
Dr.Mohammed Jasim
COMMUNITY MEDICIN
M.B.Ch.B
FICMS/CM
Sunday, November 09,
2014

MEASURES OF DISEASE
ASSOCIATION

Objectives of Epidemiology
• To determine the rates of disease by person, place and
time
– Absolute Risk
(incidence, prevalence)
• To identify the risk factors for the disease
– Relative Risk
(or odds ratio)
• To develop approaches for disease prevention
– Attributable Risk
/fraction
MEASURES OF DISEASE
ASSOCIATION
The chances of something happening can be
expressed as a risk or as an odds:
RISK
= the chances of something happening
the chances of
all
things happening
ODDS
= the chances of something happening
the chances of it
not
happening

Thus a risk is a
proportion
,
But an odds is a
ratio
.
An odds is a special type of ratio,
one in which the numerator and
denominator sum to one.
Example 1. Bookies are taking bets on the
World Series. They are giving
3:1 odds
on
the Yankees. What does this mean?
It means that they think that there it is three times as
likely that the Yankees will not win the world series as
that they will win.
Expressed as a risk, the Yankees are expected to win
one in four
opportunities

Example 2. Among 100 people at baseline,
20 develop influenza over a year.
•
The risk is 1 in 5 (i.e. 20 among 100)
The odds is 1 to 4 (i.e. 20 compared to 80)
THE
RELATIVE RISK
(RISK OR RATE RATIO)
The
relative risk
is a ratio of two risks.
Risk 1
RISK
= the chances of something happening
Risk 2
the chances of
all
things happening
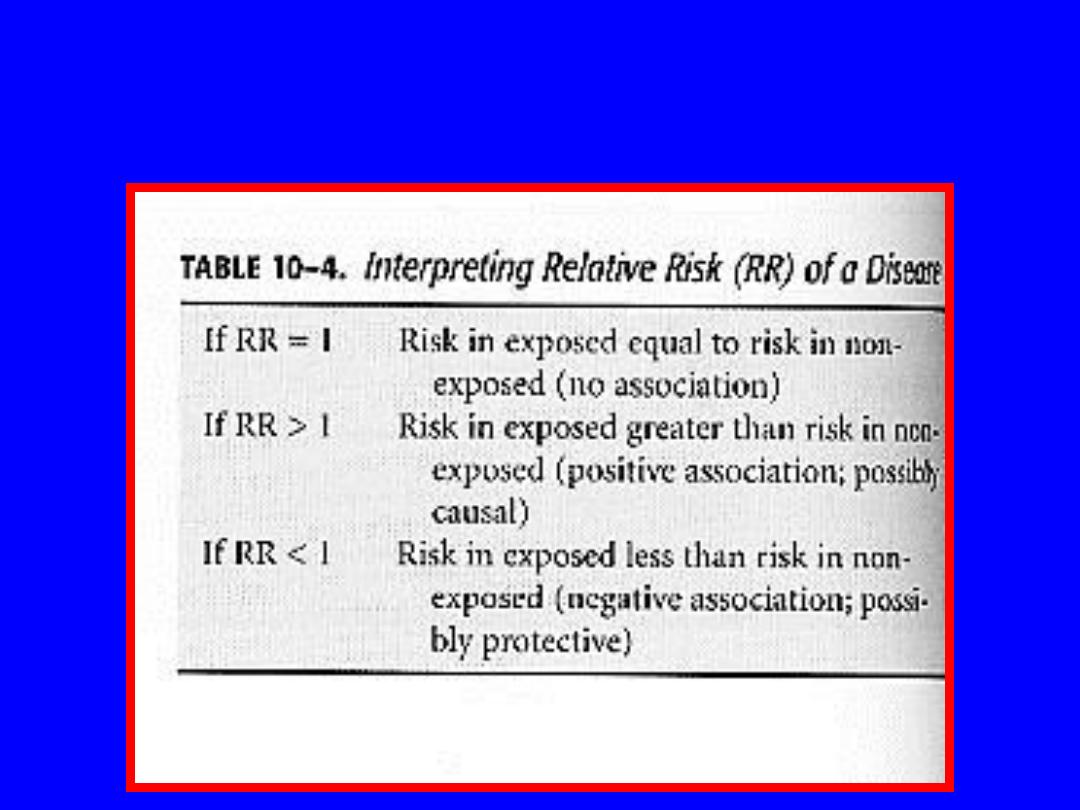
Interpreting Relative Risk
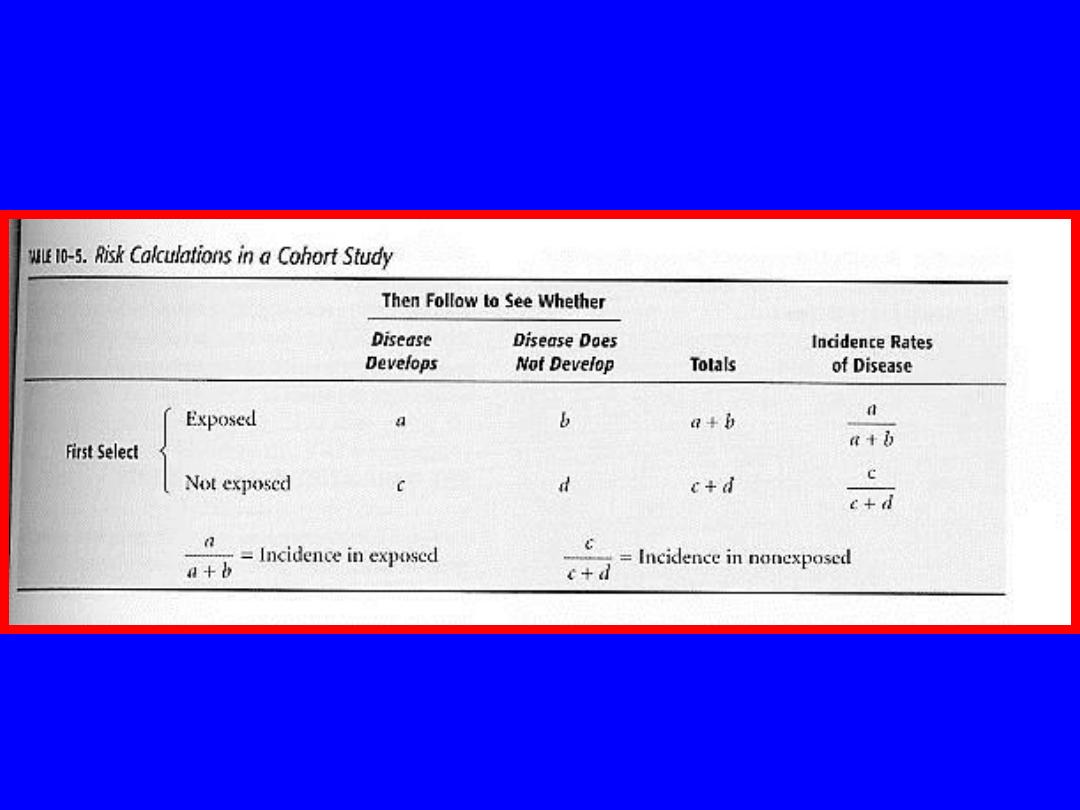
Relative Risk Calculations
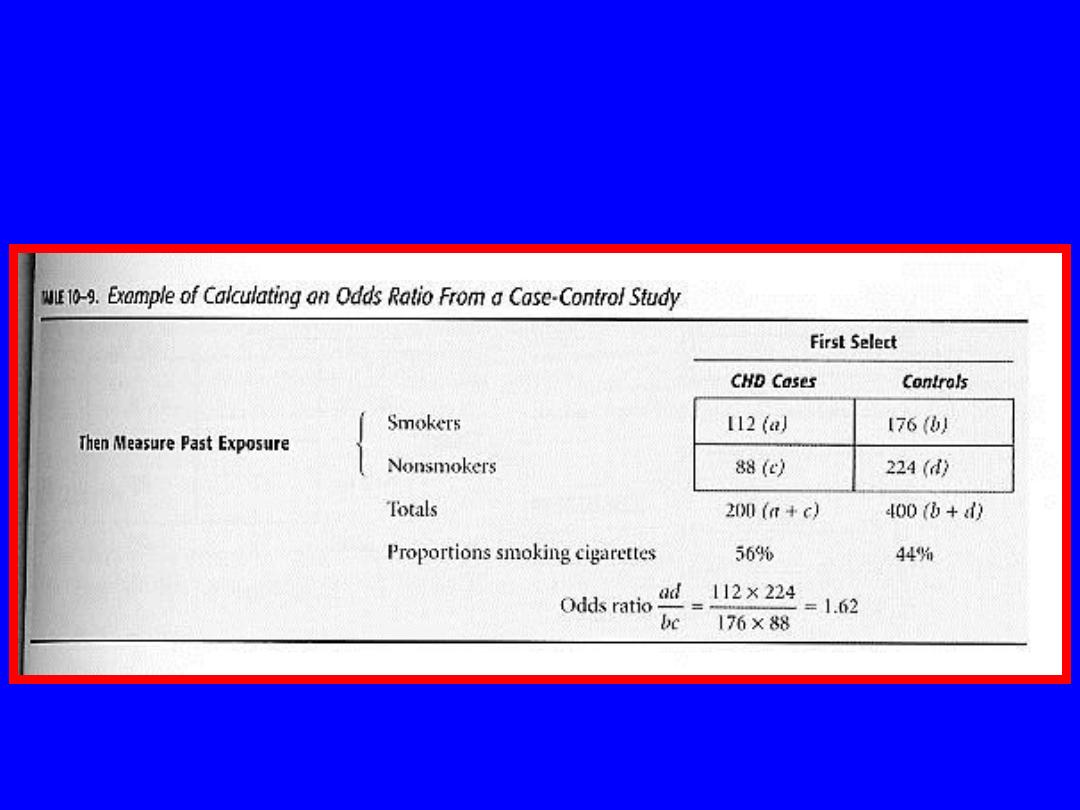
Odds Ratio in
Case-Control Studies
(cont.)

Example :
Assume that among the 100 people
at risk, 50 are men and 50 women.
If 15 men and 5 women develop
influenza, then the relative risk of
developing
influenza in men, as
compared with women
,
ODDS RATIO
ODDS
= the chances of something happening
the chances of it
not
happening
The odds ratio is a ratio of two odds

ODDS RATIO
The odds in men = 15/35
divided by
The odds in women = 5/35
15/35 : 5/45 = 3.9

is:
Risk in men = 15/50
Risk in women = 5/50
divided by:
15/50 : 5/50 =
3.0 relative
risk compared between men to woman

We conclude that the odds of men
getting influenza over the year are 3.9
times as high as the odds of women
getting influenza.
Thought question
: note that the odds
ratio in this example (3.9) is larger
than the relative risk (3.0). Is this
always the case? Is this important?

When is the Odds Ratio a Good
Estimate of Relative Risk?
• When cases are representative of diseased
population
• When controls are representative of
population without disease
• When the disease being studied occurs at
low frequency
