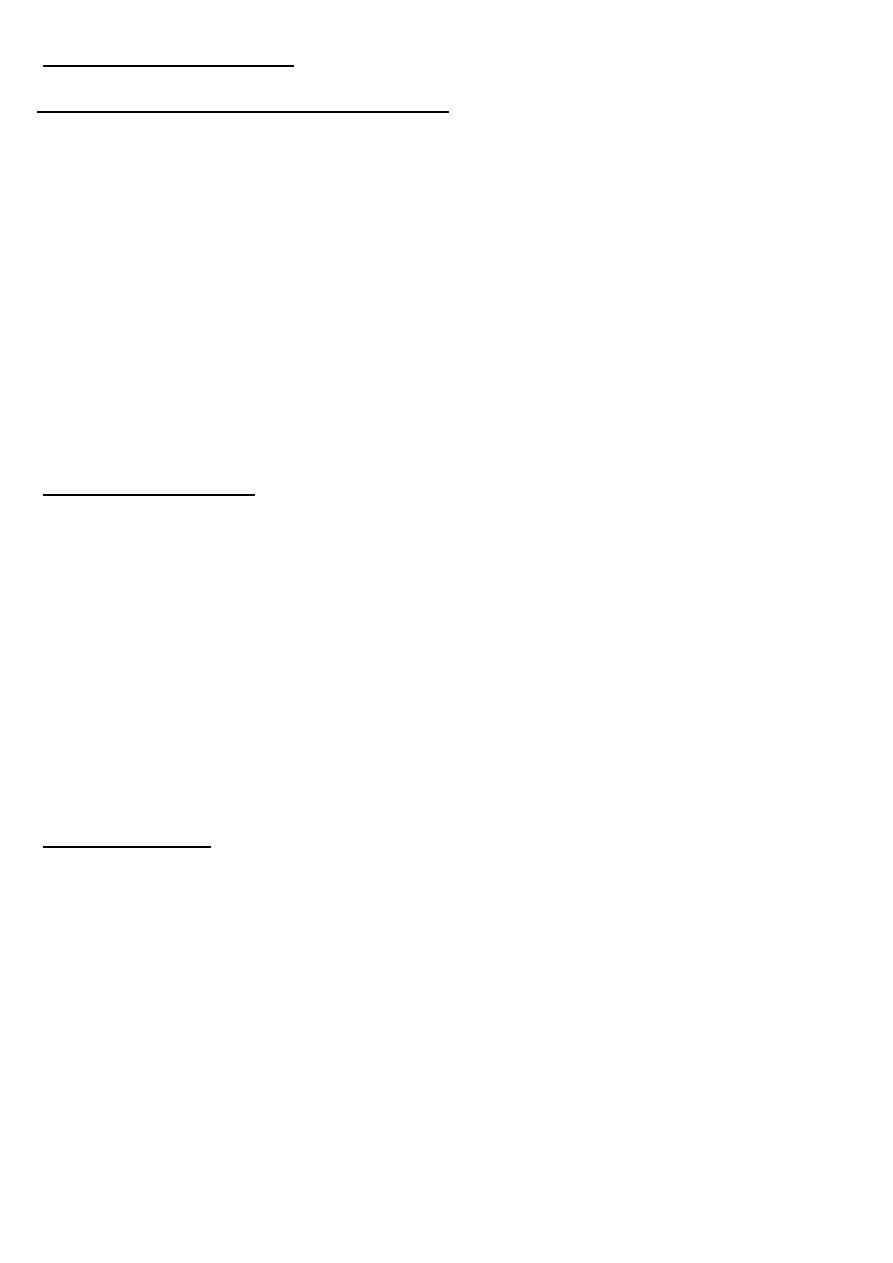
Urinary Tract Infections
Pathogenesis of Urinary tract infections
- :There are 4 possible modes of bacteria entry into the urinary tract
.Ascending infection both men and women (1
.Hematogenous in neonates (2
. Lymphatogenous spread is rare ( 3
Direct extension of infection from neighboring organs may occur in certain ( 4
.circumstances
Kidney infections
Acute pyelonephritis
– bacterial infection
,inflammation of the parenchyma and pelvis of the kidney
Ecoli 80% of the cases, klebsiella , proteus , pseudomonas, enterococci and
. staphylococcus are occasional pathogens
Ascending route from the lower urinary tract
. heamatogenus spread - staphylococcal bacteremia - renal abscesses
Clinical features
, classical presentation abrupt onset of fever chills flank pain
lower urinary tract symptoms including dysuria, frequency and urgency
. nausea , vomiting and malaise accompany more specific infection
On physical examination, the patient appears ill, febrile, tachycardia, tenderness
over the loin, some time paralytic ileus, abdominal distention, tenderness may be
found.in severe cases patient may present in shock state

Diagnosis
CBC +ESR +GUE
U / S may show obstruction
IVU may show abnormalities , general or focal renal enlargement (IVU not done
(while patient still ill
CT is very helpful,may show obstruction by ureteric stone , Radionuclide study
. may be necessary in complicated cases
Management..YOU SHOULD RELEIVE OBSTRUCTION IF PRESENT
ill and toxic hospitalization is needed, bed rest intravenous fluid, antipyretic and
parenteral antibiotics ( aminoglycoside plus ampicillin.3
rd
or 4
th
generation
. ( ceohalosporines,IV quinolones
If not toxic then treatment done as an outpatient, empiric antibiotics -
. ( fluroquinolones or TMP- SMX ) , therapy should continue for 10-14 days
Complications
usually resolves without complications, common complications are septicemia,
shock, and renal abscess, in children may cause scaring and permanent diminution
.of the renal function
Chronic pyelonephritis
Etiology & Pathogenesis
It refers to a process of renal scarification and atrophy resulting in renal
insufficiency , Repeated pyelonephritis, diabetes , calculi , analgesic nephropathy ,
and obstructive uropathy in the presence of repeated UTI can all cause loss of renal
function in adult , in children the most common cause is VUR ( vesicoureteric
. reflux ) and reflux nephropathy

Clinical Features
asymptomatic In the absence of acute infection
in severely disturbed renal function symptoms of renal failure are present
.incidentally discovered
Diagnosis
GUE - pyuria and bacteriuria -, protienuria, urine culture
.blood urea and serum creatinine may elevate ,
.KUB -irregular renal outline and small size kidneys
IVU impaired excretion of the contrast, clubbed calyces - unilateral there may be
.contralateral compensatory hypertrophy
VCUG(voiding cystourethrogram will diagnose REFLUX in children
Management - underlying causes- prevention of recurrent UTIs - unilateral
atrophic kidney with hypertension or uncontrolled infection nephrectomy may be
necessary, unfortunately the renal damage caused by chronic pyelonephritis is
.irreversible
(Renal abscess(pyonephroses
the gram negative aerobic – ascending
infected skin lesions , DM , renal calculi are susceptible to develope renal abscess
( hematoganous cause abscess in the renal cortex ( carbuncles
ascending infection cause abscess in the corticomedullary region
Clinical feature
Fever, flank pain and chills are common presenting features, nausea, vomiting
and malaise are also common, costovertibral angle tenderness may be
.found..or cases of pyelonephritis not responding to treatment
INVESTIGATIONS
CBC +ESR-GUE, urine culture may positive or negative
. blood culture - bacteremia
CT Scan is very sensitive, U / S is also useful Management
Appropriate antibiotic.. – releaving obstruction by DJ stenting, U / S or CT
guided aspiration(nephrostomy) may be needed and if not successful- open
surgical drainage may be necessary
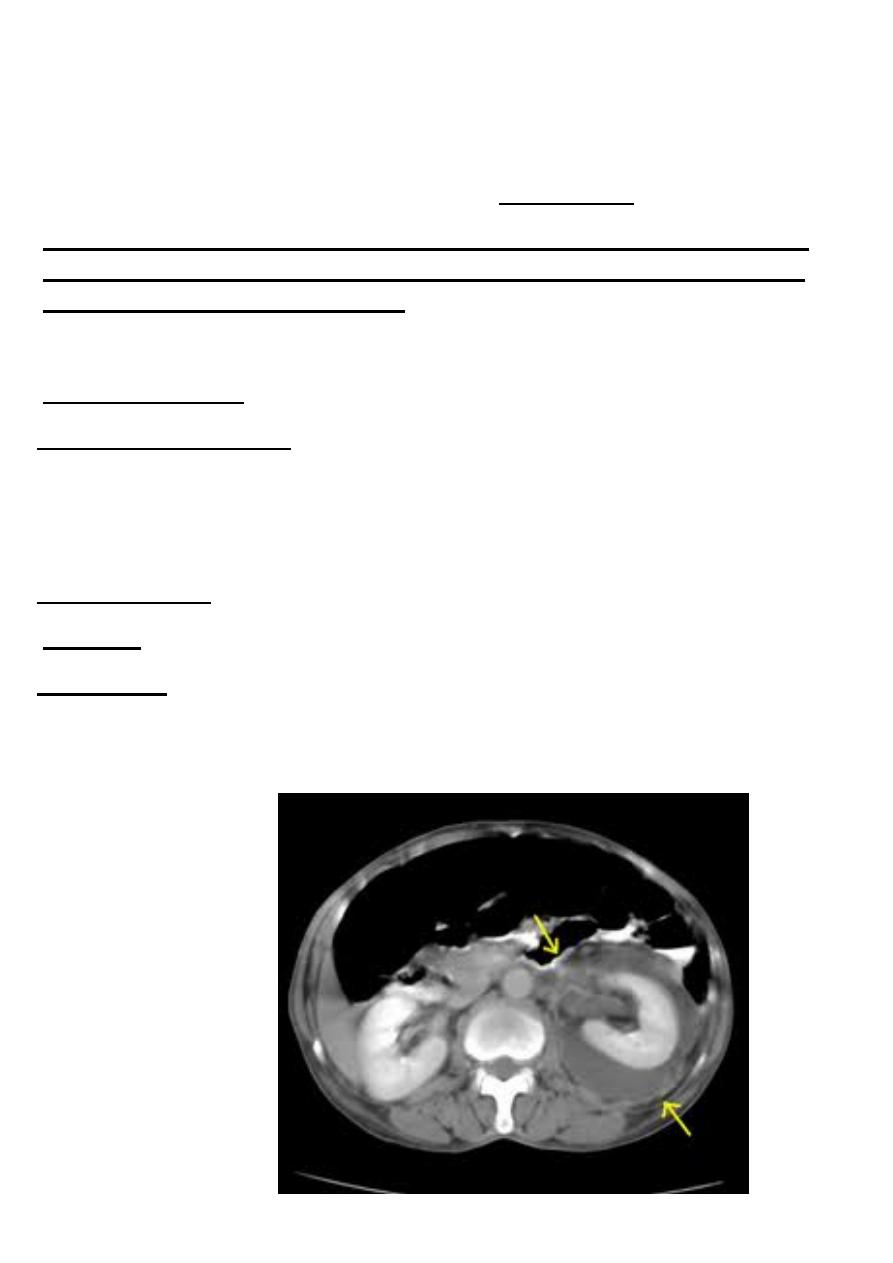
Perinephric abscess
Etiology & pathogenesis
collection of purulent material within the perinephric space - beyond the Gerota's
fascia it becomes paranephric abscess , predisposing factors are DM , urinary stasis
. or obstruction , stone and neurogenic bladder
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Managment
Drainage of the abscess ( percutaneous aspiration or by open procedure ) plus
?antibiotic therapy are the main stay of the management –Nephrectomy
!
!
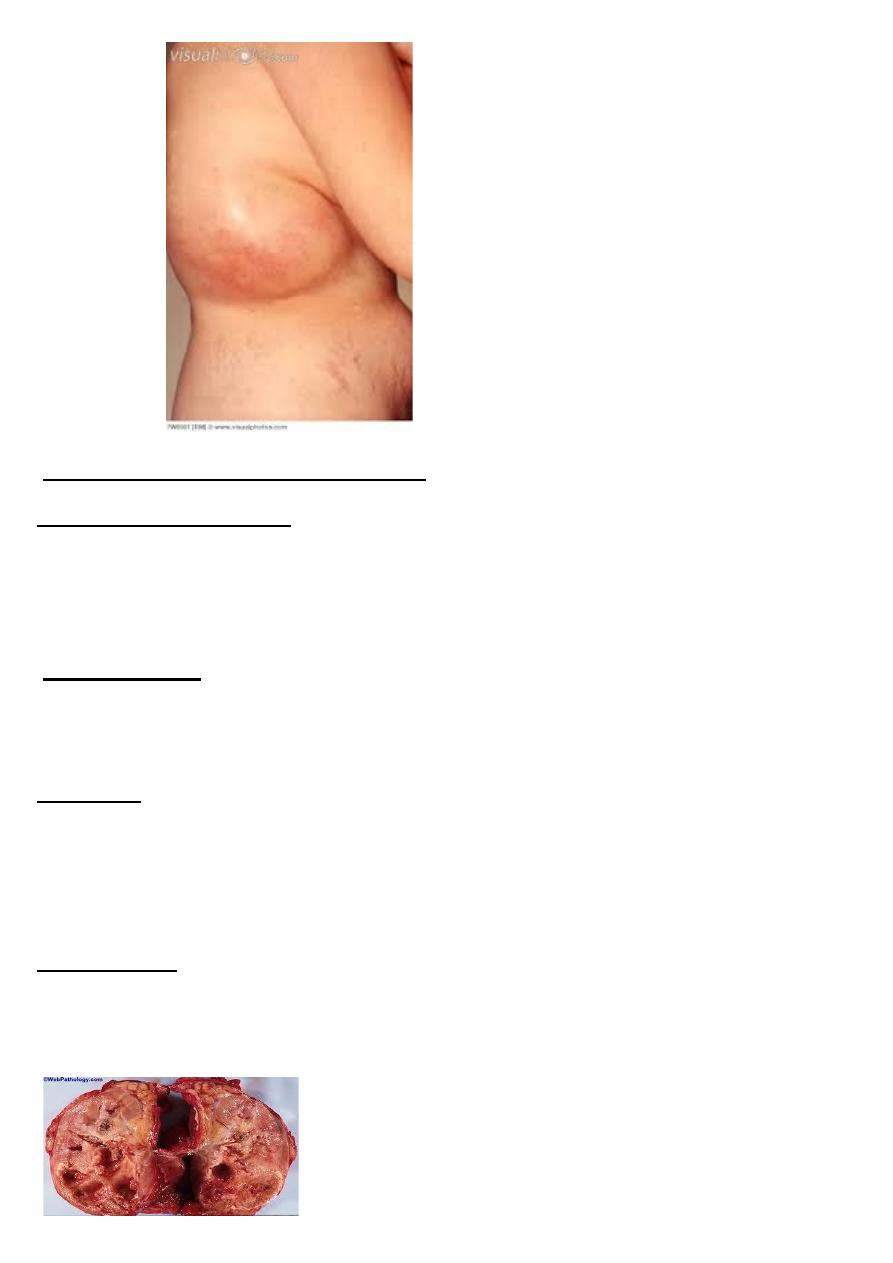
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Etiology & pathogenesis
unusual - chronic bacterial infection of the kidney - middle aged and older-
women , widespread renal destruction . The most organisms are Proteus mirabilis
, and E coli
Clinical feature
intrmitent flank pain pain , fever ,chills are found in about 70-90% of the cases ,
.palpable flank mass
Diagnosis
, GUE – protein and leukocytes , blood tests reveal anemia and leucocytosis
CT Scan is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnosis . U /S and IVU may
. be helpful
Management
Nephrectomy with excision of all involved tissues is usually required .and it is
.usually difficult nephrectomy due to sever adhesions
By:Brwa
