Lecture Two
CarbohydratesDr. Khalidah Merzah
Carbohydrates
Most abundant class of biological molecules on Earth• Originally produced through CO2 fixation during photosynthesis
Roles of Carbohydrates
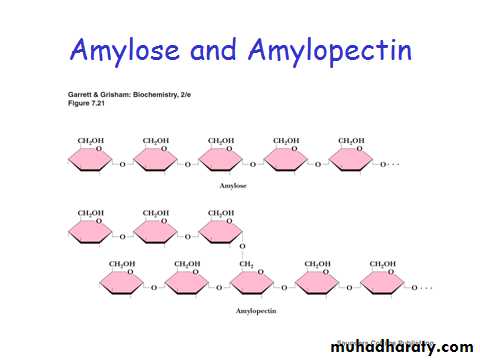
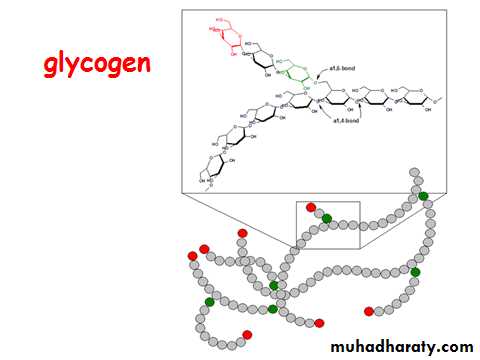
• Energy storage (glycogen, starch)
• Structural components (cellulose, chitin)
• Cellular recognition
• Carbohydrate derivatives include
DNA, RNA, co-factors, glycoproteins, glycolipids
Carbohydrates
• Monosaccharides (simple sugars) cannot be broken down into simpler sugars under mild conditions
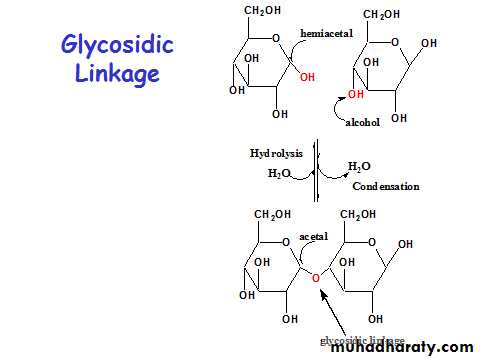
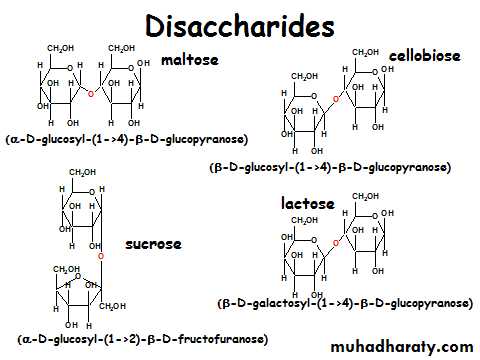
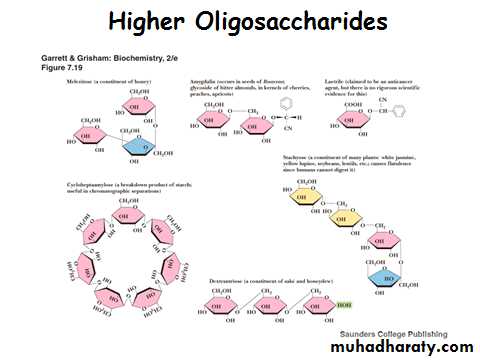
• Oligosaccharides = "a few" - usually2 to 10
• Polysaccharides are polymers of the simple sugarsMonosaccharides
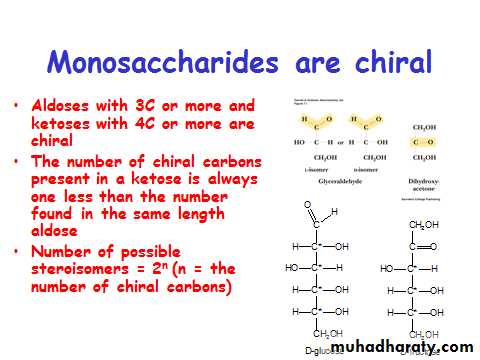
• Polyhydroxy ketones (ketoses) and aldehydes (aldoses)
• Aldoses and ketoses contain aldehyde and ketone functions, respectively
• Ketose named for “equivalent aldose” + “ul” inserted• Triose, tetrose, etc. denotes number of carbons
• Empirical formula = (CH2O)nReducing Sugars
When in the uncyclized form, monosaccharides act as reducing agents.
• Free carbonyl group from aldoses or ketoses can reduce Cu2+ and Ag+ ions to insoluble products
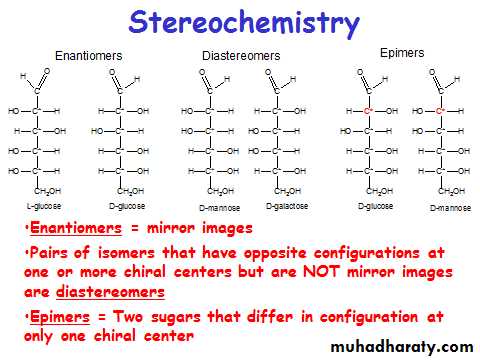
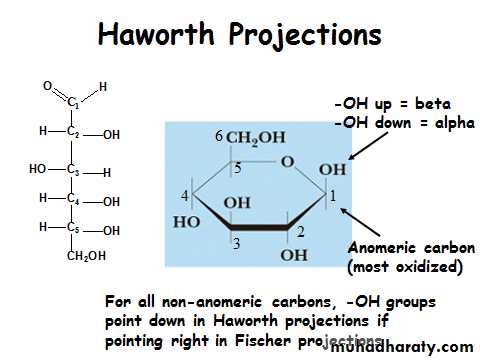
Monosaccharide structures you need to know
• Glucose• Fructose
• Ribulose
• Glyceraldehyde
• Dihydroxyacetone