Community medicine Dr.suhailla
1
Done by: - #mohdz
Screening
The identification of unrecognized disease or defect by the application of
tests, examinations or other procedures”...
Sort out apparently well persons who probably have disease from those
who probably do not”.
Not intended to be diagnostic .
”..
Different kinds of testing in medicine:-
“Diagnostic” - specifically looking for a suspected condition which is tested
for and confirmed or excluded
“Case-finding” - usually in an investigation of exposed people, to sort the
exposed and ill from the exposed and well. (E.g., test people who were in
contact with a case of tuberculosis, or check b.p. of patient who is
overweight)
“Screening” - usually no specific exposure or indication that the individual
has disease. (E.g., routine PSA testing in middle-aged males)
Types of screening:-
Mass screening, no selection of population (e.g., checking all infants for
hearing problems)
Selective screening (e.g., by age and sex: mammograms for women aged
over 40)
Multiphase screening (a series of tests, as family doctors do at annual
health exams)
Community medicine Dr.suhailla
2
Done by: - #mohdz
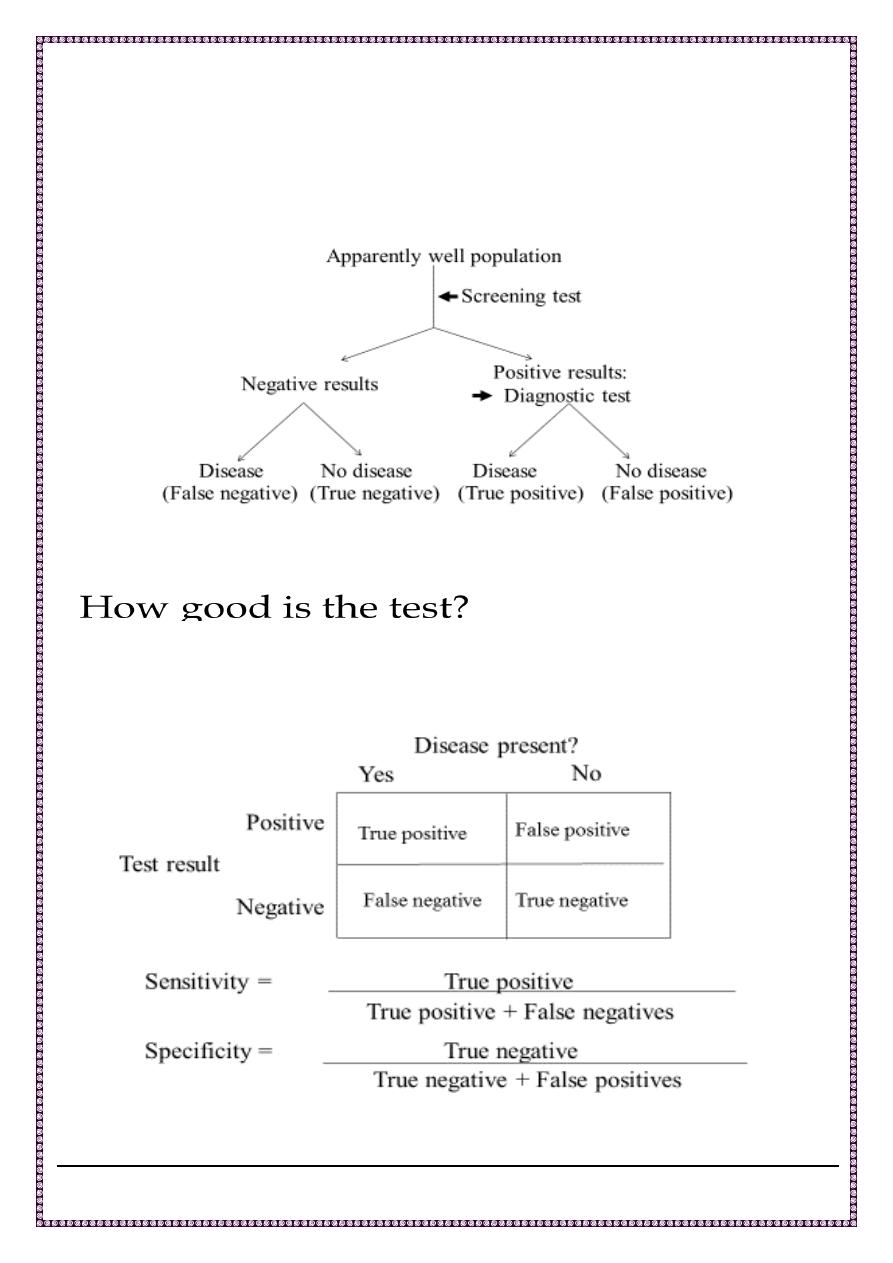
Logic of screening
Community medicine Dr.suhailla
3
Done by: - #mohdz
Characteristics of a good screening test:-
1. Valid (e.g., sensitive and specific)
2. Reliable (gives consistent results; no random errors)
3. Yield (number of cases identified per thousand screened)
4. Cost – benefit (compare costs avoided due to early detection of the
disease against cost of the screening. Does the test merely uncover more
disease that is expensive to treat without appreciable advantage?)
5. Acceptable (discomfort, hassle, cost of obtaining test)
6. Follow-up services (plan needed to deal with positive results)
When should we screen?
Screen when:
It is an important health problem (think about how to define ‘important’?)
There is an accepted and effective treatment
Disease has a recognizable latent or early symptomatic stage
There are adequate facilities for diagnosis and treatment
There is an accurate screening test
There is agreement as whom to consider as cases
Ethics
of
medical
care
:-
Remember the basic ethical principles:
1. Autonomy
2. Non-maleficence
3. Beneficence
4. Justice
Community medicine Dr.suhailla
4
Done by: - #mohdz
Ethics in screening
1. Informed consent obtained ?
2. Implications of positive result?
3. Number and implications of false positives?
4. Ditto for false negatives?
5. Labeling and stigmatization
Periodic health examination
Canadian Task Force
o Levels of evidence for interventions
I-1 Randomized controlled trials
II-1 Well-designed trial but not randomized
II-2 Cohort or case-control studies in more than one center
II-3 “Natural experiments”
Example of Periodic Health Exam: Women and
men aged 16 - 44
Immunizations
1. Polio
2. Tetanus and diphtheria
3. Travel - related
4. Rubella
Screening
1. Hypertension
2. CA cervix
3. Tuberculosis
4. STD
Community medicine Dr.suhailla
5
Done by: - #mohdz
