Obstetrical history and examination
Dr . Esraa abdulkareem al-QassabF.I.C.O.G.\C.A.B.O.G.
Taking history
Appearance : should be suitable before you enter the room.Always introduce your self.
Privacy : record the event that are not known by other family members e,g TOP.
Some women wish another person to be present if the doctor or student is male.
Opening questions: asking for patients age, date of birth
Name
AgeOccupation
Address
Blood group & Rh
For women and for her partner
GPA
G: gravida is a total number of pregnancies regardless of outcome
P: parity is the number of deliveries after 24th week of gestation whether stillbirth or live birth
A : abortion or miscarriage is the expulsion of the conceptus before 24th week of gestation
Women now pregnant and never had a pregnancy before is G1 P0---primigravida
Twin counts as 2 : pregnant at 12wk with previous delivery of twin ---- G2 P2.Women in her eighth pregnancy , she has had 6 miscarriage and 1 delivery at 32 wk of alive baby--------G8 P1 A6
LMP: 1st day of last menstrual period.
The median duration of pregnancy is 280 days (40wk) and this give expected date of deliveryEDD: is calculated by counting forward 9 months & adding 7 days.
But the cycle should be reliable , this assumes that:The cycle length is 28 days
The cycle was not straight after stopping COCP or after previous pregnancy.
At least 3 regular cycles before conception.
E,g4 / 2 / 2012
1 / 7 /2011
31 / 1 /2011
25 / 7 /2011
If the cycle is unreliable ,depend on late 1st trimester or early 2nd trimester US
The gestational age37-40 wk ----- term
<37 wk --------preterm
40-42 wk ------postdate
>42 wk---------postterm
Every 2 months = 9wk
Every 3 months = 13wk
1st TMS –up to 13 wk
2nd TMS –14- 27completed wk
3rd TMS – 28wk - delivery
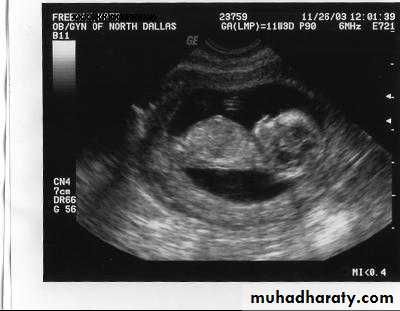
CRL Crown – rump length – 13 wk+6 daysBPD biparietal diameter, HC head circumference14 wk -20 wk
Date of admission
Chief complaint ( in the term of patient)E,g lower abdominal pain
watery vaginal discharge
vaginal bleeding
reduced fetal movement
History of present illness
History of present pregnancy
eg,in 1st trimester ---excessive nausea and vomiting , vaginal bleeding, exposure to drug or radiation and when she start ANCIn 2nd trimester any disease , UTI, vaginal bleeding, queckening.
In 3rd trimester leg oedema , symptoms of preeclampsia( headache, blurring of vision, epigastric pain)
Review of systems
Past obstetrical history:-When she get married? when she conceive? Spaces between each pregnancy.
Discuss antenatal , intrapartum , postpartum period in details
Antepartum period: e,g threatened miscarriage, GDM, PE , PTL, placenta previa, abruption,IUGR
Intrapartum period :place of delivery (home or hospital), route of delivery (VD, NVD, CS), outcome ( alive or dead, term,preterm , postdate, male, female, weight of the baby, admission to NCU, congenital anomaly).
Postpartum period: bleeding, infection, thromboembolism.
Past gynecological history:
Menstural historyPCOS: irregular cycle (unreliable date, risk of GDM)
Contraceptive history(COCP, IUCD)
Previous history of PID( risk of EP)
The date of last cervical smear &any previous treatment for cervical abnormalities (cx insufficiency or stenosis)
Previous history of PID(risk of EP)
Recurrent miscarriage(APS, IUGR,PE)
Previous gynecological surgery(myomectomy)
History of subfertility.
Past medical history:
-DM( macrosomia, IUGR, congenital anomaly, preeclampsia, stillbirth, neonatal hypoglycemia)
Hypertension(PE)
Renal diseases(PE, PTL, IUGR, worsening renal disease).
Epilepsy( increased frequency of fit, congenital anomaly)
VTE(risk or thromboembolism, PE, IUGR)
SLE( PE, IUGR)
Myasthenia gravis( maternal muscular fatigue in labour)
Past surgical history: e,g pelvic surgery
Drug history:Antihypertensive(ACEI, B-blockers)—change to methyl dopa.
Antiepileptic (continue the medication even increase the dose)
Oral hypoglycemic agents( teratogenicity?, poor control in pregnancy, risk of neonatal hypoglycemia) change to insulin.
Drug allergy.
Family history:
DM( risk of GDM)HT( PE)
Thrombo embolic ( risk of thrombophilia)
PE
Family history of congenital anomaly
Close family history of TB
Examination
BMI:- weight (kg)\height(cm)2
BMI below 20------- IUGR & increase perinatal mortality rate
BMI above 30-----GDM &HT
Blood pressure measurement:-
Measure in seated or semi recumbent position
With appropriate size cuff, obese women with a large cuff, small cuff will over-estimate the BP
Use Korotkoff V (disappearance of sound)
General examination
Cardiovascular examinationBreast examination:- women should report a new lump, Ix should not b delayed bc of pregnancy
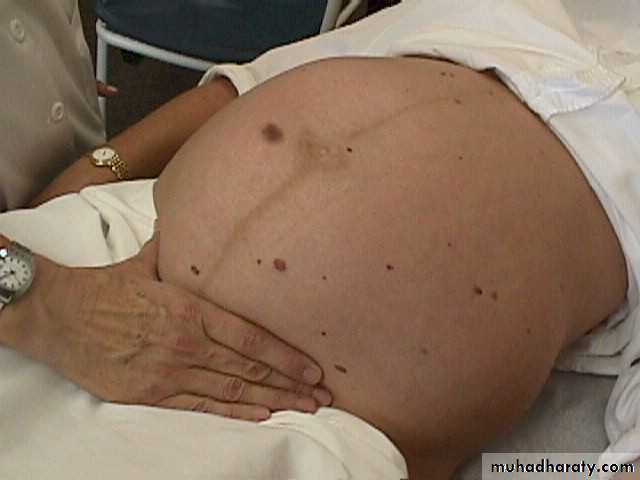
Abdominal examination: in semi-recumbent position or a pillow below one buttock to move the wt of uterus to Rt or Lt , cover the legs with sheets , ensure that the women is in comfortable position , chaperone should be present.
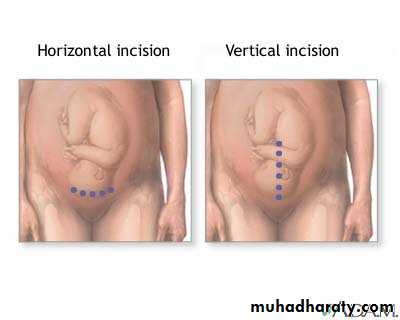
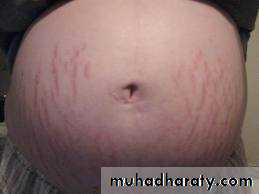
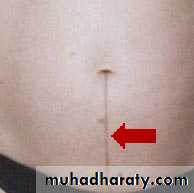
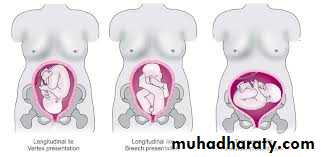
Inspection:- shape & symmetry of the uterus, any scar e,g pfanennstiel scar, linea nigra &stria gravidorum
Palpation
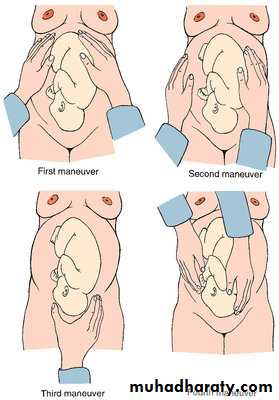
Superficial palpationObstetrical palpation:
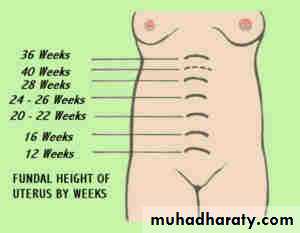
Symphysis -fundal height(SFH)
Place the tape measure from upper border of symphysis pubis to the fundus in the midline. 1cm =1wk (in late 3rd TMS 2 cm less than number of weeks)
Causes of large for date:
• Wrong date• Macrosomia
• Multiple pregnancy
• polyhydramnios
Causes of small for date:
• Wrong date
• IUGR
• oligohydramnios
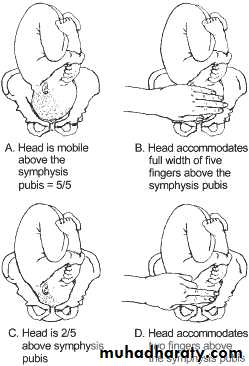
Fundal grip
Lateral grip1st pelvic grip
2nd pelvic grip