Done By :
Rasha AliDiana Bahaa’
Ruba Khalil
Tabarak Majid
Pediatric Emergencies
Pediatric emergency
Objective:1. Anatomical Differences
2. Initial Assessment & ABCDE Approach
4. RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES. STATUS ASTHMATICUS.
5. Anaphylaxis
7. POISINING.
8.Sudden infant death syndrome
9. Child abuse
10. Acute hemolysis
Pediatric Emergencies
Emergency care is about providing the right
care and support in a timely manner
Therefore we start with an emphasis on patient
safety— the ABC—the assessment of airway,
breathing, and circulation.
Emergency Care
Anatomical Differences
Smaller airways• Less blood volume
• Bigger heads
• Vulnerable internal organs
Initial Assessment
• Begins before you touch the patientform a general impression.
• Determine a chief complaint.
• The Pediatric Assessment Triangle
can help.
Pediatric Assessment Triangle
• AppearanceAwake
Aware
Upright
• Work of breathing
Retractions
Noises
• Skin circulation
These three clinical indicators reflect the overall status of a child’s cardiovascular, respiratory and neurologic systems.
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES
Causes:Acute dyspnea
Nasopharynx : choanal atresia , tonsillar hypertrophy, diphtheria.
Upper airway obstruction : vocal cord dysfunction, croup , epiglottitis.
Lower airway disorder : foreign body bronchitis asthma.
Disordered gas exchange carbon monoxide poisoning, pulmonary oedema, pulmonary hypertension.
Respiratory drive : psychogenic, brain stem tumor.
Neuromuscular : Duchene muscular dystrophy.
Other : pneumothorax.
Status Asthmaticus
HistoryPatients have severe dyspnea that has developed over hours to days. Frequently, patients have a prior history of endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation, frequent emergency department visits, and previous use of systemic corticosteroids. Patients usually present with audible wheezing.
Physical examination
Patients are usually tachypneic in early stages there is wheezing.
The chest is hyperexpanded, and accessory muscles, are used. Later wheezing may disappear, which may indicate severe airflow obstruction.
Treatment
High concentration of oxygenhumidified if possible.
rehydration
High doses of inhaled bronchodilator
the first choice is short acting beta agonist(salbutamol) given via nebulizer
Inhaled ipratopium bromide via nebulizer
Treatment
Systemic corticosteroids:-intravenous hydrocortisone 10 mg/kg
aminophylline IV 1mg/kg/hour slowly infusion over 20-30 min. with normal saline
Magnesium sulfate
Assisted ventilation
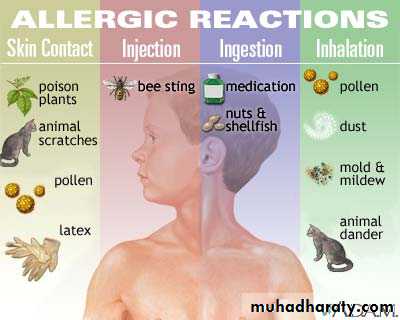
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe, systemic allergic reaction
multisystem involvement, including the skin, airway, vascular system, and GISevere cases may result in complete obstruction of the airway, cardiovascular collapse, and death
Anaphylactoid or pseudoanaphylactic reactions display a similar clinical syndrome, but they are not immune-mediated. Treatment for the two conditions is similar .
Etiology:
• Pharmacologic agents• Antibiotics especially parenteral penicillins,aspirin , nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and intravenous (IV) contrast agents.
Latex
Much attention has focused on latex-induced anaphylaxis, but it is actually quite rare.
• Stinging insects
ants, bees, hornets, wasps, and yellow jackets.
Fatal anaphylaxis can develop when a person with IgE antibodies induced by a previous sting is stung
A fatal reaction occurs within 10 to 15 minutes. Cardiovascular collapse is the most common mechanism
Foods
Peanuts, seafood, and wheat are the foods most frequently associated with life-threatening anaphylaxis.
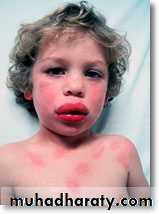
Signs and Symptoms:
Anaphylaxis involves a range of signs and symptoms from hives, wheezing and angioedema to cardiovascular collapse and death.Sneezing.
Coughing.
Itching “pins and needles”sensation on the skin .
Flushing of the skin .
Facial Edema(perioral , oral or priorbital).
Anxiety.
Palpitation.Early respiratory difficulties (eg: wheezing, dyspnea, chest tightness).
Hypotension which may progress to shock and collapse.
Serious upper airway (laryngeal) edema, lower airway edema (asthma), or both may develop, causing stridor and wheezing.
Rhinitis
Cardiovascular collapse is the most common periarrest manifestation
Gastrointestinal signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea .
Management:
Place the child in a recumbent position (elevating the feet if possible).Establish and maintain oral airway if necessary.
Give oxygen by mask, 10-12 L/min by mask; keep oxygen saturations > 97% to 98%.Start IV therapy with normal saline to keep vein open, unless severe anaphylaxis and signs of shock are evident.
Administer
Aqueous epinephrine 1:1000,0.01 ml/kg (maximum dose 0.3 ml) SC or IM in the limb opposite that in which the original injection was given.A single SC injection is usually sufficient for mild or early anaphylaxis.
Epinephrine can be repeated twice at 15- 20 minute intervals, if necessary.
In severe reactions it may be necessary to give these repeat doses at shorter intervals (10–15 minutes).
If hypotensive after epinephrine, start IV N/S 20 cc/kg bolus over 20 minutes.
Diphenhydramine 1-2 mg/kg IM or IV, up to 50 mg every 4-6h.Hydrocortisone 5-10 mg/kg up to 500 mg every 4-6h.
Ranitidine 12.5-50 mg IV q6-8h.Monitor Vital signs frequently.
Salbutamol for persistent bronchospasm.
Observe for 6-8 hours minimum with rapid response.
If protracted course monitor for 24 hours.
prevention:
Take a careful patient and family history of allergies.
Be prepared with emergency response.Monitor child for 20 minutes after injection.
Kerosene ingestion
Hydrocarbons• Description
• Toxic dose varies depending on agent involved and whether it was aspirated, ingested, or inhaled
• Common products:
• Lamp oil
• Gasoline
• Lighter fluid
• Kerosene
• Furniture polish
• Phenol
Definition
Kerosene is a hydrocarbon product of petroleum distillate, made up of paraffin and naphthenes.
In developing countries kerosene is commonly kept in the home, being extensively used for
cooking, heating and lighting. Consequently
accidental kerosene ingestion is often
seen in children in these countries.
Children at Risk
• Developmental characteristics• Peak age 1-4 years, boys more than girls
• Usually it occurs in summer more than winter ??
• Mobile & Curious by nature
• Explore their environment by putting most things in their mouths
• Imitate the behavior of others
• Inability to discriminate a toxic substance from a nontoxic one
• Drawn to attractive packaging and smell of many products found around the home
Children at Risk
• Environmental characteristics
• Toxic substances are often accessible to a child
• Improper storage
• Availability of substances in their immediate environment
• Inattentiveness of caregiver / inadequate supervision
In Our country
• SOCIOECONOMIC STATUSOver 75 % of the patients were from poor families, living in crowded conditions where kerosene is used extensively and where care and supervision of children are suboptimal.
• KEROSENE STORAGE
It is unfortunate that kerosene is usually stored
in unlocked and exposed containers. Containers
are placed on the floor, in the vicinity of
the play areas, within easy reach of infants and
toddlers. As with other studies improper storage
was found to be the main cause
How it affects the body ?
Respiratory system 90% : cough, tachypnea, cyanosisCNS 30% : Varies-restlessness, lightheadedness, rarely seizure and coma etc.
GIT : commonly mild vomiting , diarrhea ,pain.
Fever : persistent for days and it correlates with lung involvement
Assessment of the Child with a Possible Kerosene Ingestion
History:
• How was it taken?• When was it taken?
• Where was the child found?
• How much was taken?
• Amount of liquid
• How much amount available before ingestion?
• How much now in the container?
• Where is the substance stored?
Clinical Features
• Signs/• Symptoms
• Coughing and choking on initial ingestion; gradual increase in work of breathing.
• Odor of kerosene on breath.
• Dry, persistent cough; crackles, wheezes, diminished breath sounds, tachypnea.
• Nausea/vomiting, dizziness, altered mental status, dysrhythmias are possible.
Lab evaluation
• CBC shows leukocytosis ?? Is it infection ??
• Chest X ray is essential But when ??
• What are the findings ??
Chest X-Ray
• Lower lobes more than upper• Right more than left
• Patchy involvement
• Some times bilateral
• Plural effusion and consolidation were reported
• Poor correlation with clinical state.
Treatment
• The whole issue is supportive• Lung is involved or not ??
• ABCs , Oxygen , Bronchodilators, monitor Vitals
• Emesis and Gastric lavage ??
• Activated charcoal ??
• Antibiotics ??
• Steroids ??Follow-up
• Further Inpatient Care
• Patients may be safely discharged home if all of the following conditions are met:
• 1. observed in the emergency department for at least 6 hours
• 2.asymptomatic
• 3.Chest radiograph findings are normal
• They are instructed to return if respiratory symptoms develop
Complications
• Aspiration pneumonitis is the most common complication• Pneumothoraces and barotrauma are potential complications of mechanical ventilation.
• CNS complications include seizures, encephalopathy, and memory loss.
• Myocarditis and cardiomyopathy
With appropriate supportive care, most patients recover without residual complications.
Patient EducationAdvise the parents about the proper storage and labeling of harmful chemicals
Sudden Infant Death SyndromeDefinition - unexplained death of an apparently healthy infant.
Leading cause of death in infants <1 year old
Several known risk factors:
• >Mother younger than 20 years old
• >Mother smoked during pregnancy
• >Low birth weight
• >Putting babies to sleep on stomach
• >Siblings of SIDS babies
SIDS
• >Treat as any patient in cardiac or respiratory arrest
• >Resuscitate unless there is rigor mortis
• >Give emotional support for parents
• >The death of child is very stressful for the family
• >Parents guilt is overwhelming
• >Provide support in whatever ways you can
• >IT IS NOT YOUR PLACE TO JUDGE
• >Allow family time with the infant
Child Abuse and Neglect
Any improper or excessive action that injures or harms a child or infantphysical, sexual, emotional abuse and neglect
More than 2 million cases reported annually
Be aware of signs of child abuse and report it to authorities
Signs of Possible Physical and Sexual Abuse
Slap marks, bruises, abrasions, lacerations, incisionsBroken bones
Head injuries
Abdominal injuries
Bite marks
Burn marks
YOUR ROLE:
Gather information from adults without judgmentTalk with child separately
Plainly and clearly report to medical staff any finding or suspicion regarding physical or sexual abuse
Use terms suspected and possible even when talking to partner, hospital staff, police, and superiors
Acute hemolysis
A hemolysis is the premature destruction of erythrocytes.Causes: the most common cause of acute haemolysis is G6PD
Clinical presentation:
-pallor, fatigue, dizziness,
-jaundice
-fever, chills
-dark urine
-headache
-abdominal pain
Signs:
- vital signs: tachycardia, tachypnea & hypotension-ejection systolic murmur
Treatment
>During the attack:
Remove offending drugs and treat any underlying infection
Brisk hydration to ensure adequate urine out put that prevent clogging of renal tubules
Transfusion may be necessary in severe hemolysis (obtain blood sample before transfusion)
>Teaching to avoid oxidant drugs, chemicals and fava beans
>Genetic Consultation, evaluation of family members