
Lec.2
Pediatrics
6
th
stage
2016/8/21
Session notes
د.ربيع الدبوني
Diarrheoa
* Approach to a child with diarrheoa :
Definition of diarrhea :
Acute diarrhea is defined as the abrupt onset of 3 or more loose stools
per day and lasts no longer than 14 days Increase frequency and/or
liquidity of stool
or
Stool output >10 g/kg/24 hr, or more than the adult limit of 200 g/24 hr
Note: Pass of stool > 3 times in day considered diarrheoa except and
exclusively in breast feeding baby it is normal
Chronic diarrheoa is longer than 14 days in duration :
In History :
Focus on :
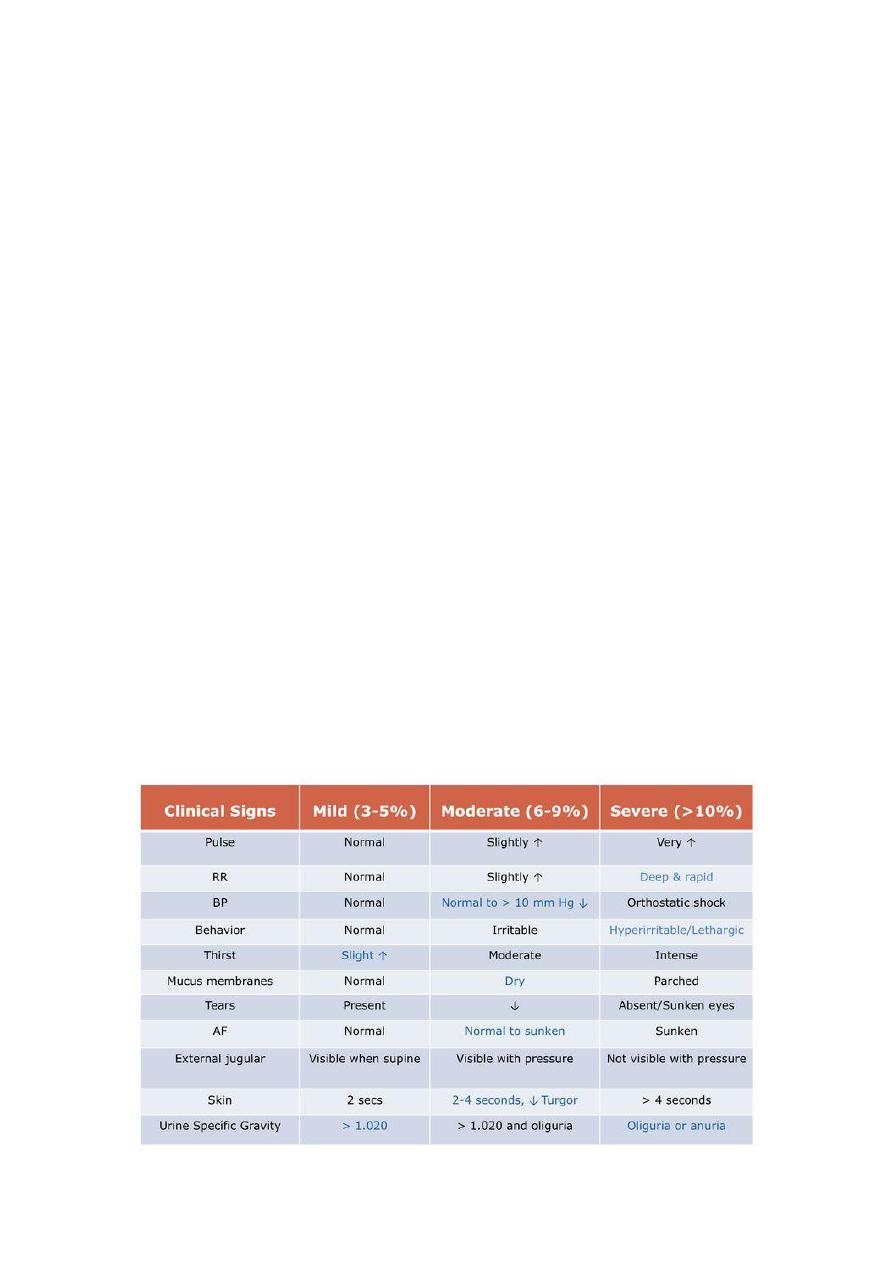
1-Volume of urine ( urine output ) : it is decreased or normal
2-thirsty ( eager to feed )
Check this important measures to assess the dehydration
#Feeding History :
1- Breast feeding :
Way of feeding (using both right and left breast each feeding time)
Regular (at least every 3 hours) or on demand
Any problem with feeding (large nipple, others)
2- Bottle feeding
Way of feeding
Way of preparation
Type of formula use (lactose free, soy milk formula, others)
Way of sterilization of the bottle (boiling, Washing, brushing)
Number of bottles
Number of feeding
Regular (at least every 3 hours) or on demand
Any problem occur after bottle feeding (diarrhea, others)
Put the bottle in freeze for cooling
Mixed feeding (breast and bottle feeding
1 No. = 30 cc ) ( الرقم
#Physical Exam :
Sign of dehydration :

How to examine the fontanelle ?
Examine it when baby is sitting and not crying
Size : normal 2.5 cm
Anterior fontanel diamond shape – close in 6-18 months
Posterior fontanel triangular shape – close in 3 months
Acute Gastroenteritis :
#investigation :
1-stool exam
2-serum electrolyte ( Na , K , Ca )
3- Random Blood Sugar ( RBS ) : as dehydration is state of starvation
4- Blood urea , creatinine ( BUN )
5- CBC ( Hb : is a marker of dehydration , RBC curve shift from right to
left EARLY stages of RBC " band form " , in case of neutrophilia + Band
form " Bandophilia will result this occured in case of " SHIGLLOSIS "
Q/ what is the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis ?
A/ Rota-virus infection
Q/ in blood film of shigllosis what you will see ?
o
The total WBC count reveals no consistent findings. A shift to the
left (increased number of band cells) in the differential WBC count
in a patient with diarrhea suggests bacillary dysentery. Leukopenia
or leukemoid reactions are occasionally detected.
o
In HUS, anemia and thrombocytopenia occur.
o
Bacteremia is rare, even in severe disease, possibly due to the
superficial nature of Shigella infection; the organism rarely
penetrates beyond the mucosa.
o
Blood culture should be obtained in children who appear toxic,
very young, severely ill, malnourished, or immunocompromised
because of their increased risk of bacteremia.
Q/ what is the result of blood film o=in dehydration state ?
Hb : normal or hemoconcentration
PCV : normal or hemoconcentration
WBC : shit to left
Platelet : normal or microagiopathic
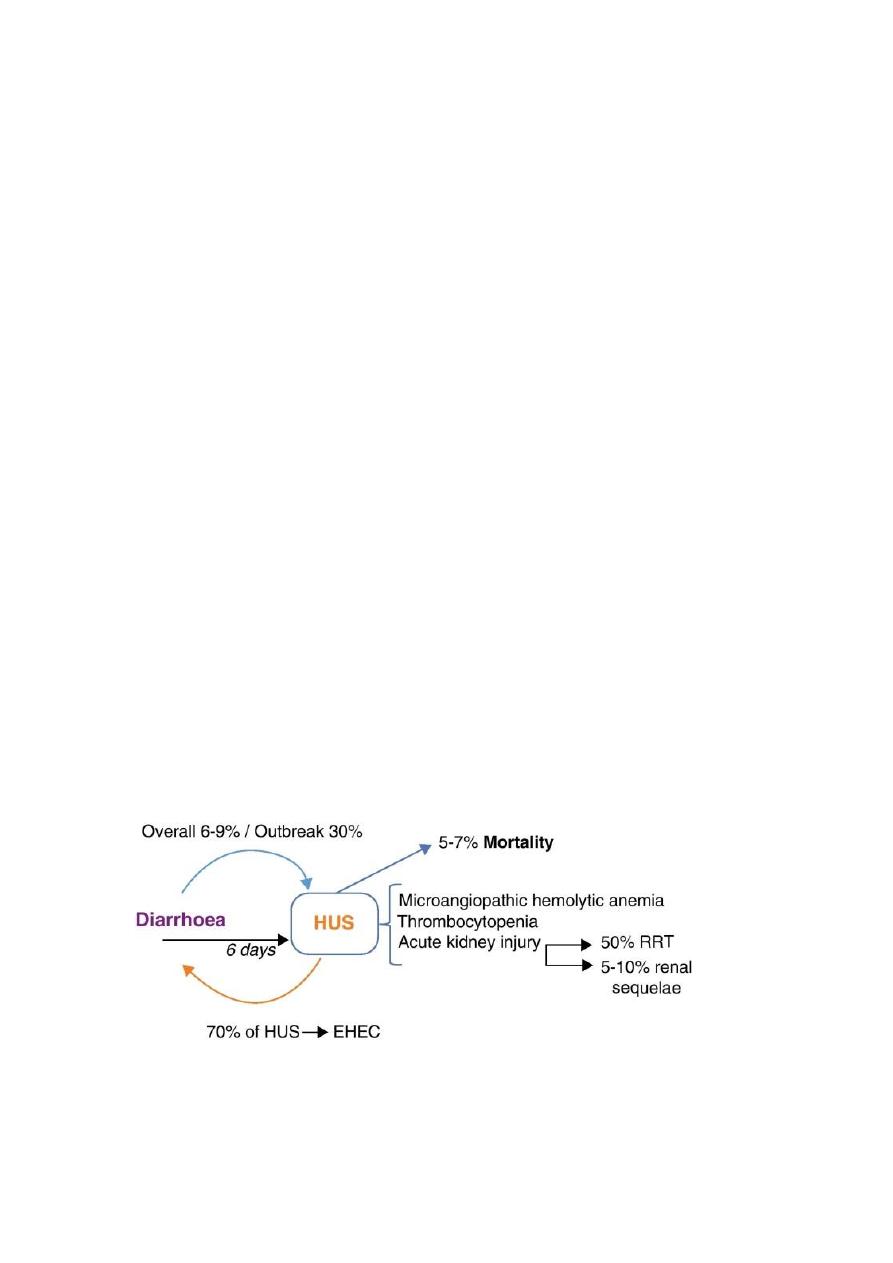
Hemolytic uremic syndrome :
Is a triad of thrombocytopenia , micro-angiopathic , uremia
Helmet shape RBC : There are numerous fragmented RBC's seen here.
Some of the irregular shapes appear as "helmet" cells. Such fragmented
RBC's are known as "schistocytes" and they are indicative of a
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA) or other cause for
intravascular hemolysis.

Normal serum electrolytes :
How you manage a patient with diarrheoa in ER ?
1-IV line ( ask the nurse to take blood sample for serum electrolyte )
2-start with fluid
3-in 2 hours wait results of investigation
4- when results complete manage the dehydration wether is iso,hypo or
hyper natremic dehydration
#General stool exam :
1-macroscopic :
Consistency , color ( normal , watery rice stool cholera
If there is no bile in the stool think about cholera , and the return of bile
to stool ( good prognostic feature )
Blood ( dysentery )
Colorless
Green stool is normal may indicate there is increased transient intestinal
Time ( green stool is as yellow stool )
2-chemical :

A-pH ( normal stool is alkaline ( intesinal – HCO ( bicarbonnate ), if acidic
is abnormal except in breast feeding , acidic ( disaccharidase )
Breast milk contains growth factor this growth induce lactofern which is
used by lactobacillus bactria that produce acid
Acidic in lactose intolerance
B.prescence of reducing agent
C.Occult blood : Toludin test , Benzidine test
3-Microscpic : to reveal if there is
Parasite , ova , trophozoite , cyst
Not talk about bacteria in microscopic exam because it usullay found in
the almost people
Differential diagnose of Pus or RBC in microscopic exam ?
If there is any pus or blood in the result we think about 4 things :
1-Infection ( Bacterial : shiglla , E.coli , campylobater jeujeni , yersinia
Parasitic : Entameoba histolytica , not Entameoba coli )
2-Cow milk allergy , soya milk
3- Inflammatory bowel disease
4-chronic diarrheoa + blood
Case : child with chronic diarrheoa , pus in the stool , Increased ESR ?
Dx : Chron's disease which confirmed by pre-anal abcess + fistula
Rx : prednisolone
Note : when talk about Giarrdia , it contain cyst , never say it has
trophozoite
Helmeniths ( worms ) : mainly stornglydosis it is chronic intesinal
disease
Rx : Yomesan ( 2 tablet chewable ) , for tenia also used
'
Approach to child with chronic diarrhea :
1-chronic diarrhea + wt loss ( FTT )
2-chronic diarrhea + without FTT
3- chronic diarrhea + blood
1*Chronic diarrhea without FTT
>14 day diarrheoa without wt loss or with increased weight
Differential diagnose :
1-lactose intolerance
2-Giardiasis

3-Toddler diarrhea
Q/ diarrhea + abdominal distension what is the DDx ?
( lactose intoerance , hypokalemia + paralytic ileus )
Q/ Chronic diarrhea with antibiotic usage produce bloody diarrhea ?
( Vit. K defeceincy because the antibiotics kill the normal flora of
intestine which produce the Vit.K defeciency )
#Lactose intolerance :
Investiagation in lactose intolerance :
pH : acidic
Reducing substance : +ve
Lactose tolerance test : flat
Increased H in expired breathing
Jejunal biobsy : low histochemical in brush border
# flat lactose intolerance test :
Carbohydrate introdued into body eg, glucose , galactose these will reach
the intestinal zone absosrped by gut mucosa , glucose absorped directly
and disturbed to the body tissue by blood circulation ,
galactose not absorp
ed directly so :
Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (or GALT) is an enzyme (EC 2.7.7.12)
responsible for converting ingested galactose to glucose.
Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase (GALT) catalyzes the second step of the
Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely:
UDP-glucose + galactose 1-phosphate glucose 1-phosphate + UDP-galactose

. The absence of this enzyme results in classic galactosemia in humans and can be
fatal in the newborn period if lactose is not removed from the diet.
Clinical Features :
Rx
: lactose free formula ( Isomil )
Soya formula used in :
1-lactose intolerance
2-Cow's milk allergy
3-Galactosemia
Know days lactose free (LF) milk is used for 2-4 weeks
Types of lactose intolerance :
1-primary ( Inborn error of metabolism ) this with poor prognosis and
presented with vomitng and diarrhea

2-Developemental ( in premature mainly this due incomplete
maturation of the newborn vital organ )
3-Secondary due to mucosal insult and it is the most common pattern
Caused by rota virus , Giardia dudenale , celiac disease , immune
response all these result in mucosal damage
Note : Giardia diagnosed by
1-trophozoite in freshly examined stool , in warm normal saline
2-dudenal biopsy or aspiration
3-If cant diagnosed by the above measures give metronidazole
Rx : 10-30 mg/kg metronidazole
In Ameobia give 50 mg/kg followed by Deluxitine furarite ( to eradicate
the ameoboid cyst )
Toddler diarrhea : diagnosed by exclusion , like Inflammatory bowel
disease in the adult , the stool color is pea + carrot soup
Tx : non-specific , increase fat or fiber , anti-spasmodic , anti-motility
Toddler age ( 2 – 4 ) years
2.Chronic diarrhea + failure to thrive ( FTT ) :
Marasmus body wt < 60% of exepected body wt
FTT : Wt is persistently below 5
th
percentile
FTT : Child who has crossed 2 major centile decreased over 3 monthes
period
FTT : Wt for height below 70% or 80% percentile
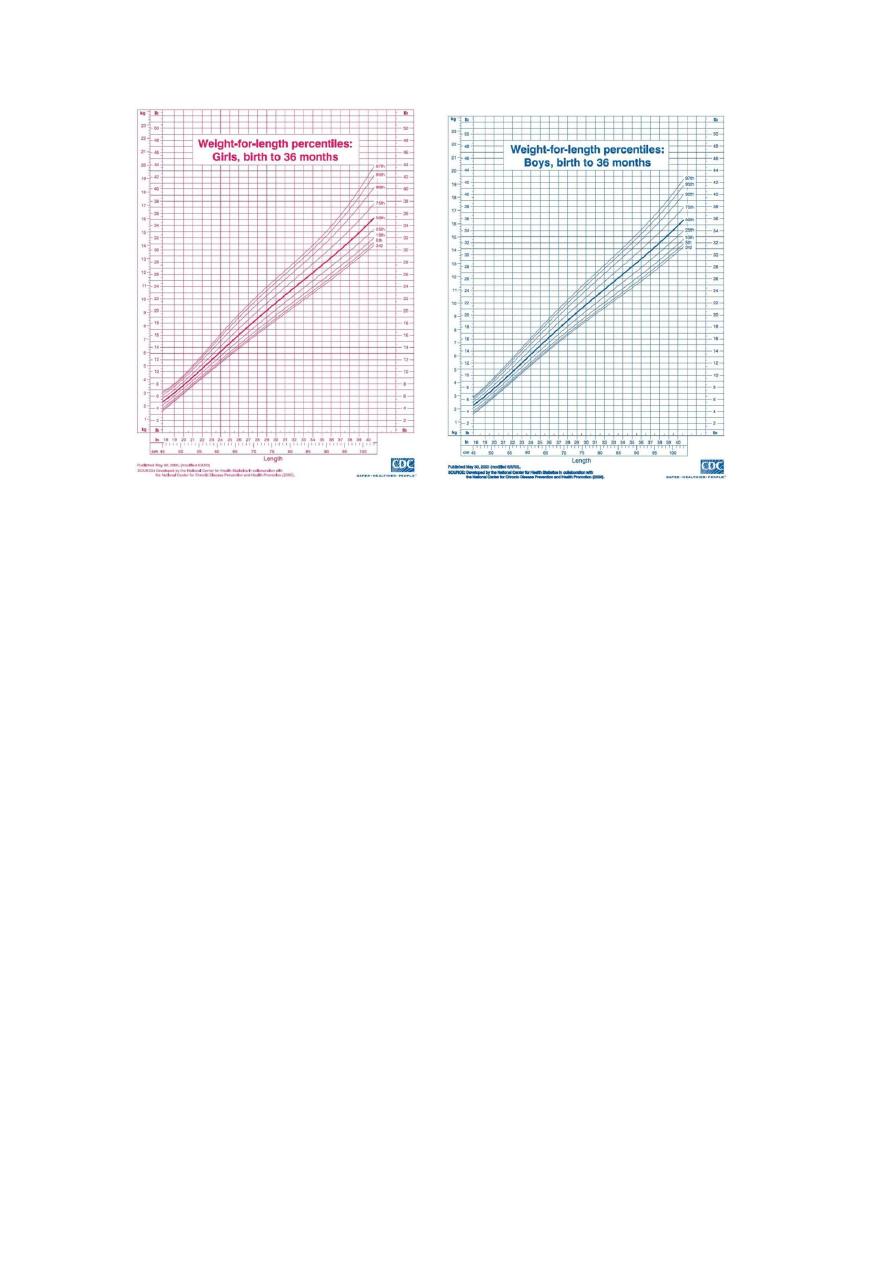
If not increased in wt is also FTT
DDx ( impt ) :
1-lactose intolerance
2-Giardiasis
3-bacterial overgrowth
4-UTI
5-Cow's milk allergy
6- Endocrinopathy ( Addison's disease , thyrotoxicosis , Viboma (
vasoactive intesinal tumor )
7-Celiac disease
#Celiac disaese :
Note : dont talk about celiac disease in child less than 8-9 monthes
Giarrdia celiac syndrome
Practical approach to child with celiac disease :

Incidence 1 : 600 in normal population has IgA defeciency
Which is more liable to celiac disease
Investigations:
1-Anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA
2-Total IgA
3-Dudenal or jejenal biobsy :
a.toatal or subtotal atrophy
b.deepening of crypt
3.infiltration of mucosa by plasma cell
IgA deficent people have a low IgA in normal , in celiac disease patient
may also has IgA deficency but need increased ratio of Anti-tissue
transglutaminase IgA to confirm celaic disease
#Clinical features :

Tx : free gluten diet ( absloute )
Complication :
1-FTT
2-failure to puberty
3-malignancy
4-more liable for GIT malignancy even with treatment
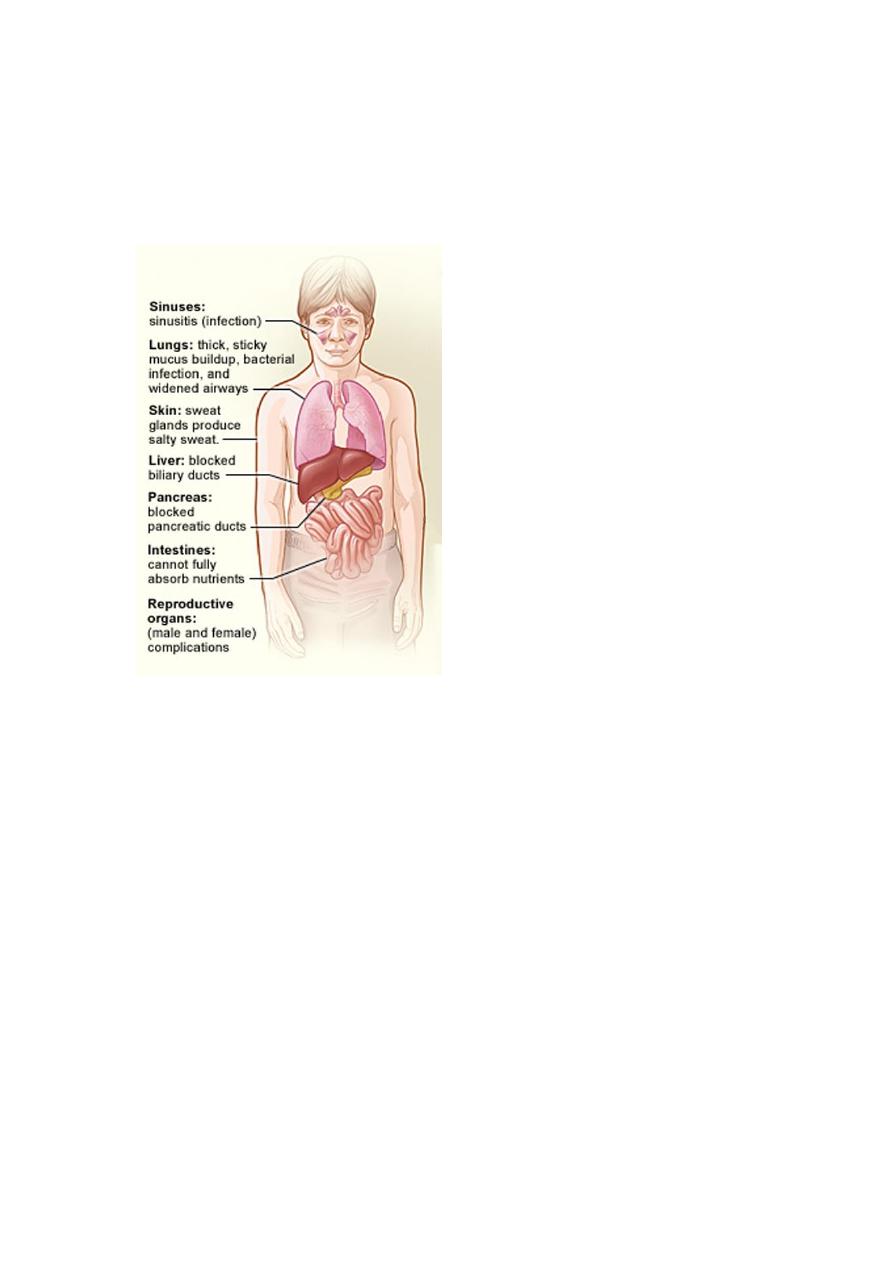
Cystic fibrosis :
Can be diagnised in the first hour of life
Clinical presentation :
Dx : sweat chloride test > 60 % mmol/l or DNA
Tx : lethal disease ( GIT pancreatin , pt die by bronchiactasis and can be
reduced by antibiotics )
Bacterial overgrowth in intestine
UTI ( important ) :
neonatal jaundice , chronic diarrhea , contipation , PUO , anemia ,
recurrent abdominal pain all these can be result in UTI
DX :
1-GUE : pus cell > 5 in high power felid ( it is suggestive )
2-Culture ( definitive ) :

Urine obtained by midstream, (for older children and adolescents) is
considered significant i.e the patient considered to have u.t.i.with
bacterial growth of a single organism of more than 100,000 colony-
forming units/unit or if there is10,000&the the child is symptomatic
In infants(not trained)the use of adhesive sterile collecting bag can be
useful if negative to exclude infection or if positive100,000 in
symptomatic with positive urine culture if any of these criteria not met
then confirmation by catheterized sample
Urine obtained by catheterization is considered significant with
bacterial growth of more than 10,000 CFU/mL. Urine obtained by
suprapubic aspiration is considered significant with any bacterial growth
.
Suprapubic percutaneous aspiration of the bladder may be performed
in young infants if they have not voided for 1 to 3 hours. Perineal bags
for urine collection are prone to contamination and are not
recommended for urine collection for culture.
The diagnosis of UTI requires a culture of the urine. Urine samples for
urinalysis should be examined promptly (within 20 minutes) or
refrigerated until cultured
Urinalysis showing pyuria (leukocyturia of >5 white blood cells
suggests infection
The presence of numerous motile bacteria in freshly voided,
uncentrifuged urine from symptomatic infants and children has a 94%
correlation with a positive culture )
VCUG is done after3weeks&is the best imaging study for determining
the presence or absence of vesicoureteral reflux, which is ranked from
grade I (ureter only) to grade V (complete gross dilation of the ureter
and obliteration of caliceal and pelvic anatomy)
Ultrasound which done in the acute illness provides limited
information about renal scarring and is performed to exclude an
anatomic abnormality

Treatment : .
Older children with acute cystitis are treated for 7 to 14 days with an
oral antibiotic
Increasing bactearial resistance has limited the usefulness of some
antibiotics such as amoxicillin.
Oral third-generation cephalosporins such as cefixime and
cefpodoxime are effective
Children with high fever or other manifestations of acute
pyelonephritis often are hospitalized for initial treatment with
parenteral antibiotics as cefotaxime and gentamicin or another
aminoglycosid. Then after initial improvement therapy can be continued
orally for a total of 14 day
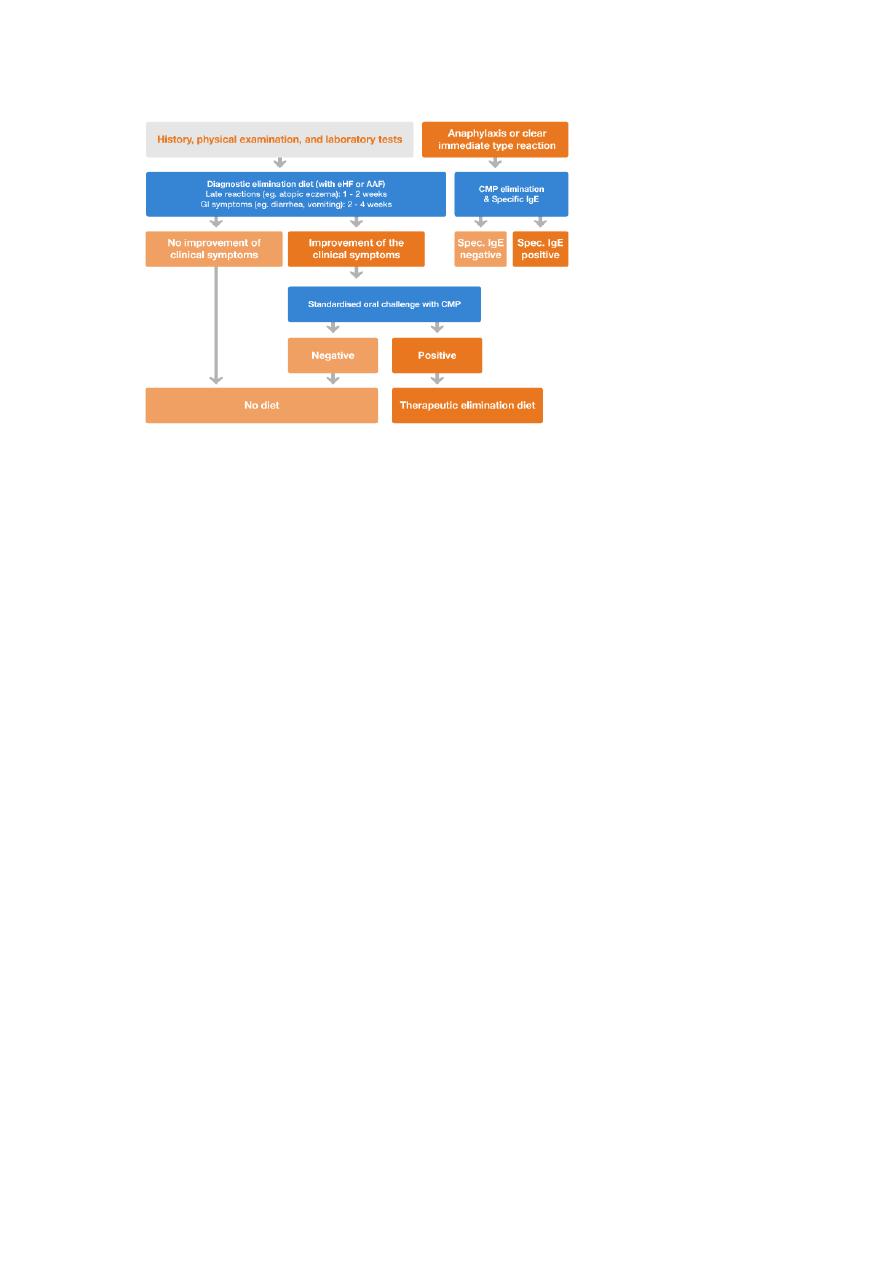
Cow's milk allergy :
Protein ( Casein ) allergy
Clinical :
Dx :
1-free milk test ( challange test )
2- specific Ig test
30-50% of Cow's milk allergy have soya milk allergy
Tx : highly extended milk formula
4*Chronic diarrheoa with blood
:
Post-Antibiotics associated pseudomembranus colitis



