Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٢٤
-
Voltage Regulation :-
Voltage Regulation
%
100
%
FL
FL
NL
R
V
V
V
V
Where
V
NL
= No load voltage
V
FL
= Full load voltage
Also we can write
%
100
%
.
int
L
R
R
R
V
Where
R
int.
= Internal resistor .
R
L
= load resistor .
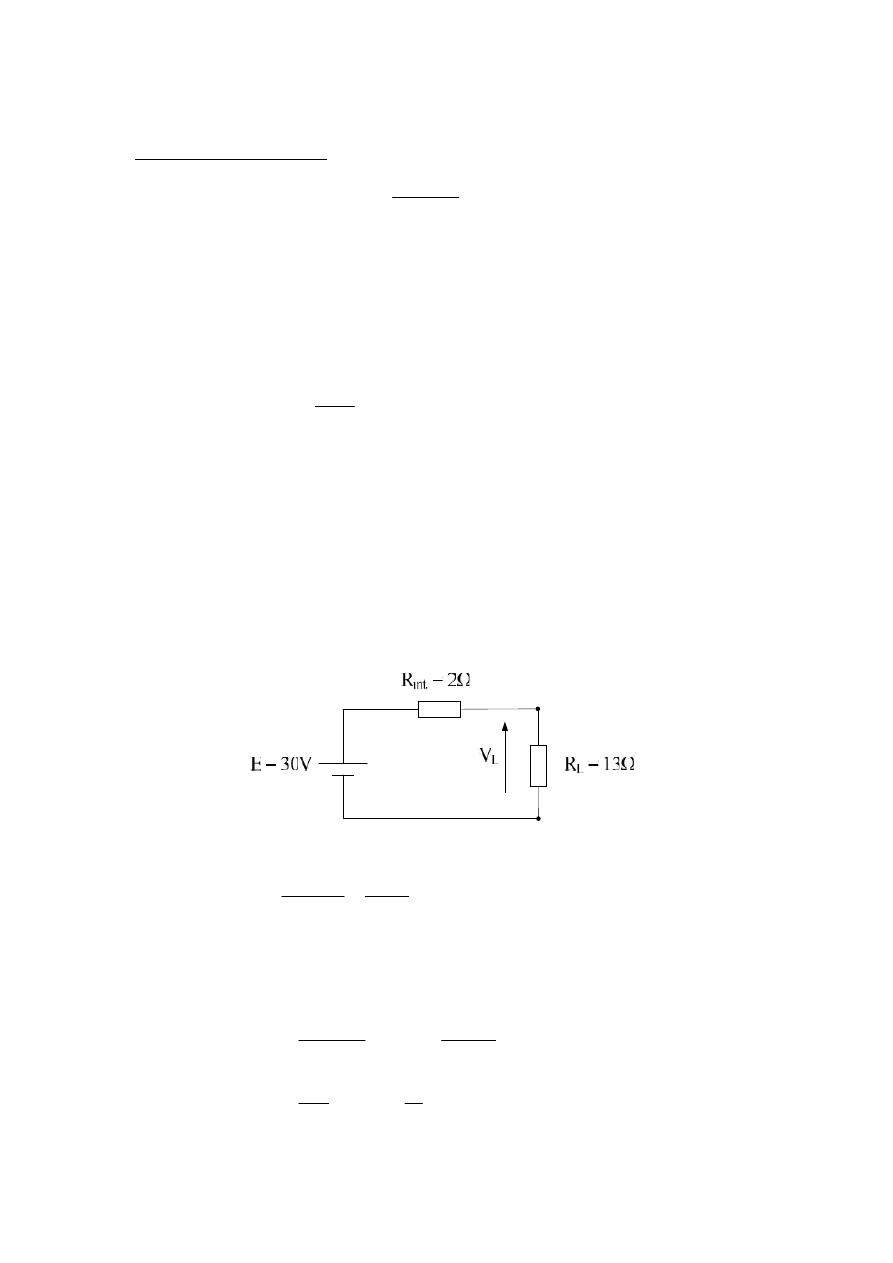
Example :- Find the voltage V
L
and power lost to the internal resistance , if the
applied load is 13
Ω , also find the voltage regulation ?
Solution :-
A
R
R
E
I
L
L
2
13
2
30
int
V
R
I
E
V
L
L
26
2
*
2
30
.
int
W
R
I
P
L
loss
8
2
.
2
2
.
int
2
%
385
.
15
%
100
26
26
30
%
100
%
FL
FL
NL
R
V
V
V
V
or
%
385
.
15
%
100
13
2
%
100
%
.
int
L
R
R
R
V
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٣٤
-
Example :- Find the current I
1
, for the network shown:
R1 = 6Ω
I
1
I = 42 mA
R
2
=24Ω
R
3
=24Ω
Solution :- All resistance in parallel , so if we define that R = R
2
// R
3
then :-
12
24
24
24
*
24
3
2
3
2
R
R
R
R
R
Hence
mA
R
R
R
I
I
28
6
12
12
10
*
42
3
1
1
Example :- Calculate I & V for the network shown
Solution :- We have a short circuit on R
2
resistance , hence no current through
R
2
, hence the above cct. Can redrawn as fellows:
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٤٤
-
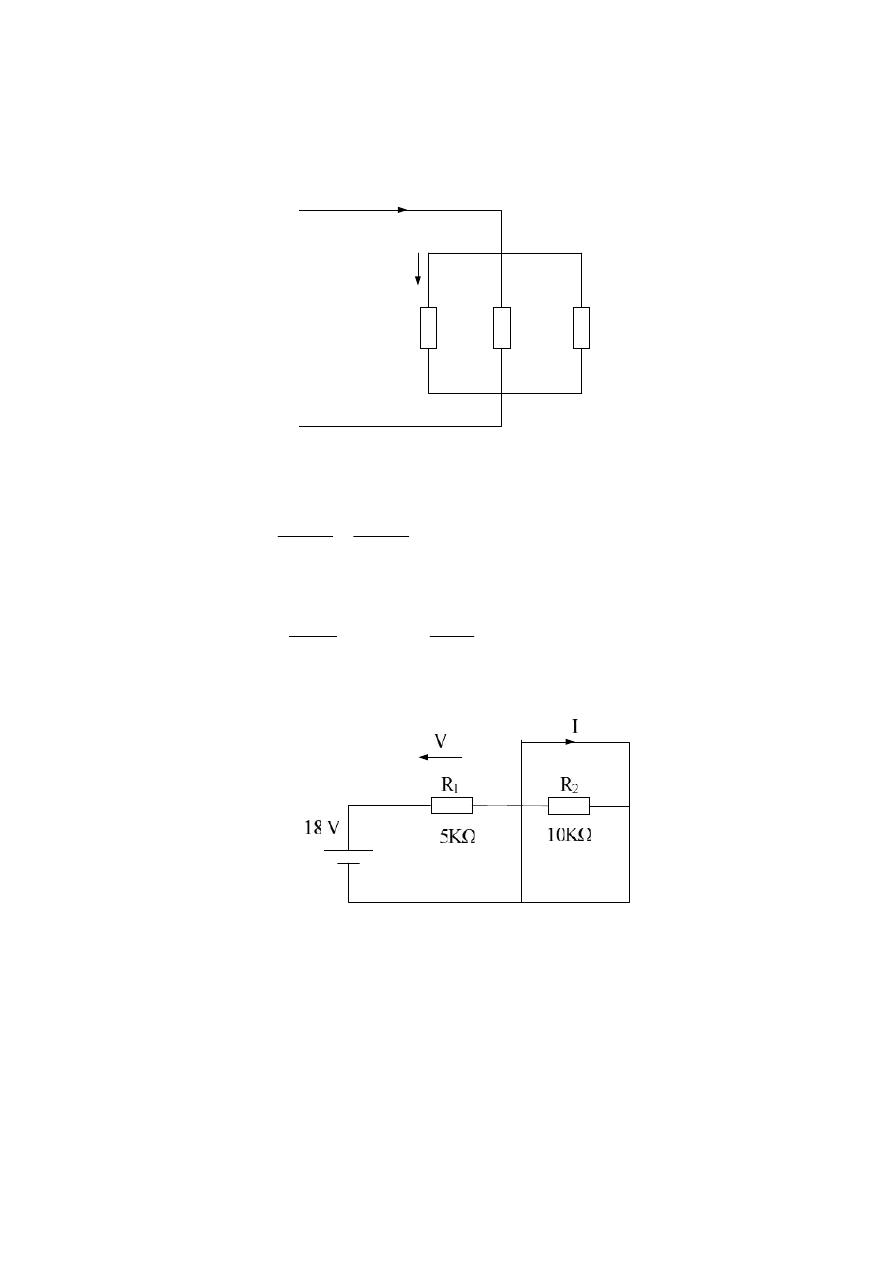
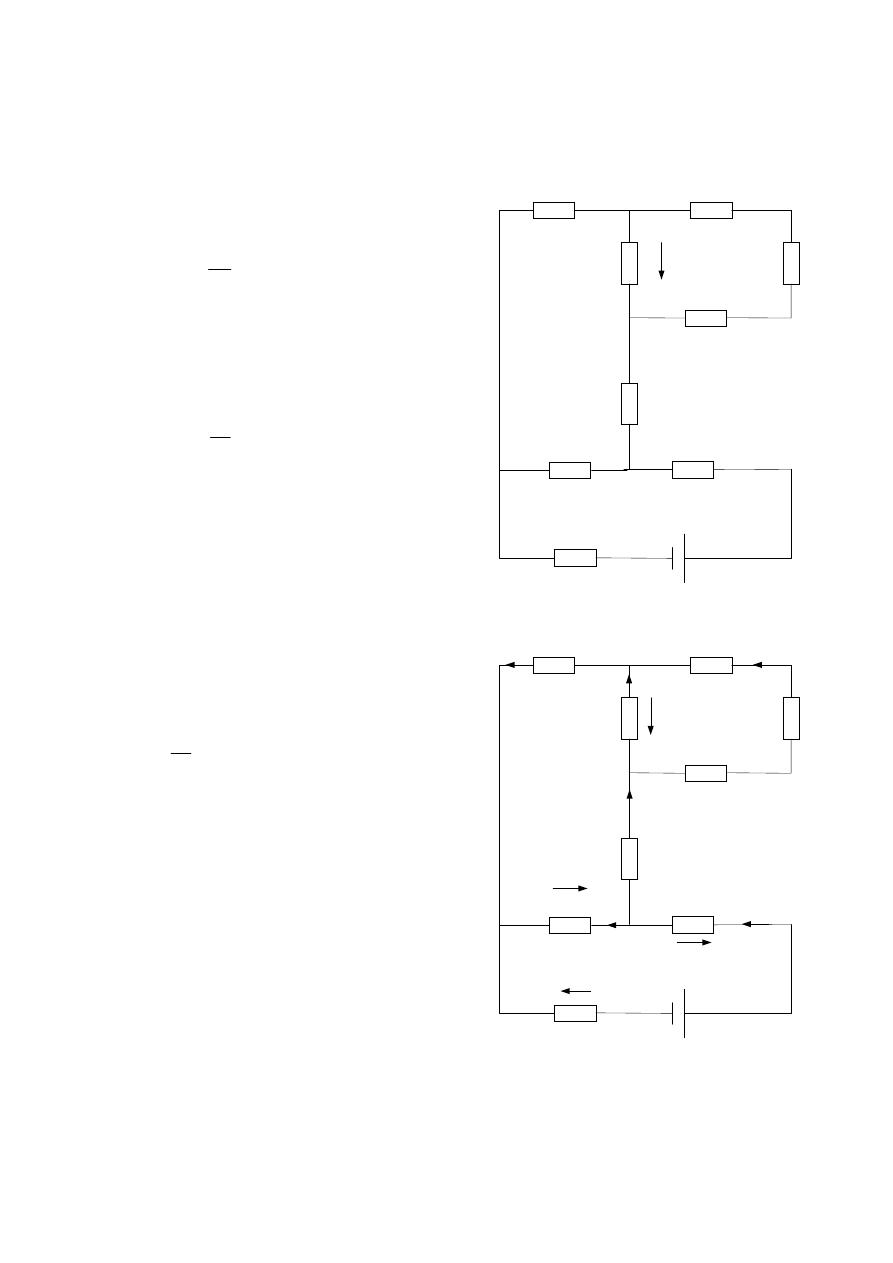
Example :- For the following cct. Network , find R
T
, I
A
, I
B
, I
C
, V
A
, V
B
, I
1
,
I
2
?
Solution :-
mA
R
E
R
E
I
T
6
.
3
10
*
5
18
3
1
V
E
R
I
V
18
.
1
6
.
3
6
9
6
*
9
2
1
2
1
R
R
R
R
R
A
R
B
= R
3
+ R
4
// R
5
6
3
6
3
*
9
4
R
C
= 3 Ω
R
T
= R
A
+ R
B
// R
C
6
.
5
3
6
3
*
6
6
.
3
A
R
E
I
T
A
3
6
.
5
8
.
16

Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٥٤
-
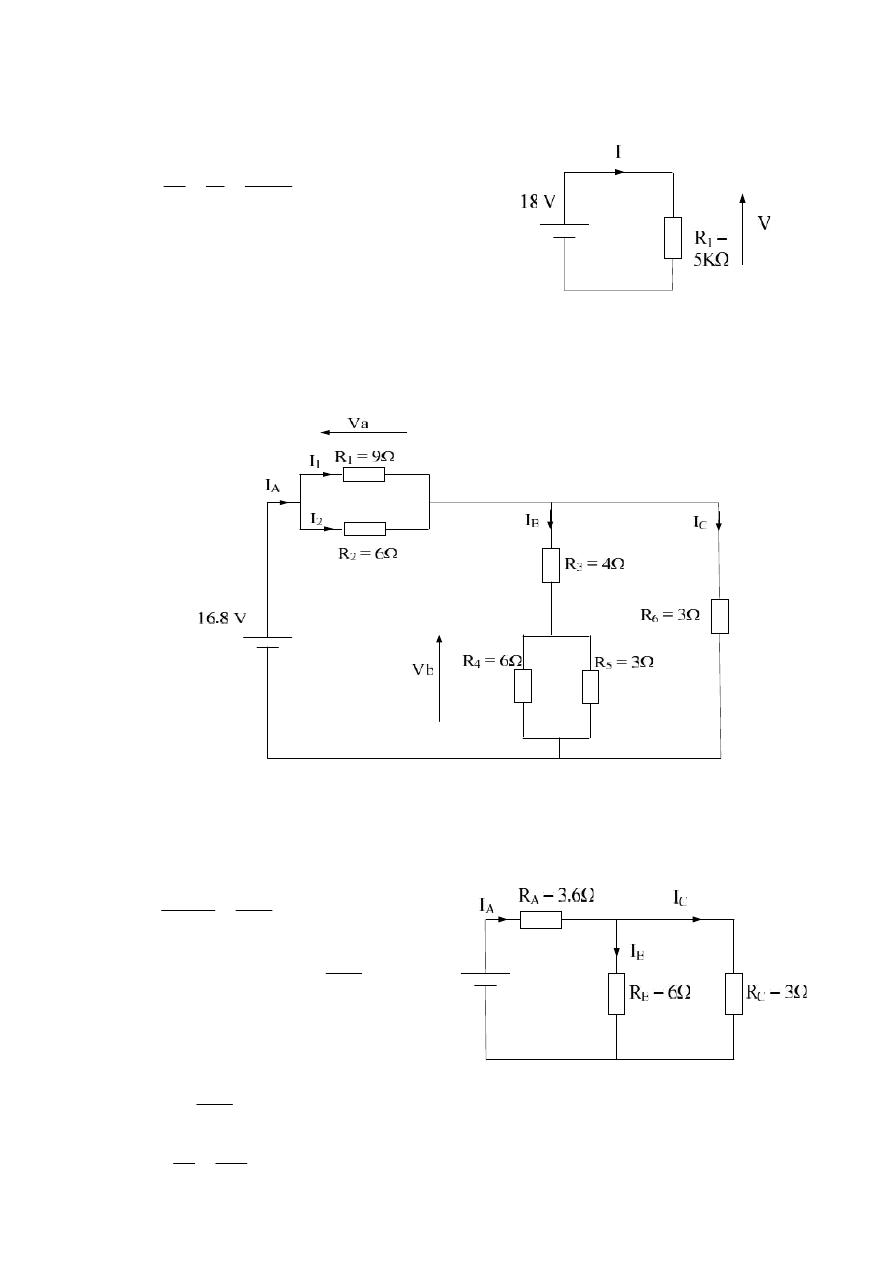
Apply C.D.R.
A
R
R
R
I
I
C
B
C
A
B
1
6
3
3
*
3
By K.C.L.
I
C
= I
A
– I
B
= 3
– 1 = 2 A
V
A
= I
A
R
A
= 3 * 3.6 = 10.8 V
V
B
= I
B
R
B
= 1 * 6 = 6 V = V
C
A
R
R
R
I
I
A
2
.
1
9
6
3
*
6
2
1
2
1
I
2
= I
A
– I
1
= 3
– 1.2 = 1.8 A
To check
E
– V
A
– V
B
= 0
16.8
– 10.8 – 6 = 0
0 = 0
Ok.
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٦٤
-
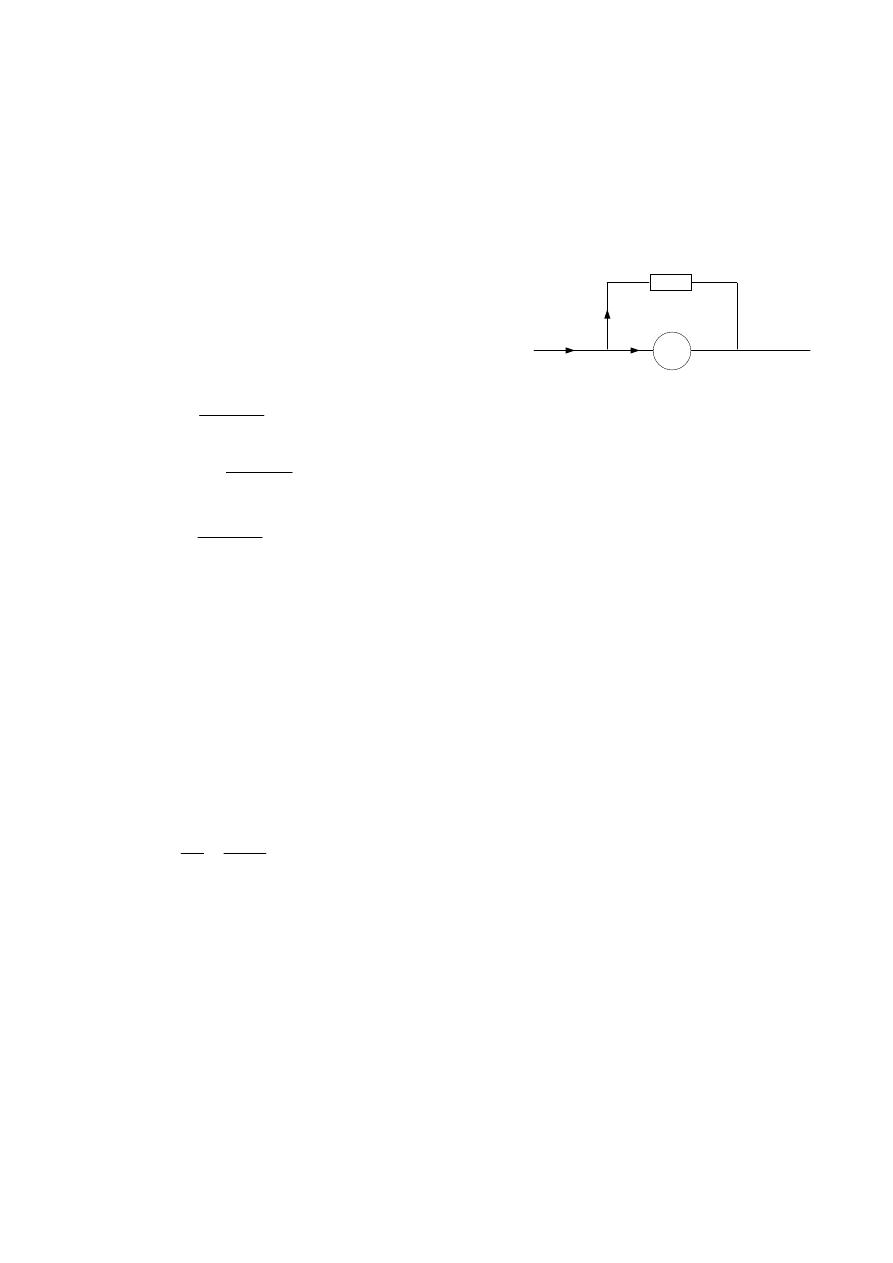
Example :- Find the resistor required to connect in parallel with the ammeter to
flow 1.2 A , if you know that the fsd ( full scale deflection ) of ammeter is 120
mA , and
the resistance of ammeter is 2.7 Ω ?
R
sh
I
sh
I = 1.2A 0.12A
A
* Another Solution:
324
.
0
7
.
2
12
.
0
A
V
V
A
I
sh
08
.
1
12
.
0
2
.
1
3
.
0
08
.
1
324
.
0
sh
A
sh
I
V
R
Solution :-
From K.C.L.
A
I
sh
08
.
1
12
.
0
2
.
1
sh
sh
A
A
sh
R
R
R
R
I
I
7
.
2
7
.
2
2
.
1
08
.
1
3
.
0
08
.
1
324
.
0
08
.
1
916
.
2
24
.
3
7
.
2
08
.
1
24
.
3
7
.
2
24
.
3
08
.
1
sh
sh
sh
sh
sh
R
R
R
R
R
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٧٤
-
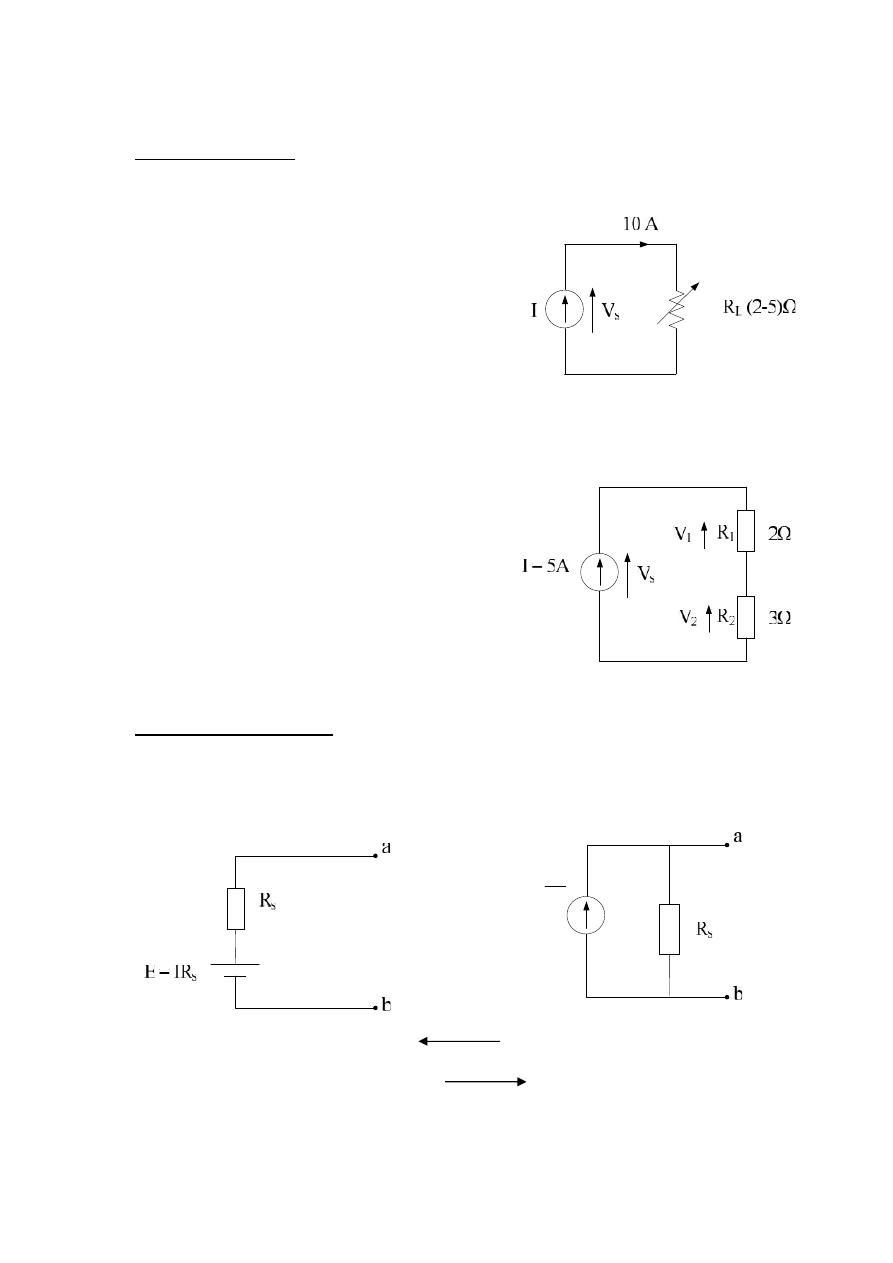
Example :- for the following cct. Network , Given that (V= 24 v), Find E ?
8Ω
E
24Ω
8Ω
4Ω
4Ω
16Ω
12Ω
6Ω
6Ω
V
8Ω
E
24Ω
8Ω
4Ω
4Ω
16Ω
12Ω
6Ω
6Ω
V
V
1
V
2
I
5
B
V
3
C
I
6
I
4
D
I
2
A
I
3
I
1
Solution :-
A
I
2
2
.
1
24
1
The same voltage ( V = 24 V ) on the
resistor R
a
=
4 +16 + 4 = 24 Ω
Hence
A
I
1
24
24
2
A
I
I
I
3
2
1
3
Also from K.C.L. I
4
= I
3
= 3A
Take the closed loop ABCDA , from
K.V.L.
V
1
– 6I
4
– V – 6I
3
= 0
V
1
= 6 * 3 + 24 + 6 * 3
V
V
60
1
A
I
5
.
2
24
60
5
A
I
I
I
5
.
5
3
5
.
2
4
5
6
Take the closed loop CBC
– V
1
– V
2
+ E
– V
3
= 0
E = V
1
+ V
2
+ V
3
E = 60 + 5.5 * 8 + 5.5 * 8
= 60 + 44 + 44
E = 148 V
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٨٤
-
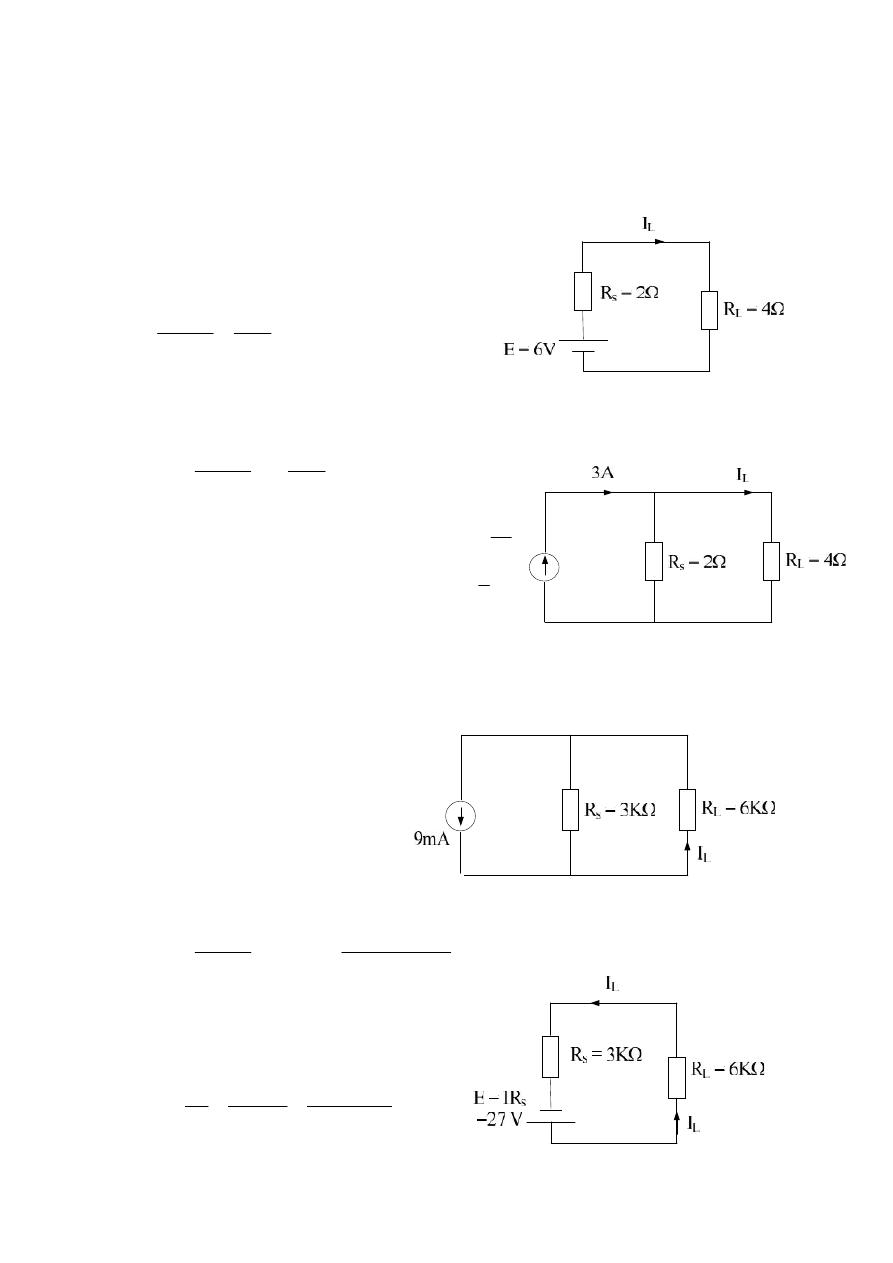
Current Source :-
Example :- Find the voltage ( V
s
) for the circuit below:
Example :- Calculate V
1
, V
2
, V
s
for the following cct.:
Source Conversions :-
A voltage source with voltage E and series resistor R
s
can be replaced by
a current source with a current I and parallel resistor R
s
as shown :-
s
R
E
I
Current source to voltage source
Voltage source to current sourc
Solution :-
V
s
= IR
L
= 10 * 2 = 20 V
if R
L
= 2 Ω
V
s
= IR
L
= 10 * 5 = 50 V
if R
L
= 5 Ω
Solution :-
V
1
= IR
1
= 5 * 2 = 20 V
V
2
= IR
2
= 5 * 3 = 15 V
V
s
= V
1
+ V
2
= 10 + 15 = 25 V
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٩٤
-
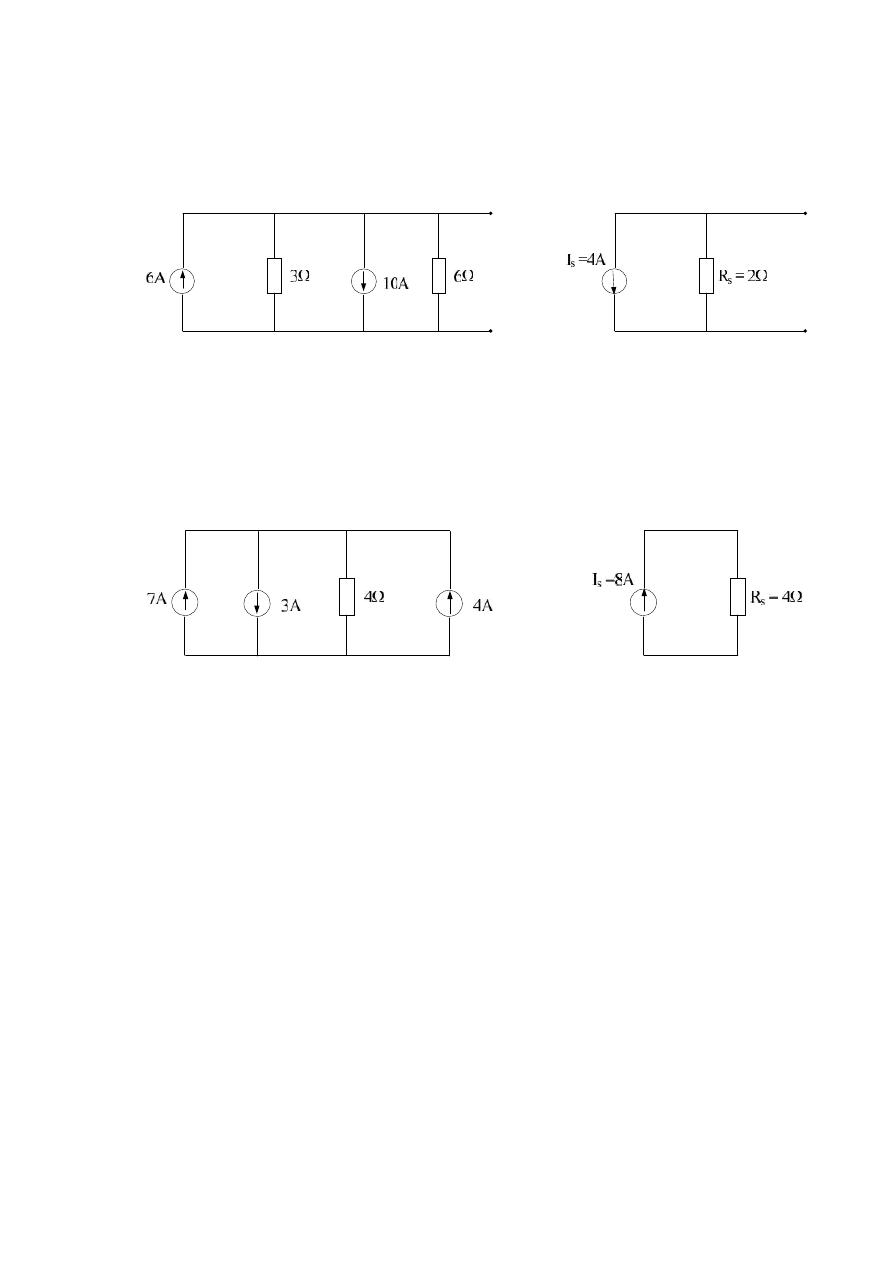
Example :- Convert the voltage source in the cct. Below to a current source,
then calculate the current through the load for each source:
A
R
E
I
s
3
2
6
Example :- Convert the current source in the cct. Shown below to a voltage
source and determine I
L
for each cct.:
Solution :-
For the current cct.
mA
I
R
R
R
I
I
L
L
s
s
L
3
10
*
6
10
*
3
10
*
3
10
*
9
3
3
3
3
For the voltage source cct.
mA
I
R
R
E
R
E
I
L
L
s
T
L
3
10
*
6
3
27
3
Solution :-
A
R
R
E
I
L
s
L
1
4
2
6
For the current source cct.
A
R
R
R
I
I
L
s
s
L
1
4
2
2
3
ﻻﺣظ ان
I
L
ﻣﺗﺳﺎوي ﻓﻲ اﻟﺣﺎﻟﺗﯾن و ﻫذا
ﺻﺣﯾﺢ
.
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
٠٥
-
Current source in parallel :-
I
s
= 10
– 6 = 4 A & R
s
= 3
Ω // 6 Ω = 2 Ω
Example :-
I
s
= 7
– 3 + 4 = 8 A
Dr. Sameir Abd Alkhalik Aziez
University of Technology Lecture (5))
-
١٥
-
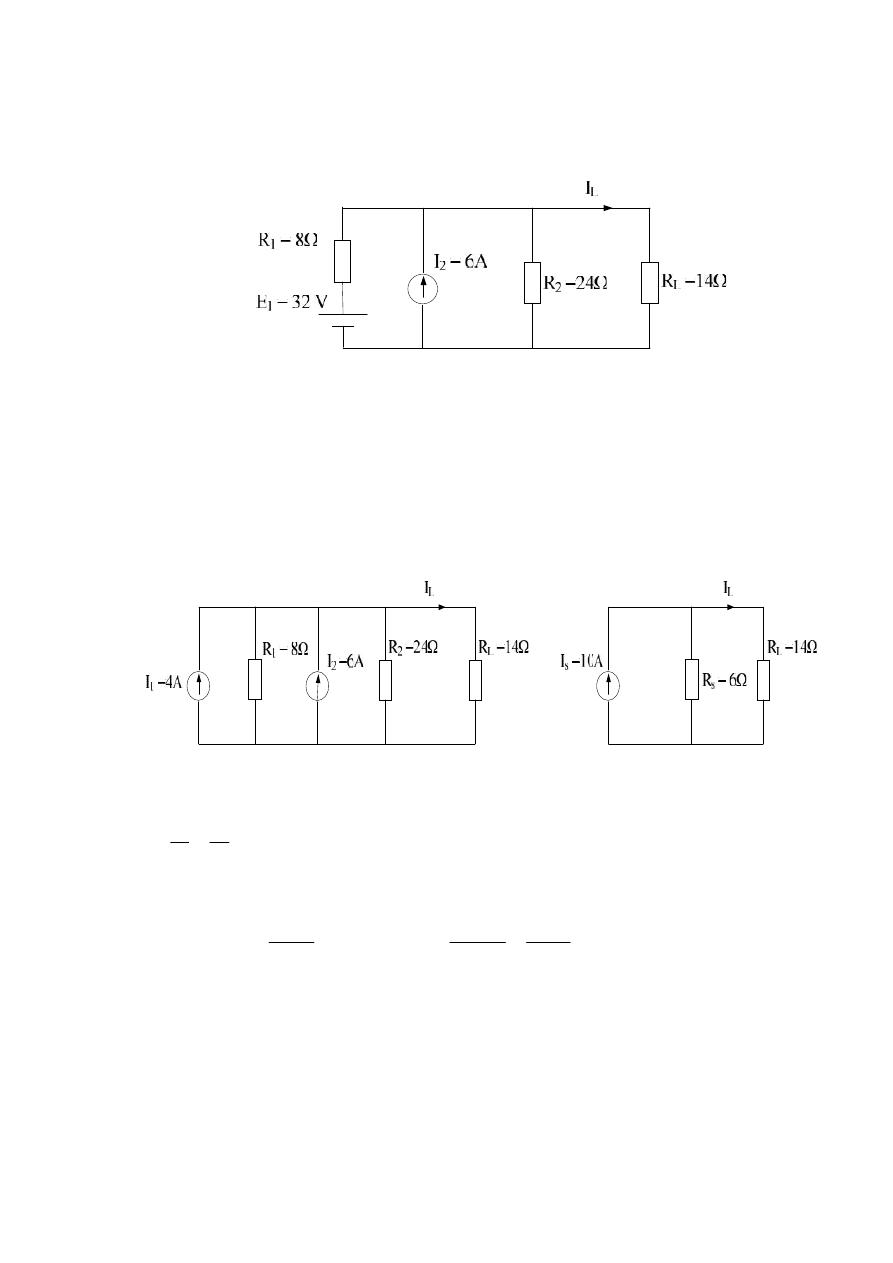
Example :- Find the load current in the following cct.:
Solution :-
A
R
E
I
4
8
32
1
1
Is = I
1
+ I
2
= 4 + 6 = 10 A
R
s
= R
1
// R
2
A
R
R
R
I
I
L
s
s
s
L
3
14
6
6
*
10
6
24
8
24
*
8
