
Embryology
Lecture -1-
05/10/2015
EMBRYOLOGY

EMBRYOLOGY
A Branch of biomedical science, it deals
with formation & development of
embryo ( from fertilized egg to a new
adult) ,other said from single cell to a
baby in 9 month.
embryogenesis
: the 1
st
8 weeks of human
development , also called (organogenesis).
Fetal period
: the period from that point on until
birth , when differentiation continues while the fetus
grows & gains weig
ht

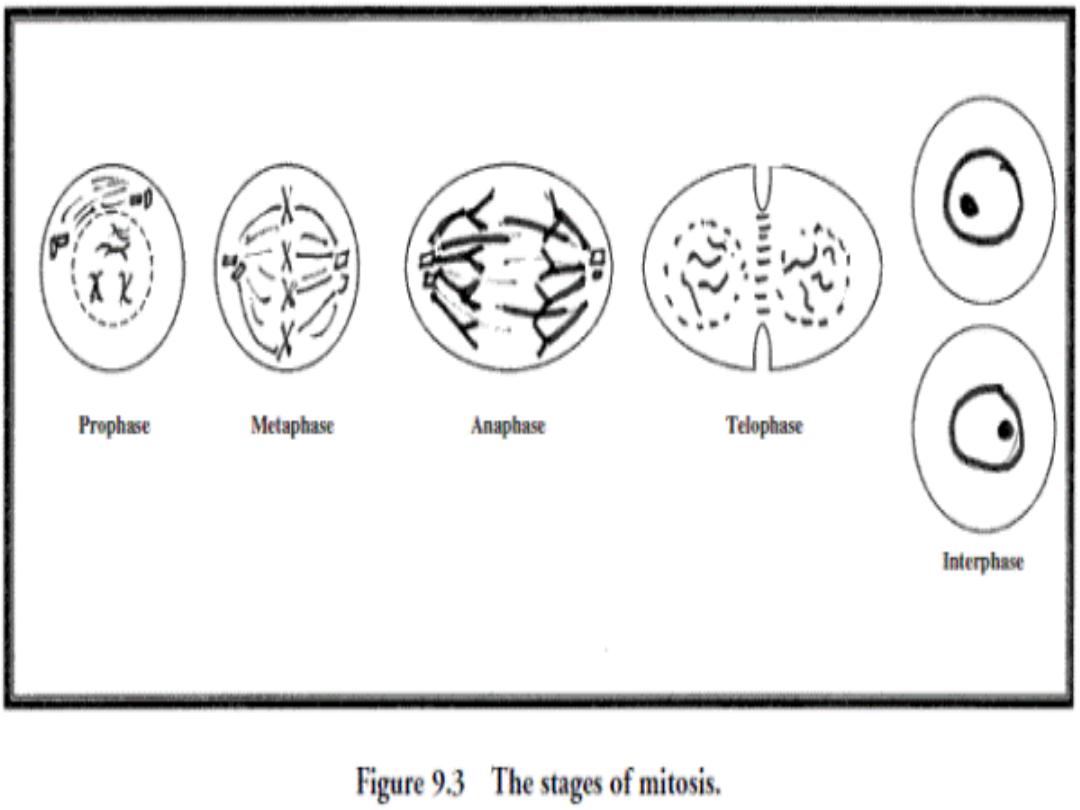
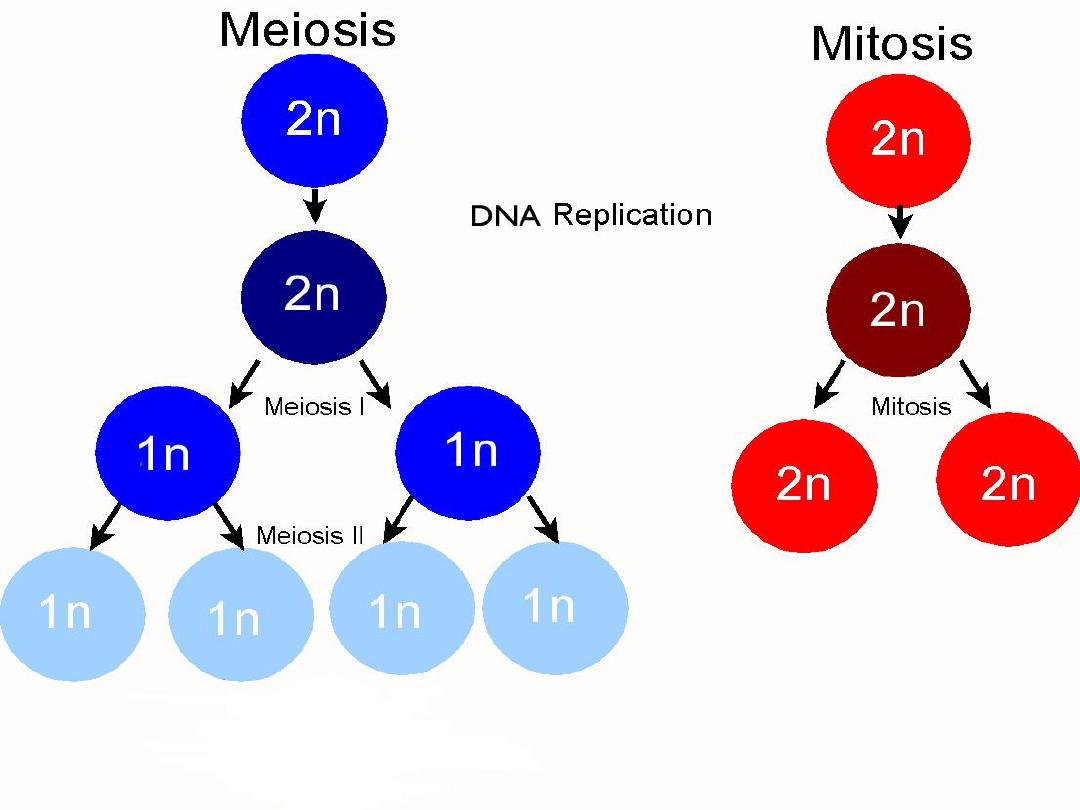
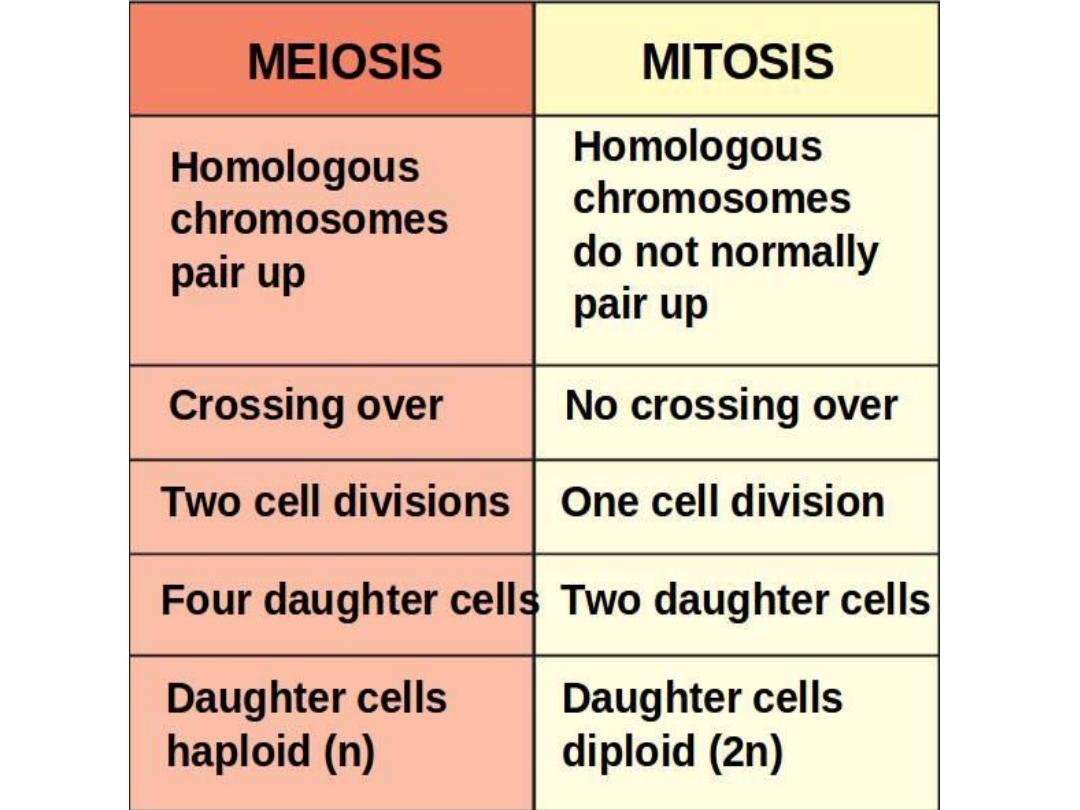
Reproduction of cell
take place by process called cell division, either:
1-
mitotis :
in somatic cells, the resulting cells from division
are diploid
2-
meiosis :
in germ cells, the resulting cells are haploid
*Cells are either somatic or germ cells & multiplication
occur either by mitosis or meiosis .
*Human development occur from fertilization.
*Each somatic cell contains diploid no. of chromosomes (46).
*Each gamet cell contains a haploid no. of chromosomes
(23).
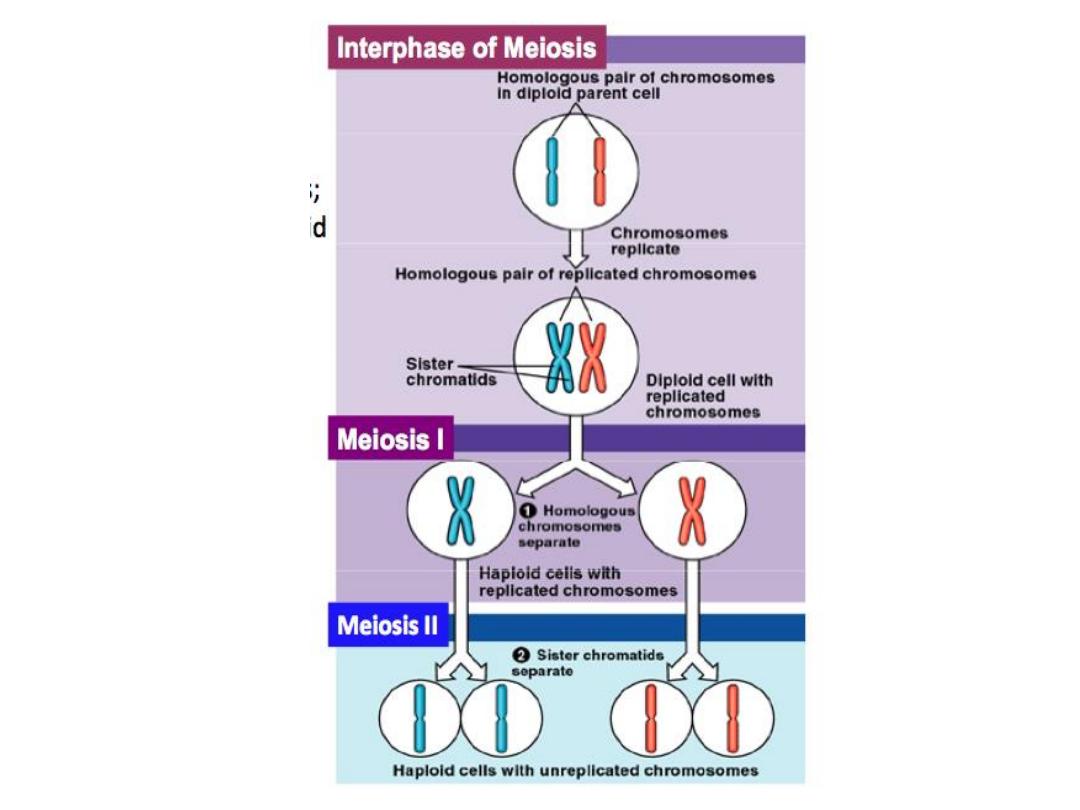
* In each somatic cells , the chromosomes (46) are arranged
as 23 pairs , 22 pairs of matching chromosomes called
autosomes ( identical) , 1 pair of sex chromosome
.
Gametogenesis
Conversion of germ cells into male & female gametes. Includes :
1-oogenesis 2- spermatogenesis
Oogenesis:
Is the process whereby oogonia differentiate into mature oocytes, it
occurs in specialized structure in the cortex of the ovary called
ovarian
follicle
.
When the female
primordial
germ cells reach the developing gonads
during 6
th
week of embryonic development, they differentiate to
oogonia
, the oogonia increase in the no. due to repeated mitotic
division & arranged in clusters by the end of 3
rd
month of gestation.
The majority of these cells continue to divide by mitosis, but some
begin meiosis & arrest in prophase of meiosis I & become
Primary
oocyte
. They continue to increase in no. till reaches its maximum
about 7 million by the 5
th
month. Then they begin to degenerate &
become
atretic.
By 7
th
month the majority have degenerated, while all
the surviving primary oocytes have entered prophase of meiosis I
surrounded by a layer of flat follicular epithelial cells, both of them
(oocyte+follicular cells) called
primordial follicle .

At birth all primary oocytes (nearly 600000-800000)
started prophase of meiosis I but instead of
proceeding into metaphase, they enter
diplotene
stage
(resting stage).
During childhood, most of them become atretic;
only approximately 40000 are present at puberty, &
fewer than 500 will be ovulated.
*Maturation of oocytes begins before birth.
*Maturation of oocytes continues at puberty.
* Maturation of sperm begins at puberty.

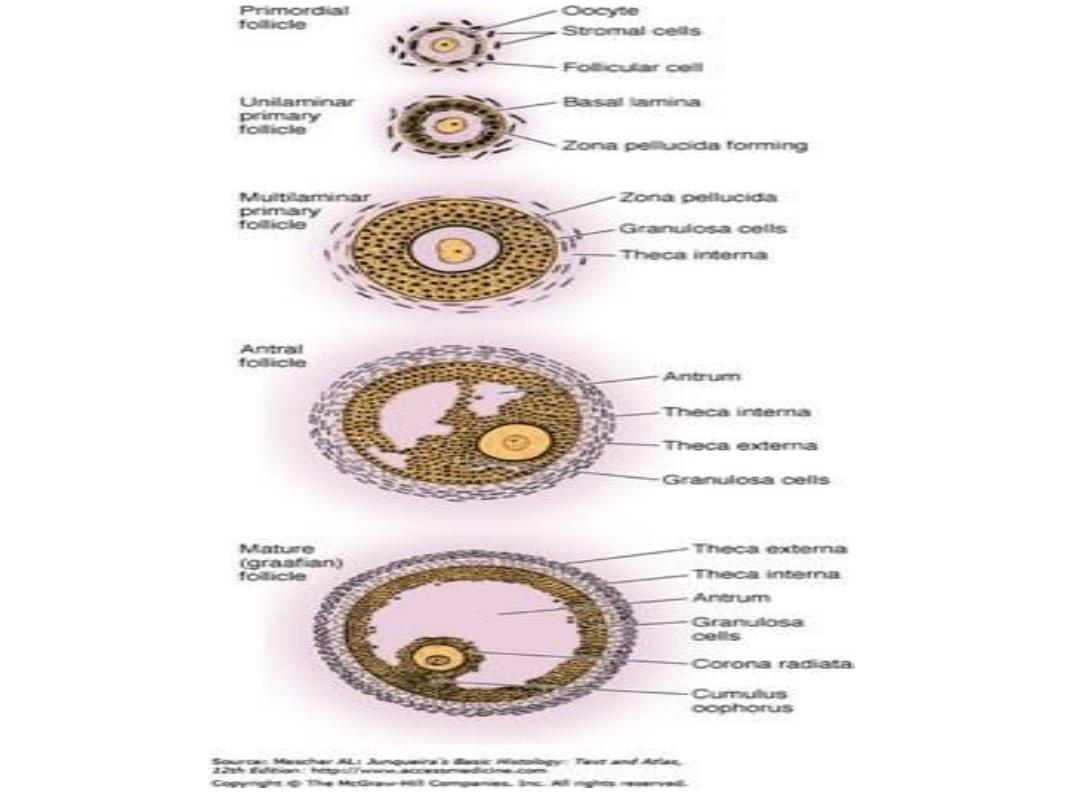
Maturation of ovarian follicle
*
primordial follicle:
ovum surrounded by single layer of flattened
cells called (follicular or granulosa cells), later these cells become
cuboidal.
*
primary follicle (preantral) :
when the follicular cells become
stratified layer of granulosa cells around oocyte & secrete a layer
of glycoproteins on the surface of oocyte (zona pellucida).
*
secondary follicle (antral) :
when fluid –filled spaces appear
between granulosa cells. Coalescence of these spaces forms the
(antrum). The granulosa cells at the periphery called (theca), the
outer layer called (theca externa), while the inner layer called
(theca interna).
*
Mature (Graafian follicle) or (preovulatory):
when the antrum
enlarges & the granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte remain
intact forming
cumulus oophorus,
the mature follicle here is
about 20-25 mm in diameter.

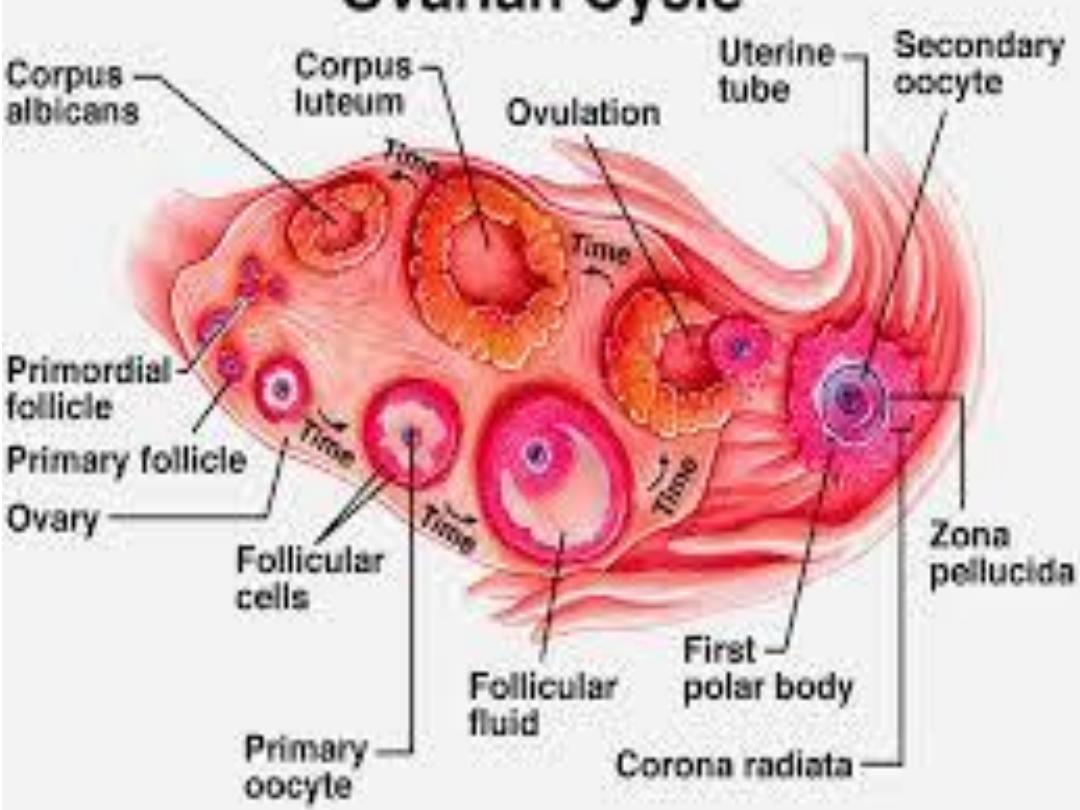
With each ovarian cycle, a no. of follicles begin to
develop, but usually only one reaches full maturity, the
others degenerate & become atretic. When the
secondary follicle is mature, a surge in
luteinizing
hormone (LH),
induces the preovulatory growth phase.
Meiosis 1 is completed, resulting in formation of 2
daughter cells of unequal size each with 23 single
structured chromosomes (one, the
secondary oocyte,
receives most of the cytoplasm; & the other, the
1
st
polar body,
receives none.
The cell then enters meiosis 2 but arrests in
metaphase approximately 3 hours before ovulation.
Meiosis2 completed only if the oocyte is fertilized;
otherwise, the cell degenerates approximately 24 hours
after ovulation.

Thank You
for your listening
