Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
1
Labor & Delivery
Labor
• Labor is the physiologic process by which a fetus is expelled form the
uterus to the outside world.
• It Is the process where by painful , regular uterine activity (contraction)
with progressive cervical effacement and dilatation accompanied by
decent of the presenting part leads to expelled of the fetus from the
uterus at or beyond 24 completed weeks of pregnancy.
Definitions
• Preterm labor – Prior to 37 weeks
• Term – 37 to 42 weeks
• Post term – After 42 weeks
• Post dates – After 40 weeks
Term Labour
PTL prolonged
1 LMP
24 w 28 w 37 w 40 w 42 w
Diagnosis
Labor diagnosis is usually made retrospectivelly.
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
2
A. symptoms:
1. true labour pain : colicky pain in abdomen & back characterized by:
2. Show – blood stained mucous.
3. SROM one in four women experience SROM before onset of labor. Labor
usually follows.
B. Signs:
o
palpable or recorded uterine contraction
o
effacement and dilation of the cervix
o
formation of forewater
Onset of Labor
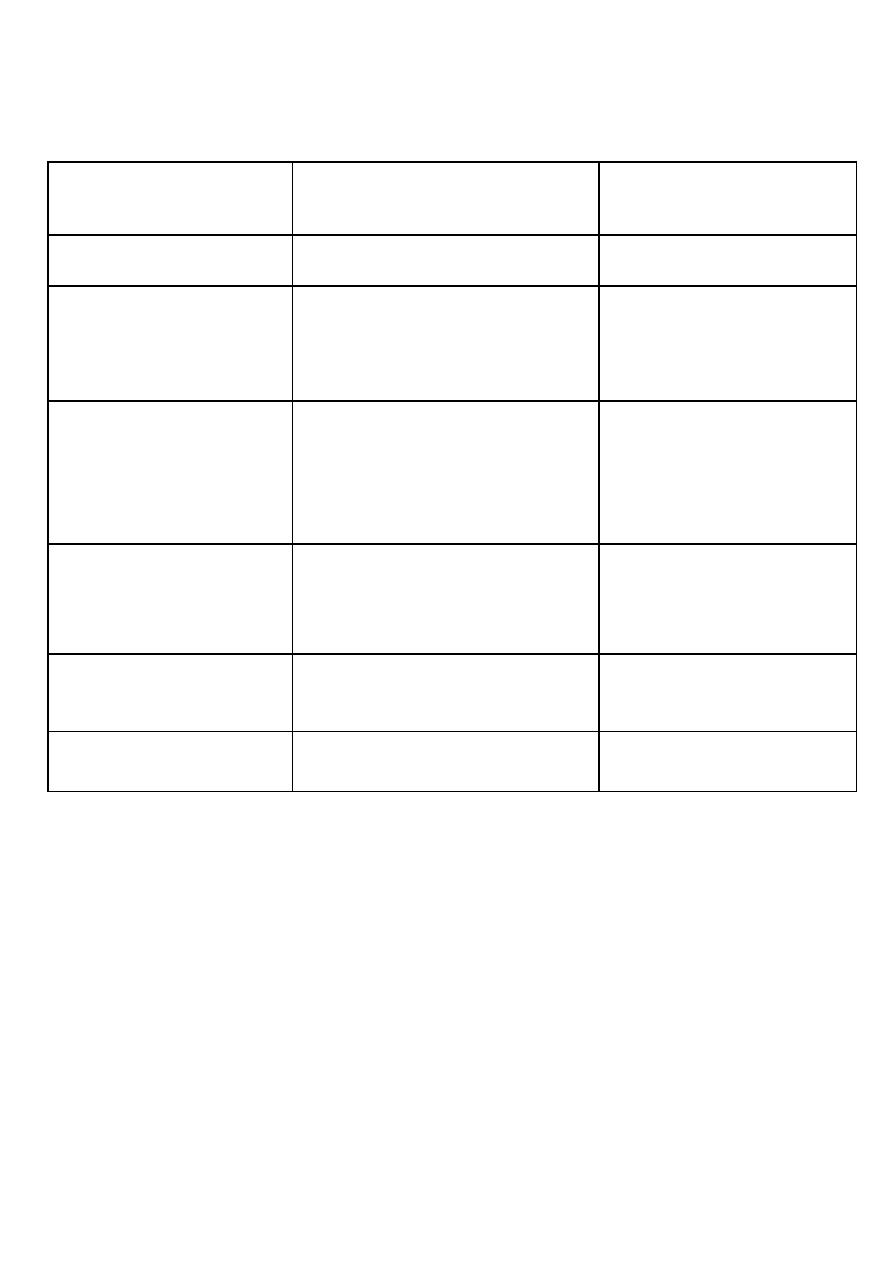
False labour pain
True labour pain
Character
Irregular
regular
contractions
Short duration, not
progressive
Progressive (increase in
frequency and
intensity)
Interval between
contractions
and intensity
Not associated with
effacement and
dilation of the
cervix
Associated with
effacement and
dilation of the cervix
Changes in the
cervix
Not associated with
bulging of
membranes
Associated with bulging
of membranes
Membranes
Relieved by
sedation
Not relieved by
sedation
Response to
analgesia
Not followed by labour
Followed by labour
Labour
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
3
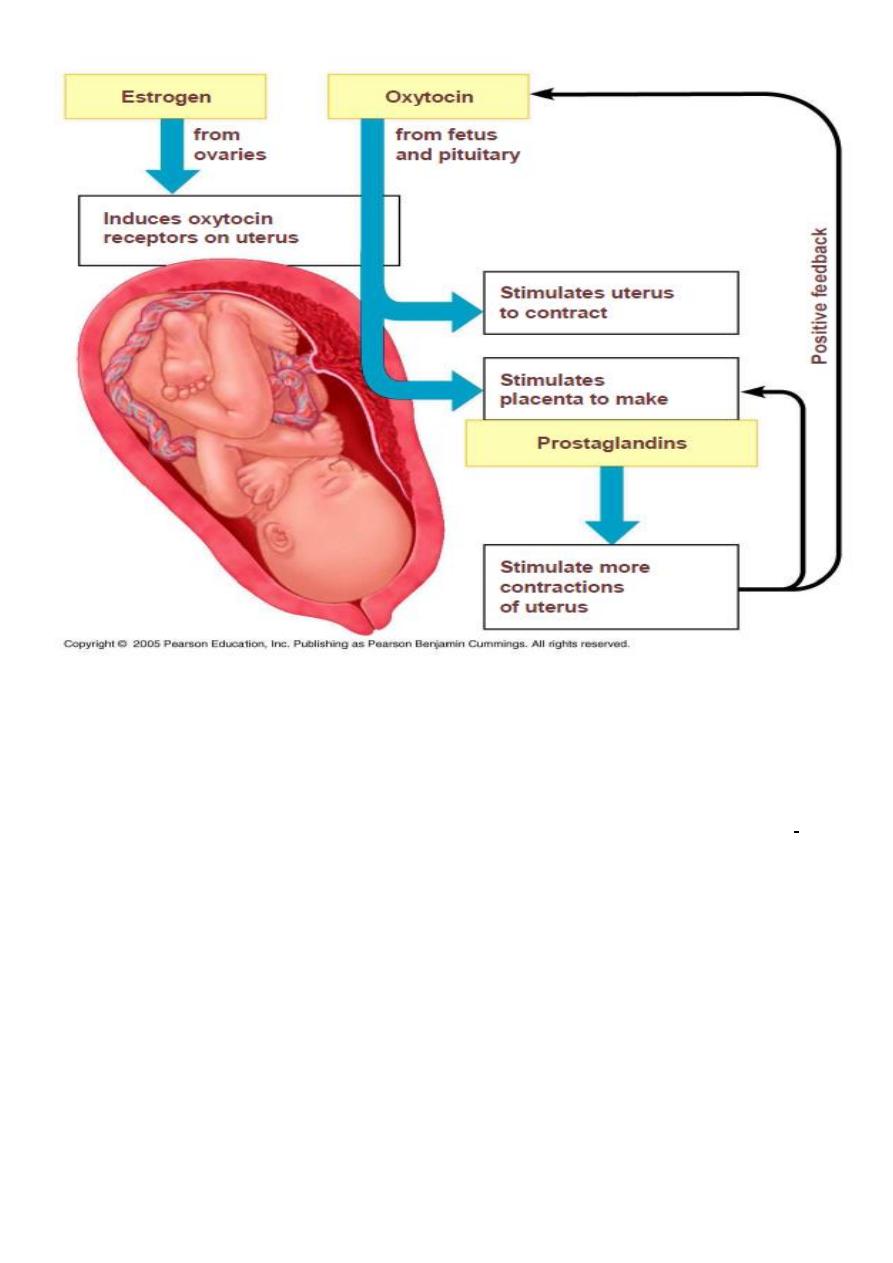
• Progesterone withdrawal :because it maintains uterine quiescence by
suppressing PG production , inhibiting communication between
myometrial cells & preventing oxytocin release.
• Estrogen: opposes the action of progesterone & increases uterine
estrogen receptors
• Oxytocin
• Prostaglandins
• Fetal effect:fetal adrenal gland produces cortisol stimulating the
conversion of progesterone to estrogen.
The initiation of labor
Labor is influenced by combination of factors include:
1-
Myometrial cells contraction &retraction in
response to increase intracellular Ca under the
effect of oxytocin &PG in addition increase in
the number of gap junction by PG leading to the
development of the thicker,actively contracting
upper segment,while the segment becomes
thinner &more streched eventually the cervix
being taken up to efface & then dilate.
2-
Reduce cervical resistance with softtening,
thinning (ripening) due to increase proteolytic
activity & reduction in collagen &elastin under
the influence of PG in addition to increase in
water content of cervix under the effect of
interleukins.
3-
As labour becomes established pressure from
the fetal presenting part against the cervix is
relayed via a reflex arc involving the spinal cord
& results in increased oxytocin release from the
maternal posterior pitutairy (Fergusson reflex).
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
4
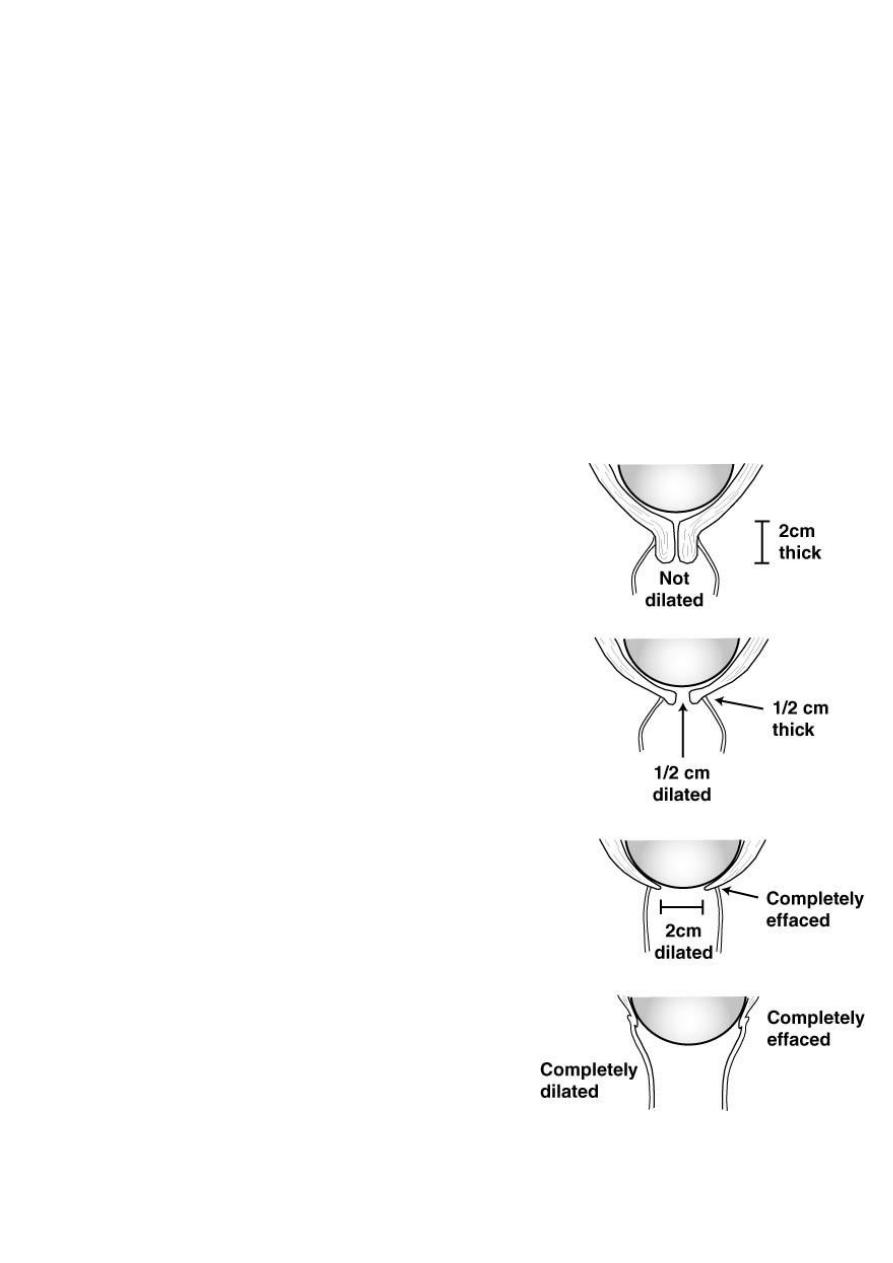
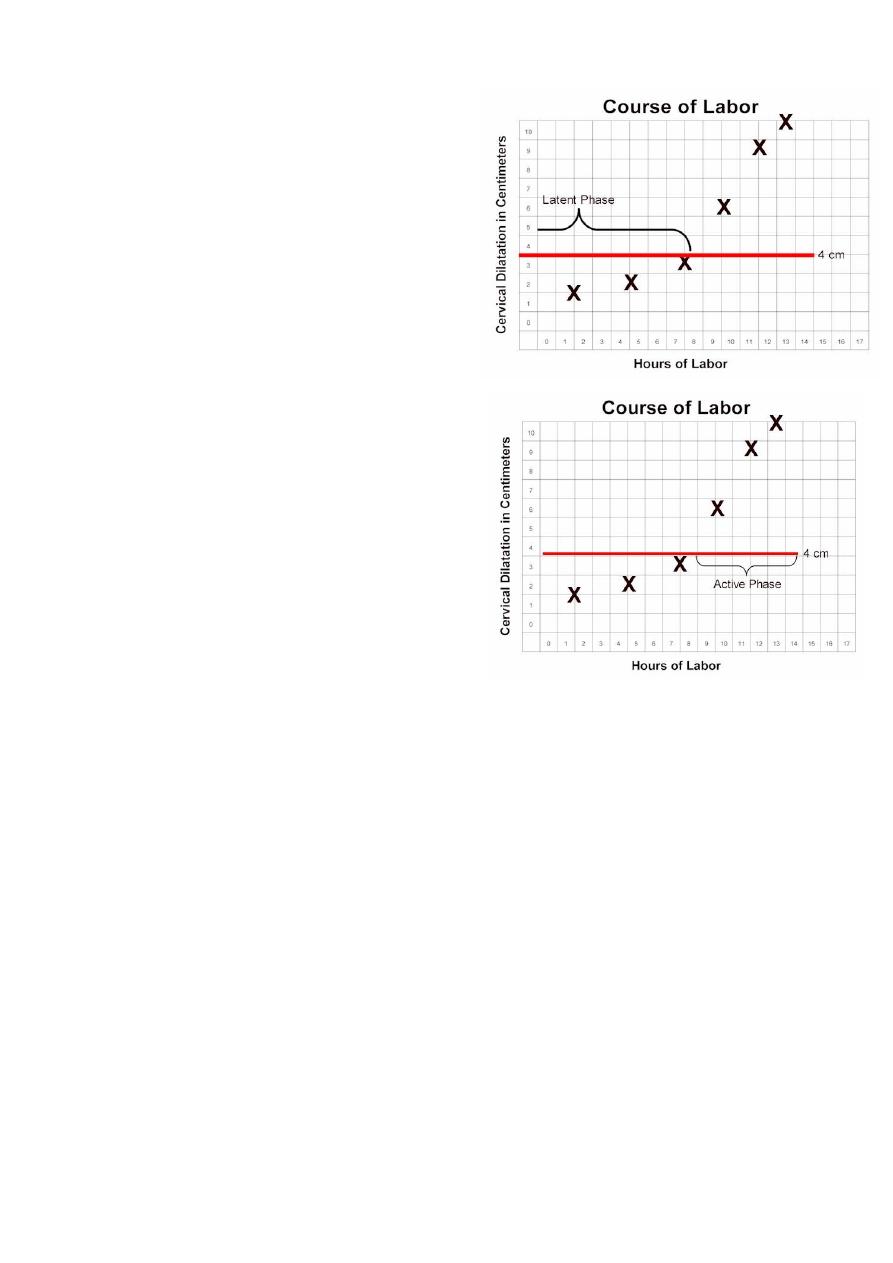
Stages of labor:
first stage of labor:
begins with the onset of labor and ends with complete (10
cm) dilatation of the cervix.
Duration of the first stage:
• The first stage is the longest, averaging 8–12 h for primigravidas or 6–8 h
for multiparas.
• However, the first stage of labor may be markedly shorter or longer
depending on the 3Ps.
• During this stage the progress of labor is assesed mostely depending on
cervical dilatation.
• It is divided into 2 phases:
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
5
Latent Phase Labor
From the onset of labour till 4 cm dilatation
• Contractions may or may not be
painful
• The cervix becomes fully effaced
• Can talk or laugh through
contractions
• Lasts between 3-8hr being shorter in
multiparous
Active Phase Labor
• From 4cm till full(10cm) dilatation
• Regular, frequent, usually painful
contractions
• Dilate at a rate of 1cm/hr or more.
• Are not comfortable with talking or
laughing during their contractions
• Lasts 2-6hr being shorter in
multiparous
Second Stage:
• Interval between full cervical dilation to complete delivery of the baby.
• Progress of labour is estimated by descent of the presenting part through
the maternal pelvis and expulsion of the fetus.
• Indications of second stage:
• Increased maternal show
• Pelvic/rectal pressure
• Maternal urge to push.
• Divided into 2 phases,the passive from full dilatation till the onset of
involuntary expulsive contractions &the active from urge to push till
delivery of fetus which should not last longer than 2hr in primi &1hr in
multiparus.

Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
6
Third Stage:
• The time from fetal delivery to delivery of the placenta
• Three signs of placental separation:
– Lengthening of umbilical cord
– Gush of blood
– Fundus becomes globular and raises up
– Usually upto 30 minutes
Fourth Stage:
• Begins with birth of the placenta and ends 1-2 hour later
• Highest risk to maternal well-being
• Observations- examine uterus for firmness, inspect cervix, vagina,
perineum for lacerations and tears, evaluate maternal vital signs, examine
the baby
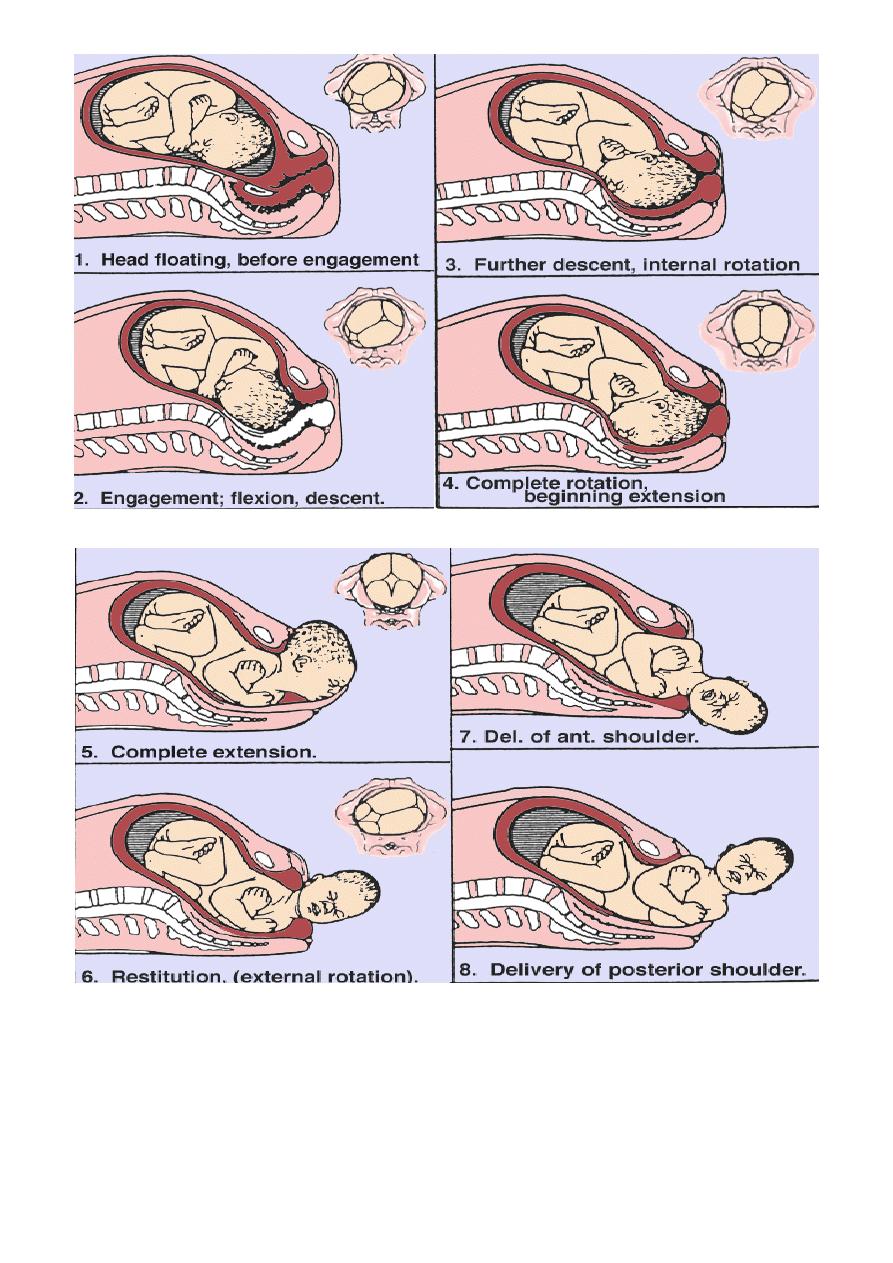
Mechanism of Labor
• The series of changes in position & attitude that the fetus undergoes
during its passage through the birth canal.
• Engagement
• Descent
• Flexion
• Internal rotation
• Extension
• Restitution
• External rotation
• Birth of the shoulders& body
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
7
THE CARDINAL MOVEMENTS OF LABOUR
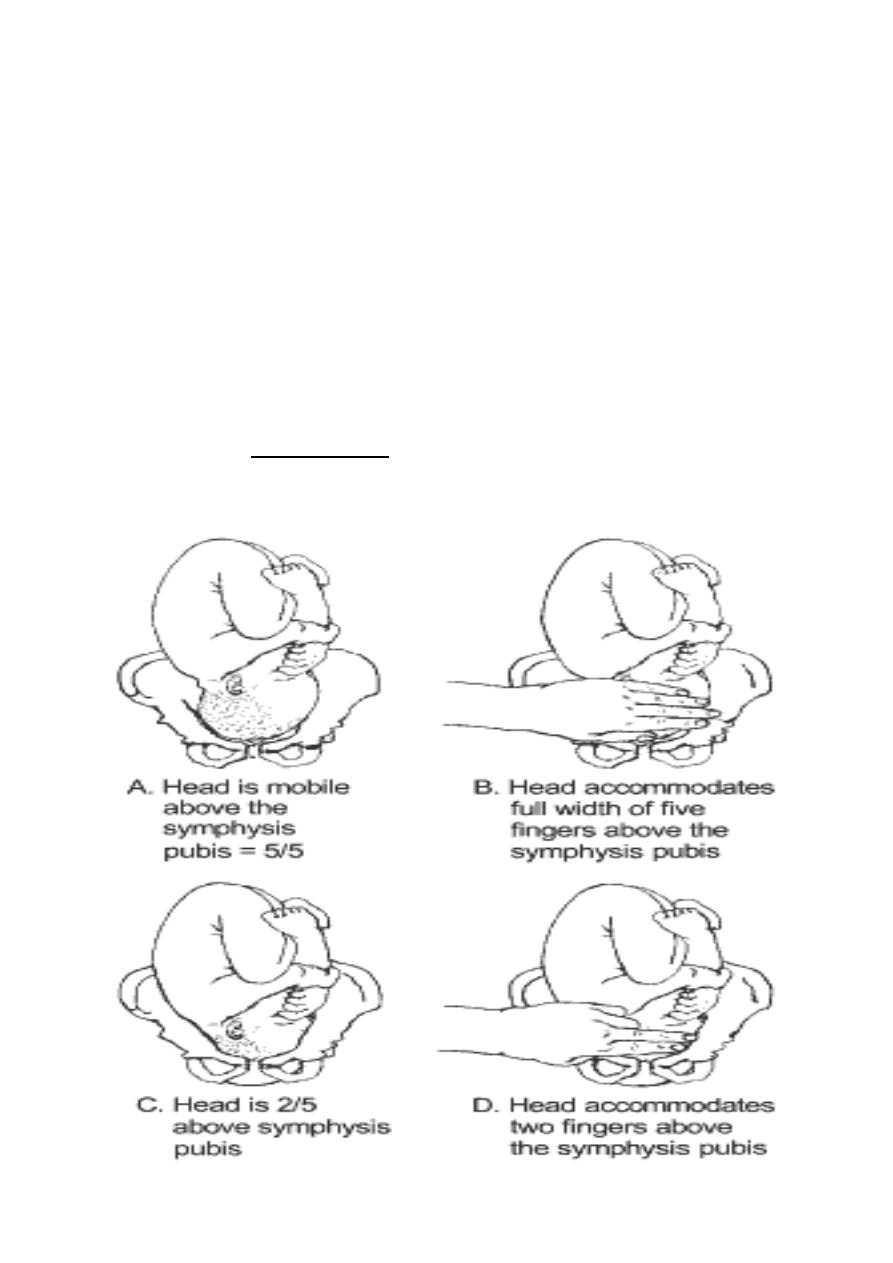
1-ENGAGEMENT
The head enters the pelvis in transverse or oblique diameter
Engagement occurs when the greatest transverse diameter (BPD) of the
presenting part passes through the pelvic inlet ,it occurs in nulliparous before
labour or only in labour in majority of multiparous women.
• Engagement can be determined by vaginal or abdominal examination,
• The number of fifths of the head palpable abdominally is used to detect
engagement, if> than2/5
th
of fetal head is palpable abdominally ,the head
is not yet engaged, an occiput at the ischial spines vaginally means
engaged head (station zero)
Abdominal palpation for descent of the fetal head
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
8
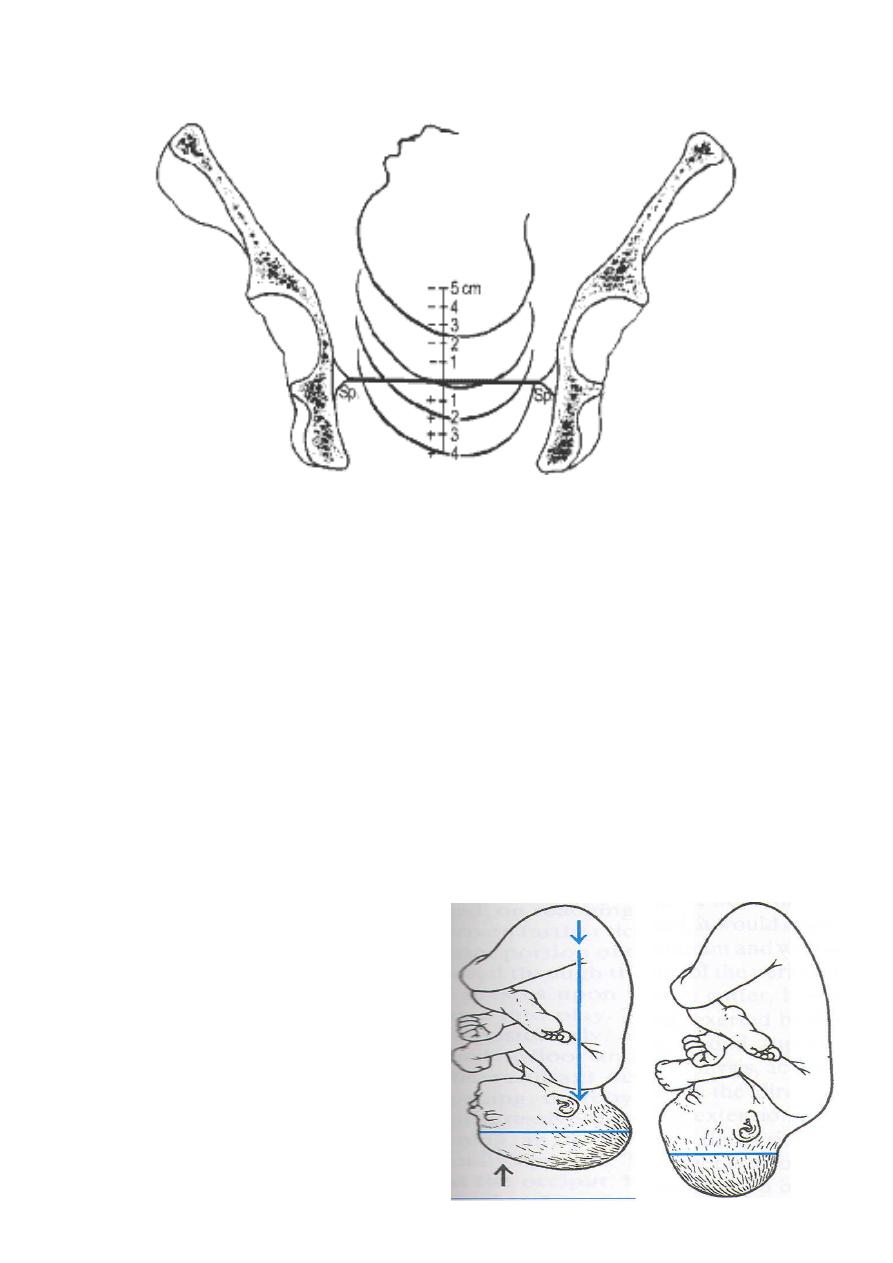
Assessing descent of the fetal head by vaginal examination.0 station is at the
level of the ischial spine .
2-Descent
• Downward passage of presenting part through the pelvis.
• During the 1
st
stage& early 2
nd
stage of labour, descent of the fetus is
secondary to uterine action.In the active phase of 2
nd
stage of labour
,fetal descent is helped by voluntary use of abdominal muscel & pushing.
3-Flexion
Occurs as the head descends due to the shape of the bony pelvis and
resistance of pelvic floor soft tissues, this allows smallest diameter of
fetal head to pass through the pelvis.
Lever action producing ftexion of the
head; conversion from occipitofrontal
to suboccipitobregmatic diameter
typically reduces the anteroposterior
diameter from nearly 12- to 9.5 cm.

Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
9
4- Internal Rotation
• With well flexed head the occiput will be the leading point & on reaching
the sloping gutter of the levator ani it will rotate about 45 degrees
anteriorly to the midline under the symphysis.
• Internal rotation brings the AP diameter of the head in line with the AP
diameter of the pelvic outlet.
5- EXTENSION
• When the flexed head reaches the perineum it undergoes extension the
head escapes from underneath the symphysis pubis & distends the vulva.
Crowning the largest diameter of the fetal head is encircled by the vulvar ring
• The head is born by further extension & the occiput acts as a fulcrum point
as the bregma, forehead, nose, mouth & chin pass successively over the
perineum

Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
10
6- Restitution
• When the head is free of resistance, it aligns itself with the
shoulders,which have entered the pelvis in the oblique position rotating
through 1/8
th
of the circle.
7- External Rotation:
The shoulders rotate into direct anterio-posterior orientation with further
descent. This encourages the fetal head to return to its transverse position
through a further 1/8
th
of acircle.
The ant shoulder slips under the pubis by lateral downword flexion of the fetal
body then post shoulder will be delivered & the rest of the body will follow
Obstetrics Lec 6 Dr. Aseil
11
Maral Jawdat
