
1
6
th
stage
Pediatric
lec.2
د.رياض العبيدي
Session notes
2016/8/22
Breast feeding is the best for every infant , these only its
contraindications
1) Galactosaemia
2) Maternal HIV infection
3) Anti-neoplastic drugs
4) Tetracycline
5) Lithium
o Causes of diarrhea in bottle fed infant?
1.improper hygiene of the rubber piece or bottle.
2.improper preparation.
o How to calculate caloric needs in bottle fed infant?
-daily requirement =100-120kcal/kg/24hrs.
-each (1)oz=(20)calories. الممسوحة القمة
-500/20=25(oz).
If he feed 5times/24hrs,so( 5 )oz for each feed is required.
***********************
Signs of good feeding ?
For baby:-
Urination and bowel motion start to work
Smile and not cry
Good activity

2
Sleep after feeding
For mother :-
Disappear of pain.
Note :-Let down reflex is felt by the mother when she wants to
feed her baby.
Fluid requirement by the baby is 100-150 ml/kg//Calories 100 -
120 kCal/kg, in the first yr of his life.
If baby wt is (4kg) & he is (3mo) old ,is that appropriate ?
-No, he should be 6kg now , so he is FTT-every (mo) his wt should
be increased (700gm).
Always ask :-why you don't fed him from your breast in case of
bottle fed infant??
Rotavirus vaccine :-
-Two brands :- monovalent & pentavalent vaccine.
-Both vaccines are given orally.
How to manage GE ( gastorentritis ) ?
(the case we saw in the ward)
Examine :- (3mo)old baby ,lying in the bed with cannula in the Rt hand &
Iv fluid set line,he is NOT dyspneic ,slightly pale,slightly thin with
abdominal distension(flanks distended on sides).
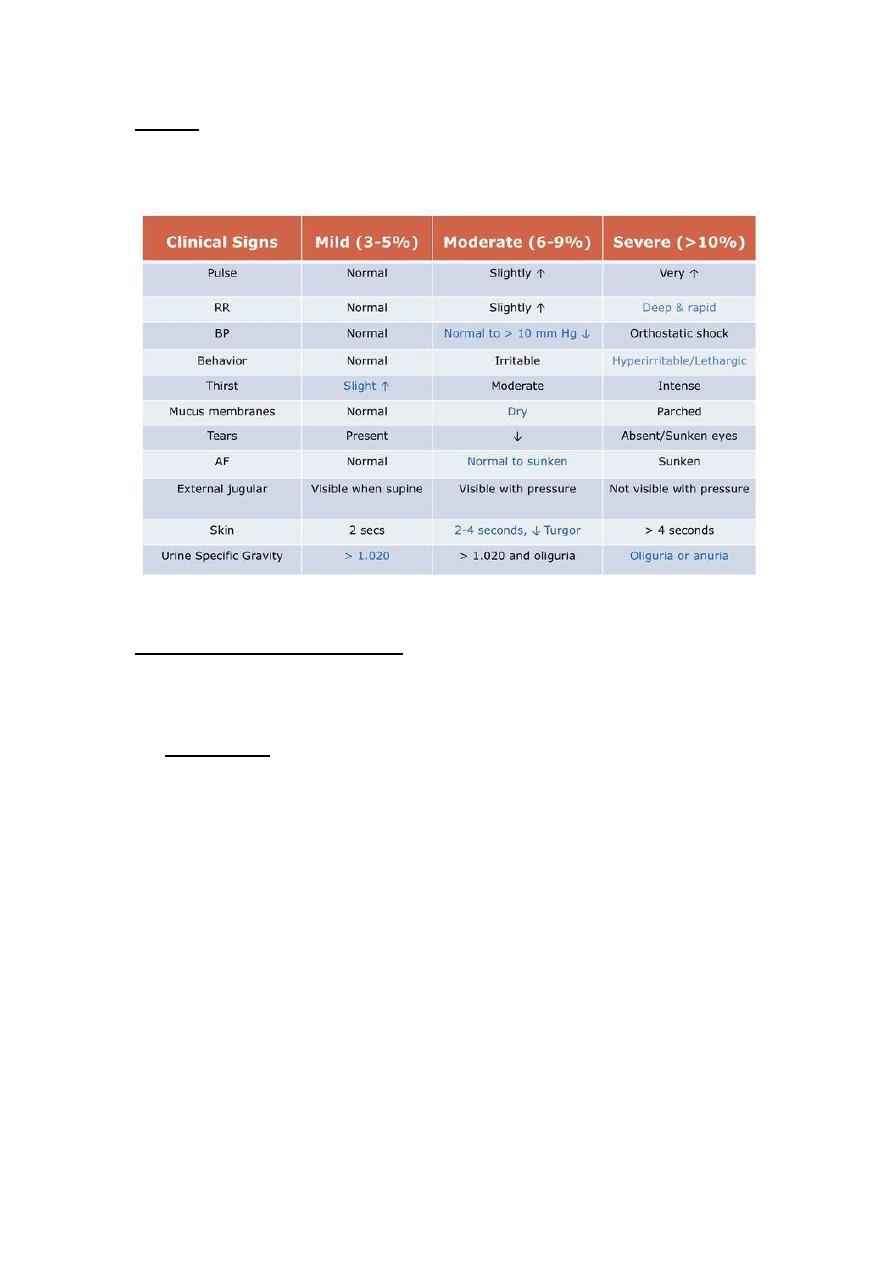
For dehydration :-
1.is he dehydrated or NOT?
2.what kind of dehydration?
3.needs ORS or IVF?
4.before all these steps ,blood should be drawn for Na,Cl&K?(the result
will come within 1/2hr) during this time ,you had given the fluid
shot(20ml/kg)NS over 1hr…for (3)times .
5.Reassess :is he still dehydrated ? if yes GIVE ANOTHER SHOT.
Over 6rs then give the maintainence.
Once we feel he can tolerate the oral STOP the parenteral .
6.potassium infusion shouldn't be forgotten.
3
Note :- for sunken eye ,try to look from sides to assess.
Skin turgor not done in abdominally distended child/infant, but in the
chest, a punch of skin is drawn & allowed to return ..
Abdominal distension in infant:-
1.paralytic ileus.(less movement of bowel)fluid level in erect position
radiography.
On auscultation:-sluggish bowel sounds.
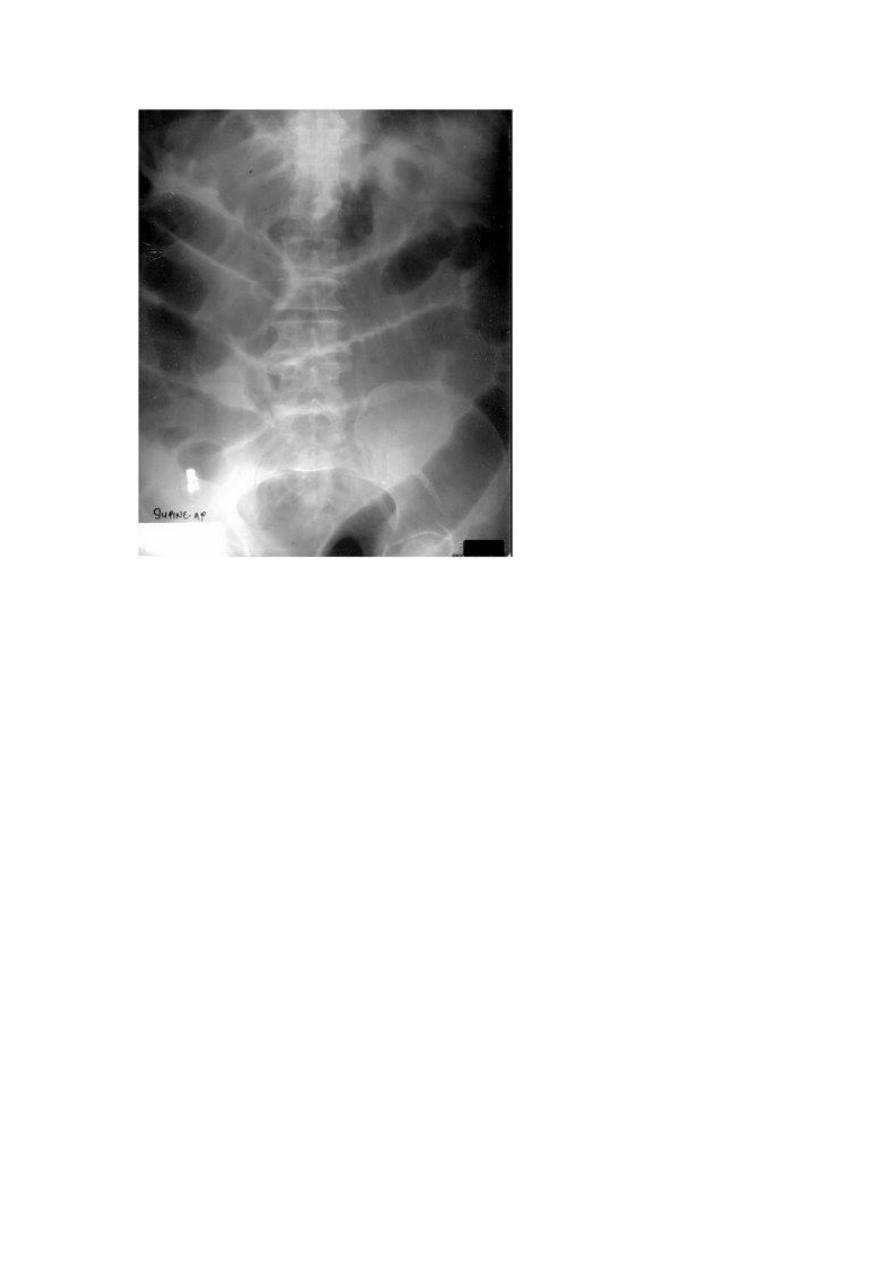
4
(fluid level in paralytic level).
2.lactose intolerance.
How to diagnose hypernatremic dehydration(>150mEq/L)
?
1.jittery movement.
2.increased muscle tone.
3.hyperreflexia.
4.altered consciousness
5.seizures
6.irritability
7.doughy skin مثل العجينة
8.Hx of fever , diarrhea& anorexia but without vomiting.
9.Hx of caloric concentration in milk preparation.
(2yrs)with GEthink of poisoning (food from outside)..ask about
other family members.
5
Fever + bloody diarrhea+abd.painshigellosis , E.histolytica (lives
in vegetables ,NOT in water) does'nt lead to fever,don't give flagyl
(IV)in case of E.histolytica,oral flagyl is effective.
IV flagyl indicated in
1.NEC.
2.brain abscess/hepatic abscess/lung abscess.
3.Appendicitis with susceptibility to perforate.
4.intestinal collection .
Pseudomembranuous enterocolitis :- pt came shocked ,
abdominal distension,toxic.
Intussception cases present mostly between (9mo-12mo)/
diagnostic test:-US (target sign),,Ba enema.
How to manage a case with poisoning?
1.assess the poisoned child/baby,is he very sick or mildly sick?
2.PR,BP,RR,Temperature?
3.is the substance swallowed ,poisonous or NOT?
4.features(syndromic)?
Cholinergic :- pupillary dilatation,abdominal cramps,retention
of urine.
Anticholinergic:-
MAO:-

6
Paracetemol:-wait (4)hrs ,( >150mg/dl )in blood =level of
toxicity,,give N –acetyl cysteine(anti-dote).
*Measure the level of liver enzymes,& level of drug in the
blood.
*Complication:-hepatic failure&acidosis.
Morphine:-constipation,respiratory depression
(grunting),hypotension,pin point pupil,abdominal
distension,flushing of faceimmediately give Naloxone (0.1
mg/kg)may be repeated /put on ventilator.
Iron
Hypnotics
**dose of toxicity always multiply the dose by (10).
Concentrate on these features:-
1.PR:-bradycardic or NOT?
2.salivation?
3.urine?
4.drowsy baby or not?
5.bowel sound?

7
6.pupil reaction:-pin point morphine,,fully dilated:-anti-
cholinergic(Biscopan,antihistamine).
**within (2)hrs ,is the best time to manage a case of poisoning.
Contraindications of charcoal?
1)abdominal distension.
2)paralytic ileus.
**case of celiac disease:-from session of Dr.Rabea.
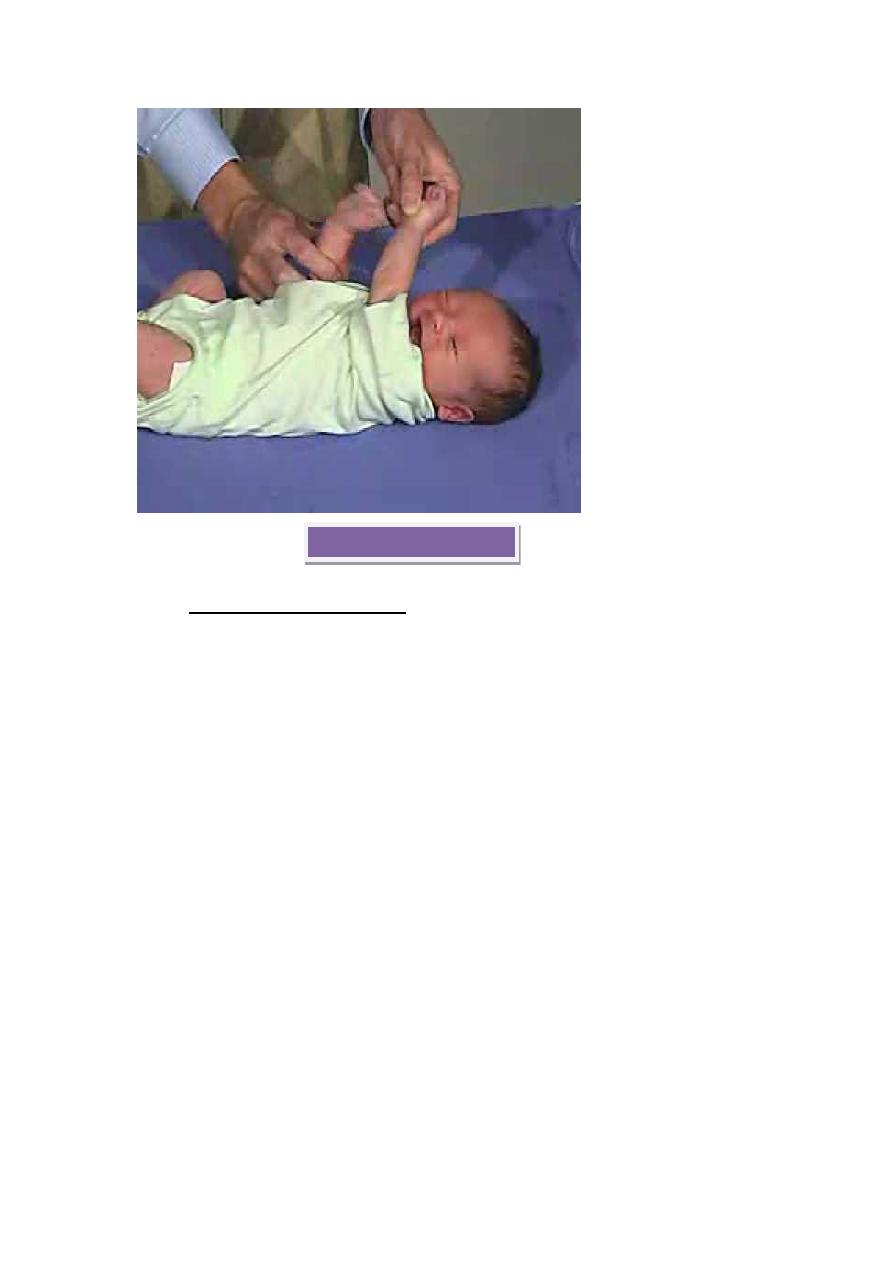
Case of hypotonic (floppy child):-
Presentation:-
--hypocalcemic child with shortened fourth metacarpals&shortened 4
th
metatarsal bone, Short stature,dental maldevelopment,scarf sign of
hypotonia"lt elbow can be brought to Rt shoulder easily",mental
retardation,small HC,precocious puberty in boys,seizures.
8
Investigations in this case:-
1.S.Ca
2.S.mg
3.VitD :low;;as parathyroid hormones stimulate its release,it may
be normal .
4.MRI
5.CT
**hypotonic CP:here always cerebellum involvement is present
due to encephalitis.
**AEDs are indicated (lamotrigeine+sodium valproate).
Scarf sign in hypotonic
baby



