Third Week of Development
(Trilaminar Germ Disk)

The main events during this period:
• Gastrulatin.
• Formation of the notochord.
• Establishment of ^ body axes.
• Growth of ^ embryonic disc(cephalocaudally).
• Further development of ^ trophoblast.


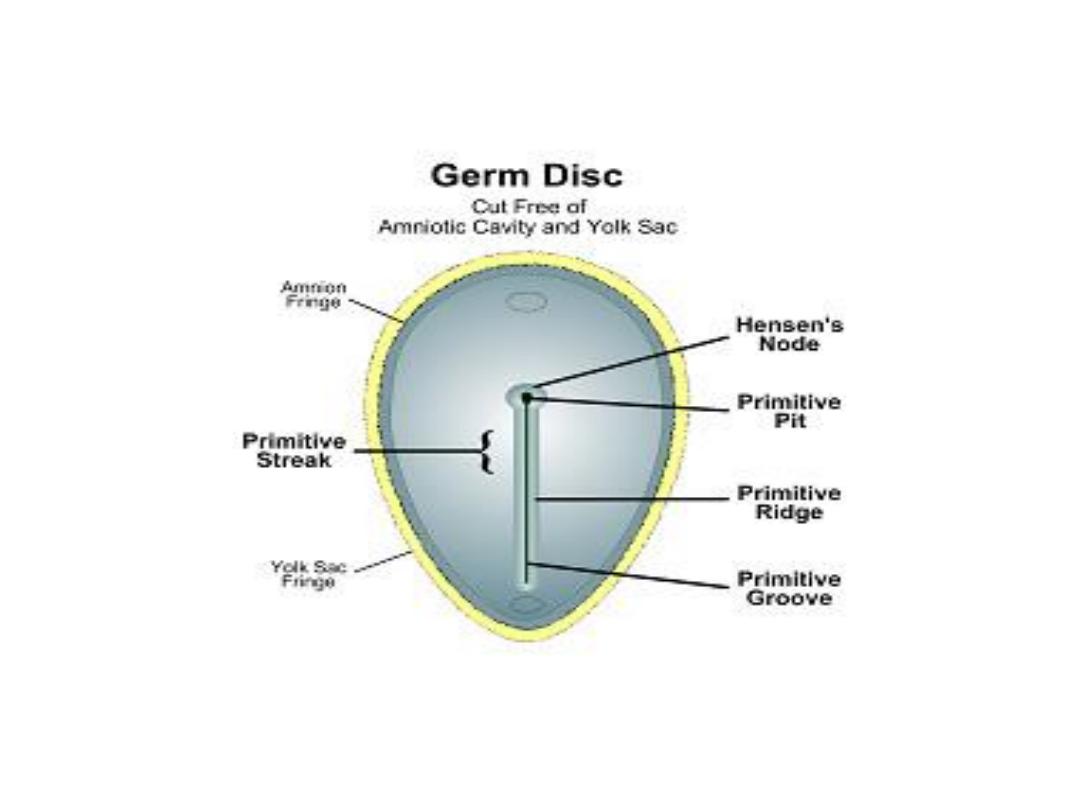
Gastrulation
• The process that establishes all three germ layers ( ectoderm,
mesoderm, & endoderm), which begins with ^ formation of ^
primitive streak
.
• ^ Primitive streak: a narrow groove formed on ^ surface of ^
epiblast, which is clearly visible at 15- 16 days embryo.
• ^ cephalic end of ^ streak, ^
primitive node,
consists of a
slightly elevated area surrounding ^ small
primitive pit
.
• Cells of ^ epiblast migrate toward ^ primitive streak, upon
their arrival, they detach from ^ epiblast & slip beneath it, this
inward movement is known as
invagination
.
• Once ^ cells have invaginated ,some displace ^ hypoblast,
creating ^ embryonic
endoderm.

• Some cells come to lie between ^ epiblast & newly created
endoderm to form
mesoderm
.
• Cells remaining in ^ epiblast then form
ectoderm
.
• Epiblast layer is ^ source of all ^ germ layers.
• Oropharyngeal membrane
at ^ cranial end of ^ disc consists of
small region of tightly adherent ectoderm & endoderm
without mesoderm.
• Cloacal membrane
at ^ caudal end of ^ disc similar to ^
orophangeal memb.
• ^
Prechordal plate
forms between ^ tip of ^ notochord & ^
oropharyngeal membrane & is derived from ^ 1
st
cells that
migrate from ^ node in cephalic direction.

• As more & more cells move bet. ^ epiblast & hypoblast layers,
they begin to spread laterally & cranially.
• Gradually, they migrate beyond ^ margin of ^ disc & establish
contact with ^ extraembryonic mesoderm covering ^ yolk sac
& amnion.

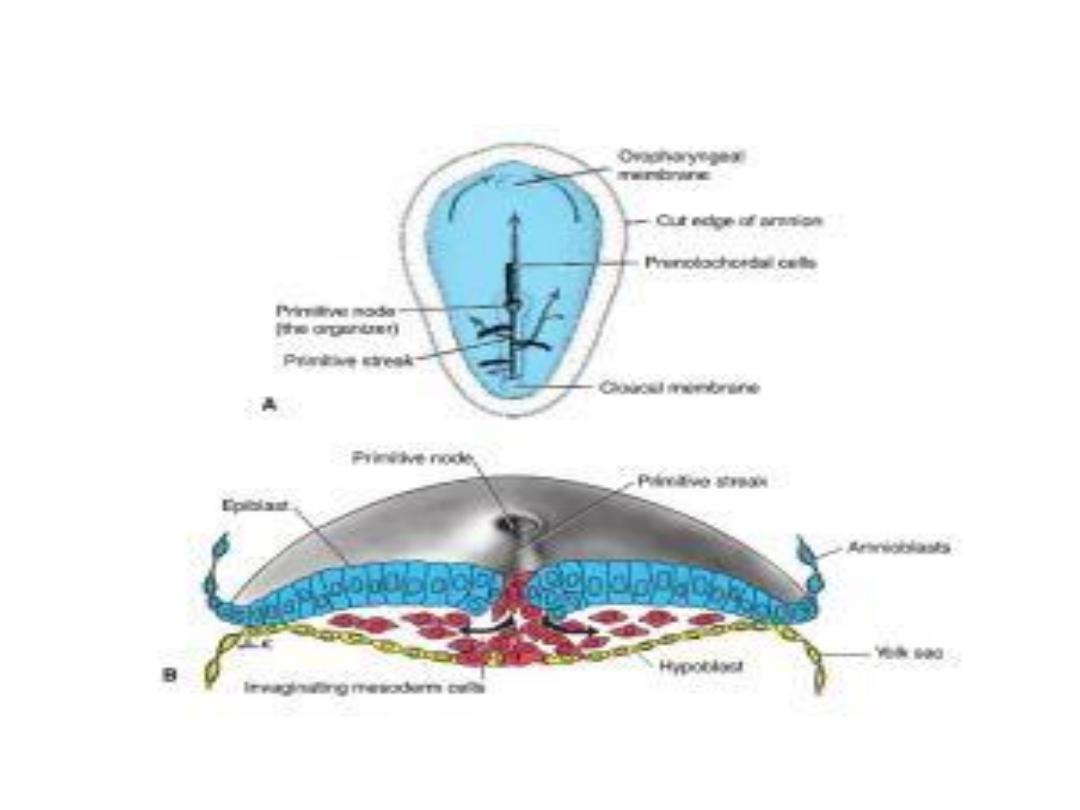
Formation of the Notochord
• Prenotochordal cells
invaginating in ^ primitive node move
forward cranially in ^ midline until they reach ^ prechordal
plate, these cells become intercalated in ^ hypoblast for a
short time at ^ midline then form ^
notochord plate.
• Cells of ^ notochordal plate proliferate & detach from ^
endoderm & form a solid cord of cells , ^
definitive notochord.
• ^ Cranial end forms first, & caudal regions are added as ^
primitive streak assumes a more caudal position.
• ^ notochord & prenotochordal cells extend cranially to ^
prechordal plate & caudally to ^ primitive pit.

• The primitive pit forms an indentation in ^ epiblast, ^
neurenteric canal
temporarily connects ^ amniotic & yolk sac
cavities.
• When ^ cloacal memb. appears, ^ posterior wall of ^ yolk sac
forms a small diverticulum that extends into ^ connecting
stalk called ^
allantoenteric diverticulum, or allantois,
appears
around ^ 16
th
day of development.

Establishment of the body axes
• Establishment of ^ body axes, anteroposterior, dorsoventral,
& left-right, takes place before & during ^ period of
gastrulation.
• Cephalic & caudal ends of ^ embryo are established before ^
primitive streak is formed.
• There are groups of genes which control ^ process of
gastrulation & establishment of ^ body axes.

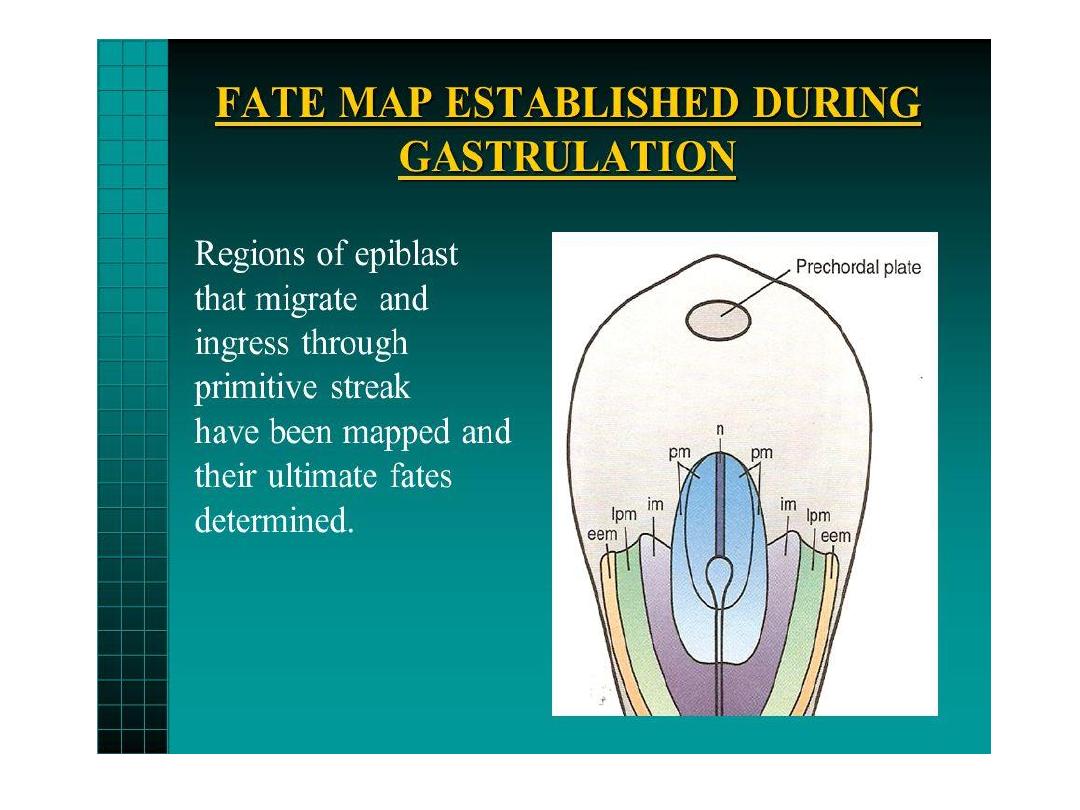
Fate map established during
gastrulation
• Regions of ^ epiblast that migrate through ^ primitive streak
have been mapped, & their ultimate fates have been
determined
.
• For ex. cells that ingress through ^ cranial region of ^ node
become prechordal plate & notochord; those migrating at ^
lateral edges of ^ node& from ^ cranial end of ^ streak
become paraxial mesoderm; cells migrating through ^
midstreak region become intermediate mesoderm; & those
migrating through ^ more caudal part of ^ streak form lateral
plate mesoderm.

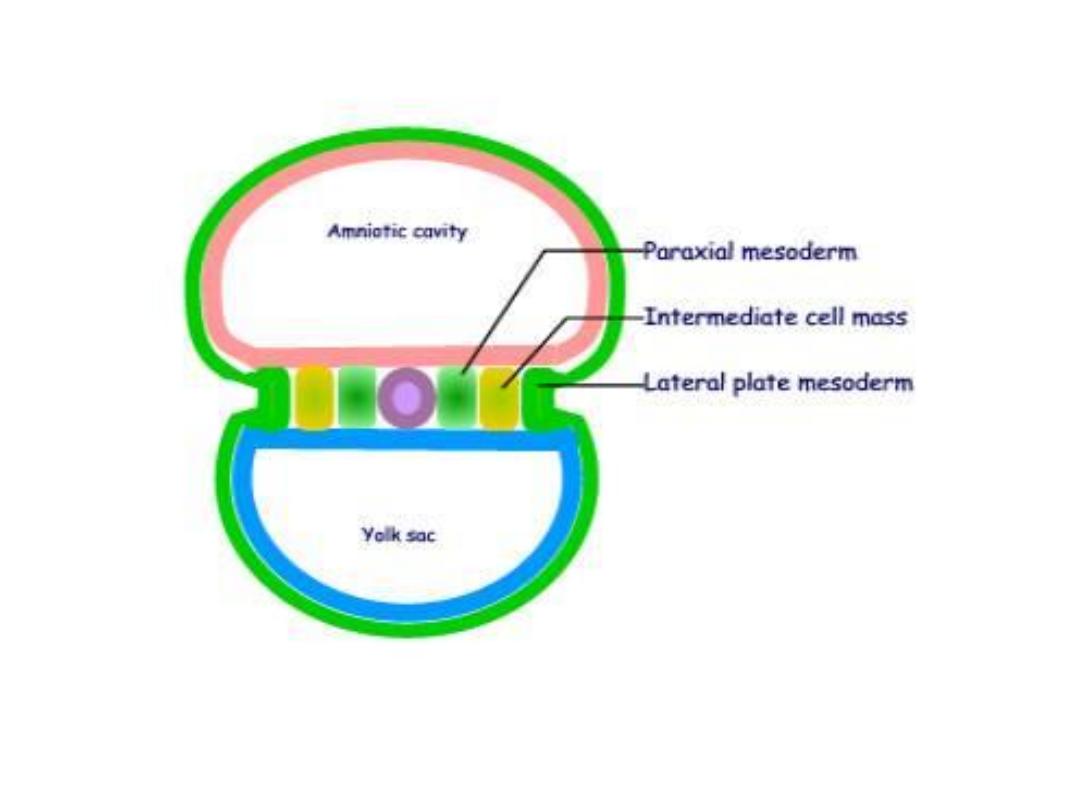
Growth of the embryonic disc
• The embryonic disc, initially flat almost round, gradually
becomes elongated, with a broad cephalic & narrow caudal
end.
• Continuous migration of cells from ^ primitive streak in
cephalic direction leads to growth & elongation of ^ cephalic
region.
• The migration of cells from ^ primitive streak forward &
laterally continues until ^ end of 4
th
week.
• In ^ cephalic region, germ layers begin their differentiation by
^ middle of ^ 3
rd
week, whereas in ^ caudal part,
differentiation begins by ^ end of ^ 4
th
week.

Thus gastrulation (formation of germ layers)
continue in caudal segments while cranial
structures are differentiating, causing ^ embryo
to develop cephalocaudally.

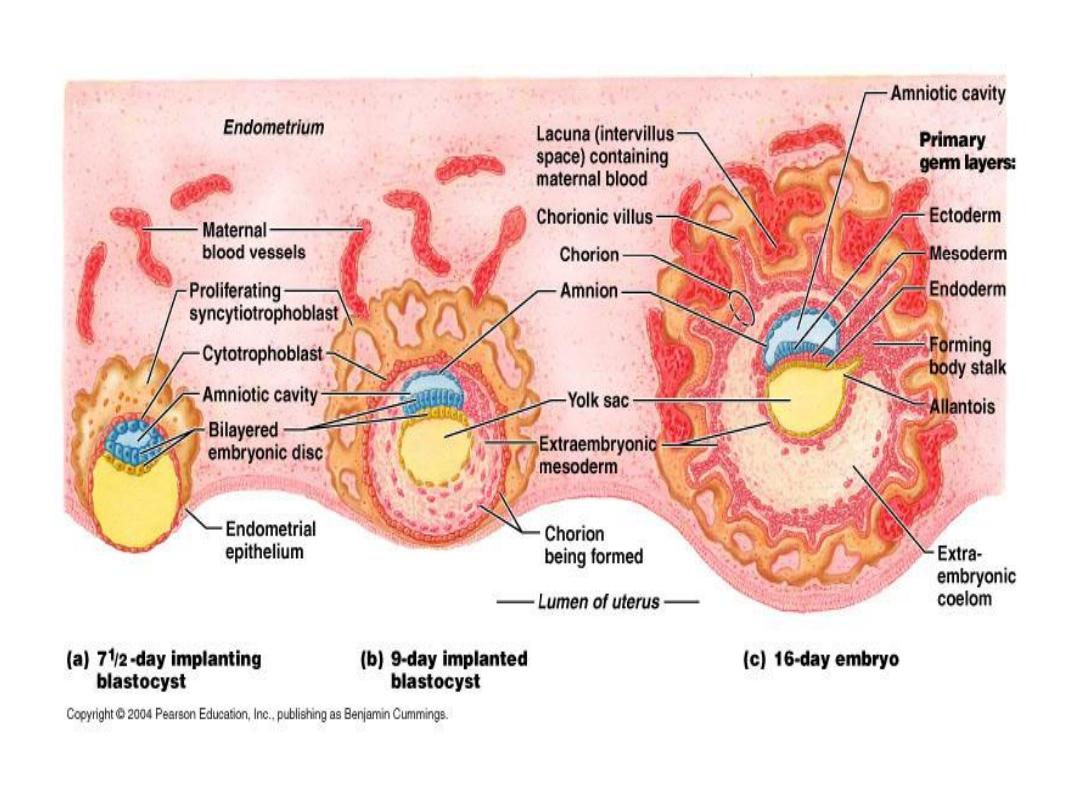
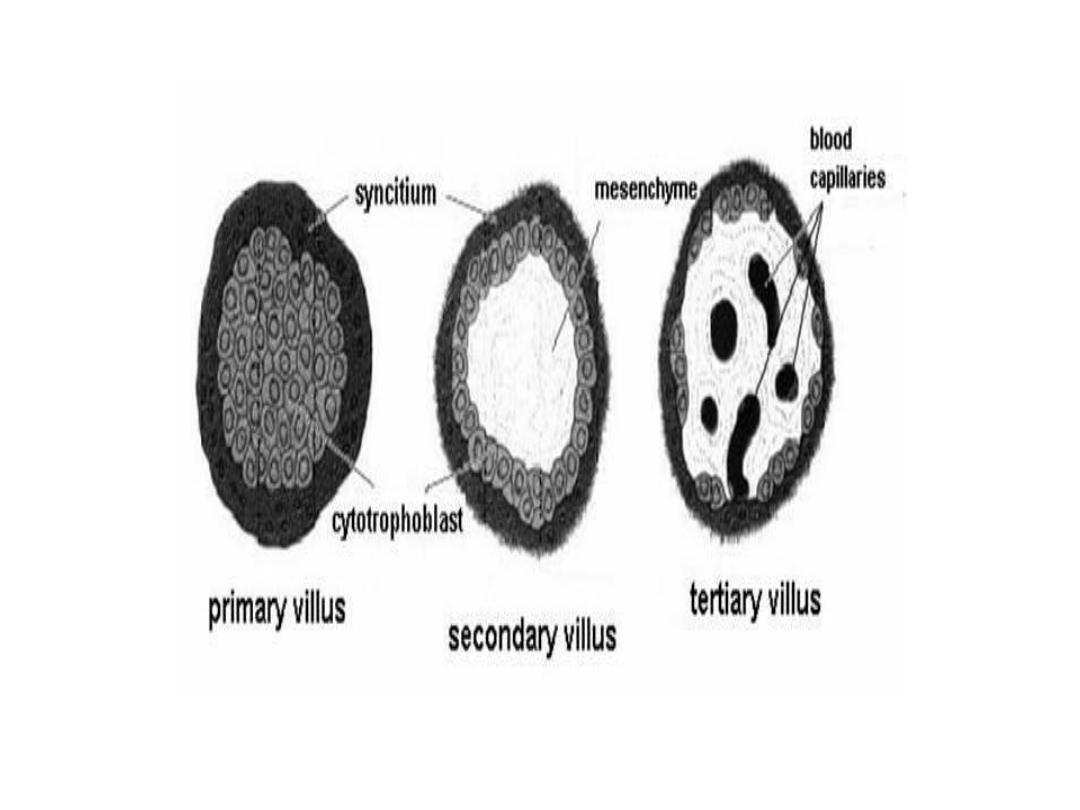
Further development of ^ trophoblast
• By ^ beginning of ^ 3
rd
week, ^ trophoblast is characterized by
primary villi
that consist of a cytotrophoblastic core covered
by a syncytial layer.
• During further development, mesodermal cells penetrate ^
core of primary villi & grow toward ^ decidua, here are called
secondary villi.
• By ^ end of ^ 3
rd
week, mesodermal cells in ^ core of ^ villus
begin to differentiate into blood cells & small blood cells
forming villus capillary system, ^ villi are called
tertiary or
definitive placental villus.

• Capillaries in tertiary villi make contact with capillaries
developing in ^ mesoderm of ^ chorionic plate & in ^
connecting stalk, these vessels , in turn, establish contact with
intraembryonic circulatory system, connecting ^ placenta & ^
embryo.
• Hence, when ^ heart begins to beat in ^ 4
th
week of
development, ^ villus system is ready to supply ^ embryo with
nutrients & oxygen.
• Meanwhile, cytotrophoblast cells in ^ villi penetrate into
overlying syncytium until they reach ^ maternal
endometrium, here they contact with similar extensions from
^ neighboring villus stems forming a thin
outer
cytotrophoblast shell.

• Villi that extend from ^ chorionic plate to ^ decidua basalis
called
stem or anchoring villi,
those that branch from ^ sides
of stem villi are
free (terminal) villi,
through which exchange
of nutrients & other factors will occur.
• By ^ 19
th
-20
th
day ^ embryo is attached to its trophoblastic
shell by a narrow connecting stalk.