Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٩٢
-
Voltage divider Rule :-
T
R
R
E
R
R
E
R
I
V
2
2
2
2
2
.
.
.
Voltage divider rule
V
n
= Voltage across R
n
E = The ( emf ) voltage across the series elements .
R
T
= The total resistance of the series circuits .
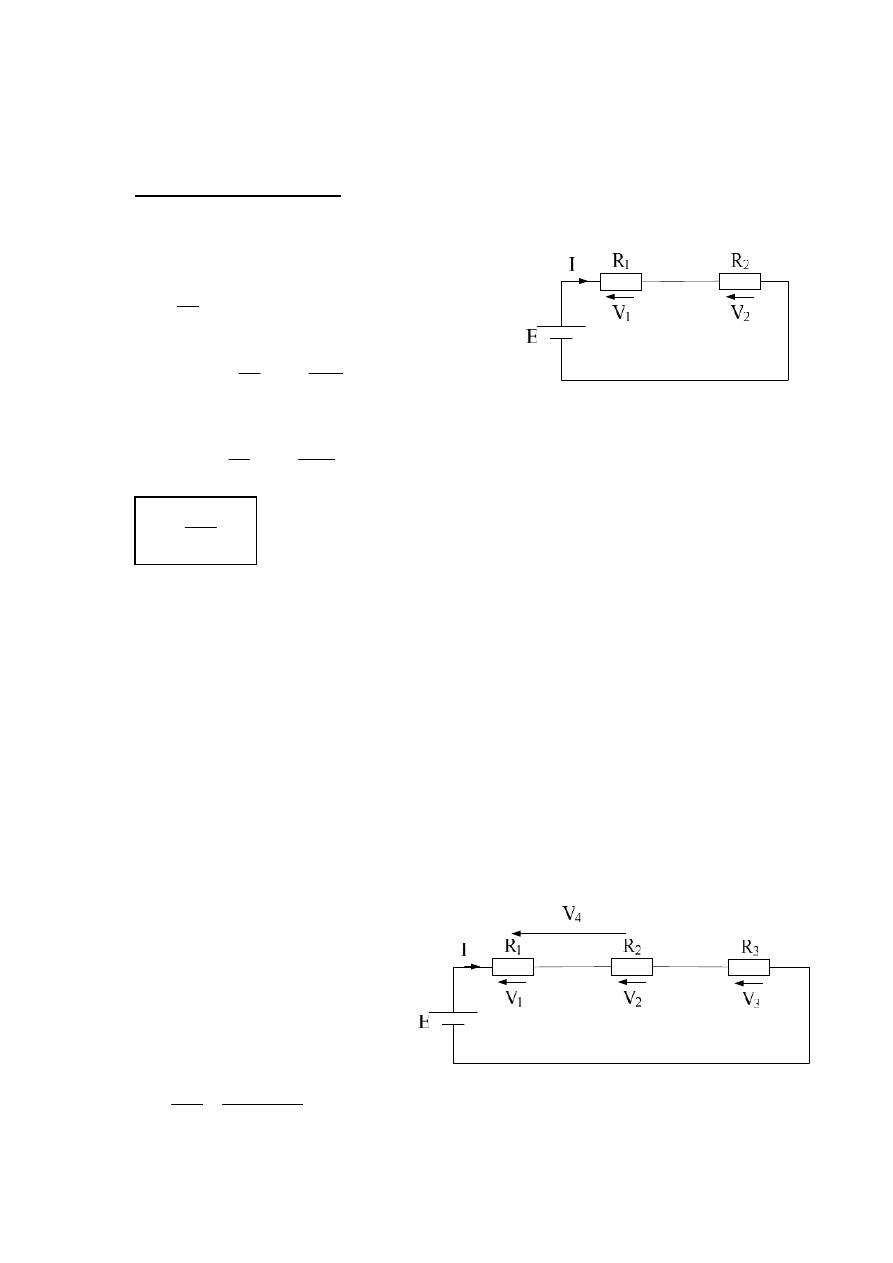
Example :- Using voltage divider rule , determine the voltage V
1
, V
2
, V
3
and
V
4
for the series circuit in figure below , given that ; R
1
= 2K
Ω , R
2
= 5KΩ ,
R
3
= 8KΩ , E = 45 V ?
Solution :-
R
T
= R
1
+ R
2
T
R
E
I
T
T
R
R
E
R
R
E
R
I
V
1
1
1
1
.
.
.
T
n
n
R
ER
V
V
R
E
R
V
T
6
10
*
15
45
*
10
*
2
3
3
1
1
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٠٣
-
V
R
E
R
V
T
15
10
*
15
45
*
10
*
5
3
3
2
2
V
R
E
R
V
T
24
10
*
15
45
*
10
*
8
3
3
3
3
V
R
E
R
R
V
T
21
10
*
15
45
*
10
*
7
3
3
2
1
4
or V
4
= V
1
+ V
2
= 21V
To check:
E
– V
1
– V
2
– V
3
= 0
E = V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
45 = 6 + 15 + 24
45 = 45
Active Potential :-
رﻣوز اﻻرﺿﻲ
a
b
V
a
= 14 V
V
b
= 8 V
V
ab
= 6 V
V
ab
is the voltage difference between the
point a and point b
V
ab
= V
a
– V
b
= 14
– 8 = 6V
V
ba
= V
b
– V
a
= 8
– 14 = - 6V
V
ab
= - V
ba
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
١٣
-
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
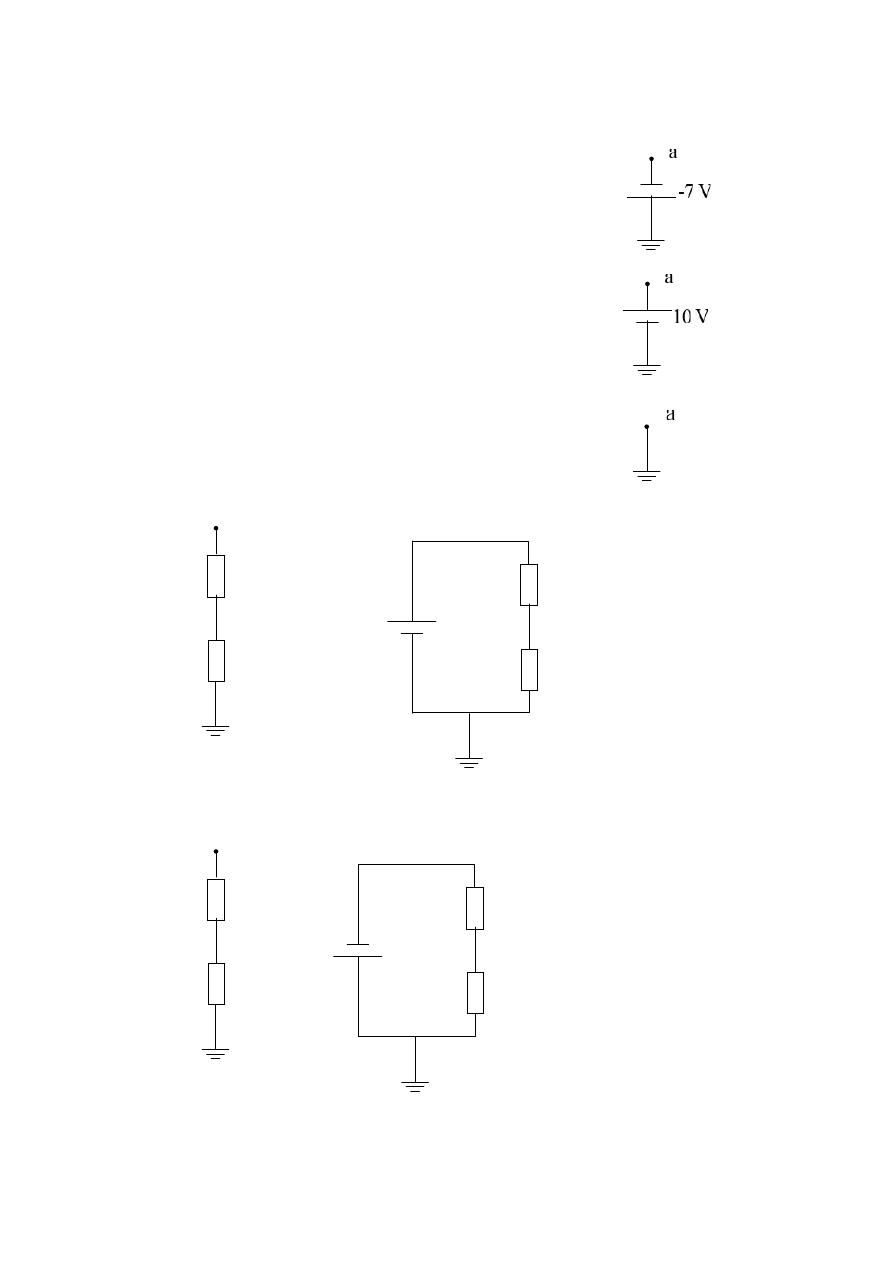
20 V
E = 20 V
R
1
R
2
R
1
R
2
-12 V
E = -12 V
V
a
= -7 V
V
a
= 10 V
V
a
= 0 V
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٢٣
-
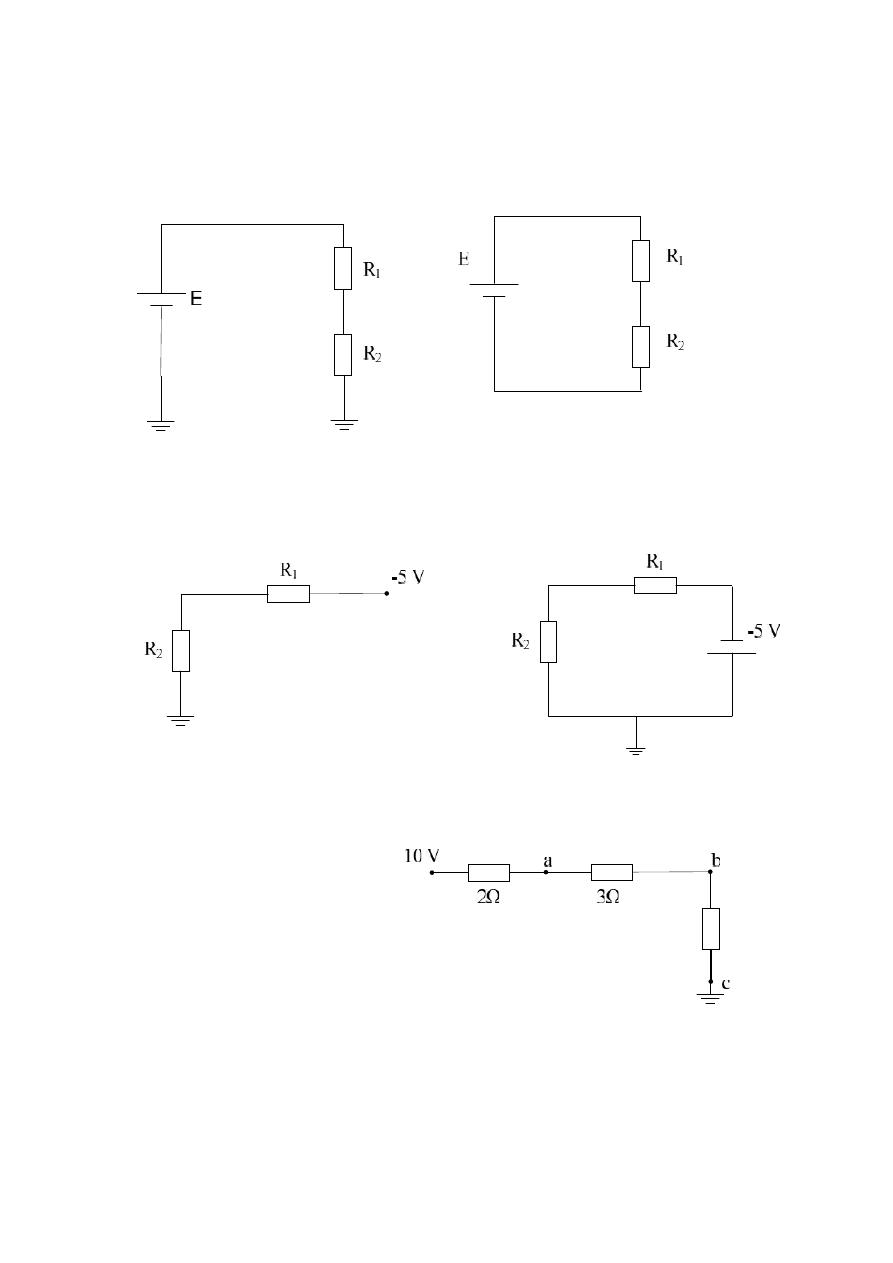
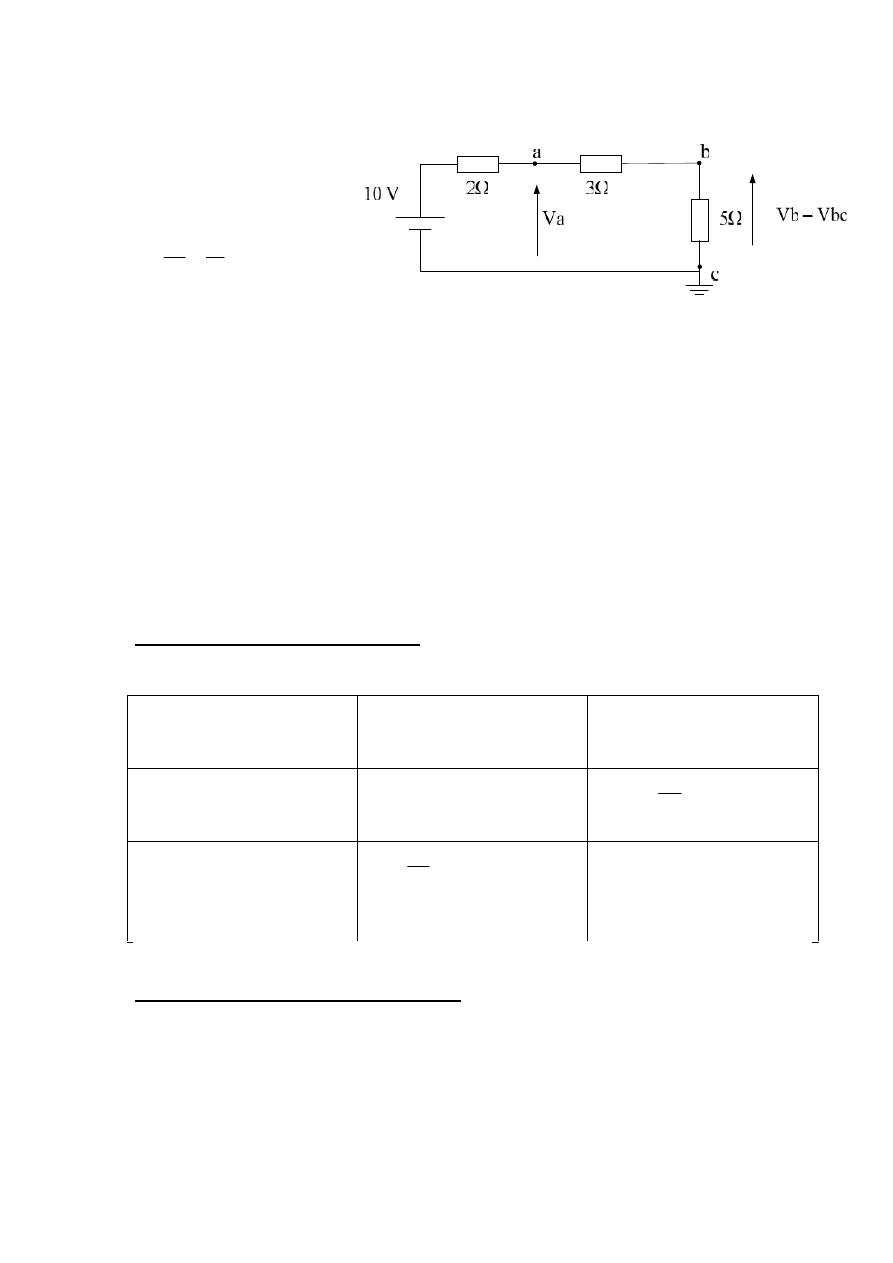
Example :- Find V
a
, V
b
, V
c
, V
ab
, V
ac
and V
bc
for the following diagram .
Solution :-
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٣٣
-
E
– V
2
– V
a
= 0
V
a
= E
– V
2
= 10
– (2 * 1) = 8 V
V
b
= V
5
= (1 * 5) = 5 V = V
bc
; V
c
= 0 V
or
E
– V
2
– V
3
– V
b
= 0
V
b
= E
– V
2
– V
3
= 10
– 2 – 3 = 5 V
V
ab
= V
a
– V
b
= 8
– 5 = 3 V
V
ac
= V
a
– V
c
= 8
– 0 = 8 V
V
bc
= V
b
– V
c
= 5
– 0 = 5 V
Equivalence of actual sources :-
Voltage
Source
Current
Source
Open
Circuit
Voc = E
I = 0
o
o
oc
G
I
V
1
Short
circuit
o
sc
R
E
I
V = 0
I
sc
= I
o
Kirchoff's Current Law ( K.C.L. ) :-
The algebraic sum of ingoing currents is equal to the out going currents
at any point .
out
in
I
I
Or , At any point , the algebraic sum of entering and leaving current is zero .
R
T
= R
1
+ R
2
+ R
3
= 2 + 5 + 3 = 10 Ω
A
R
E
I
T
1
10
10
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٤٣
-
0
I
I
1
I
5
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
1
+ I
2
+ I
4
= I
3
+ I
5
Or
I
1
+ I
2
+ I
4
- I
3
- I
5
= 0
At a
I
1
= I
2
+ I
3
13 + 5
– I = 0
Or
I
1
- I
2
- I
3
= 0
18
– I = 0
At b
I = 18 A
-I
1
+ I
2
+ I
3
= 0
b
a
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٥٣
-
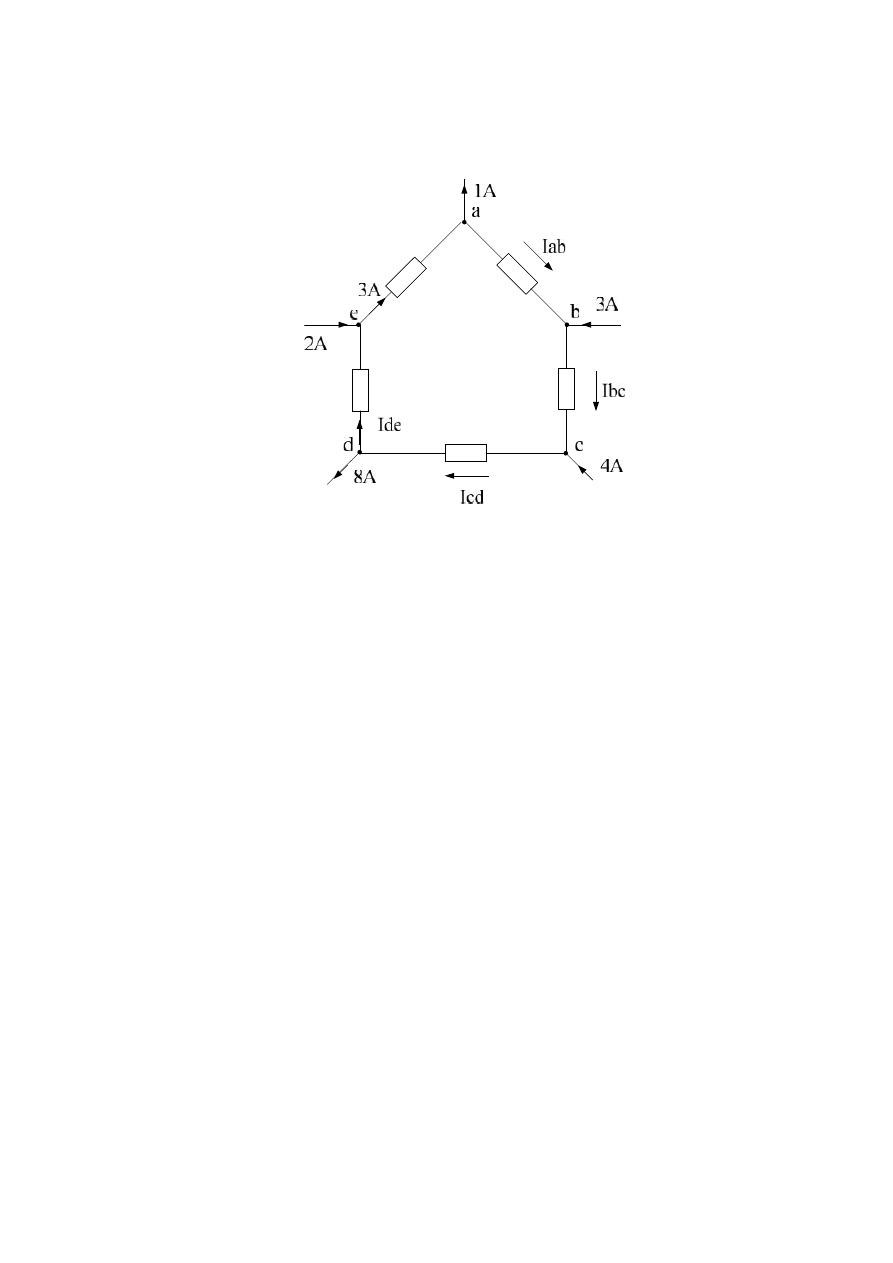
Example :- Find the current in each section in the cct. Shown ?
Solution :-
At node a
3
– 1 – I
ab
= 0
2
– I
ab
= 0
I
ab
= 2 A
At node b
I
ab
+ 3
– I
bc
= 0
2 + 3
– I
bc
= 0
I
bc
= 5 A
At node c
I
bc
+ 4
– I
cd
= 0
5 + 4
– I
cd
= 0
I
cb
= 9 A
At node d
I
cd
– 8 – I
de
= 0
9
– 8 – I
de
= 0
I
de
= 1 A
At node e
2
– 3 + I
de
= 0
2
– 3 + 1 = 0
0 = 0 check .
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٦٣
-
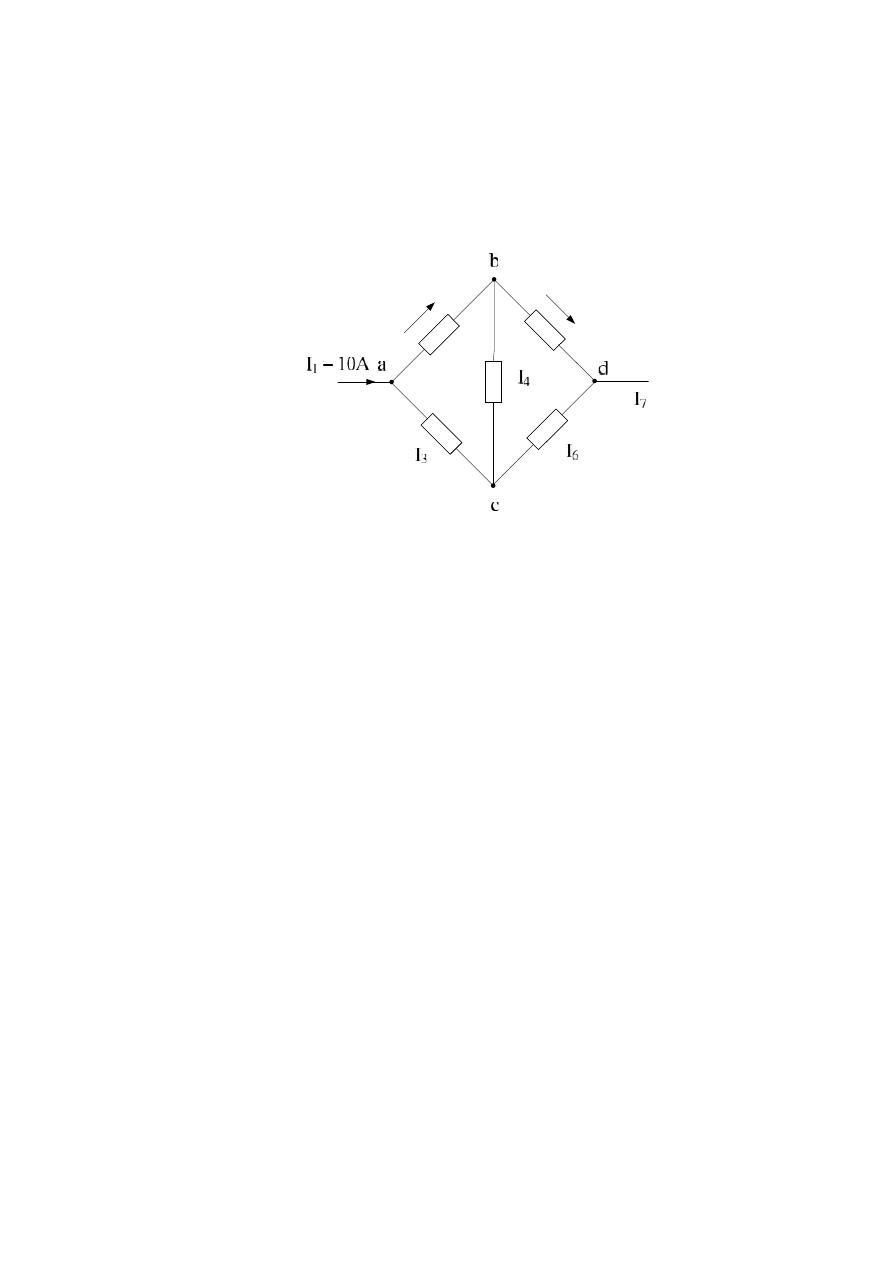
Example :- Find the magnitude and direction of the currents I
3
, I
4
, I
6
, I
7
in the
following cct. Diagram?
I
2
= 1
2A
I
5
= 8A
Solution :-
leave
enter
I
I
I
1
= I
7
= 10 A
At node a ; suppose I
3
is entering
I
1
+ I
3
– I
2
= 0
10 + I
3
– 1
2
= 0
I
3
= 2 A
At node b;
I
2
enter , I
5
leave ,
I
4
must be leaving
I
2
= I
5
+ I
4
12 = 8 + I
4
I
4
= 12
– 8 = 4 A
At node c;
I
4
enter , I
3
leave ,
I
6
leave
I
4
= I
3
+ I
6
4 = 2 + I
6
I
6
= 2 A
At node d;
I
5
and I
6
enter , I
7
leave
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٧٣
-
I
7
= I5 + I
6
10 = 8 + 2
10 = 10
Ok.
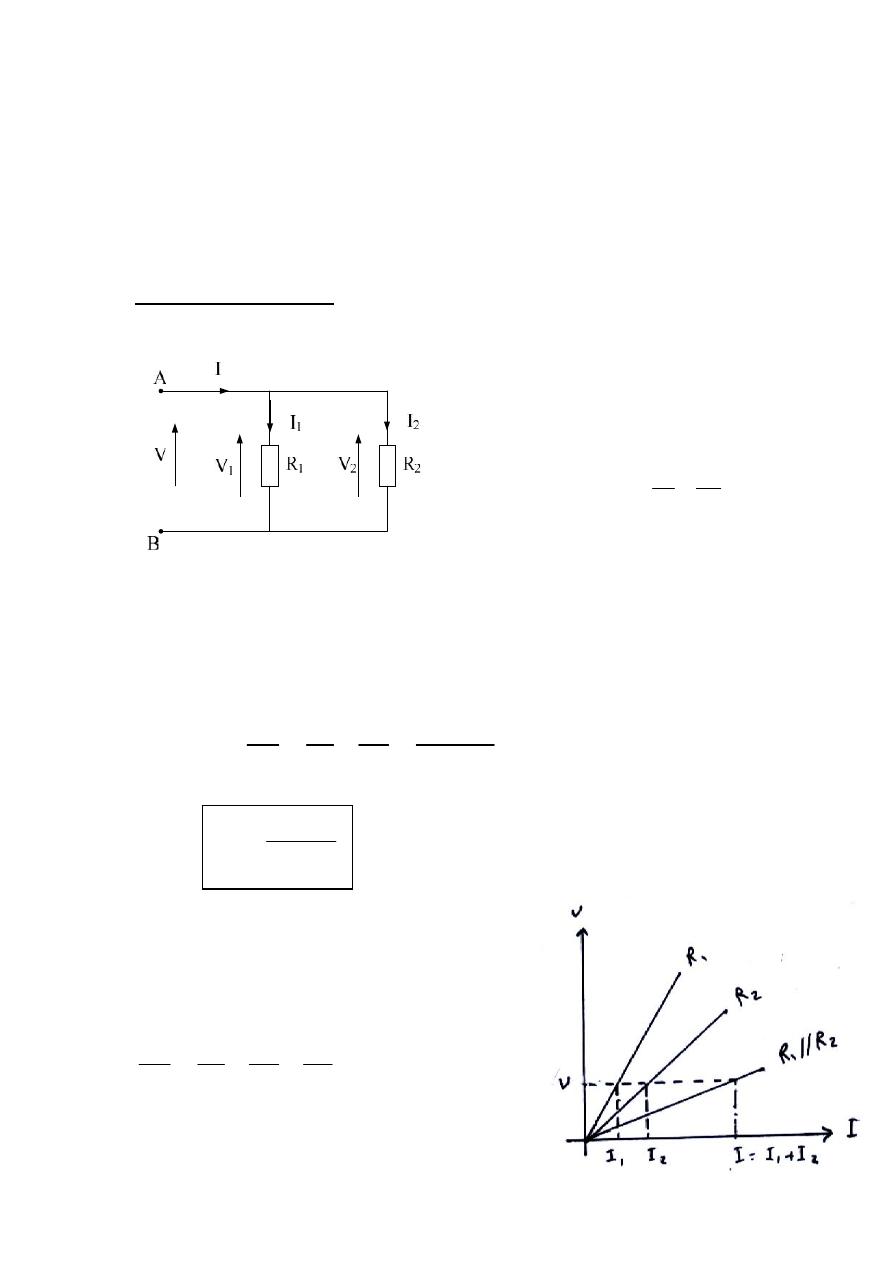
Resisters in Parallel :-
or
I = V ( G
1
+ G
2
)
I = VG
T
Where
G
T
= G
1
+ G
2
Hence
2
1
2
1
2
1
.
1
1
1
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
T
or
In the same minner , if we have three resistors
in parallel , then:
3
2
1
1
1
1
1
R
R
R
R
T
From K.V.L.
V = V
1
= V
2
From K.C.L.
I = I
1
+ I
2
From Ω.L.
2
2
1
1
R
V
R
V
I
= V
1
G
1
+ V
2
G
2
= V
1
( G
1
+ G
2
)
2
1
2
1
.
R
R
R
R
R
T
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٨٣
-
3
2
1
2
1
3
1
3
2
.
.
.
.
.
1
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
T
2
1
3
1
3
2
3
2
1
.
.
.
.
.
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
T
And , if we have N of parallel resistance , then
N
T
R
R
R
R
R
1
1
1
1
1
3
2
1
Also
P
T
= P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
1
2
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
R
V
R
I
I
V
P
Source power
T
T
T
T
T
s
R
E
R
I
EI
P
2
2
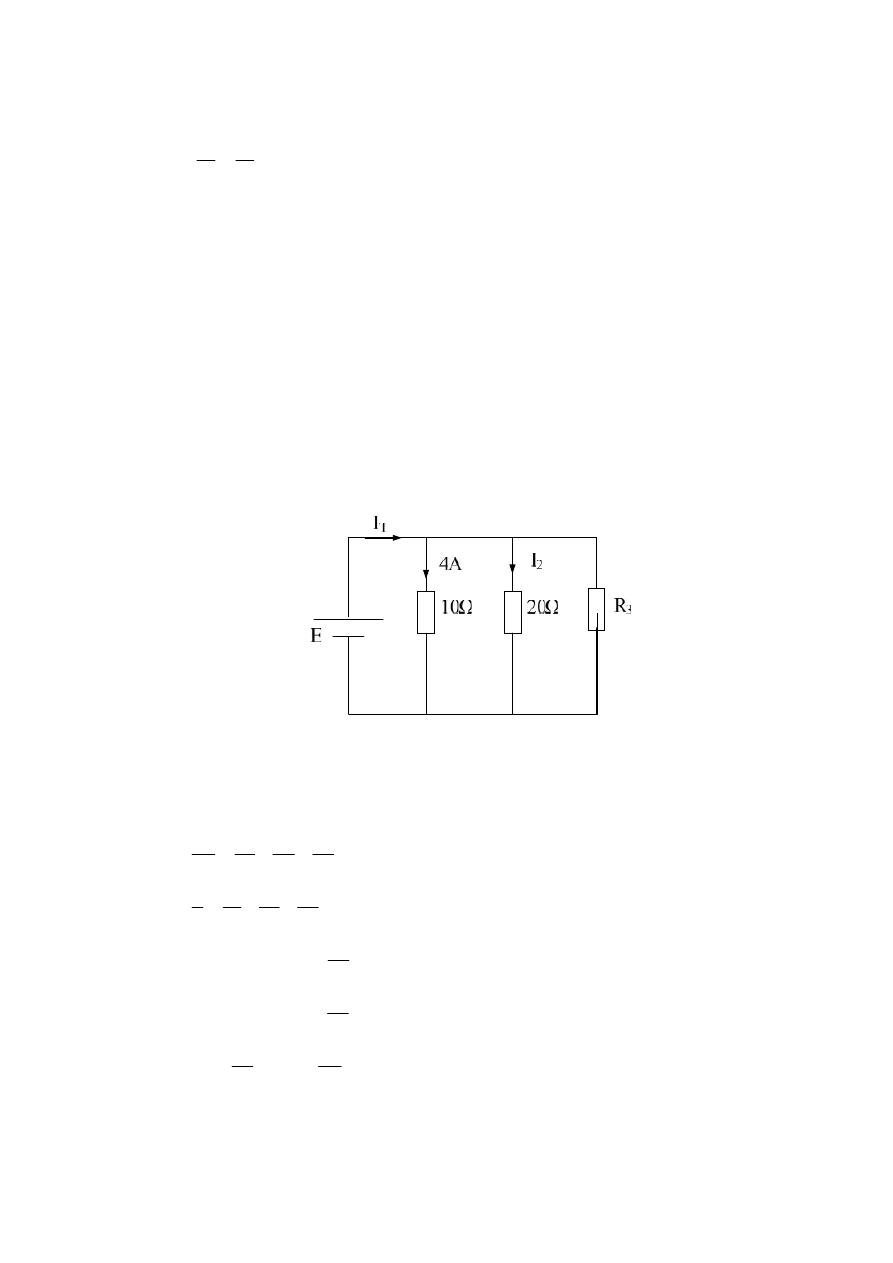
Example :- For the following cct. Find R
T
, P
T
, I
T
, I
b
?
Solution :-
ﻓﻲ ﺣﺎﻟﺔ ﻛون ﻗﯾم اﻟﻣﻘﺎوﻣﺎت ﻣﺗﺳﺎوﯾﺔ
2
4
8
N
R
R
T
A
R
E
I
T
T
8
2
16
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٩٣
-
A
R
E
I
branch
2
8
16
1
W
R
I
P
T
T
T
128
2
.
8
2
2
or
P
T
= E.I
T
= 16 * 8 = 128W
or
P
T
= P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
+ P
4
W
128
32
32
32
32
8
*
2
8
*
2
8
*
2
8
*
2
2
2
2
2
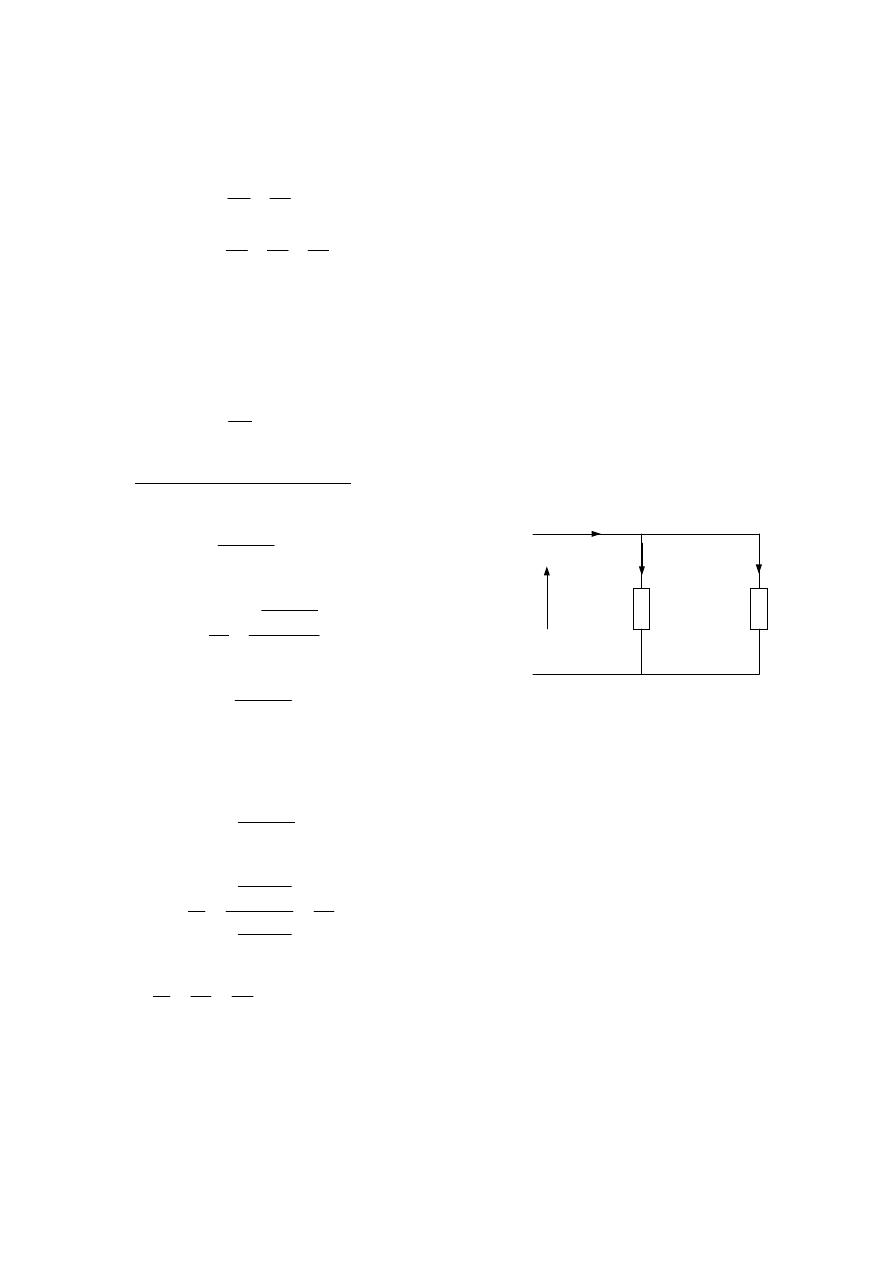
Example :- For the parallel network in fig. below , find :-
a) R
3
, b) E , c) I
T
, I
2
, d) P
2
; given that R
T
= 4 Ω ?
Solution :-
a)
10
1
.
0
1
1
1
.
0
1
05
.
0
1
.
0
25
.
0
1
05
.
0
1
.
0
25
.
0
1
20
1
10
1
4
1
1
1
1
1
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
1
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
R
T
b)
E = V
1
= I
1
R
1
= 4 * 10 = 40 V
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٠٤
-
c)
d)
W
R
I
P
80
20
.
2
2
2
2
2
2
or
2
2
2
2
R
V
P
, or P
2
= I
2
V
2
Current division Rule :-
R
1
R
2
I
2
I
1
I
V
In the same miner
2
1
1
2
R
R
R
I
I
Also
1
2
2
1
1
2
1
2
2
1
R
R
R
R
R
I
R
R
R
I
I
I
2
1
1
2
2
1
G
G
R
R
I
I
A
R
E
R
V
I
A
R
E
I
T
T
2
20
40
10
4
40
2
2
2
2
2
1
2
1
.
R
R
R
R
I
V
1
2
1
2
1
1
1
.
R
R
R
R
R
I
R
V
I
2
1
2
1
R
R
R
I
I
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
١٤
-
Example :- For the following circut. , find V , I
1
and I
2
?
100Ω
0.1Ω
I
2
I
1
5A
V
Solution :-
0999
.
0
1
.
100
10
1
.
0
100
1
.
0
*
100
.
2
1
2
1
R
R
R
R
R
T
V = I . R
T
= 5 * 0.0999 = 0.4995 V
A
V
I
004995
.
0
100
1
A
V
I
995
.
4
1
.
0
2
To check
I = I
1
+ I
2
5 = 0.004995 + 4.995
5 = 5 Ok.
Example :- Determine the resistance R1 in the figure below?
Solution :-
I = I
1
+ I
2

Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (4))
-
٢٤
-
or
I
2
= I
– I
1
= 27
– 21 = 6 mA
V
2
= I
2
R
2
= 6 * 10
-3
* 7 = 42 mV
V
1
= V
2
= 42 mV
2
10
*
21
10
*
42
3
3
1
1
1
I
V
R
or
2
7
7
*
10
*
27
10
*
21
1
1
3
3
2
1
2
1
R
R
R
R
R
I
I
