1
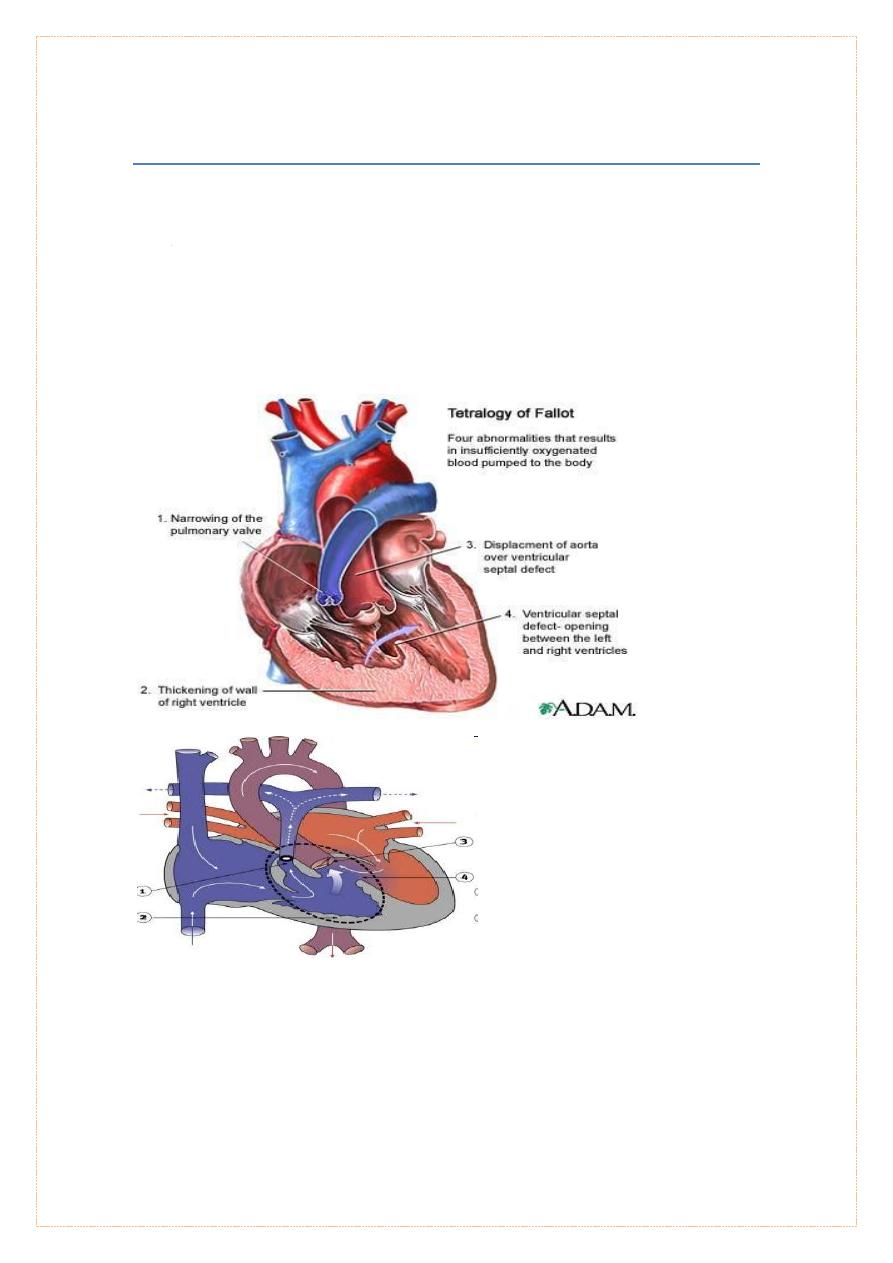
Tetralogy of fallot (TOF)
Commonest cyanotic congenital heart disease in children above the age of
two years constituting almost 75 % of all blue patients.
Four constituents of tetra logy as described originally by Fallot consist of :-
1. Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
2. Pulmonic stenosis
3. overriding or dextroposed aorta, and
4. Right ventricular hypertrophy
Pathophysiology :-
pulmonic stenosis causes right ventricular hypertrophy , increase in right ventricular
pressure -- increasing severity of pulmonic stenosis reduces the flow of blood into
the pulmonary artery and increases the right to left shunt -- as the systolic
pressures between two ventricle are identical there is little or no left to right shunt
and the VSD is silent ------------

2
The right to left shunt is also silent since it occurs at insignificant difference in
pressure between the right ventricle and the aorta --
the flow from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery occurs across the
pulmonic stenosis producing an ejection systolic
the severity of cyanosis is directly proportional to the severity of pulmonic stenosis,
but the intensity of the systolic murmur is inversely related to the severity of
pulmonic stenosis.
Clinical features : -
1. Become symptomatic any time after birth
2. Paroxysmal attack of dyspnea
3. Cyanosis may be present from birth or make its appearance some years
after birth
4. Commonest symptoms are dyspnea on exertion and exercise intolerance
5. Patients assume a sitting posture – squatting – as soon as they get
dyspneic. it is not specific for TOF, it is the commonest congenital lesion
in which squatting is noted
Normal growth and development. Babies who have tetralogy of Fallot may not gain
weight or grow.
Squatting (a compensatory mechanism) is uniquely characteristic of a right-to-left
shunt that presents in the exercising child.
increases the peripheral vascular resistance which diminishes the right-to-left
shunt and increases pulmonary blood flow.
On physical examination :
-
1. Cyanosis , clubbing, parasternal impulse, a systolic thrill.
2. Normal first sound,
3. Single second sound and
4. An ejection systolic murmur.
Investigations : -
ECG : right axis deviation with right ventricular hypertrophy///Echocardiography .

3
Chest X – ray :
Boot shaped heart (it means apex is lifted up & there is a concavity in the region of
pulmonary artery)
Oligaemic lung fields
Hilar vessels are few, lung vessels also few, large rt. Venricle.
Treatment
:
Management of complications and correction of anemia
Treatment of Anoxic spells :
1- Knee chest position, calming.
2- Oxygen .
3- NaHCO3.
4- beta-blockers (propranolol )
5- morphine to reduce ventilatory drive .
6-a vasopressor such as epinephrine, phenylephrine.
7-intubation, sedation
Correction of anemia
Consider operation
complication
1. Cerebral thrombosis
2. Brain abscess.
3. SBE
4. D-Transposition of the Great Arteries
5. paediatric

4
- The aorta arises from the RT ventricle, pulmonary artery from the LTventricle -aorta
is anterior and to the right of the pulmonary artery
Survival : by the foramen ovale and the ductus arteriosus. after birth, ductus begins
to close, severe hypoxemia ensues, within the 1st few days of life
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
1. Cyanosis and tachypnea in the 1st days of life. heart failure is less common.
2. is a medical emergency.
3. prolonged severe hypoxemia& acidosis, lead to death in neonatal period.
4. The precordial impulse normal, or parasternal heave .
5. S2 usually single and loud.
6. Murmurs absent,or a soft systolic ejection murmur at the midleft sternal
border
DIAGNOSIS
ECG: normal neonatal right-sided dominant pattern.
-CXR : mild cardiomegaly, a narrow mediastinum ( egg-shaped heart), normal early
increased pulmonary blood flow after 1st wk or two of life
-Arterial PO2 is low and does not rise appreciably after the patient breathes 100%
oxygen (hyperoxia test).
-Echocardiography .
-Catheterization .
TREATMENT
1-infusion of prostaglandin E1 should be initiated immediately to maintain patency
of the ductus arteriosus and improve oxygenation (dosage, 0.01–0.20 μg/kg/min).
2-kept warm.
3-correction of acidosis and hypoglycemia .
4-Rashkind balloon atrial septostomy .
5-the arterial switch (Jantene) operation is performed within the 1st 2 wk of life
