
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
COMMUNITY MEDICIN
M.B.Ch.B
FICMS/CM
Sunday, October 12,
2014

Epidemiology in medicine
Measurements of disease
frequency
Ratio, rate ,proportion
Prevalence & incidence
Measurements of mortality and morbidity


• Types of Calculations
:
Ratios
Proportions
نسبة
Rates
معدل

• K=10^x
• X=
any power u choose to get an clear
number and in some calculation its
fixed

A
ratio
is
Simply one quantity divided by another.
The entities represented by the two.
- Numbers
are not required
to be related
to one another.
In other words, the Individuals in the
numerator can be different from those in
the denominator.

Eg
: sex ratio
M/F
In a defined population the no. of
male was 100 and the no. of females
was 200 .
Ratio= f/m = 200/100
so the female to male ratio is 2:1

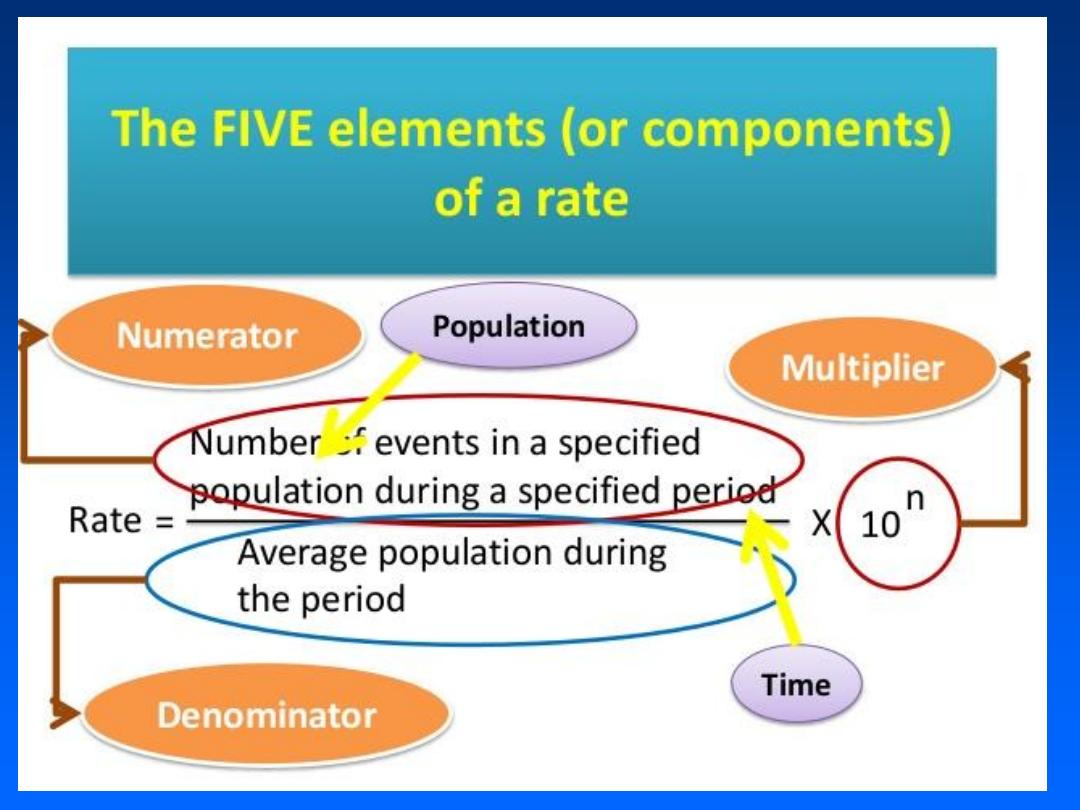
A
rate
is
also one
quantity
divided by another, -
-but
time
is an integral
part of the denominator and
entities
represented
time is a must in denominator
Individuals in the numerator are
included and related to one
another


• A
proportion
is
Also one quantity divided by another,
but the
entities represented
Proportions
Known as
fractions,
are often
expressed as percentages and range
from 0 to1 or 0% to 100%
Individuals in the numerator are
included and related to one another ,
and equal to the total

Eg:
percent of female in a
population
in a defined population (300) the no.
of male was 100 and the no. of
females was 200
Proportion of females = F/ population
=200/300*100%
=67% of population are females


eg:
in a defined population (100 in year
2014) the no. of measles case was
20
.
• rate of measles infection
• =no. of cases on specific time *k
• population at risk for that year
• = 20 / 100 = 0.2 *10
• = 2 cases of measles per 10 persons
in year 2014

Ratio:
Division of two unrelated
numbers
Proportion:
Division of two related
numbers;
Rate:
Division of two numbers; time
is always in denominator(it’s a
proportion)
Unfortunately,
the term
rate
is often incorrectly used
for describe

Second part
• Disease occurrence

• Prevalence (
تفشي
,
انتشار
)
Measuring the frequency of all current
cases in a population ( burden)
Useful in assessing the impact of
health problem.
P= No. of all cases /population * k
(eg: pre 1000 or per 1000)


• Incidence (
حدث
,
حالة
)
Measuring the occurrence of new
cases in certain time
To estimate the risk of a disease and
study prevention program
I
n
= No. of new cases /population at
risk * K

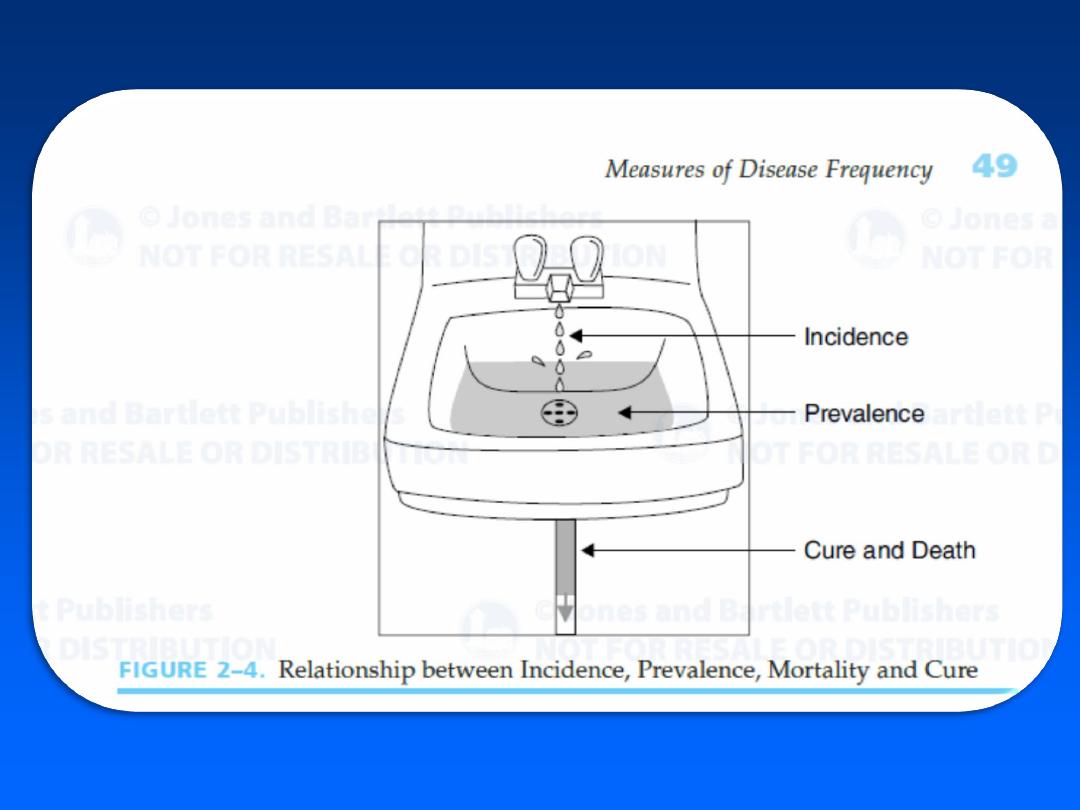
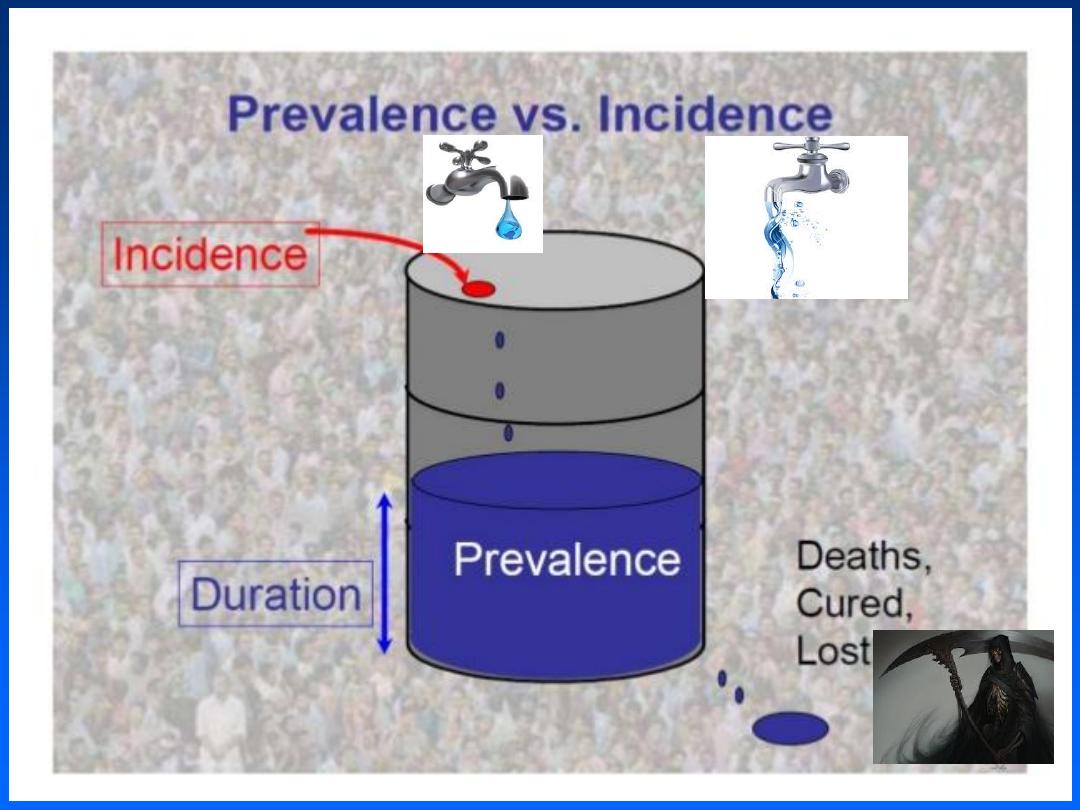

Burden


Population
at risk
Existing
cases
Deaths,
cures, etc.

Factors influencing
observed prevalence:
1. long duration of health event
2. prolongation of life of affected person
3. increase in new cases
4. In-migration of cases
5. Out-migration of non-cases
6. in-migration of susceptible people
7. Better reporting, improved diagnostic
facilities(media affect )

Types of prevalence
• Point prevalence
• Period prevalence

Attack rate:
Number of new cases of
disease that develop (usually during
a defined and short time period) per the
number in a healthy population
at risk at the start of the period.
This cumulative incidence measure is
usually reserved for infectious disease
outbreaks.
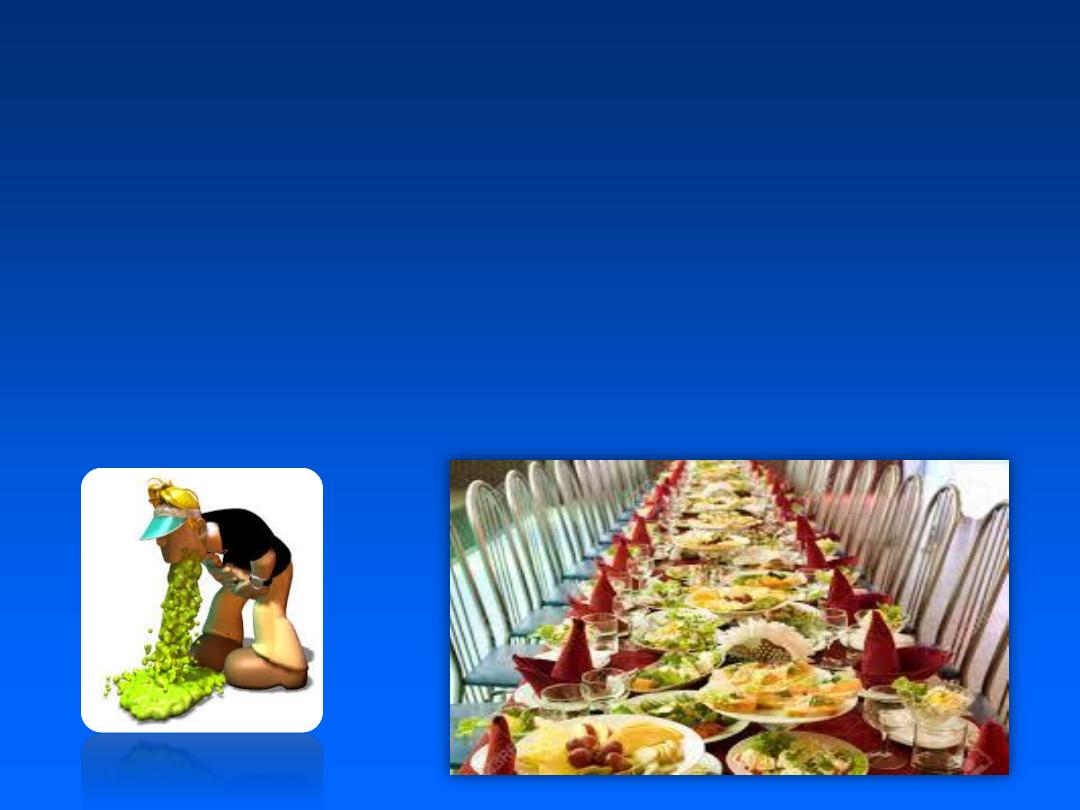

For example
,
the 24-hour attack rate for
food poisoning was 50%
among people who eat
chicken salad at the banquet.

Secondary attack rate
:
Attack
rate
among contacts
2
nd
attack rate :
Incidence among contacts*K
contacts

Case fatality rate:
Number of
deaths per number of cases of
disease.
CFR=
No. of death for certain disease *K
all cases of disease

Crude mortality rate
• Mortality rate from all cases
• CMR = No. of deaths * k
No. of population

Specific mortality rate
• Mortality rate from specific causes
• MR(for specific) = No. of deaths * k
No. of population

Sex Specific mortality rate
• Mortality rate from specific sex causes
• MR(for specific X) = No. of deaths * k
No. of population
of X


THANK YOU
