
1
|
P a g e
Levels of preventions
dr.m.jASSIM
• Primordial
• Primary
• Secondary
• Tertiary
Definition:
• Prevention programs and clinical services reduce burden of disease through a network of
health services and community participation to control an health event and work in
steps .
• These steps or levels insure a scientific and sound approach of medical interfere and
community education in a way that no program overlaps with other program .
Primordial prevention
The prevention of health events by acting at the earliest level on risk factors
Health education is its main mod
Best Suitable for non-communicalbe disease
Keys:
non specific , general
Eg: medicine advices in mass media

2
|
P a g e
Primary prevention
The prevention of health events by acting at the earliest level on specific factors or
vectors (removing the possibility of occurring of the health event)
Secondary prevention
Stopping progress of health event by halting the disease to prevent complication
Tertiary prevention
Every thing have accrued
Its aim to limit impairment and minimize suffering
3
|
P a g e
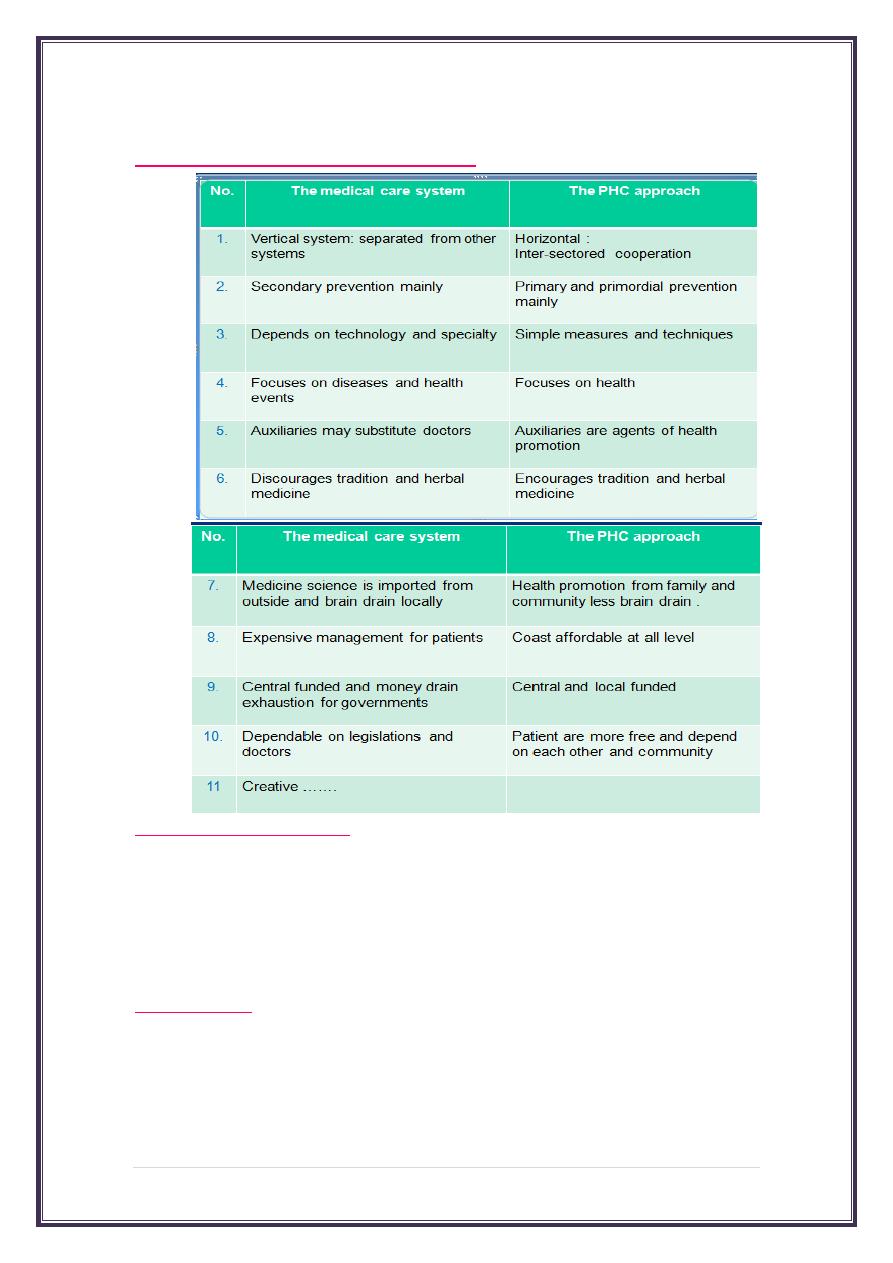
PHC Vs Hospital ( مهم جدا جداquize):-
Limitation of medical system
1. Economic : teaching ,training and looking after staff and doctors .
2. Brain drain: doctors need new advance building and techniques to cop with more
advanced medicine
3. Growing population increases brain drain and burden existent hospitals .
4. Developing of drug resistant : need new drug supply chain .
Referral system
1. Ideally patients will be managed locally at district PHC.
2. Complex patient will be transferred to district PHC for special needs.
3. Complicated patient and some emergency will be transferred to hospitals.
4. Special diseased patient will be transferred to special centers locally.
4
|
P a g e
Aim of referral system
I.
Order flow of patients.
II.
Better diagnosis and better treatment service.
III.
Decrease burden on hospitals and doctors and patients.
IV.
Completing PHC.
V.
Better source management.
Priorities of health problem
1. Incidence & prevalence
2. Morbidity & mortality
3. Curability
4. Cost-benefit, cost-effective
5. Communicability
6. Preventability
Pillars of PHC
Intersectoral cooperation
Community participation
Appropriate technology (support of health system)
Obstacles to PHC
1. Political resistance
2. Professional group (breast feeding ,medication)
3. Public figures
4. Religious people
5. Medical industries and advertising
Population pyramid
It is a skeleton of population arranged according to age it differs from country to other
according to developing scale
Developing countries Developed countries End stage communities
(developed)

5
|
P a g e
The inverse low in our health system
