1
Obstetrics Dr.Aseil
BREECH PRESENTATION
Definition:
When the buttock of the fetus occupy the pelvic inlet & the head is felt in the fundus
of uterus . It is the most common types of malpresentations, The dominator is the sacrum, the
position is usually sacro-anterior.
Incidence:
Breech presentation occurs in 40% at 26
th
wk, 20% at 30 wk of gestation and 3% at
term.
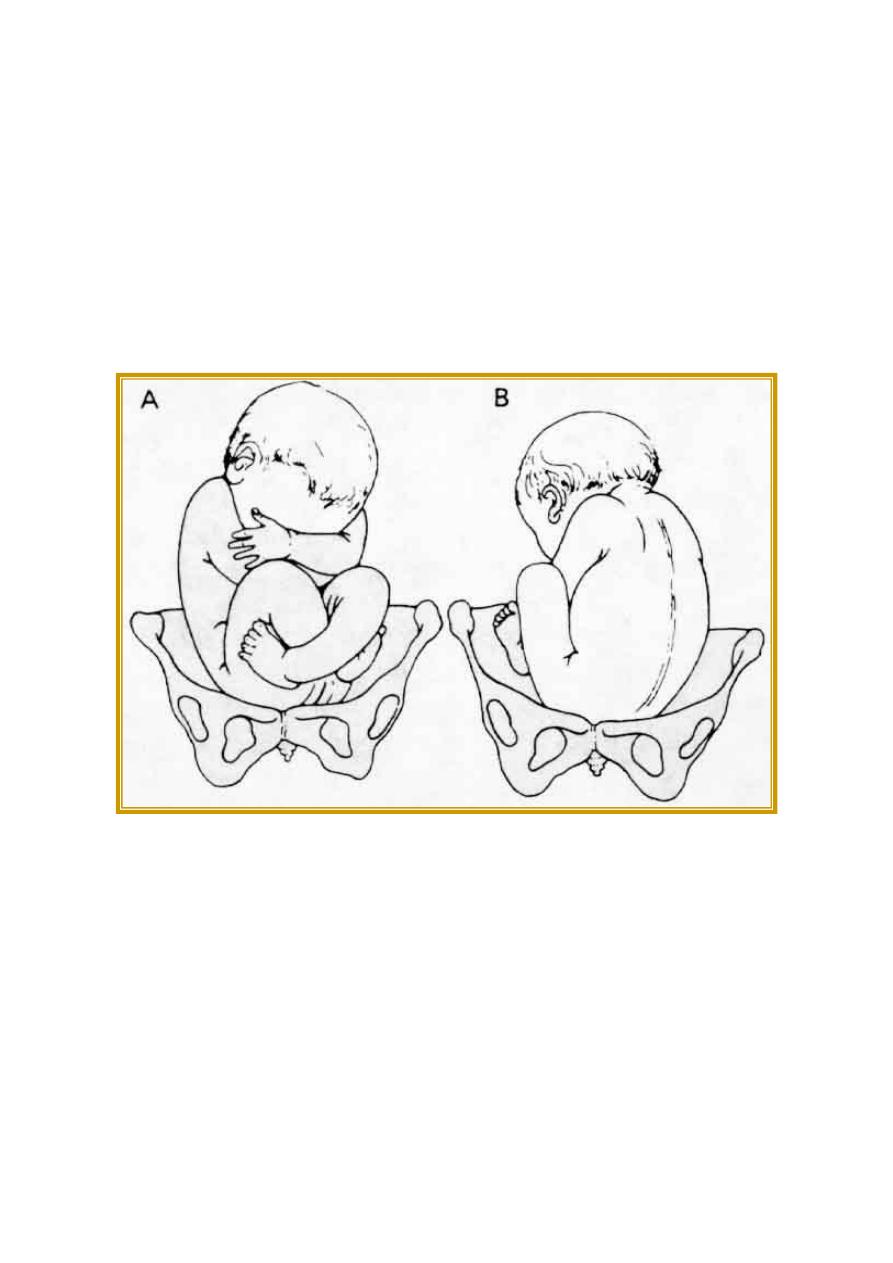
Figure 21-2. Breech presentations. A: Right sacrum posterior (RSP) position. B: Left sacrum
anterior (LSA) position. (Redrawn and reproduced, with permission, from Bumm E: Grundiss zum
Studium der Geburtshilfe. Bergmann, 1922)
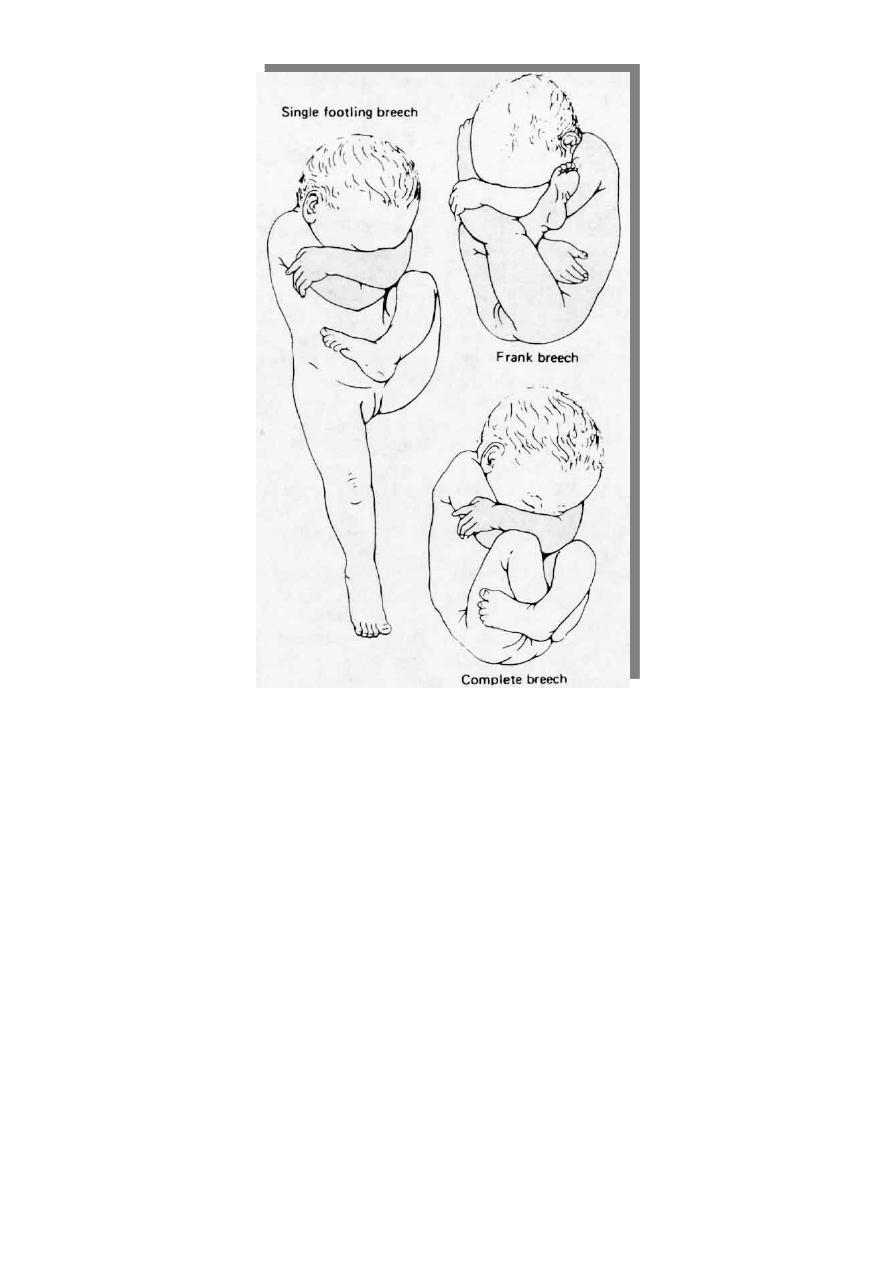
THE 3 TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION:
* Frank : Hips are flexed, knees are extended. It is the commonest
* Complete: The hips and knees are flexed
* Incomplete : The feet or knees are the lowermost presenting part below the buttock.
o Single footling : one of the lower extremities is lowermost.
o Double footling : Both of the lower extremities are lowermost
2
PREDISPOSING FACTORS :
1. Prematurity
2. Uterine abnormalities : - Malformation(bicornute ut.); - Fibroids
3. Fetal abnormalities :
- CNS Malformations; - Neck Masses
4. Multiple gestations
5. Placenta previa
6. Polyhydramnios, Oligohydramnios
7. Multi parity ,pelvic tumor
Clinical presentation
Symptoms:
Pain under the ribs
Indigestion
Hard mass at the hypochondrium
Fetal movements in the lower abdomen

3
On examination :
fundal grip is the head of the fetus with +ve ballottement, the lie is longitudinal, pelvic grip is
occupied by the buttock.
Fetal heart sound is heard by sonicaid above the umbilicus.
DIAGNOSIS :
Clinical feature (history&exam)
Ultrasound safe and useful tool for diagnosis of breech presentation, gestational age,
viability, presence of congenital anomalies, hyperextension of the head of the fetus, types of
the breech, presence of oligo or polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancy, weight of the fetus to
decide the mood of delivery.
X-Ray in late pregnancy if ULS not available
Complication of breech
Maternal complication:
Increased maternal mortality and morbidity
Prolonged labor
Maternal distress
Puerperal sepsis
High incidence of C/S rate
Increased manipulation and trauma to the birth canal &PPH
Fetal complication:
1. Increased fetal mortality and morbidity
2. Cord prolapse (foot ling)
3. intra ventricular hemorrhage
4. Prematurity
5. S.R.O.M
6. Entrapment of the fetal head(Asphyxia)
7. Fetal trauma(Brachial plexus leading to Erbs pulsy and intra abdominal organ injury)
Management of a breech presentation:-
A. External Cephalic Version ( ECV ).
B. Caesarean section.
C. Vaginal delivery.
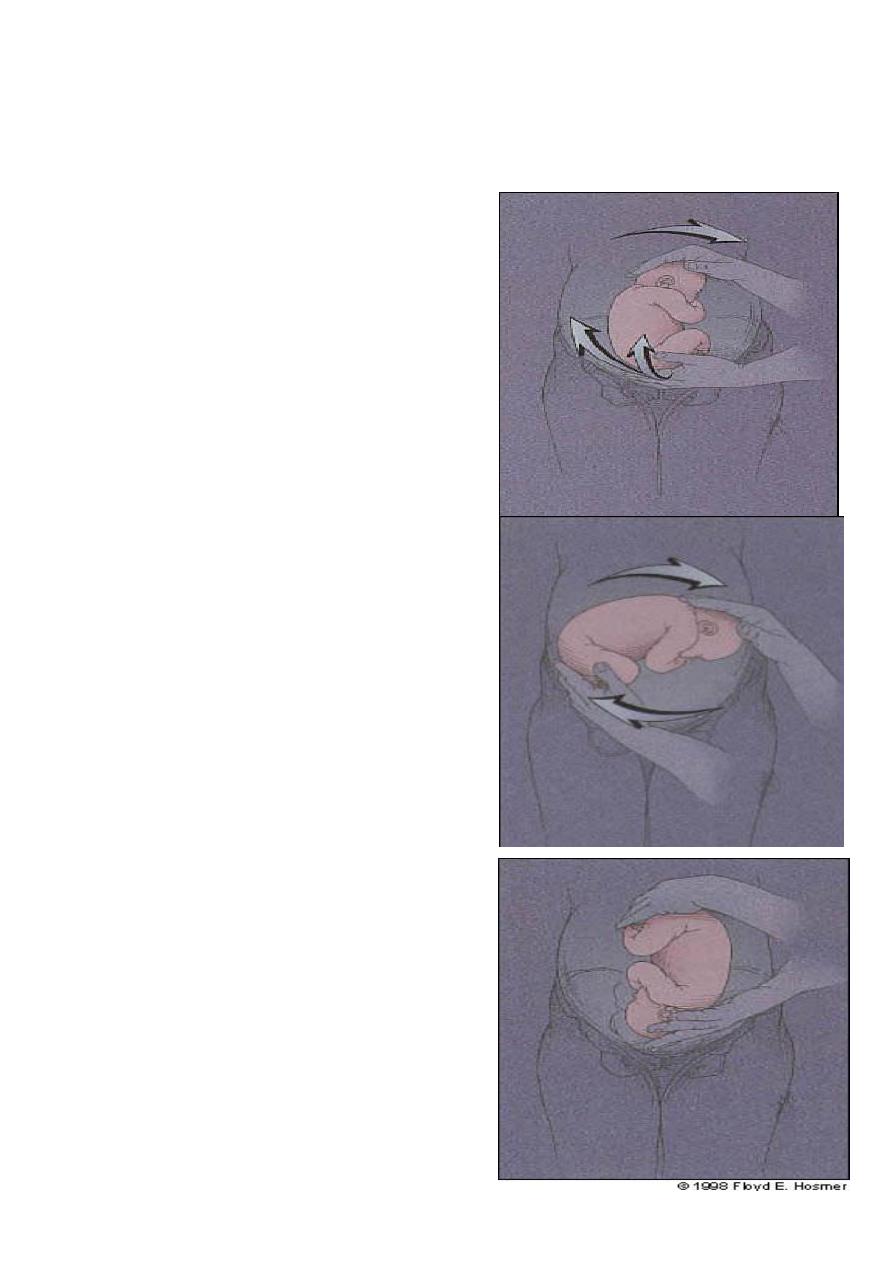
A- External Cephalic Version:
Changing the presentation of the fetus from breech to cephalic presentation by manipulation
through anterior abdominal wall ,it reduces the number of Caesarean section due to breech
presentation.
4
ECV is usually carried out by experienced obstetrician at 38 weeks of gestation in a hospital
with faccilities & theater for Caesarean section available. it is mildly uncomfortable and it is
occasionally performed with tocolytics such as ritodrin and nefidipin.
FHS should be checked before and after the procedure, if the patient is RH –ve, anti- D should
be given to the patient.
Risks of ECV:
1- Abruptio placenta.
2- Premature rupture of membrane.
3- Cord prolapse.
4- Fetal bradycardia.
Contra-indications:
Multiple pregnancy.
APH, P.Previa.
Ruptured membranes, poly or oligohydramnios.
Significant foetal abnormalities.
Need for CS for other indications.
Previous scar in the uterus( C.section or
myomectomy )
Pre-eclampsia or PIH.
MANAGEMENT DURING LABOR
Type of Delivery
Vaginal delivery:
o Spontaneous
o Assisted breech
o Breech extraction
Cesarean of delivery

5
C- Section Indication
A large or small fetus ( > 3.500 gr &< 2500)
Extended neck
Uterine scar (C/S , myomectomy)
Footling presentation
Any degree of contraction or unfavorable shape restriction
Previous perinatal death or children suffering from birth trauma
Any obstetric problem: Placenta previa, gestational diabetes, PIH and pre-eclampsia.
Primigraivid.
C- Assisted Vaginal Delivery :Pre-requests for vaginal delivery:
1- Normal size fetus( 2.5 – 3.5 kg ).
2- Good pelvimetry assessed clinically and some times by X-ray or CT pelvimetry scan can also be
used.
3- Flexed neck.
4- Multiparous.
5- Breech deeply engaged..
6- Obstetric unit and staff experienced in vaginal breech delivery.
7- NO fetal congenital abnormality.
8- Extended ( Frank ) and flexed ( complete )breech.
Management of labour :
Fetal wellbeing and progress of labour should be monitored carefully by partogram and CTG, if
fetal distress was supected, fetal blood sampling from buttocks provides an accurate assessment
of the acid- base status .
Technique :
Assisted breech delivery is based on the fact of hands- off i.e.
Pulling on the baby should not be tried to facilitate the delivery, fully dilation of the cervix should
be diagnosed first.
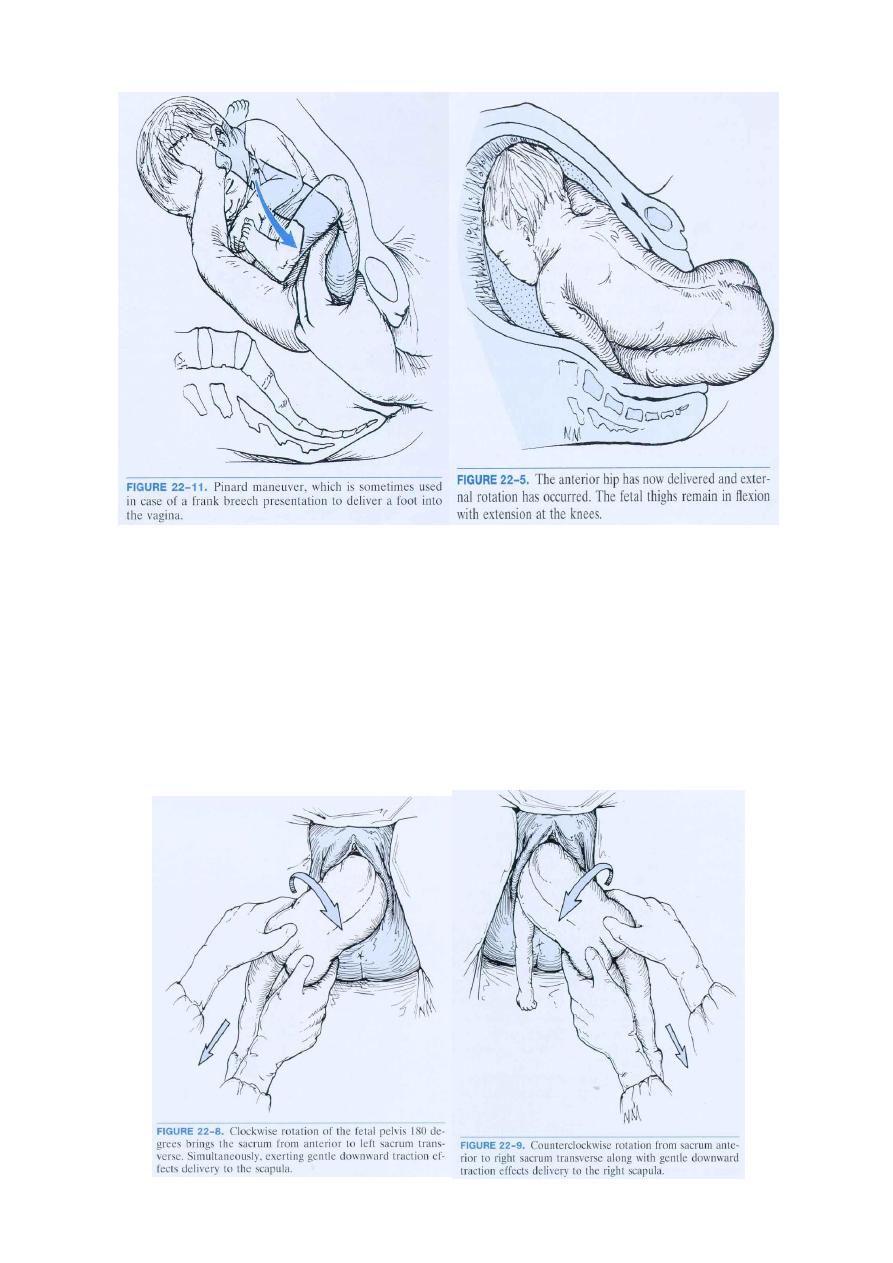
Delivery of the buttock
When the buttock will be visible the perineum, then prepaeations for the delivery are made. The
buttocks will lie in the anterio-posterior diameter. Once the anterior buttock is delivered and the
anus is seen over the fourchette an episiotomy can be done.
Delivery of the legs and lower body
: If the legs are flexed they will delivered
spontaneously, if they are extended, Pinards maneuve is used, using a finger to flex the knee joint
extend the hip joint. With uterine contraction and maternal bearing down the lower will delivered,
then a loop of cord should drawn down.
6
Assisted Delivery of Frank Breech
Delivery of the shoulders:
The shoulders enter the pelvis in the transvers diameter.As the anterior shoulder rotates to ant-
post diameter of outlet (clockwise) the scapula become visible &a finger placed above the
shoulder will help to deliver the arm. As the posterior shoulder reaches the pelvic floor,it too
rotates anteriorly(anti clockwise) .Once the scapula becomes visible,delivery of the 2
nd
arm follow.
Loveset’s manoeuvre copies these natural movements &will be used if the arms were extended .
Assisted Delivery of Frank Breech
7
With delivery of the shoulders, the breech should allowed to hang for at least 1 minute so that the
weight of the baby will promote flexion of the head and the head will enter the pelvis then
application of short curved obstetric forceps to the head is indicated, another method to deliver
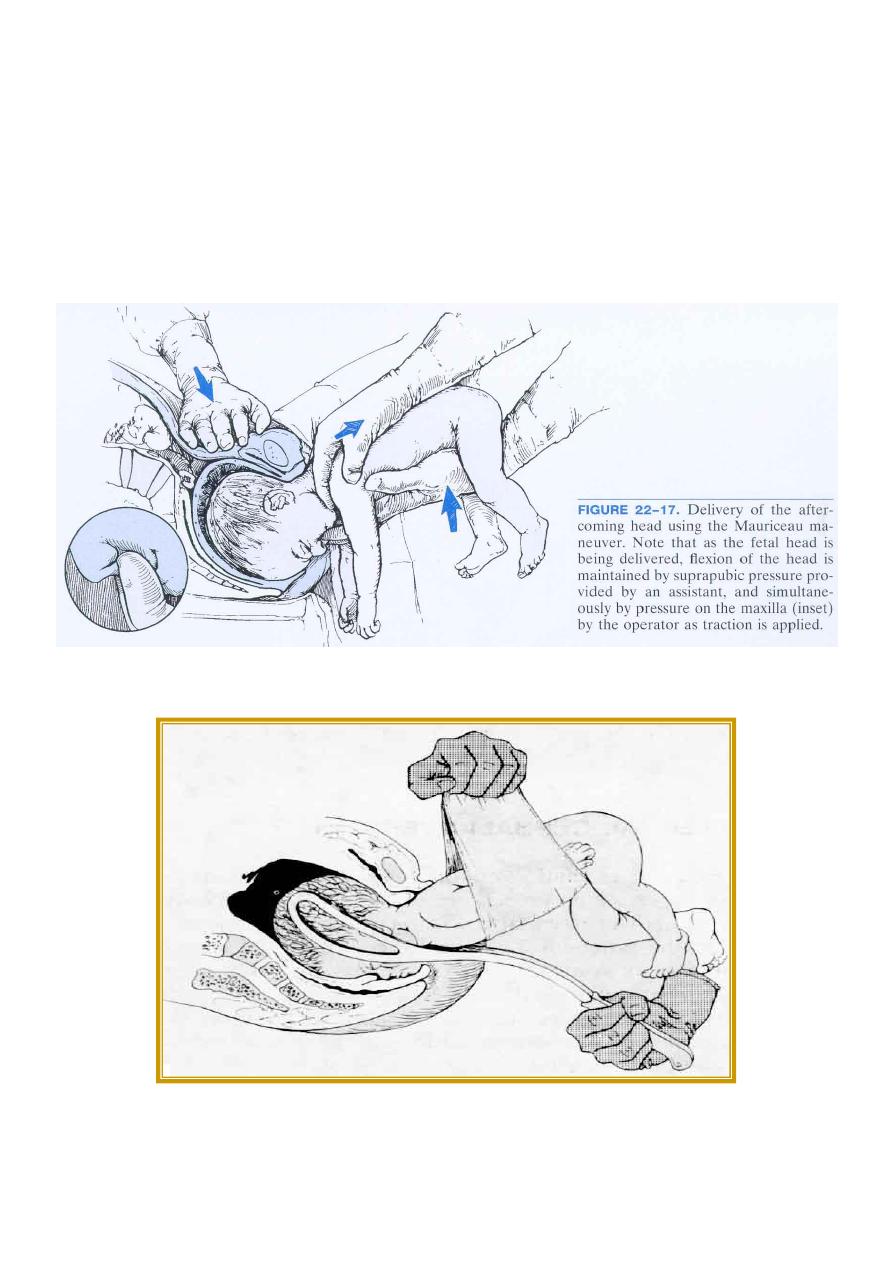
the head is Mauriceau- Smellie- Veit manoeuvere (jaw and shoulder traction method ) the baby
lies on obstetrician’s arm with downward traction being leveled on the head via a finger in the
mouth and one on each maxilla. Delivery will occur with first downward and then upward
movement ( as with the instrumental delivery ).
Mauriceau Maneuver
Mechanism of Labor in Breech Delivery
Figure 21-12. Application of Piper forceps, employing towel sling support. The forceps are
introduced from below, left blade first. Aiming directly and intended positions on sides of the
head. (Reproduced, with permission, from Benson RC:Handbook of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 8
th
ed. Lange, 1983)
8
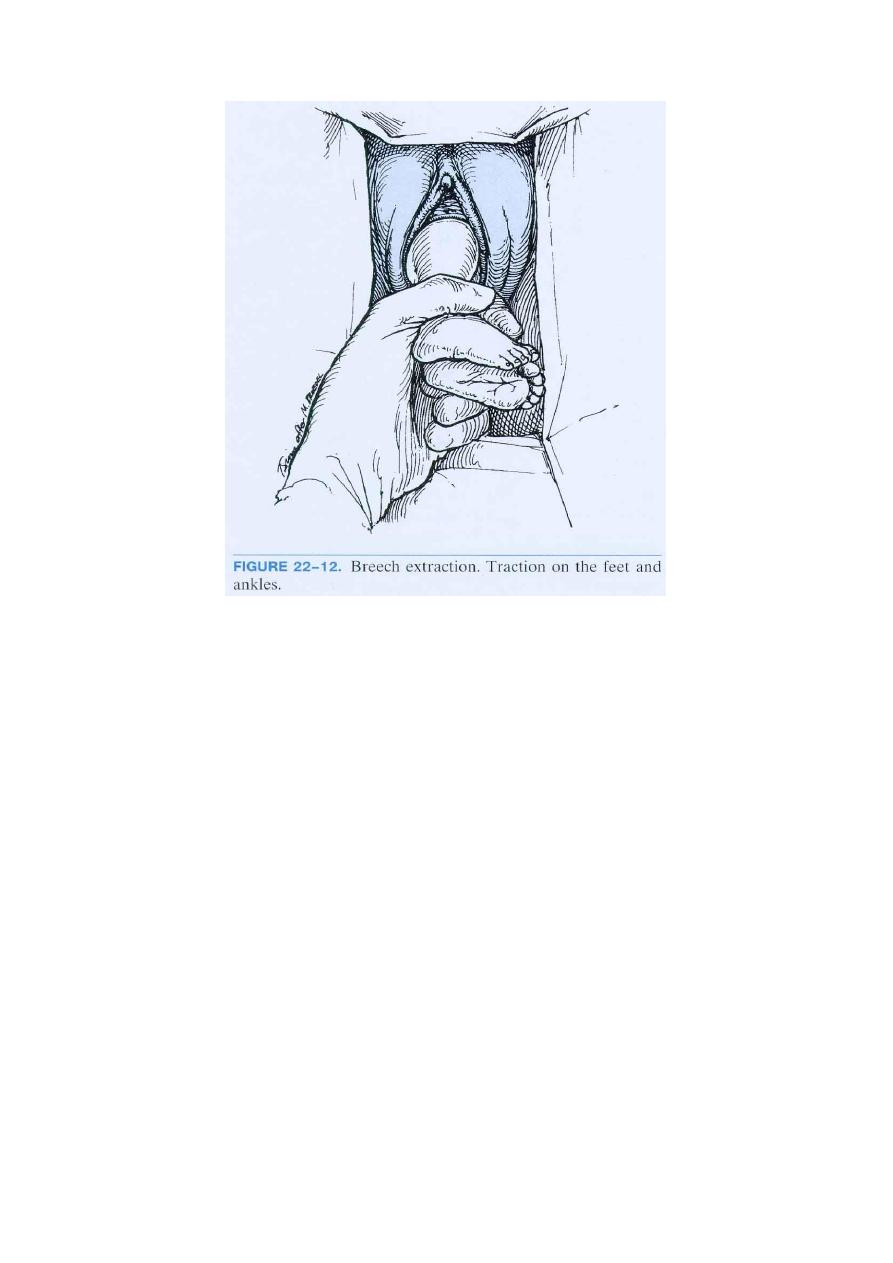
Complete or Incomplete Breech Extraction
