Pediatrics
Lec 1
INTRODUCTION AND DEFINITIONS
! Pediatrics is concerned with the health of infant, children and
adolescence. Their growth and development and their opportunity
to achieve full potential as adults
! Children (0-21) year make up slightly less than 1/3 of population in
the USA.
! More than century ago pediatric emerged as medical specialty in
response to increasing awareness that the health problem in
children differ from those in adult and that the child response to
illness and stress varies with age.
! In the late 19th century in the USA, of every 1000 of children born
alive; 200 children might be exposed to die before age of 1 year
because of condition such as dysentery, pneumonia, measles,
diphtheria, and whooping cough.
! The effort of the pediatrician, scientist, pioneer in the public
health have led to a better understanding of the origin and
management of many problems of infant.
! Mortality rate in the USA decrease in the past 1/2 century from
75/1000 live birth in 1925 to about 6.9/1000 in 2000.
1

Pediatrics
Lec 1
In the developing country
! 90% of children in the early 21st century are born into the developing or third
world.
! According to current Unicef data1000 infant die each hour, 970 of
these deaths occur in the developing country.
! According to WHO: 10.5 million of child younger than 5 year died in
1999; of these 99% lived in the developing countries.
Cause of death attributed to:
Under 1 year
! Perinatal condition
! Short gestation/ low birth weight
! Complication of pregnancy
! Respiratory distress syndrome
! Infection
! Intrauterine hypoxia/ asphyxia
! Congenital malformation deformities/ chromosomal abnormalities
! Sudden infant death syndrome
! Injuries and adverse events
1-4 years
! Injuries (unintentional)
! Congenital malformation deformities/ chromosomal abnormalities
! Malignant neoplasm.
! Homicide.
! Disease of the heart.
5-9 years
! Injuries (unintentional)
! Malignant neoplasm
! Congenital malformation deformities/ chromosomal abnormalities
! Homicide.
! Disease of the heart.
2
Pediatrics
Lec 1
10-14 years
! Injuries (unintentional)
! Homicide.
! Suicide.
! Malignant neoplasm
! Disease of the heart.
15-19 years
! Injuries (unintentional)
! Homicide.
! Suicide.
! Malignant neoplasm
! Disease of the heart.
MORTALITY RATES
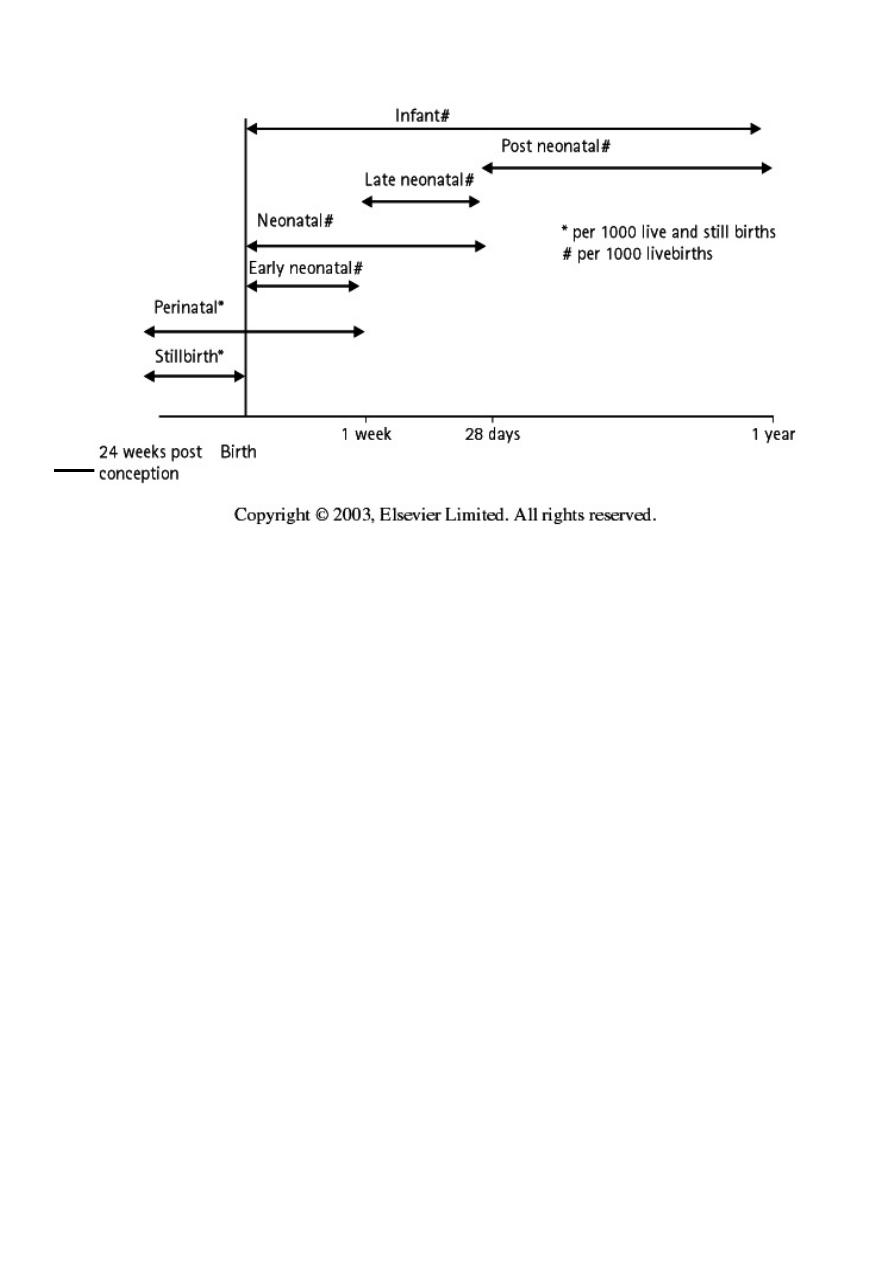
! LIVE BIRTH: Any infant, who breathes, has a heart beat or pulsation
of the umbilical cord is defined as a ‘live birth’, irrespective of
gestation or the duration of the signs of life.
! STILLBIRTH: is defined now as being a child born at 24 or more
weeks post conception who shows no signs of life, although, up until
1992, the definition required that they were born at least 28 weeks
post conception.
! THE UNDER-5 MORTALITY RATE, widely used, particularly in
poorer countries, is defined as the annual number of deaths in
children under 5 years of age per 1000 live births.
! AGE-SPECIFIC DEATH RATES are the number of deaths in an age
group per 1000 individuals in that age group.
3
Pediatrics
Lec 1
Deaths in the first year of life
! Of all deaths in childhood (age 0–14), 70% occur within the first year
of life, 46% within the first month and 35% within the first week.
! In the neonatal period, a substantial proportion of deaths are
related to congenital anomalies and prematurity.
Prevalence of many congenital anomalies appears to have declined,
particularly that of anomalies of the central nervous system this decline
attributed to:
! Widespread introduction of screening for neural tube defects in
pregnancy
! Changes in diet.
! Use of periconceptual folate supplements.
Congenital anomalies remain an important cause of death after the
neonatal period, accounting for 24% of all deaths between 1 month and
1 year of age.
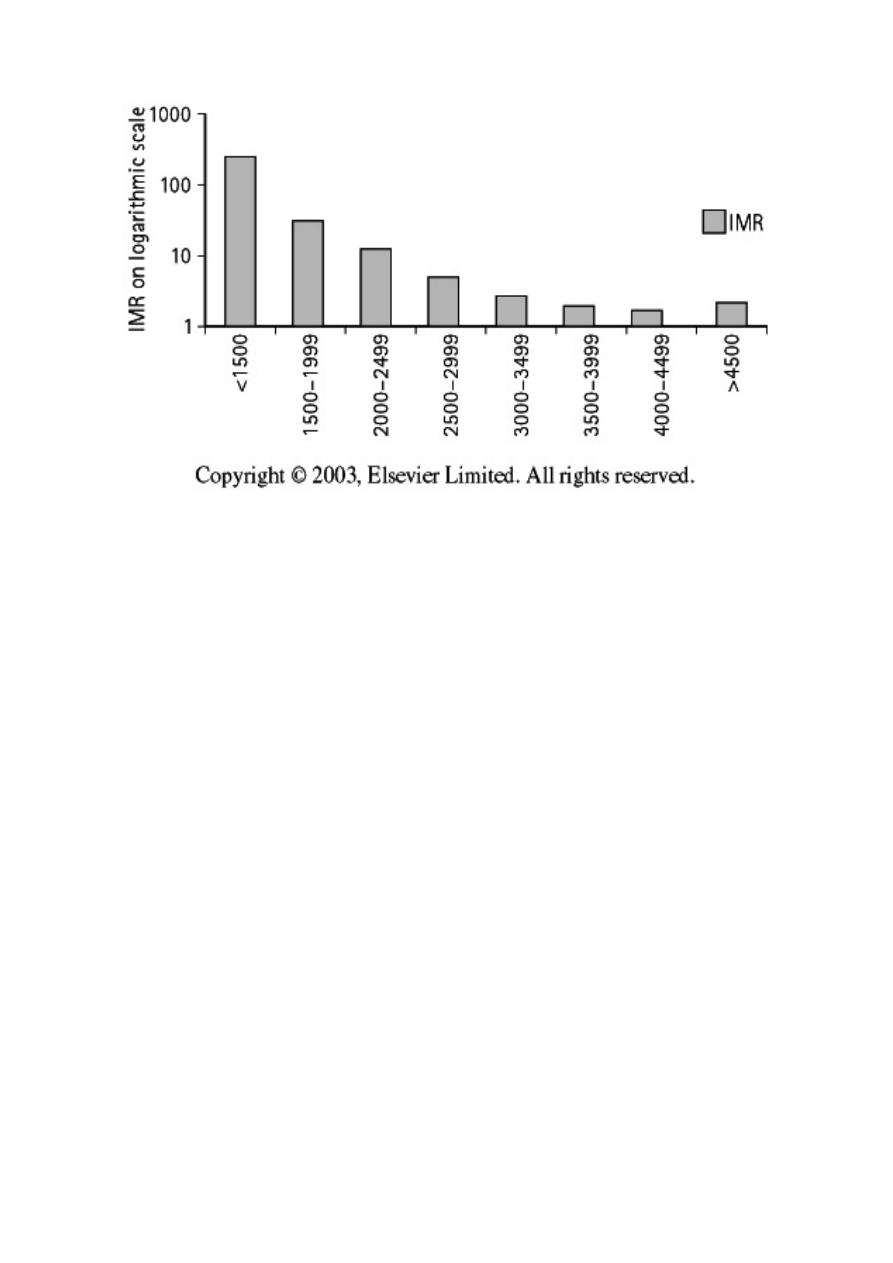
! Birth weight, reflecting both gestation and intrauterine growth, is
the strongest predictor of the risk of death in the first year of life.
4
Pediatrics
Lec 1
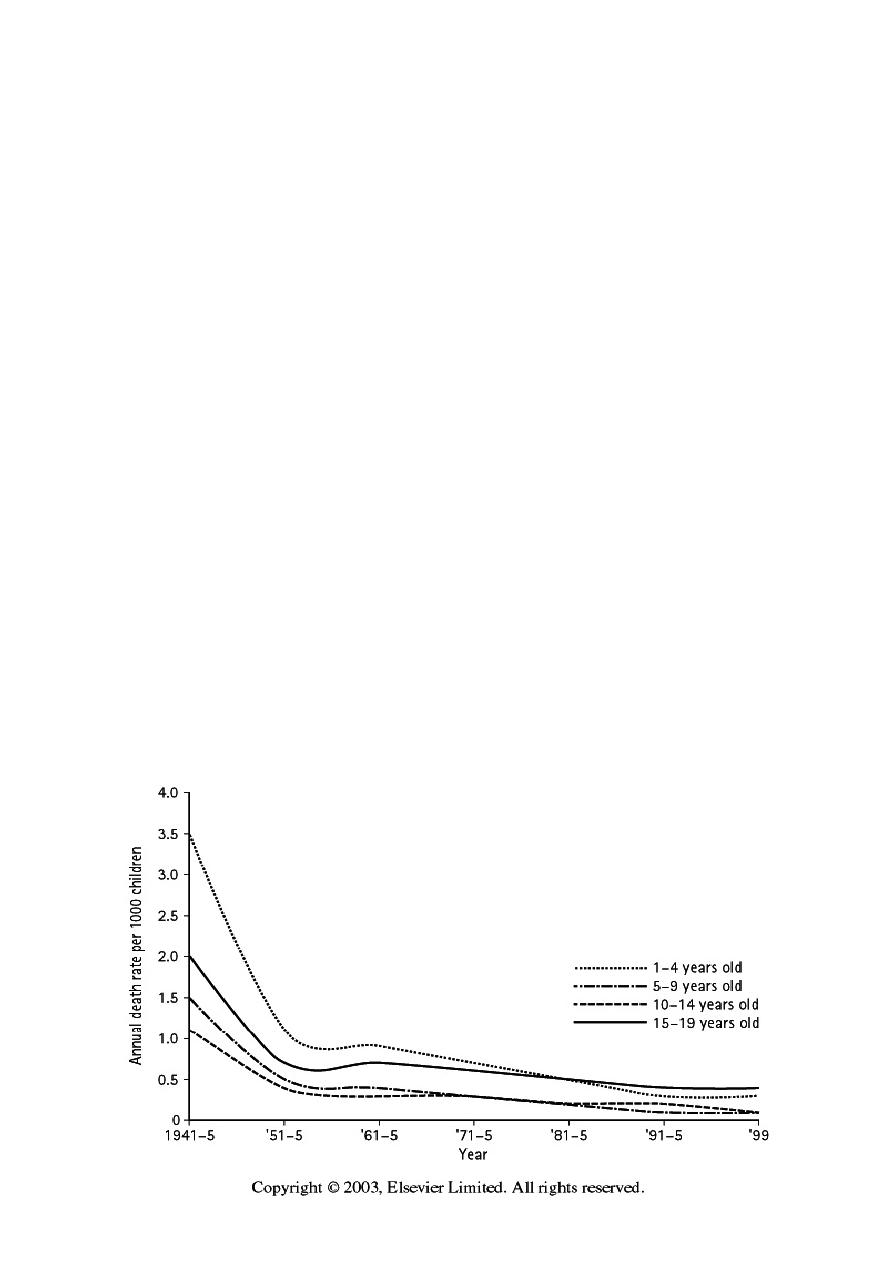
Deaths in older children
! The risk of death drops rapidly after the first year of life.
! Death rates then begin to rise again after the age of 15, particularly
in boys and largely as a result of the increasing risk of injuries.
! Injury and poisoning remain responsible for the greatest proportion
of deaths in older children.
5
