
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
1
Intrapartum
Fetal Monitoring
Fetal surveillance during labor is an essential element of good obstetric care
because of the fact that intrapartum hypoxia and acidosis may develop in any
pregnancy. Unfortunately, currently available risk assessment profiles do not
predict all instances of intrapartum fetal distress.
On the basis of antepartum maternal history, physical examination, and
laboratory data, 20% to 30% of pregnancies may be designated high risk, and
50% of perinatal morbidity and mortality occurs in this group. However, the
remaining 50% occurs in pregnancies that are considered to be normal at the
onset of labor.
Methods of fetal heart rate during labour
1. Auscultation of FHR: is performed every 15 min after uterine
contraction during 1
st
stage of labour, & at least every 5 min in 2
nd
stage of
labour.
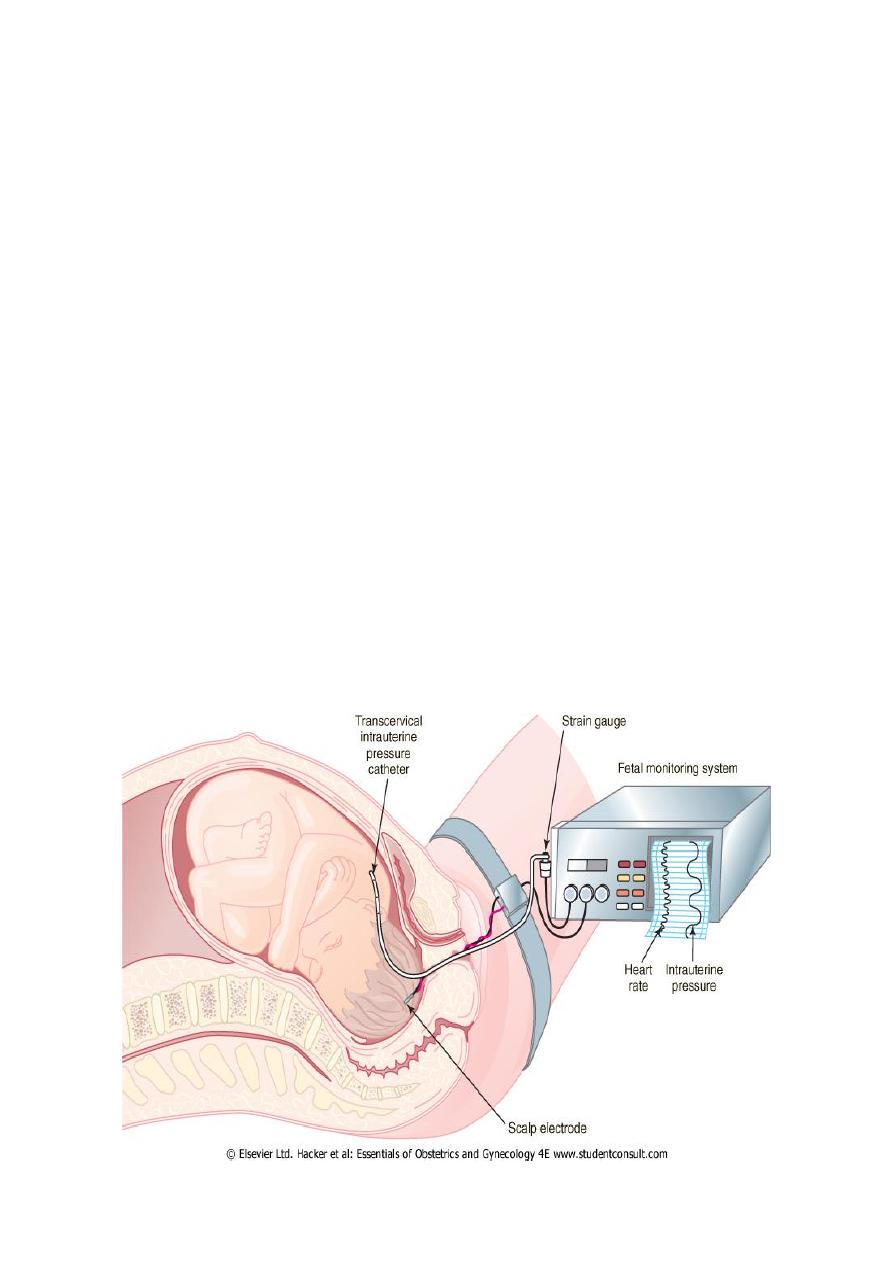
2.Continuous electronic fetal monitoring:
External EFM
Internal EFM
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
2
Indications for the continuous EFM
High risk pregnancies
IOL and Augmentation of
Labour.
Reduced FM.
PTL.
APH/IPH
Oligohydramnios
Hypertension.
Abnormal FHR detected.
Malpresentation in labour.
DM.
Multiple Gestation.
Previous CS.
Abdominal Trauma.
Prolonged ROM.
Meconium Liq
Continuous EFM allows reporting of FHR & UC by means of monitor that prints
results on 2 channel strip.
External: FHR-UC record can be obtained by use of external transducers that
placed on maternal abdomen
Internal monitoring can be carried out by placing a spiral electrode on fetal scalp
to monitor FHR &placing a plastic catheter trans-cervically in to amniotic cavity
to monitor UC, this technique require rupture of membrane & at least cx
dilatation 2cm.
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
3
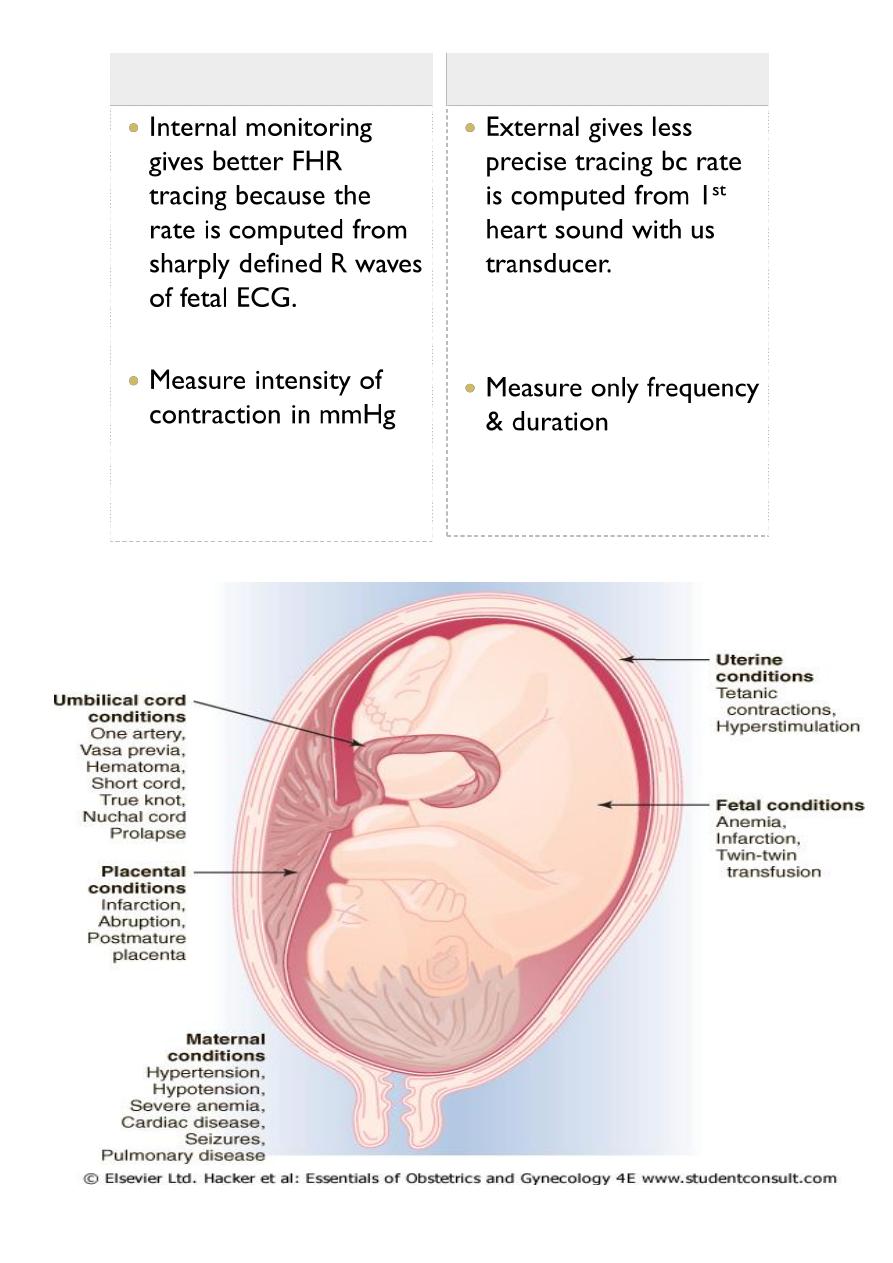
Clinical conditions that associated with fetal distress in labour
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
4
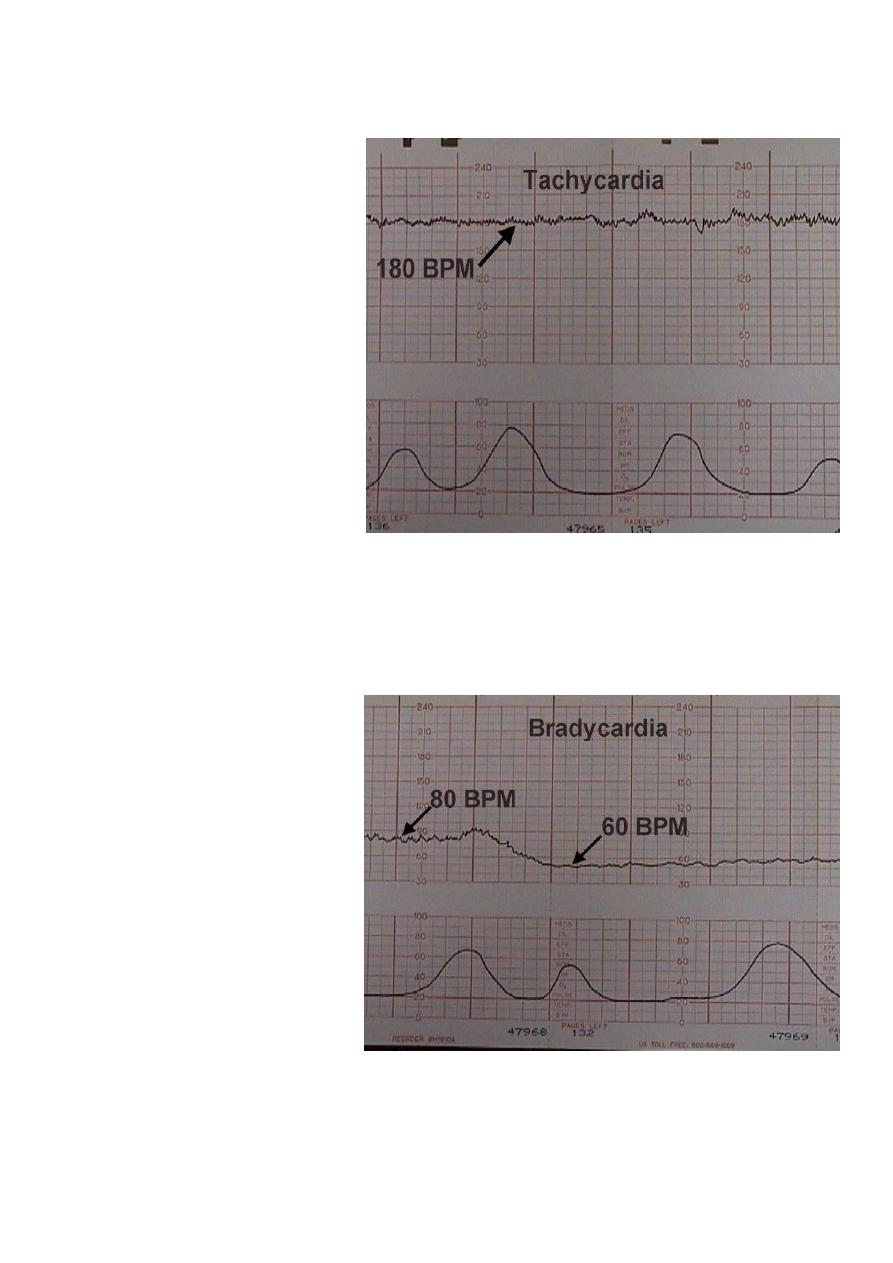
Fetal tachycardia (> 160 bpm)
◦ Fever,
Chorioamnionitis
◦ Maternal
hyperthyroidism
◦ Drugs (tocolytics, etc.)
◦ Fetal hypoxia
◦ Fetal anemia
◦ Fetal arrythmia
◦ Prematurity
Mx depend on clinical
situation
Fetal bradycardia <110 bpm
Postdates
Drugs
Arrhythmia's
Hypothermia
Increased Vagal tone
Cord compression
Acute Hypoxia
Congenital H/disease
drugs
Mx depends on the clinical
situation. (Observation or expedite Delivery).
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
5
Periodic FHR changes
No change
Acceleration : FHR increases in response to uterine contraction, this is a
normal response
Deceleration: FHR decreases in response to uterine contraction( early,
late, variable, mixed) all except are abnormal except early deceleration
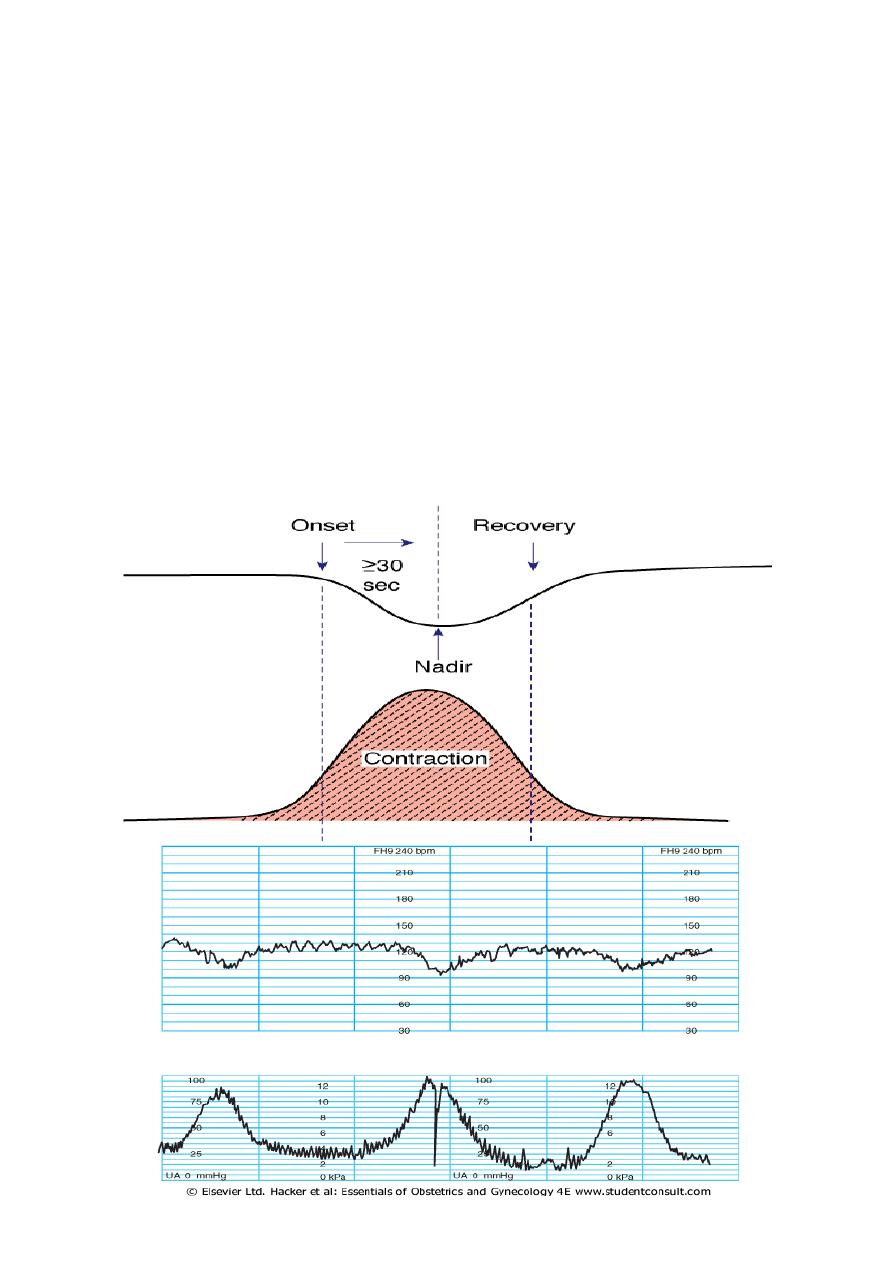
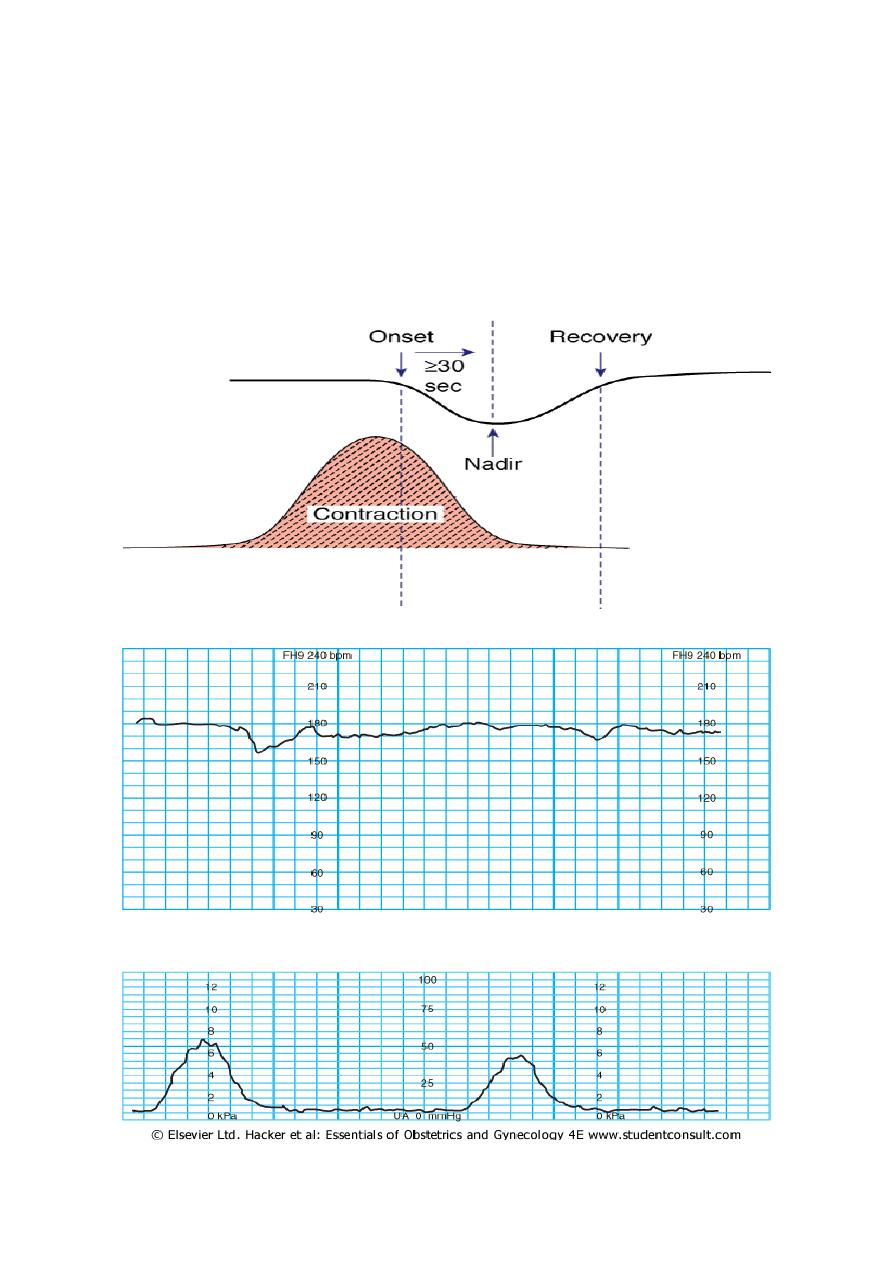
Early deceleration(head compression)
This pattern usually has an onset, maximum fall & recovery coincident
with onset , peak & end of the contraction.
This pattern is not associated with fetal distress & is seen with engagement of
fetal head , bc pressure on fetal head leads to increased intracranial pressure
that elicits a vagal response
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
6
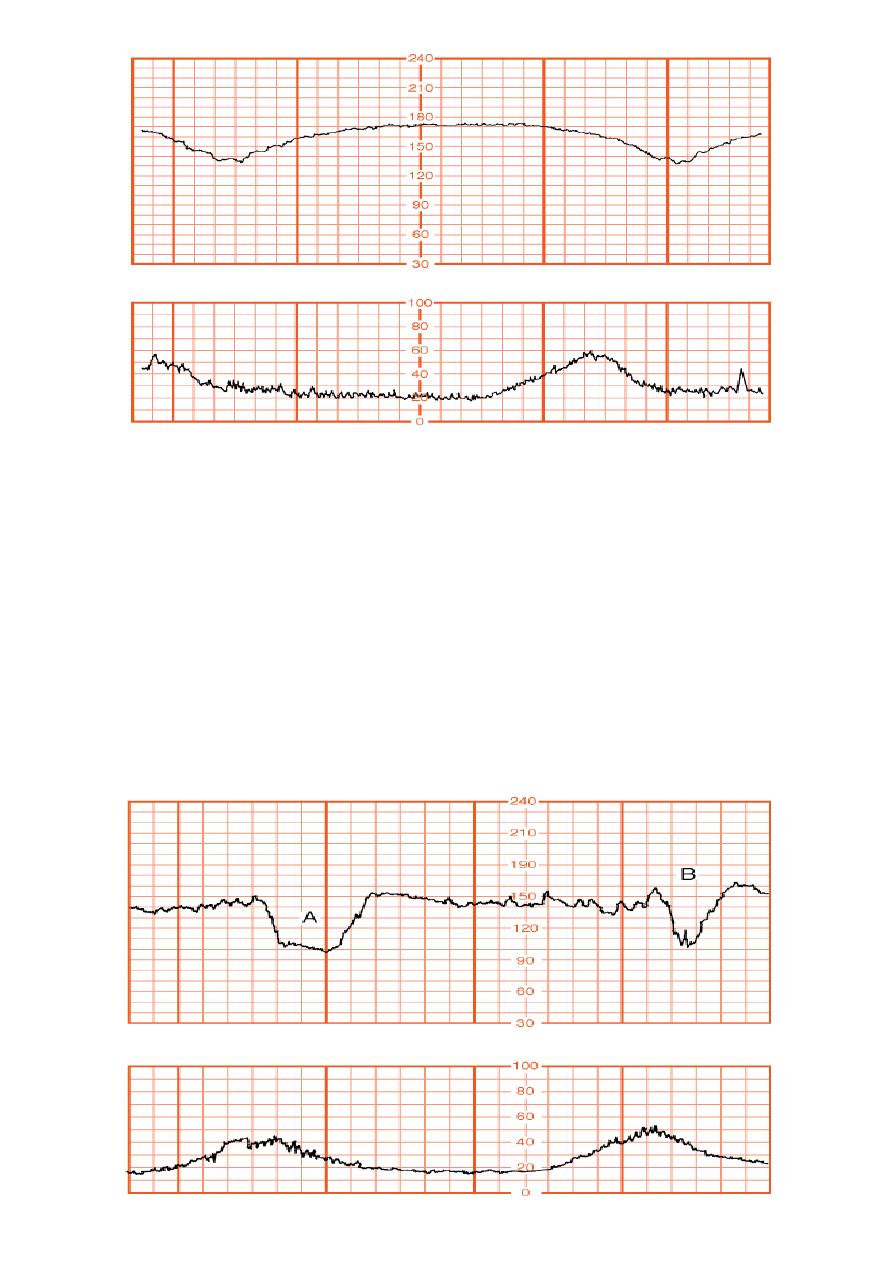
Late deceleration(uteroplacental insufficiecy)
This pattern has an onset, maximal fall& recovery that are shifted to the
right in the relation to contraction
Mild: < 15 bpm drop in FHR
Moderate: 15-45 drop in FHR
Sever: > 45 bpm
Sever repetitive late deceleration are indicative of fetal metabolic acidosis
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
7
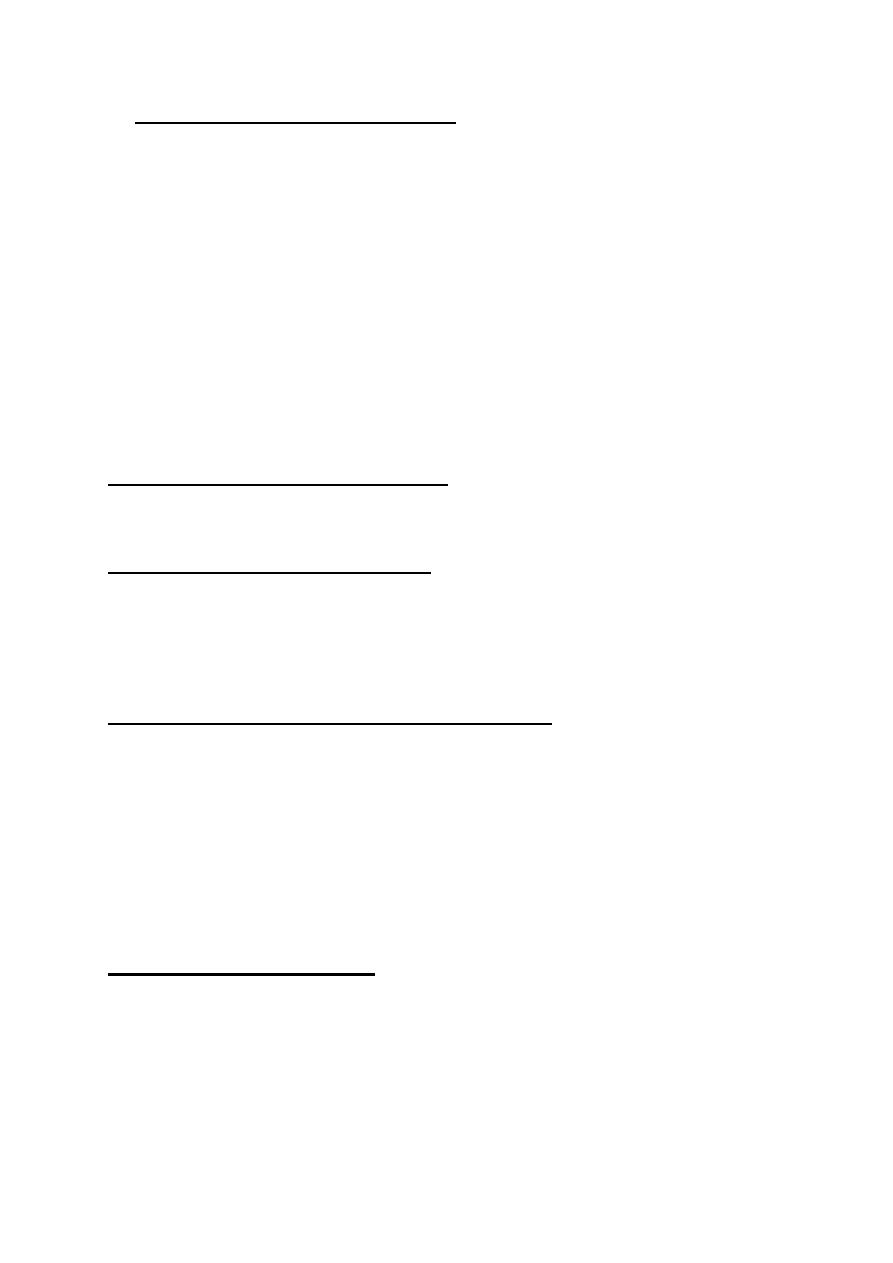
Variable deceleration( cord compression)
This pattern has a variable time of onset, variable form & may be non
repetitive
This pattern occur in cord compression
Severity of variable dec is graded by duration of the deceleration :
-mild < 30 sec
-moderate 30-60 sec
-sever > 60 sec
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
8
Mx of suspected fetal distress
1. Improve placental blood supply:
A- correct maternal hypovolaemia or hypotension by:
-
Place the mother in left lateral position to avoid aortocaval compression.
-
Intravenous fluid
-
Vasoconsrictors e,g ephedrine , for vasodilatation secondary epidural
analgesia
B- decrease uterine activity by:
-
Stop oxytocin infusion
-
Remove vaginal PG if given recently.
-
Use bolus tocolytic e,g terbutaline
2. Improve maternal oxygenation:
Oxygen therapy should be used for short period of time
3. Improve umbilical blood flow:
improve amniotic fluid volume: transcervical amnioinfusion can reduce cord
compression, by infusion of 500 ml of hartmann s solution over 20-30 min
followed by 250 ml\hr
4. Decide if delivery is indicated based upon:
Clinical test such as CTG or results of secondary tests of fetal wellbeing
Obstetrical risk facctors
Untreatable fetal complications e,g abruption or cord prolapse
Secondary tests of fetal wellbeing
Vibroacoustic stimulation :
Nonreactive tracing with loss of fetal acceleration & loss of beat –beat
variability ( in antepartum or intrapartum period) needs further evaluation by
placing vibroacoustic stimulaion on maternal abdomen to induce FHR
acceleration , presence accelerations for 15 sec & of 15 beats\min within 15 sec
after stimulation indicate absence of fetal acidosis
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
9
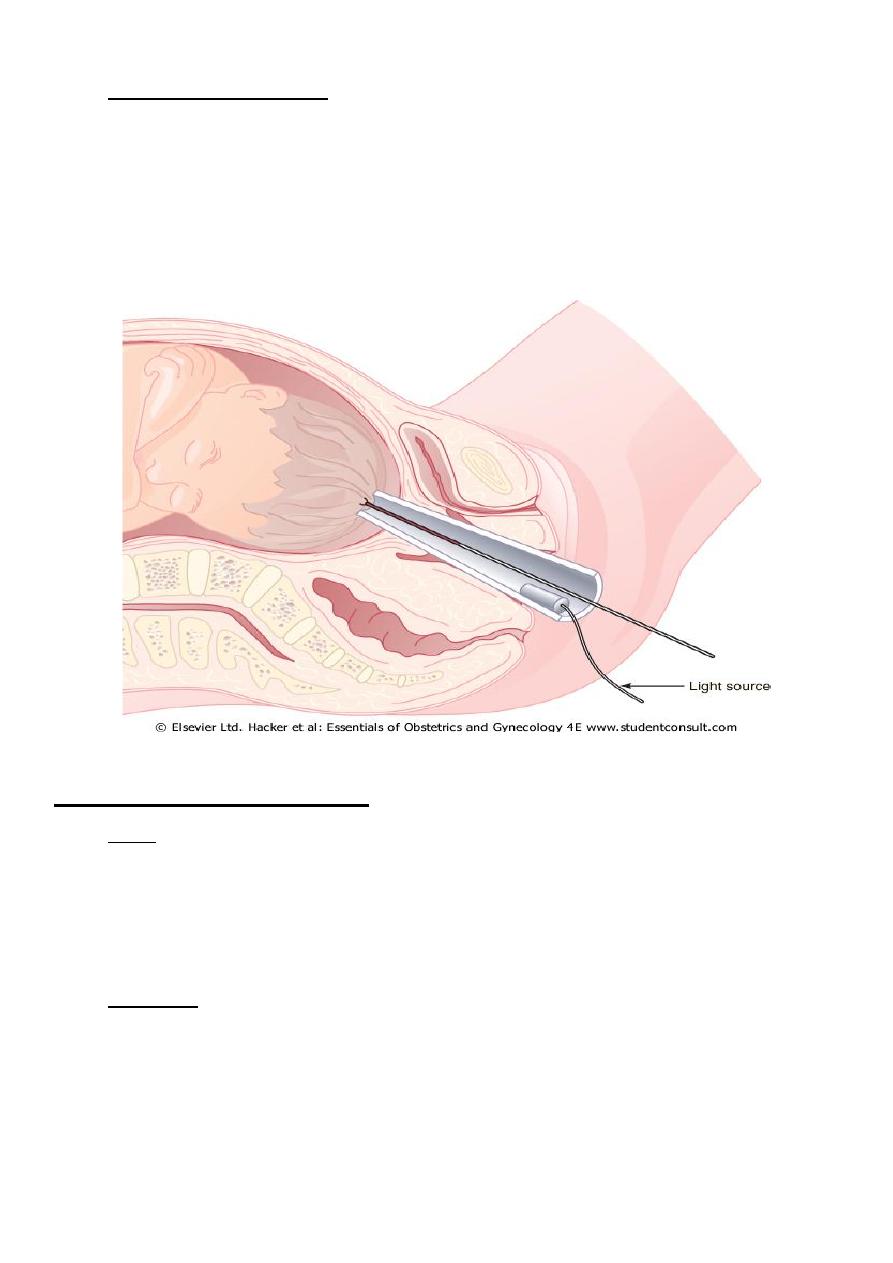
Fetal blood sampling: is secondary test of intrapartum wellbeing , blood is
obtained from fetus by placing transvaginal amnioscope against fetal skull
, cervical mucus is removed with cotton swab , a 2X2 cm lancet is used for
scalp incision ,& adrop of blood is aspirated into long heparinized capillary
tube.
lower limit of normal pH is 7.20 , less than 7.20 indicate fetal acidosis , base
excess should be measured to differentiate metabolic from respiratory acidosis.
Contraindications for FBS
Fetal
Premature –less than 34 ks
Active Herpes
Known HIV,Hep B,C positive status.
Thrombocytopenia.
Maternal
Unfavourable Cx
Malpresentation(face etc) uncertain??
Pl Praevia or APH
Sepsis
Obstetrics/ Dr. Eman
10
Scalp stimulation:
Intrapartum test
scalp stimulation is an alternative to scalp blood sampling. This based on the
observation that acceleration of the heart rate in response to pinching of the
scalp with an Allis clamp just prior to obtaining blood was associated with a
normal pH.
Fetal pulse oximetry:
Another intra-parum test of fetal wellbeing.
A unique pad-like sensor is inserted through the cervix and positioned against
the fetal face, where it is held in place by the uterine wall.
