
Obstetrics
Dr. Aseel
1
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
Genital system
Amenorrhea – The most common presenting symptom of pregnancy is cessation of periods, in a
woman having regular menstruation
Quickening – 16-20 weeks; described as a flutter & is difficult to distinguish from peristalsis; will
gradually increase in intensity & frequency.
(Braxton Hicks contractions) from the 2nd trimester onwards , the uterus undergoes irregular
painless contractions ..They may cause some discomfort late in pregnancy and may account for
false labour pain .
LEUCORRHOEA - The normal vaginal discharge increases during pregnancy because of excess
oestrogen and may form a complaint However, a pathological discharge, e.g., monilial infections
which is common in pregnancy must be excluded.
Round ligament strain – Pain is felt along the round ligament and in the groin. Pain unilateral and
left-sided, (dextroflexion ). It is due to stretching of the nerve fibres in the round ligaments.
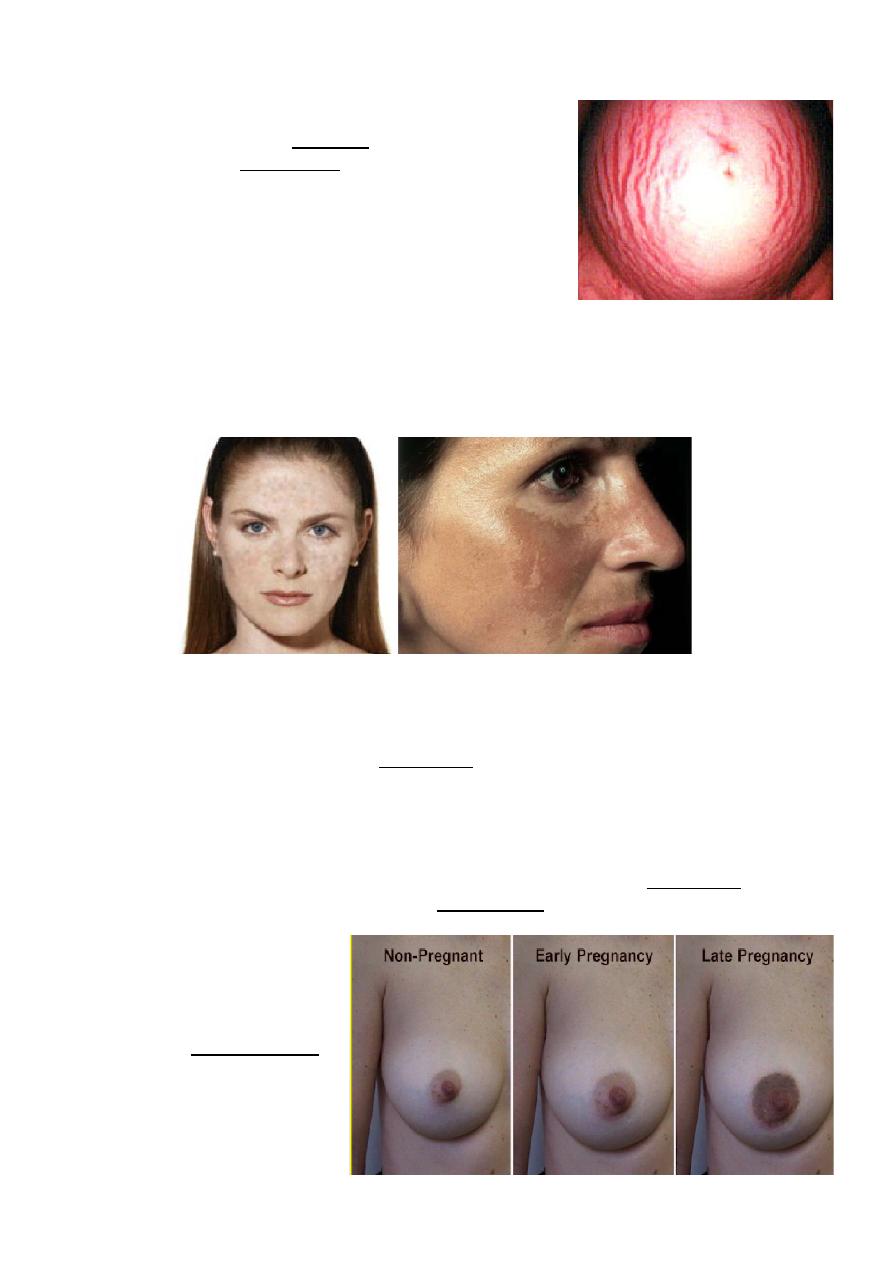
Changes in the vagina - The vagina becomes soft , warm, moist with increased secretion and violet
in colour (Chadwick's sign) due to increased vascularity. Vaginal mucosa thickens & the rugae
(vaginal folds) become pronounced (to allow expanding without trauma during delivery).
Changes in the vulva : It becomes soft, violet in colour
Oedema and varicosities may develop
GIT
Nausea and Vomiting of pregnancy (NVP)
Is the most common medical condition in pregnancy.
Occurs in approximately 50% of pregnancies and is most marked at first 3 months of
pregnancy.
It is usually most severe in the morning (Morning Sickness) but can occur at any time .
The pathogenesis of NVP is poorly understood and probably results from rapidly rising serum
levels of human chorionic gonadotropin
Appetite changes
The pregnant woman dislikes some foods and odours while desires others
Reduced sensitivity of the taste buds during pregnancy creates the desire for markedly sweet,
sour , or salt foods .

Obstetrics
Dr. Aseel
2
Pica - Deviation may be so extreme to the extent of eating blackboard chalk , coal or mud
Ptyalism - It is excessive salivation .
Gastric Reflux (Heartburn)
Gastric reflux commonly occurs as a result of delayed gastric emptying, decreased intestinal
motility, and decreased lower esophageal sphincter tone.
Information on lifestyle modification includes maintaining upright positions (especially after
meals), sleeping in a propped up position and dietary modifications (e.g. small frequent meals,
eat slowly, reduction of high-fat foods and caffeine).
Antacid preparations .
Constipation - It is treated by
(a) evacuation of the bowel at the same time each day (bowel training)
(b) diet rich in fiber in the form of vegetables, fruits, and bran
(c) avoid dehydration by increasing fluid intake.
(d) increase physical activity and avoid sedentary life.
Haemorrhoids :Treatment includes diet modification, topical soothing preparations and rarely
surgery.
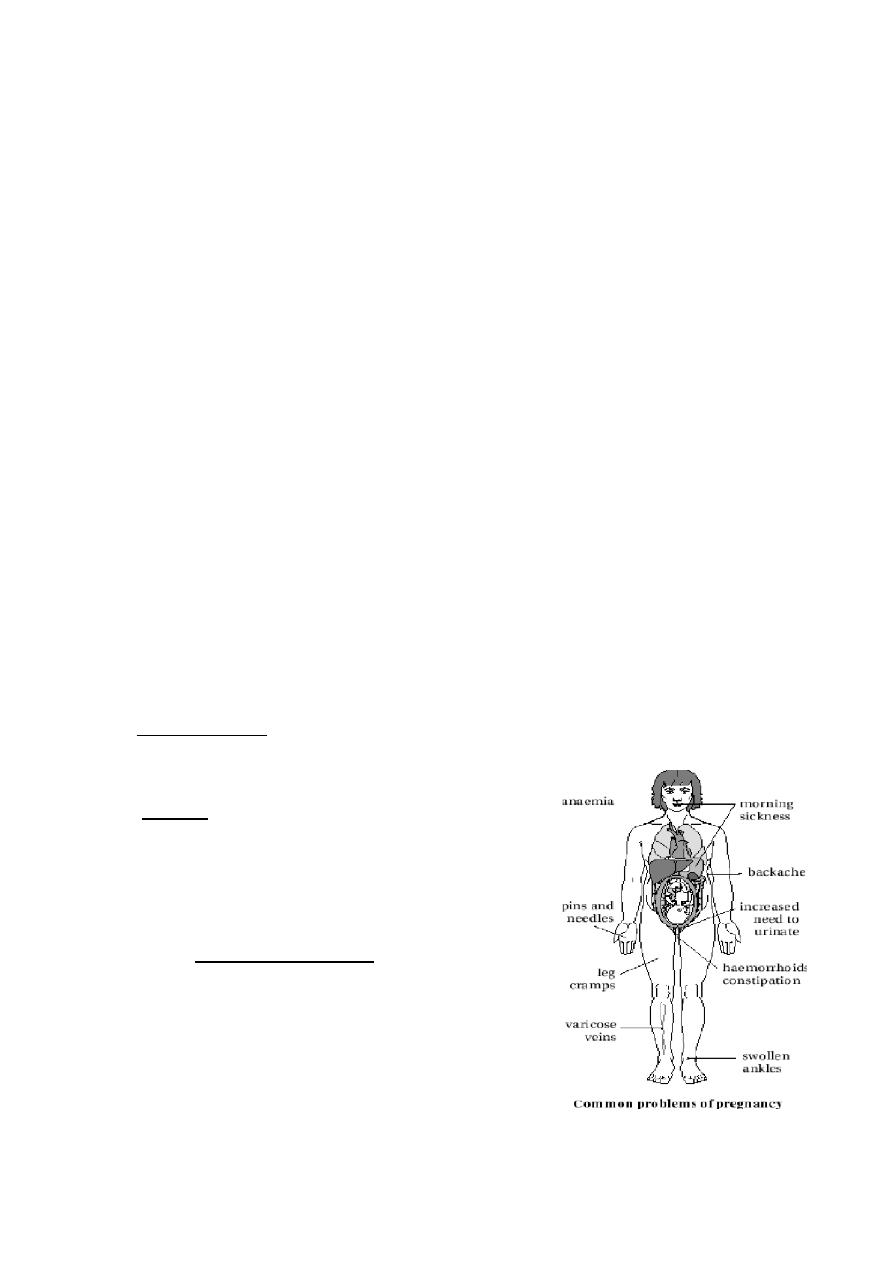
Urinary system
Bladder and urethra:
Frequency of micturition in early pregnancy due to :
i - Pressure on the bladder by the enlarged uterus .
ii - Congestion of the bladder muscosa .
Urinary stress incontinence - may develop for the first time during pregnancy (due to
decreased intraurethral pressure and decreased length of the urethra) and
spontaneously relieved later on
Skin Changes
In abdomen:
Linea Nigra - pigmentation in midline below the umbilicus
Stria gravidarum
Pigmentation in the lower abdomen, flanks , inner thighs,buttocks & breast and increase
Obstetrics
Dr. Aseel
3
as pregnancy advances.
It starts pink (stria rubra) then becomes pale to
white (stria albicans) after delivery, which
persists. (Primigravida has stria rubra only ,while
multigravida has both S.R and S.A).
It may be due to mechanical stretching or
increased glucocorticoids which results in rupture
of the elastic fibers in the dermis and exposure of
the vascular subcutaneous tissues
In face
Chloasma gravidarum (mask of pregnancy) - a butterfly pigmentation on the cheeks and nose .
It usually disappears few months after labour .
Breast signs
i) First month :
increased size & vascularity (dilated veins) , mastodynia may be present which ranges from
tingling to frank pain due to hormonal responses of the mammary ducts and alveolar
system
ii) Second month :
increased pigmentation of the nipple & areola and prominence of Montgomery tubercles
(non pigmented nodules) around the primary areola
iii) Fourth month :
a pigmented area
appears around the
primary areola called
the secondary areola
Obstetrics
Dr. Aseel
4
Musclo-skeletal system
Backache is treated by:
(a) more periods of rest.
(b) use of maternity corset.
(c) local heat in the form of hot water bag
(d) analgesics given systemically or as local creams, Paracetamol is the drug of choice.
Oedema and varicose veins because of Increased venous pressure in the lower limbs :
Varicose Veins treatment:
1. avoid long periods of standing and encourage active exercise.
2. avoid constricting clothes.
3. keep the legs elevated while sitting and during sleep.
4. use of elastic stockings. These should be removed at night and applied before getting
out of bed in the morning
CVS
Peripheral Vasodilatation
blood flow to the skin, particularly in the hands and feet generally giving the pregnant women a
feeling of warmth
Increases the congestion of nasal mucosa leading to a
common complaint of nasal obstruction and bleeding
(epistaxis).
CNS
Fatigue is very common in early pregnancy and reaches a
peak at the end of the first trimester. Rest, lifestyle
adjustment and reassurance are usually all that is required.
Fatigue also occurs in late pregnancy, when anaemia
should be excluded.
Insomnia is also very common and due to a combination of
anxiety, hormonal changes and physical discomfort. Mild
physical exercise before sleep may help but drug treatment
should be avoided.
Tension headaches

Obstetrics
Dr. Aseel
5
Peripheral paraesthesia Fluid retention leads to compression of peripheral nerves. This often leads
to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Interventions include wrist splints, steroid injections and analgesia.
Other nerves can be affected, e.g. lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
Clinical examination
Estimation of uterine size by vaginal examination is reasonably accurate in early pregnancy compared to
after 12 weeks gestation.
Hegar’s sign = 6-12 weeks; softening & compressibility of the lower uterine segment (the uterine isthmus),
results in exaggerated uterine anteflexion during the 1st 3 months of pregnancy
ballottement = 16-28 weeks (passive movement of the unengaged fetus).
Diagnosis of pregnancy
The hormone B-hCG is secreted by the trophoblastic tissue or placenta. This increase in pregnancy
and peaks at 10 weeks. The levels of this hormone can be measured by blood or urine.
Ultrasound Visualization of fetus (u/s) = 5-6 weeks;
Fetal heart tones (u/s) = 6 weeks; by doppler = 17 weeks;
fetal stethoscope = 17-19 weeks
Fetal movement palpated = 19-22 weeks
F
o
r
m
a
t
t
e
d
B
y
M
o
h
a
m
m
e
d
M
u
s
a
