
1
DESCRIPTIVE STUDIES
Person, Place and Time
Descriptive Epidemiology
• Includes activities related to characterizing the distribution of
diseases within a population.
Analytical Epidemiology
• Concerns activities related to identifying possible causes for the
occurrence of diseases.
Descriptive Epidemiology
• Epidemiological equivalent of the game “20 Questions”
Animal, mineral or vegetable?
• In Descriptive Epidemiology:
Who? - person
Where? - place
When? - time
2
PERSON
• WHO is getting the disease?
• Many variables are involved and studied, but factors such as
sex, age & race often have a major effect.
Characteristics of Person
• Age
• Sex
• Ethnic group
• Socioeconomic status
• Nativity
• Religion
• Marital status
• Occupation
Descr
ip
tiv
e
Epide
miolo
gy
PERSON
PLACE
TIME
Think of this as the
standard dimensions
used to track the
occurrence of a
disease.
3
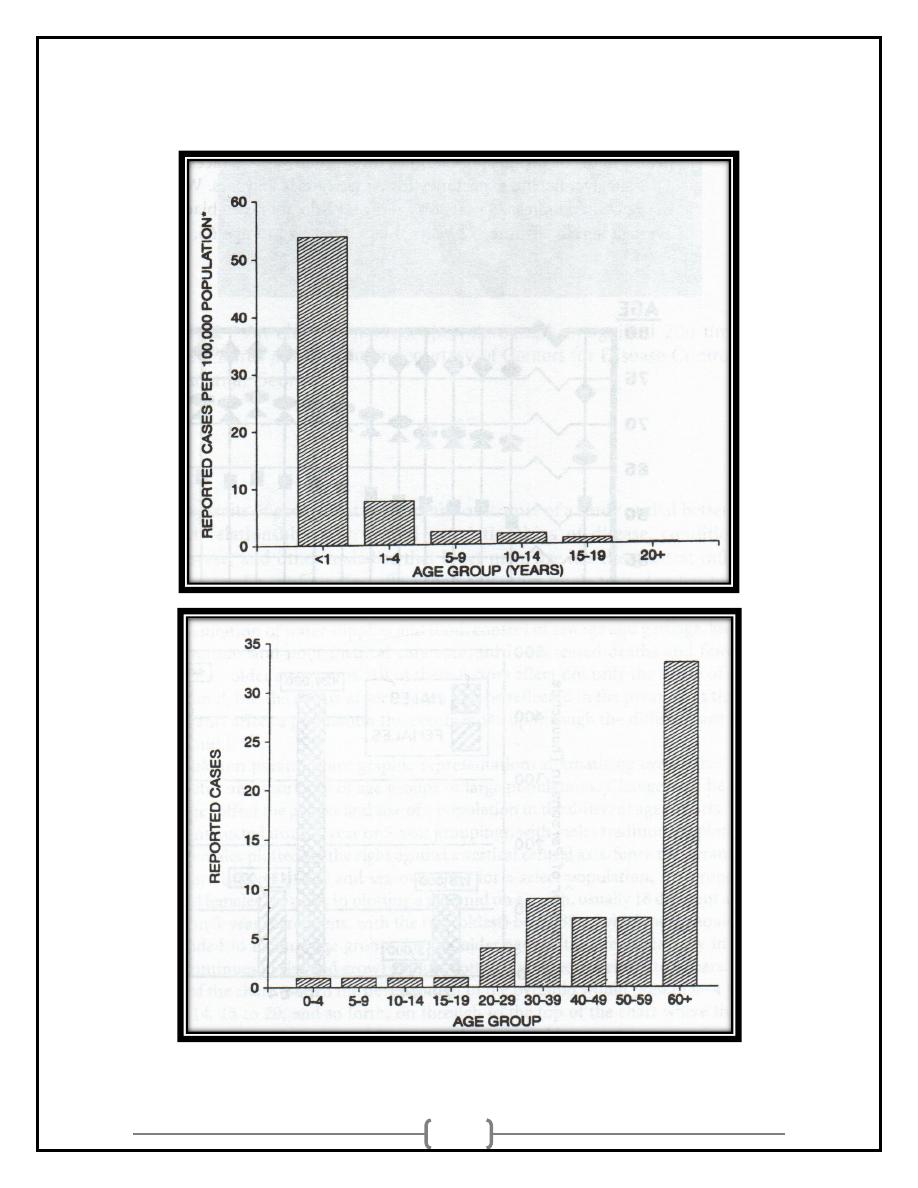
Age
4
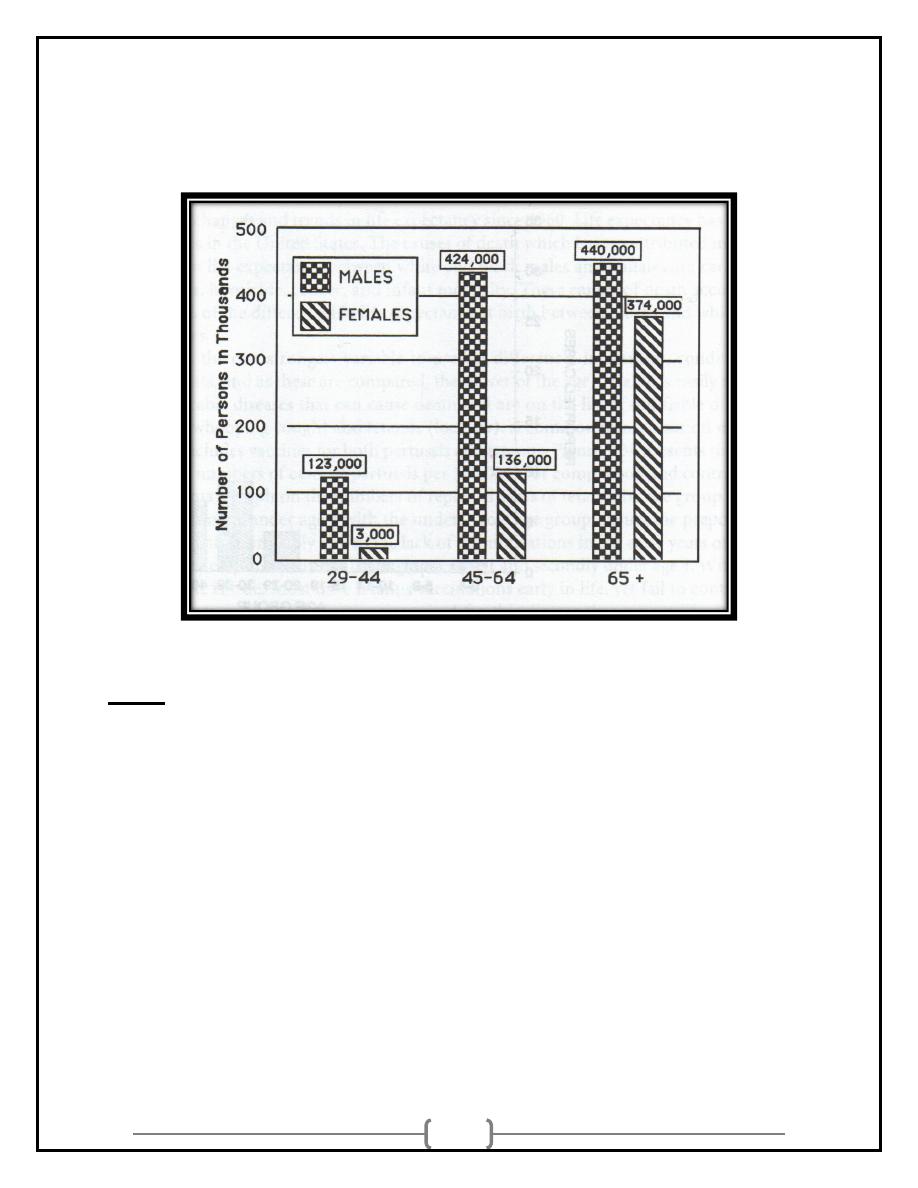
Sex
TIME
• WHEN does the disease occur?
“Temporal”
Range from hours to decades
• Type of disease dictates “time” element to be used
• Graphic format often used
y-axis (vertical) - frequency
x-axis (horizontal) - time
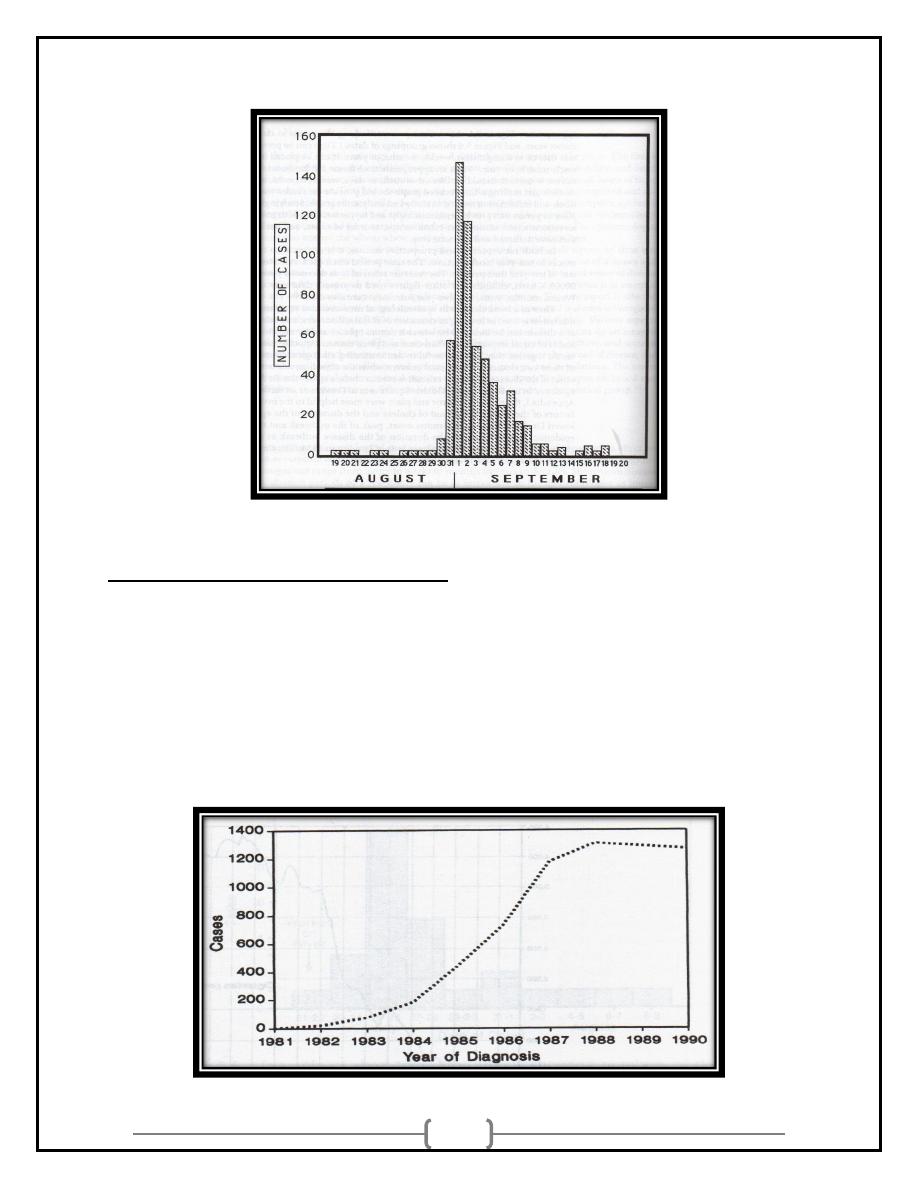
5
Characteristics Relating to Time
• Secular change (long-term)
• Point epidemics (short-term)
• Cyclic trends
• Seasonal variation
Secular Change:
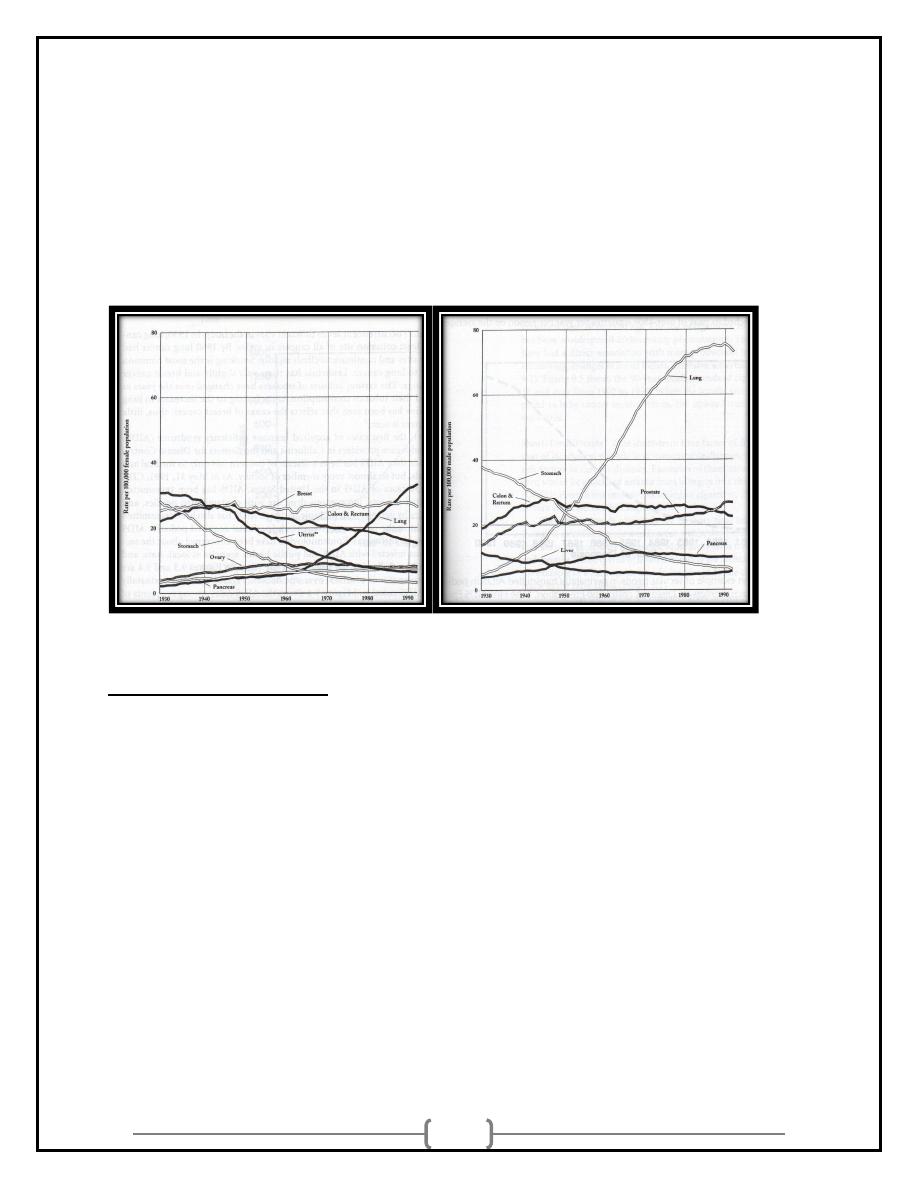
6
Secular Change
• Secular changes (“temporal variation”) occur slowly over long
periods of time
Longer than one year
POINT EPIDEMICS:
• Short-term changes occur over limited time frames
Hours
Days
Weeks
Months
• Used for short-term exposures or diseases with short incubation
and/or illness durations
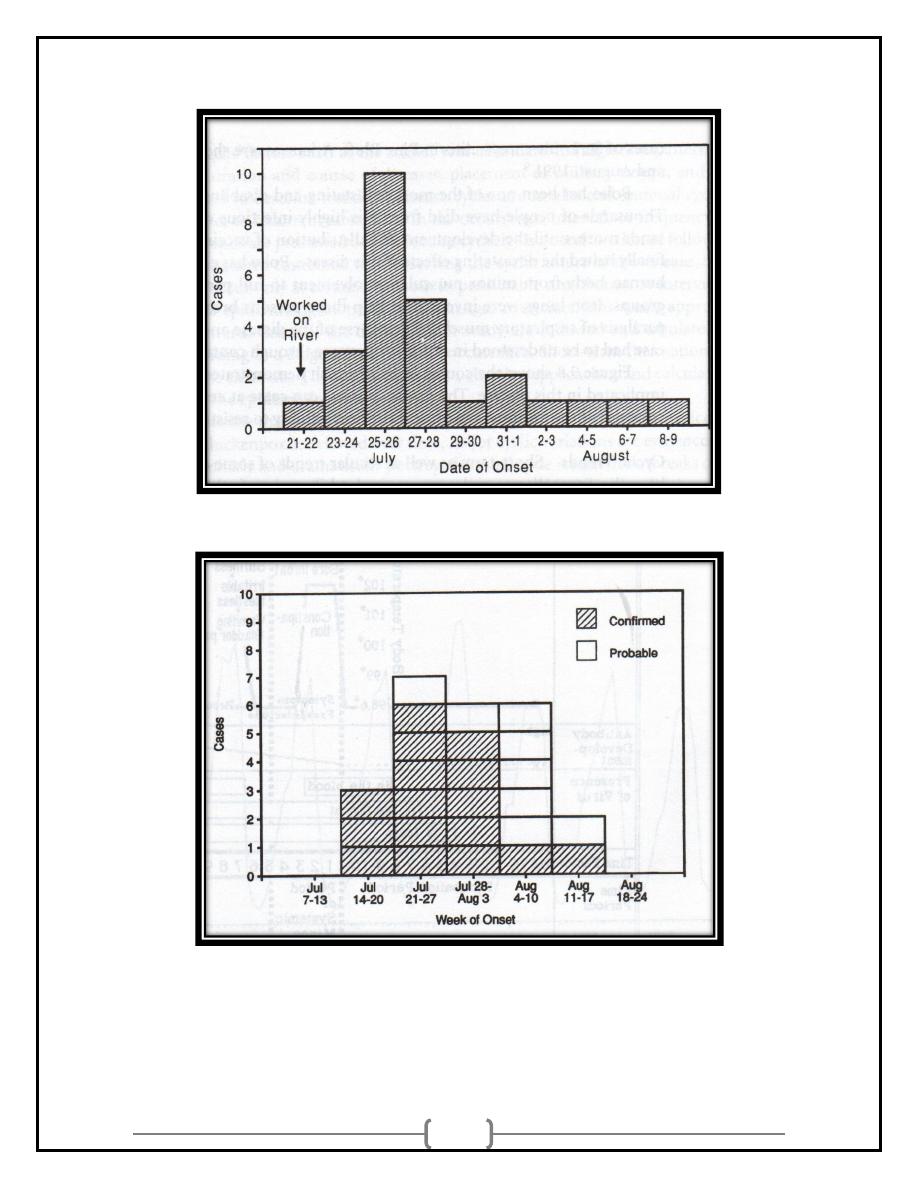
7
8
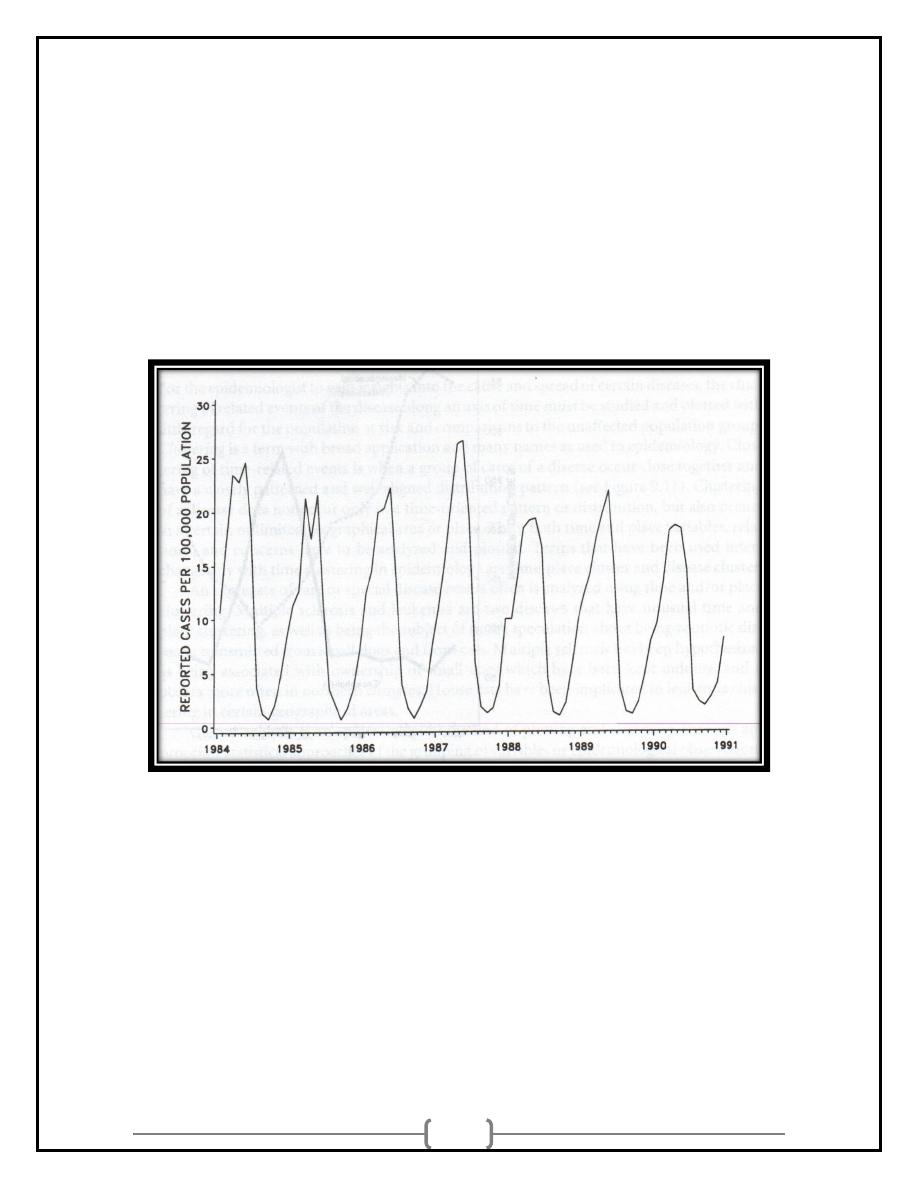
CYCLIC TRENDS:
• Cyclic trends may be either long-term or short term events.
• Some are “seasonal” while others are cyclic due to other factors:
Immigration
School year
Military deployment
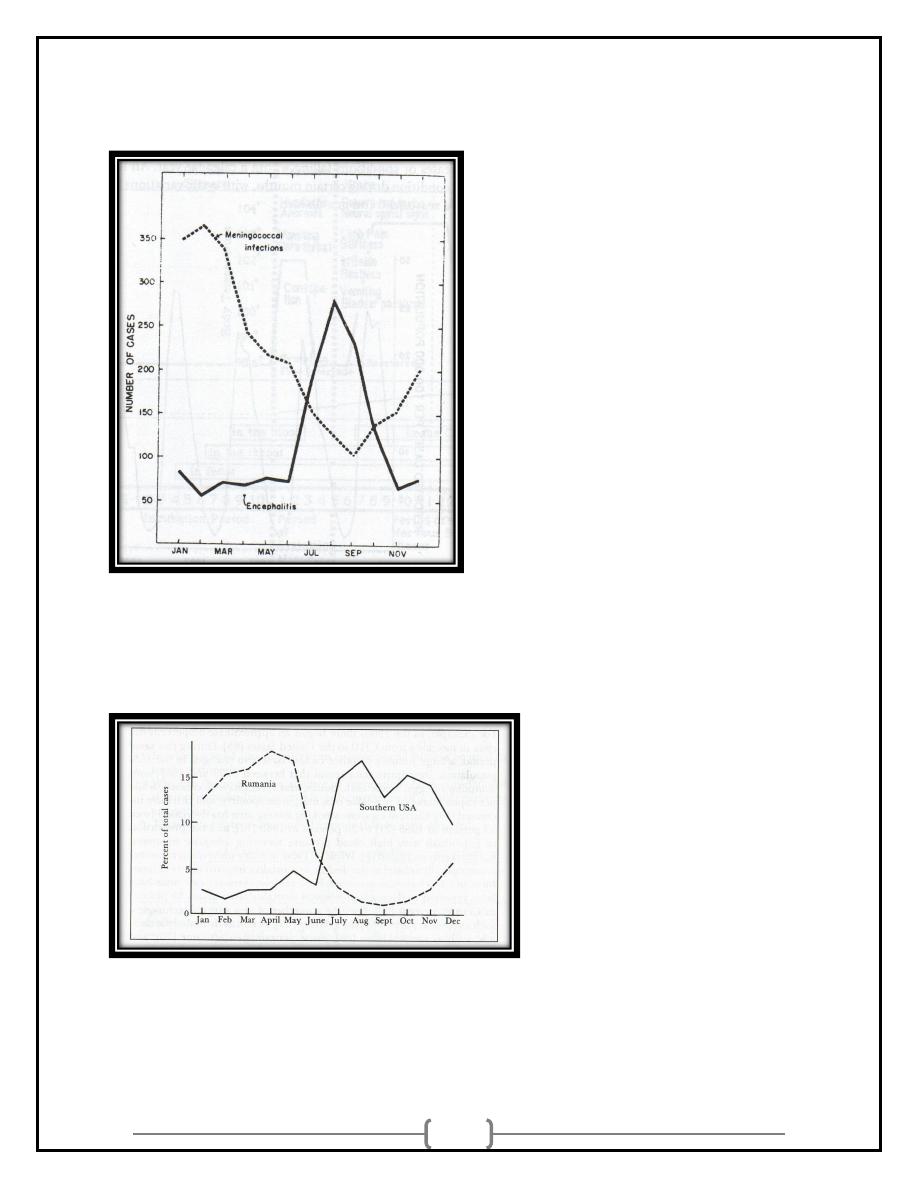
9
Seasonal Variation
• Seasonal variation can be
seen for some diseases
or conditions falling within
a calendar year
• Seasonal variation can
be
used
to
suggest
possible etiology.
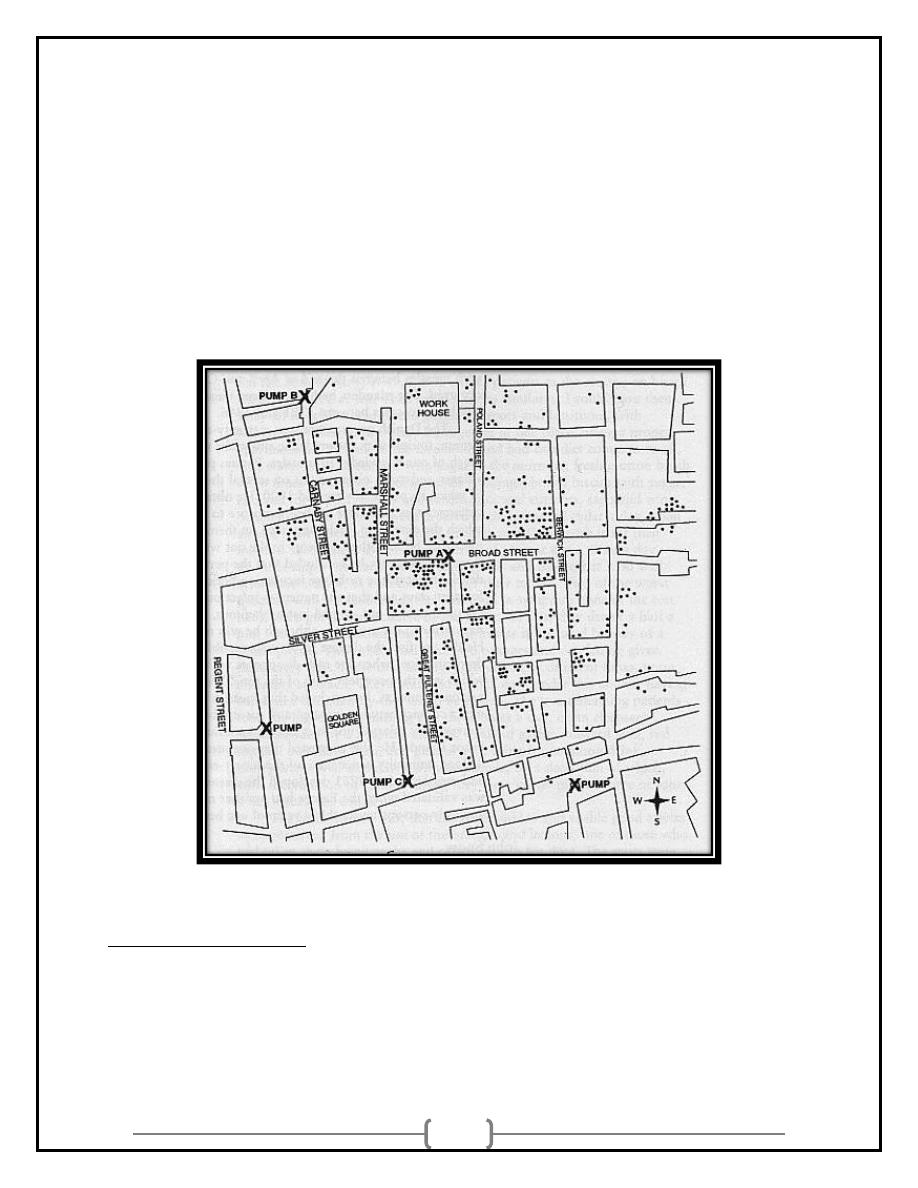
10
PLACE
• WHERE are the rates Higher? Lower?
• Geographic location of source
• Geographic location of reservoir
John Snow and Cholera
5 Criteria of Place:
•
Rate observed in all ethnic groups in the area
•
Rate NOT observed in persons of similar groups inhabiting
other areas
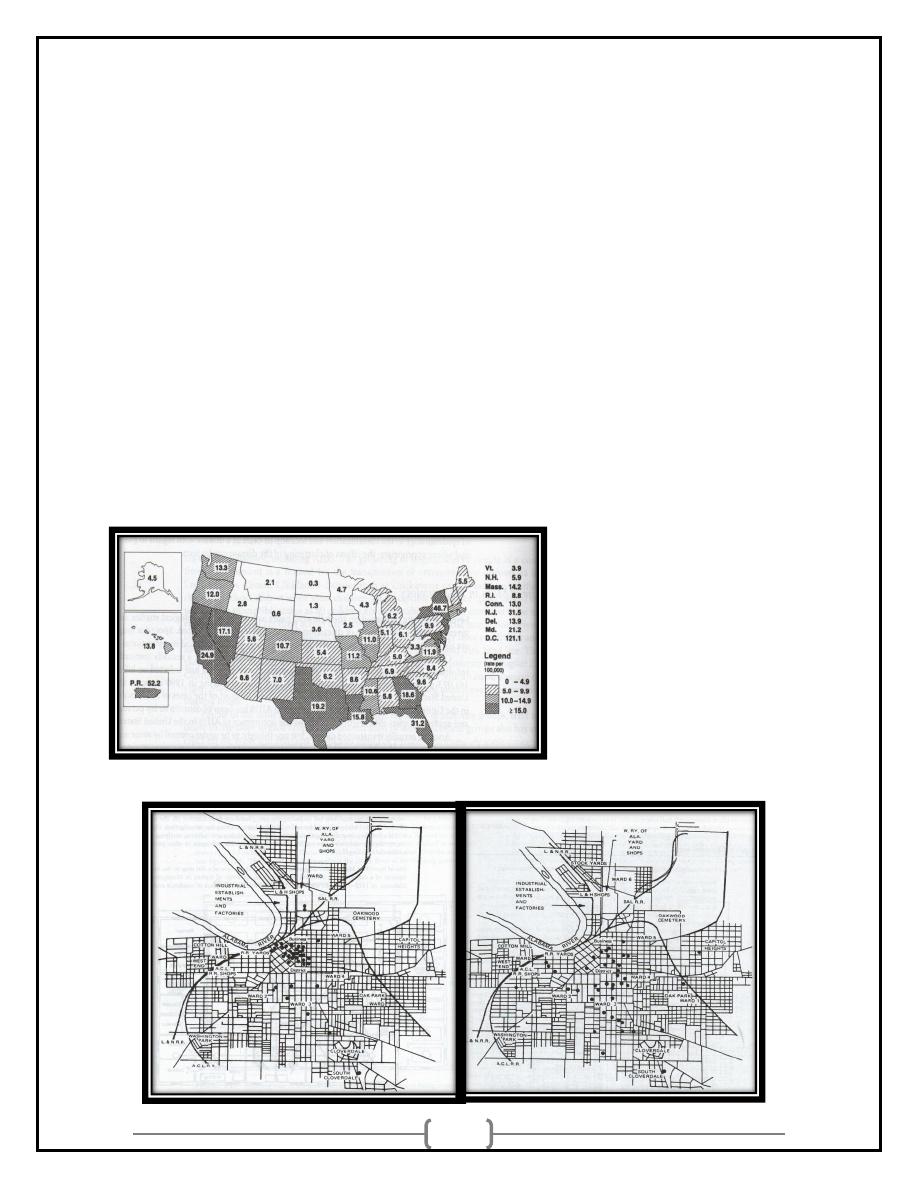
11
• Healthy persons entering area get ill at same frequency
• People who leave do NOT show similar levels
• Similar levels of infestation in other species (if zoonotic disease)
Characteristics Relating to Place
• International
• Variation within countries
Urban-rural
Local
• Building Maps
Place
Local
Building Maps
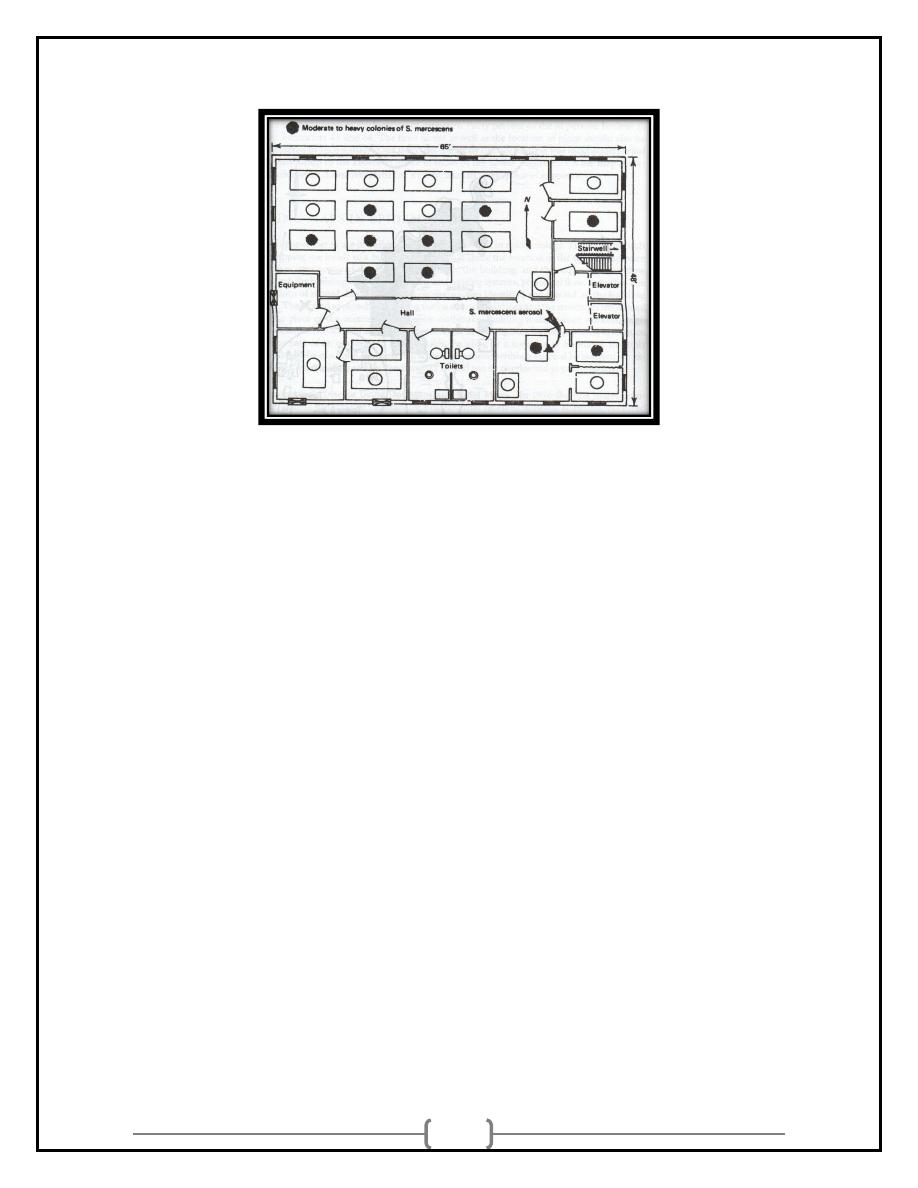
12
Interactions of Time and Place
• Time-place clustering.
• Migration.
