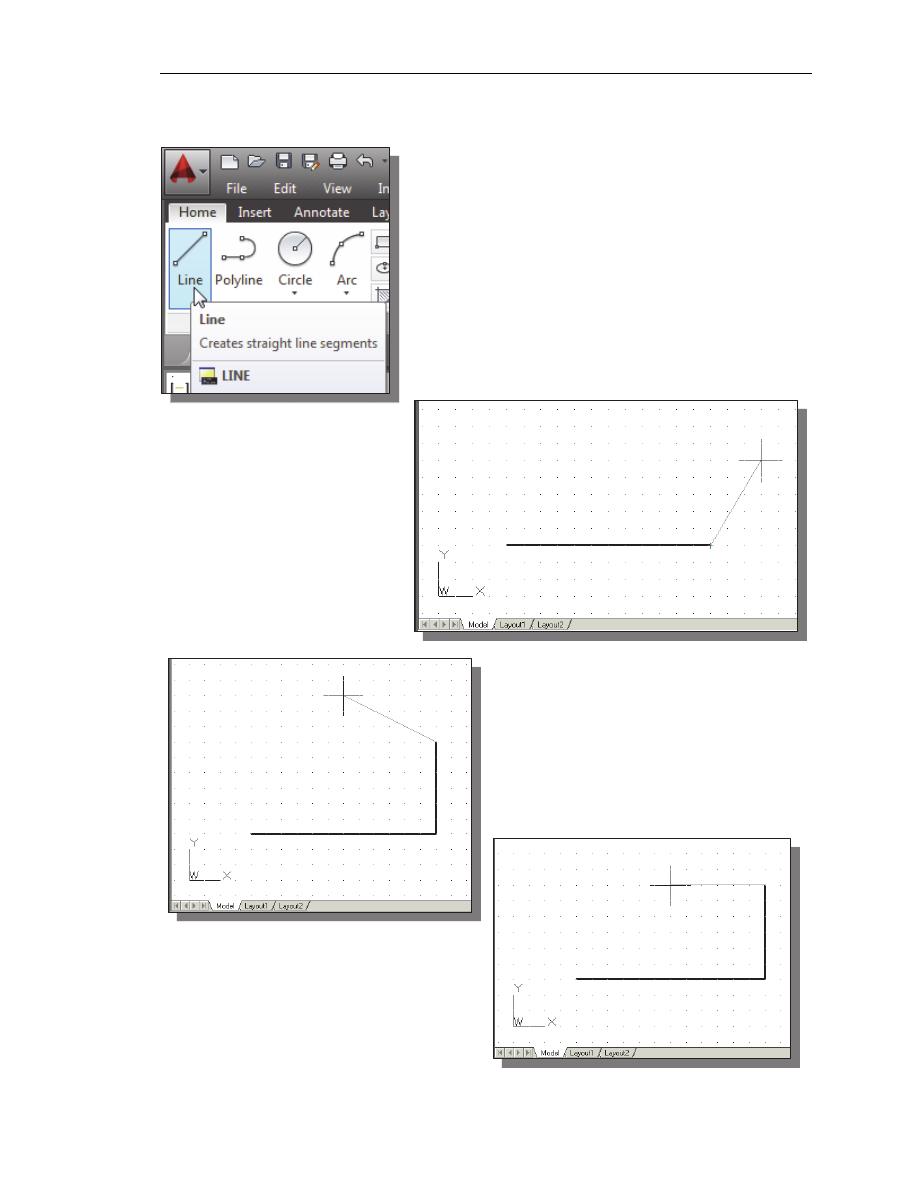
1. Select the Line command icon in the Draw toolbar.
In the command prompt area, near the bottom of the
AutoCAD graphics window, the message “_line
Specify first point:” is displayed. AutoCAD expects
us to identify the starting location of a straight line.
2. To further illustrate the usage of the different input
methods and tools available in AutoCAD, we will
start the line segments at an arbitrary location.
Start at a location that is somewhere in the lower left
side of the graphics window.
3. We will create a
horizontal line by using
the relative rectangular
coordinates entry
method, relative to the
last point we specified:
@6,0
[ENTER]
4. Next, create a vertical line by using the
relative polar coordinates entry
method, relative to the last point we
specified: @3<90
[ENTER]
5. Next, we will use the direct input
method. First, move the cursor
directly to the left of the last
endpoint of the line segments.
1-32 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
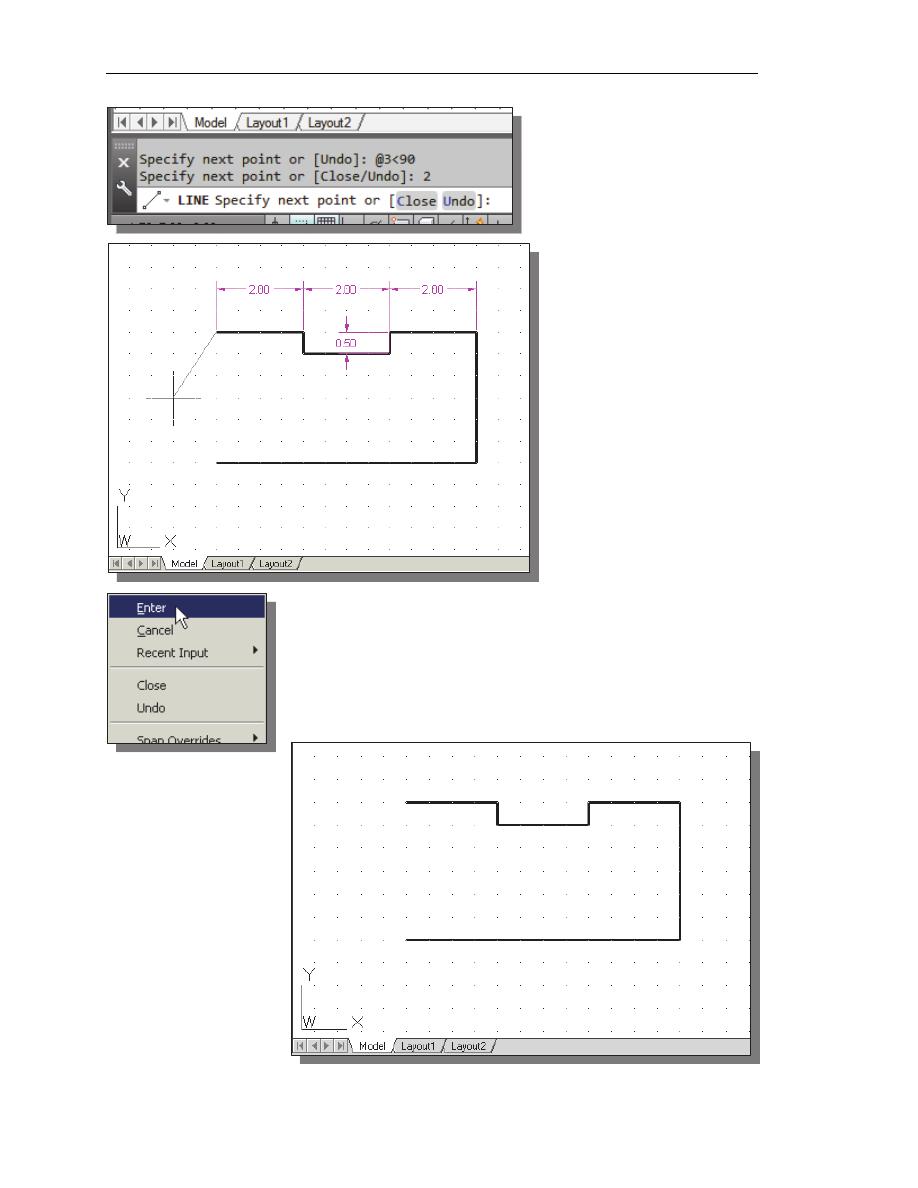
6. Use the direct distance
entry technique by
entering 2
[ENTER]
.
7. On your own, repeat the
above steps and create
the four additional line
segments, using the
dimensions as shown.
8. To end the line command, we can either hit the [Enter] key
on the keyboard or use the Enter option, right-mouse-click
and a popup menu appears on the screen.
9. Select Enter with the left-mouse-button to end the Line
command.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-33
Using the ERASE Command
The vertical line on the right was created as a construction line, to aide the
construction of the rest of the lines for the design. We will use the Erase command to
remove it.
1. Pick Erase in the Modify toolbar. The
message “Select objects” is displayed in
the command prompt area and
AutoCAD awaits us to select the objects
to erase.
2. Select the vertical
line as shown.
3. Click once with the
right-mouse-button
to accept the
selection and delete
the line.
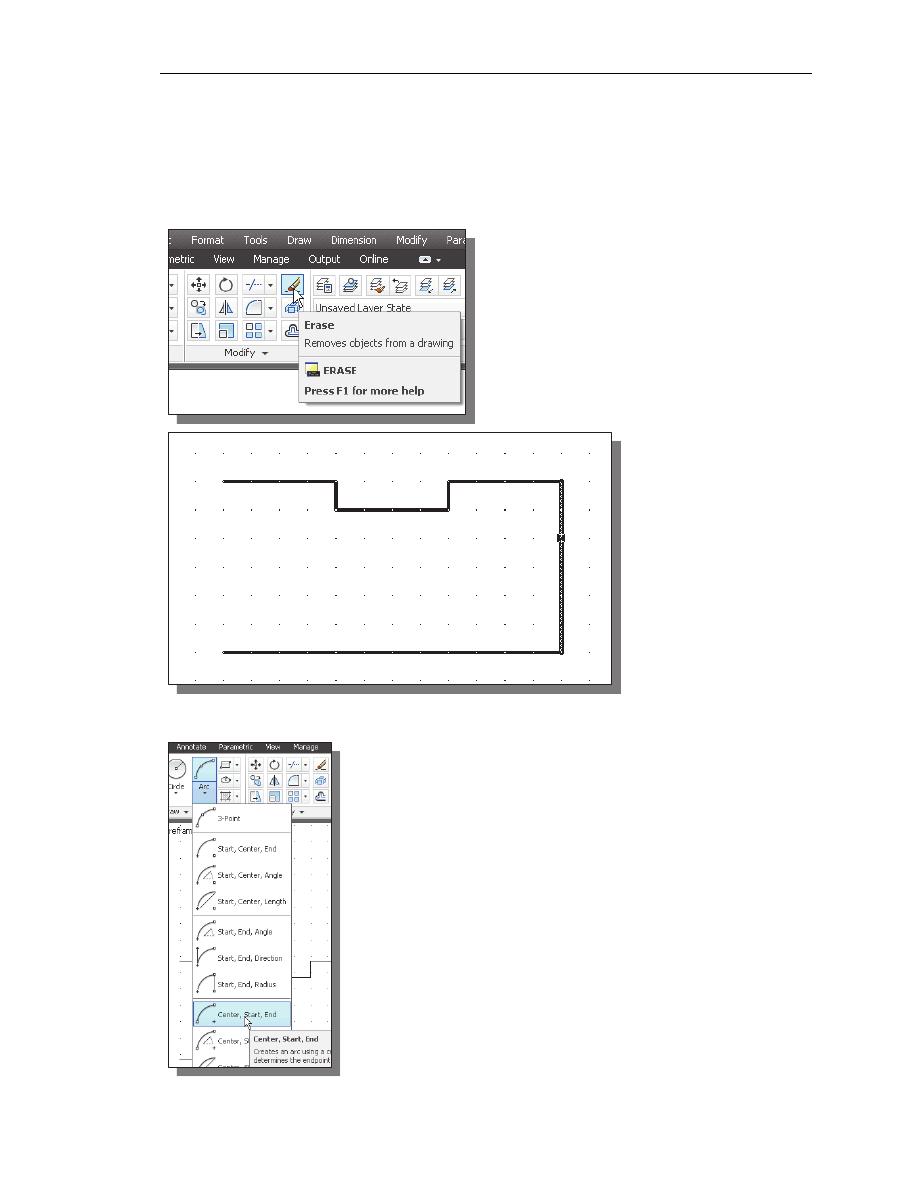
Using the Arc Command
1. Click the down-arrow icon of the Arc command in the
Draw toolbar to display the different Arc construction
options.
AutoCAD provides eleven different ways to create arcs.
Note that the different options are used based on the
geometry conditions of the design. The more commonly
used options are the 3-Points option and the Center-Start-
End option.
2. Select the Center-Start-End option as shown. This option
requires the selection of the center point, start point and
end point location, in that order, of the arc.
1-34 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
3. Move the cursor to the
middle of the two horizontal
lines and align the cursor to
the two endpoints as shown.
Click once with the right-
mouse-button to select the
location as the center point of
the new arc.
4. Move the cursor downward
and select the right endpoint
of the bottom horizontal line
as the start point of the arc.
5. Move the cursor to the right
endpoint of the top horizontal
line as shown. Pick this point
as the endpoint of the new
arc.
6. On your own, repeat the
above steps and create the
other arc as shown. Note
that in most CAD packages,
positive angles are defined
as going counterclockwise;
therefore the starting point
of the second arc should be
at the endpoint on top.
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-35
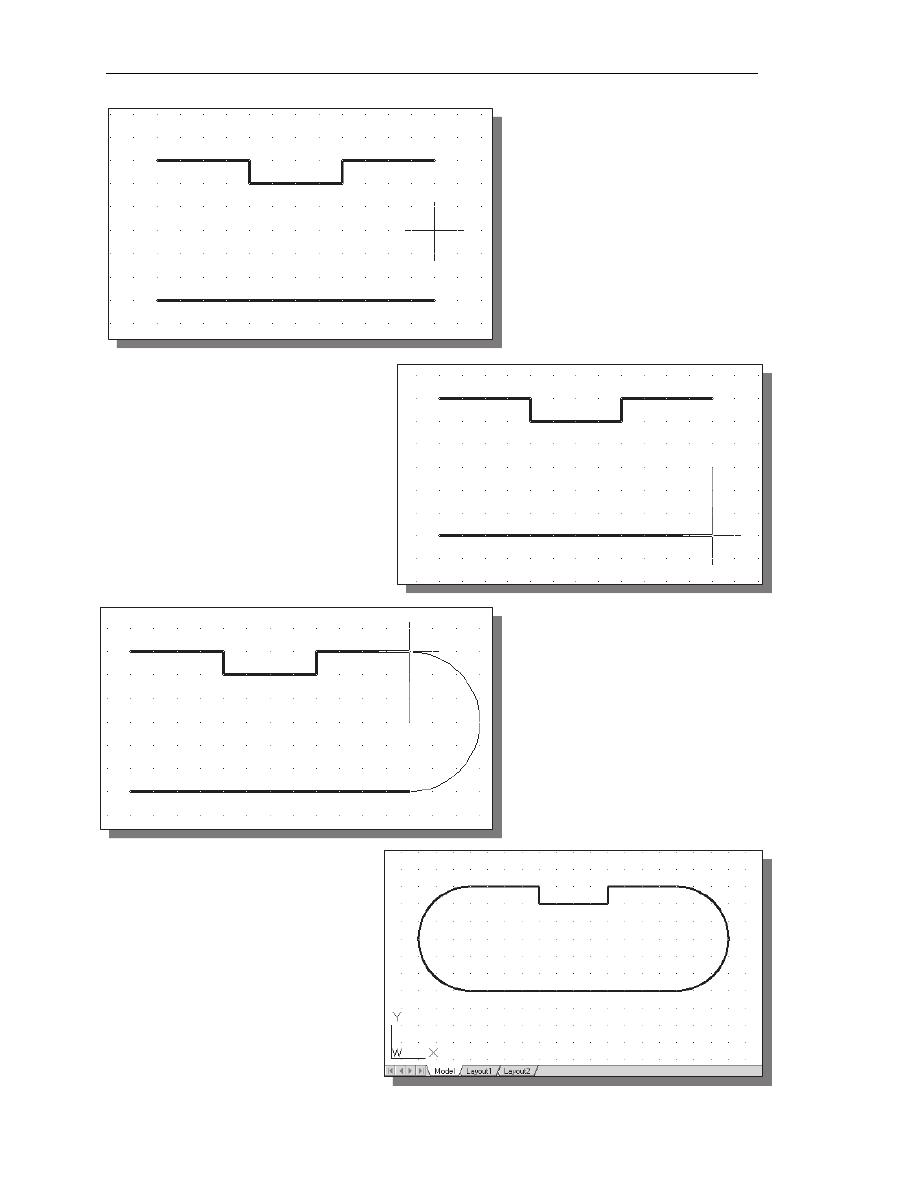
Using the Circle Command
1. Select the [Circle]
[Center, Diameter]
option as shown.
2. Select the same
location for the arc
center as the center
point for the new circle.
3. In the command
prompt area, the
message “Specify
diameter of circle:” is
displayed. Specify
diameter of circle:
1.25
[ENTER]
4. On your own, create the other circle and complete the drawing as shown.
1-36 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
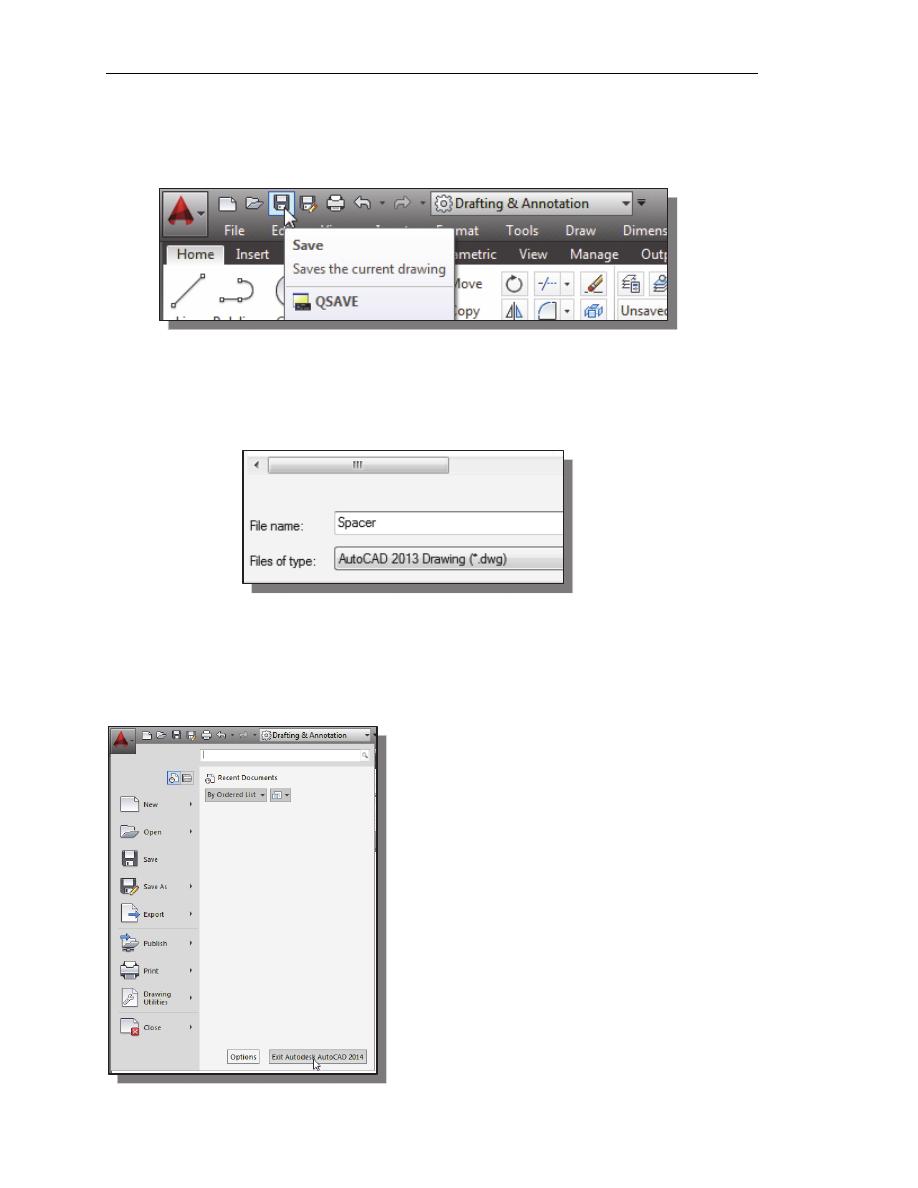
Saving the CAD Design
1. In the Quick Access Toolbar, select: [Save]
Note the command can also be activated with quick-key combination of
[
Ctrl
]+[
S
].
2. In the Save Drawing As dialog box, select the folder in which you want to store
the CAD file and enter Spacer in the File name box.
3. Click Save in the Save Drawing As dialog box to accept the selections and save
the file. Note the default file type is DWG, which is the standard AutoCAD
drawing format.
Exit AutoCAD 2014
To exit AutoCAD
®
2014, select Exit
AutoCAD in the Menu Bar or type QUIT at
the command prompt. Note the command can
also be activated with quick-key combination
of [
Ctrl
]+[
Q
].
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-37
Review Questions:
(Time: 20 minutes)
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using CAD systems to create
engineering drawings?
2. What is the default AutoCAD filename extension?
3. How do the GRID and SNAP options assist us in sketching?
4. List and describe the different coordinate entry methods available in AutoCAD?
5. When using the Line command, which option allows us to quickly create a line-
segment connecting back to the starting point?
6. List and describe the two types of coordinate systems commonly used for planar
geometry.
7. Which key do you use to quickly cancel a command?
8. When you use the Pan command, do the coordinates of objects get changed?
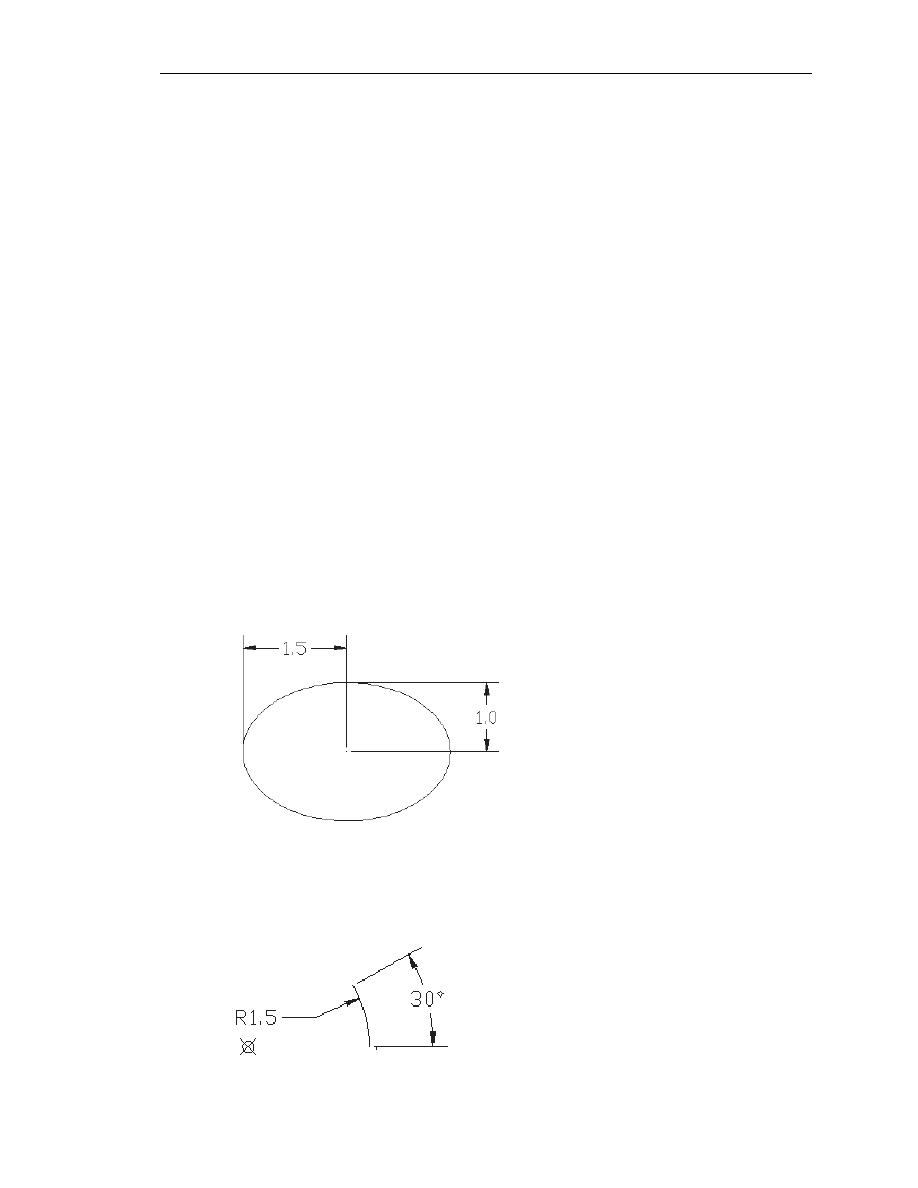
9. Find information on how to draw ellipses in AutoCAD through the Autodesk
Exchange, and create the following arc. If it is desired to position the center of the
ellipse to a specific location, which ellipse command is more suitable?
10. Find information on how to draw arcs in AutoCAD through the Autodesk Exchange
and create the following arc. List and describe two methods to create arcs in
AutoCAD.
1-38 AutoCAD
®
2014 Tutorial: 2D Fundamentals
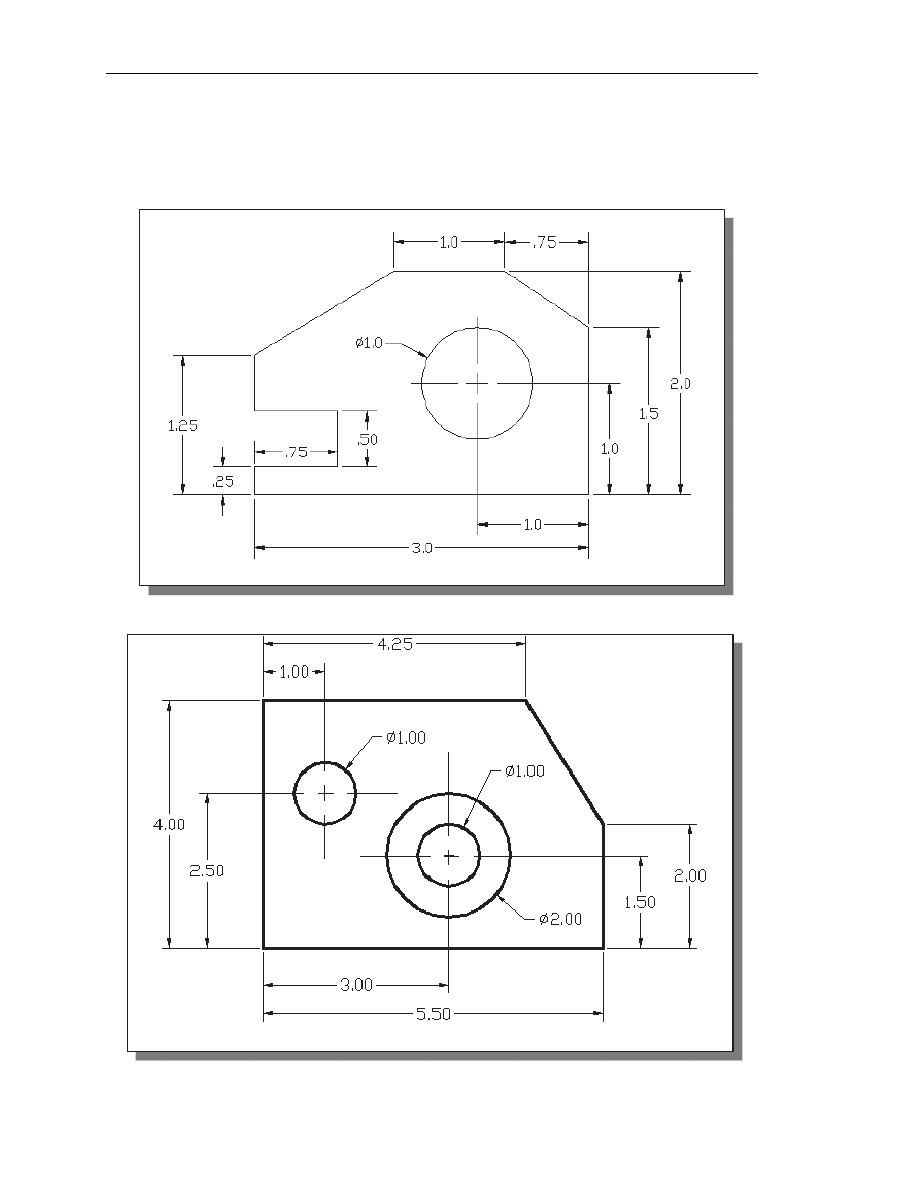
Exercises:
(All dimensions are in inches.) (Time: 60 minutes)
1. Angle Spacer
2. Base Plate
AutoCAD
Fundamentals
1-39
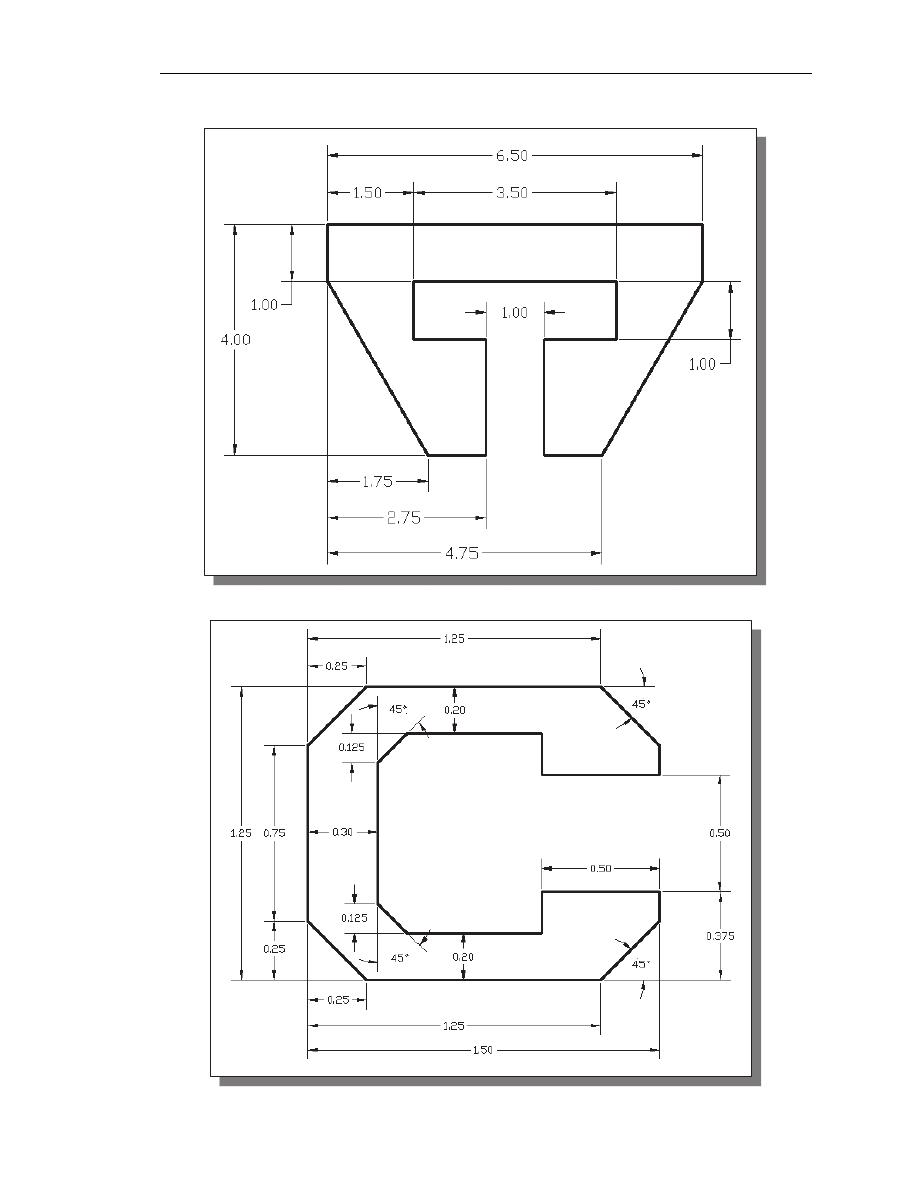
3. T-Clip
4. Channel Plate

