
CARDIOVASCULAR
SYSTEM 1
by
Dr. Suhair Majeed

Cardiovascular System:
This system consists of the heart, major
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and
veins.
The main function of this system is to
deliver oxygenated blood to cells and
tissues and to return venous blood to the
lungs for gaseous exchange.

1- heart :
The heart is a modified blood vessel that
serves as a double pump and consists of
four chambers. On the right side, the atrium
receives blood from the body and the
ventricle propels it to the lungs.

Cont.
The left atrium receives blood from the
lungs and passes it to the left ventricle,
from which it is distributed throughout
the body.
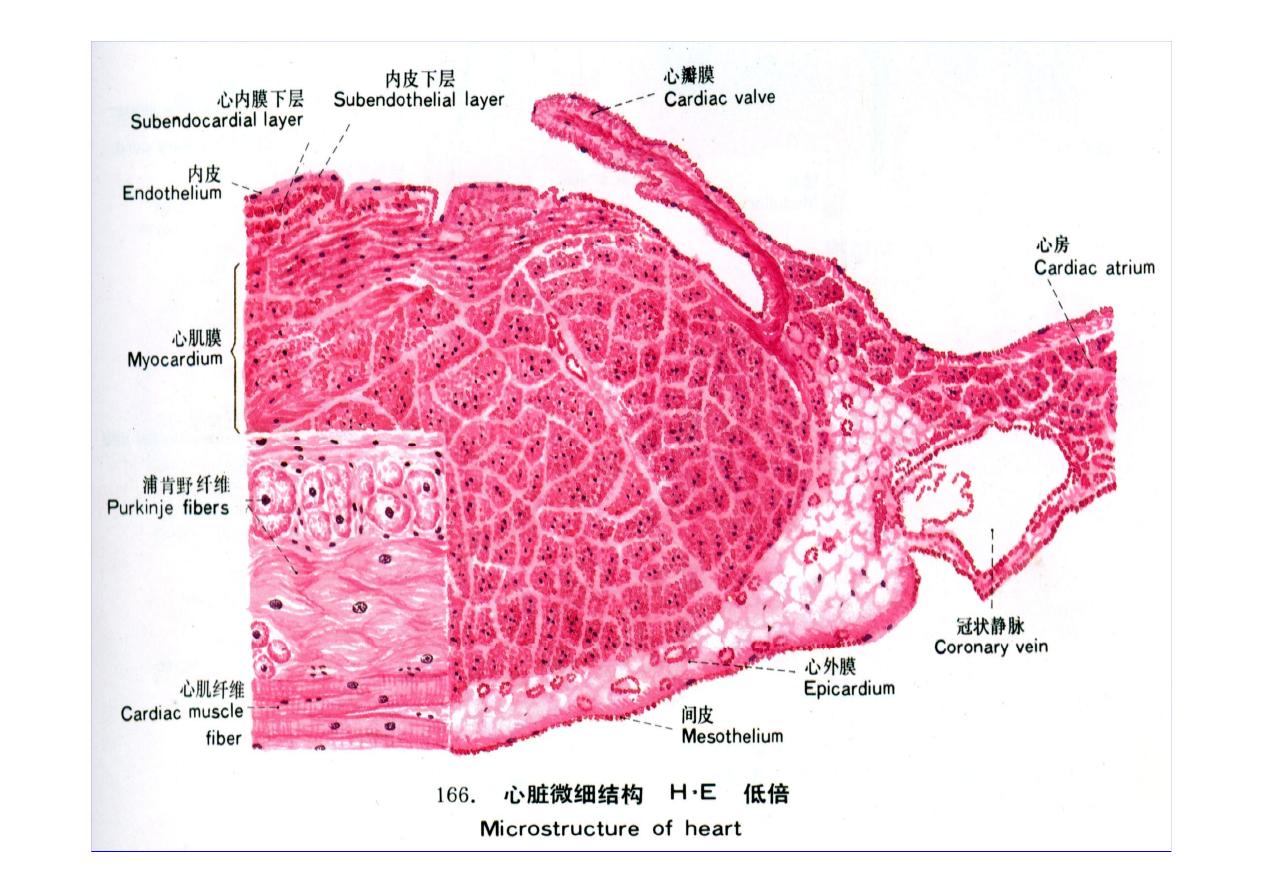
The wall of the heart consists of an
inner lining layer (endocardium), a
middle muscular layer (myocardium),
and an external layer of connective tissue.
(epicardium).
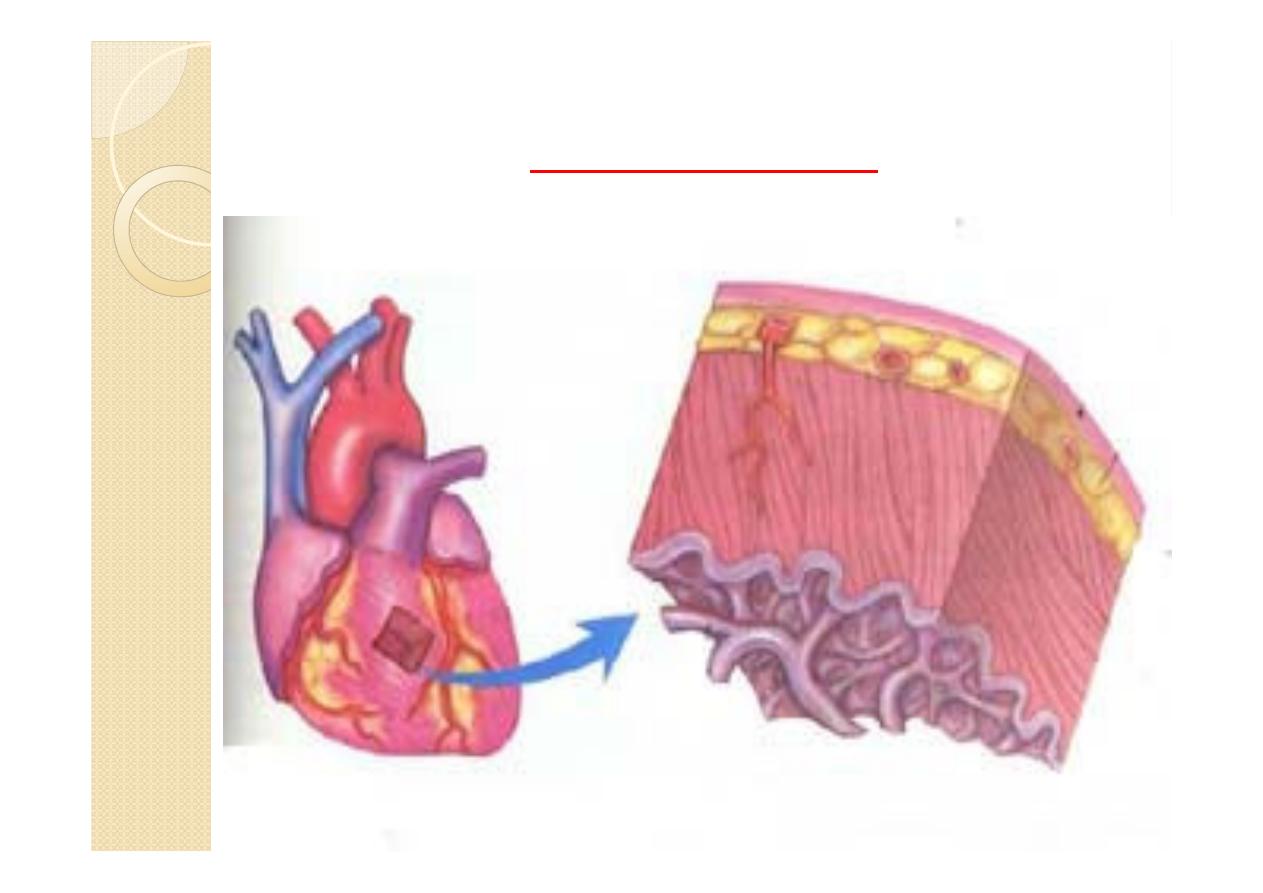
Heart Wall

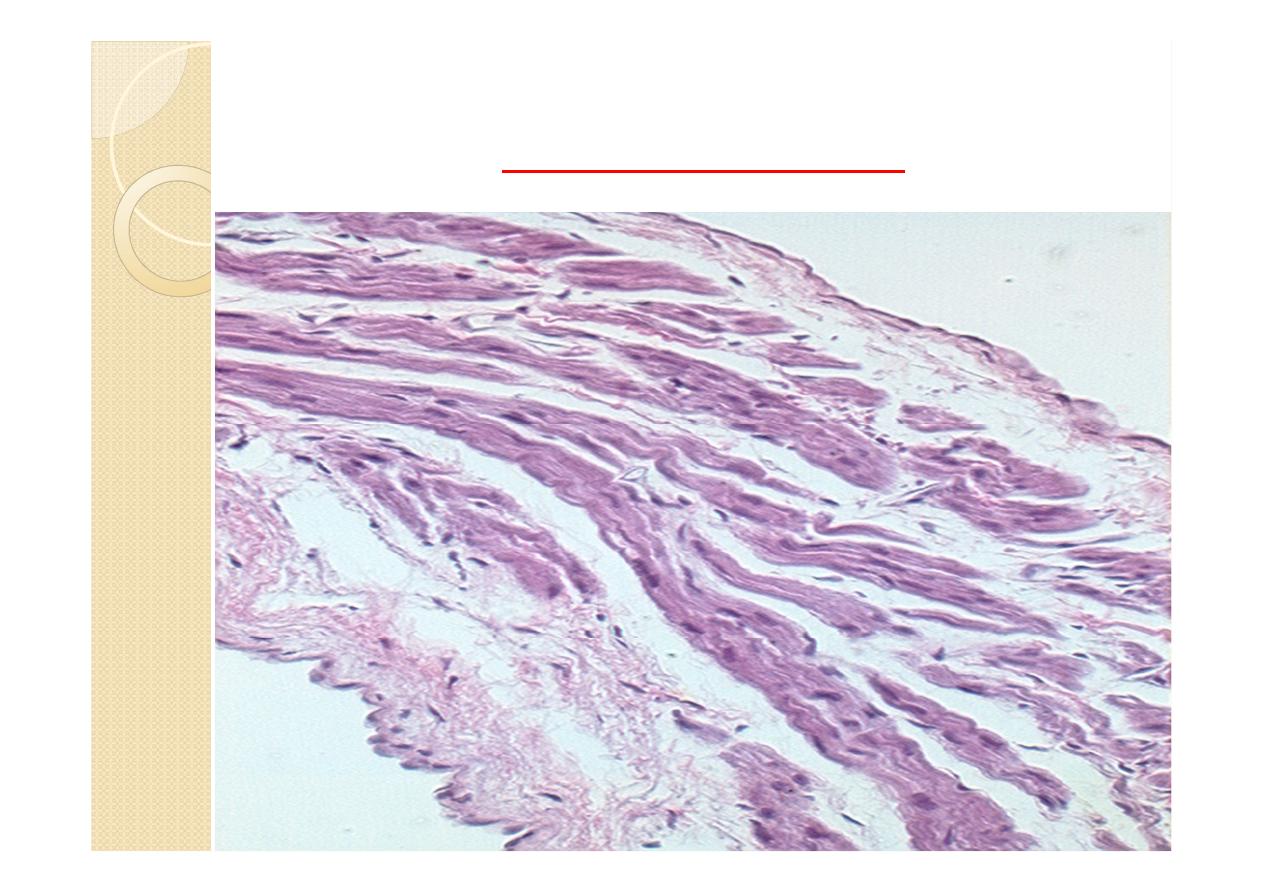
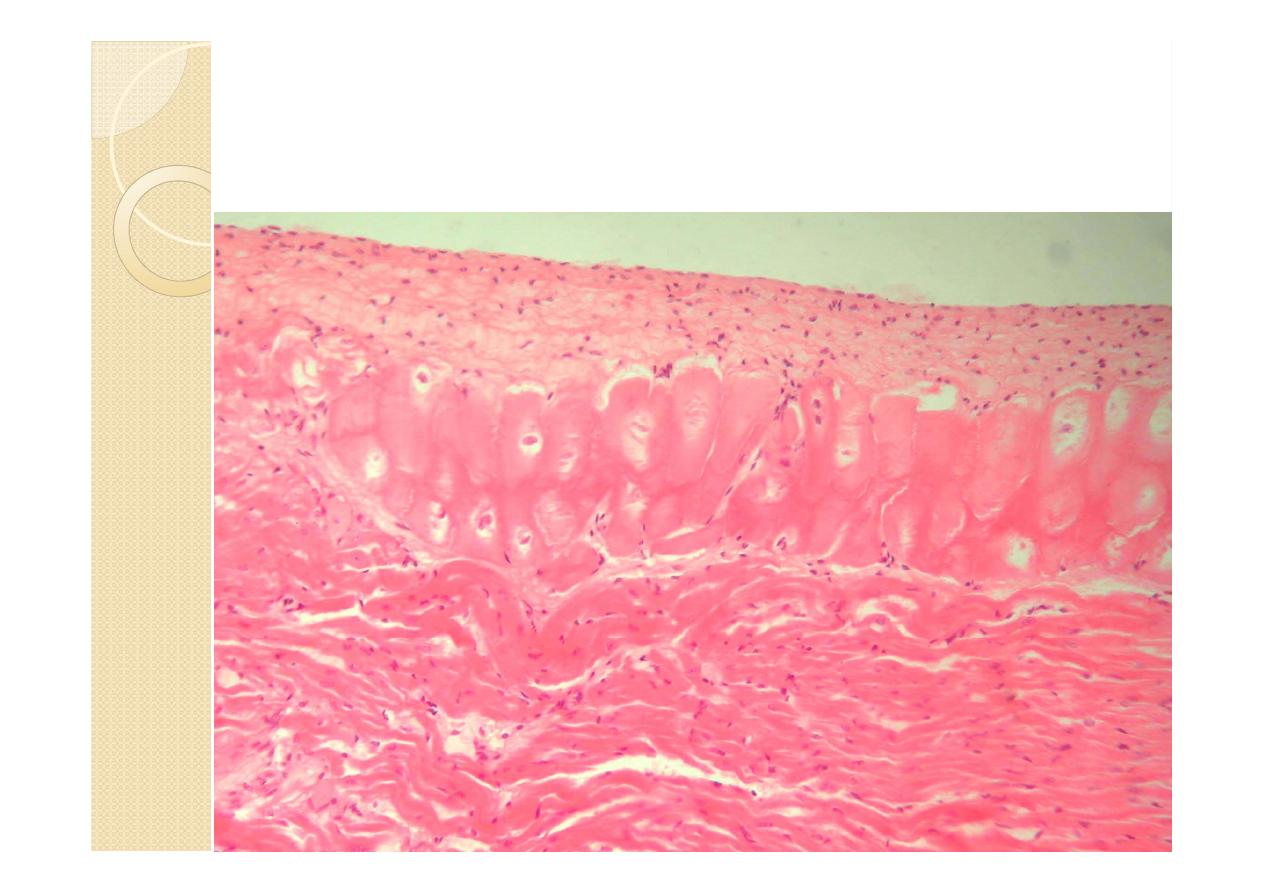
1-Endocardium :
The endocardium forms the inner lining of
the atria and ventricles and is continuous
with and comparable to the inner lining of
blood vessels.
It consists of a single layer of polygonal
squamous (endothelial) cells with oval
or rounded nuclei
Cont.
The endothelial cells rest on a continuous
layer of fine collagen fibers, separated from it
by a basement membrane.The fibrous layer is
called the subendothelial layer. Deep to it is
a thick layer of denser connective tissue
that forms the bulk of the endocardium and
contains elastic fibers and some smooth muscle
cells.

Cont.
a loose connective tissue constituting the
subendocardial layer binds the
endocardium to the underlying heart muscle
and contains collagen fibers, elastic fibers,
and blood vessels.
In the ventricles it also contains the
specialized cardiac muscle fibers of the
conducting system (purkinje fibers ).
Endocardium

Purkinje fibers
Purkinje fibers are thicker and larger than
cardiac muscle fibers and contain a greater
amount of glycogen. They also contain fewer
contractile filaments. Purkinje fibers are part
of the conduction system of the heart. These
fibers are located beneath the endocardium
on either side of the interventricular septum
and are recognized as separate tracts.

Cont.
Because Purkinje fibers branch throughout
the myocardium, they deliver continuous
waves of stimulation from the atrial nodes to
the rest of the heart musculature via the gap
junctions.
This produces ventricular contractions
(systole) and ejection of blood from both
ventricular chambers.
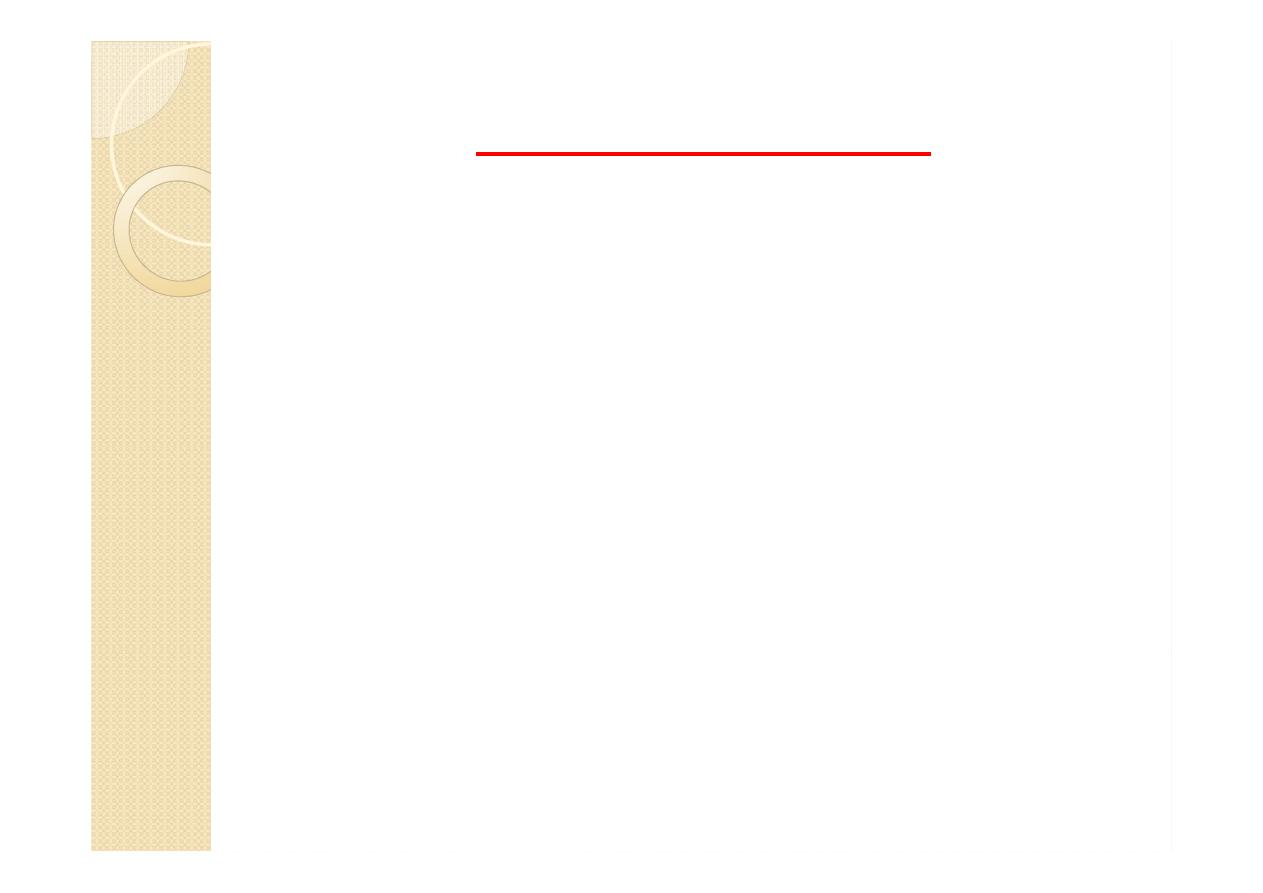
Purkinje fibers
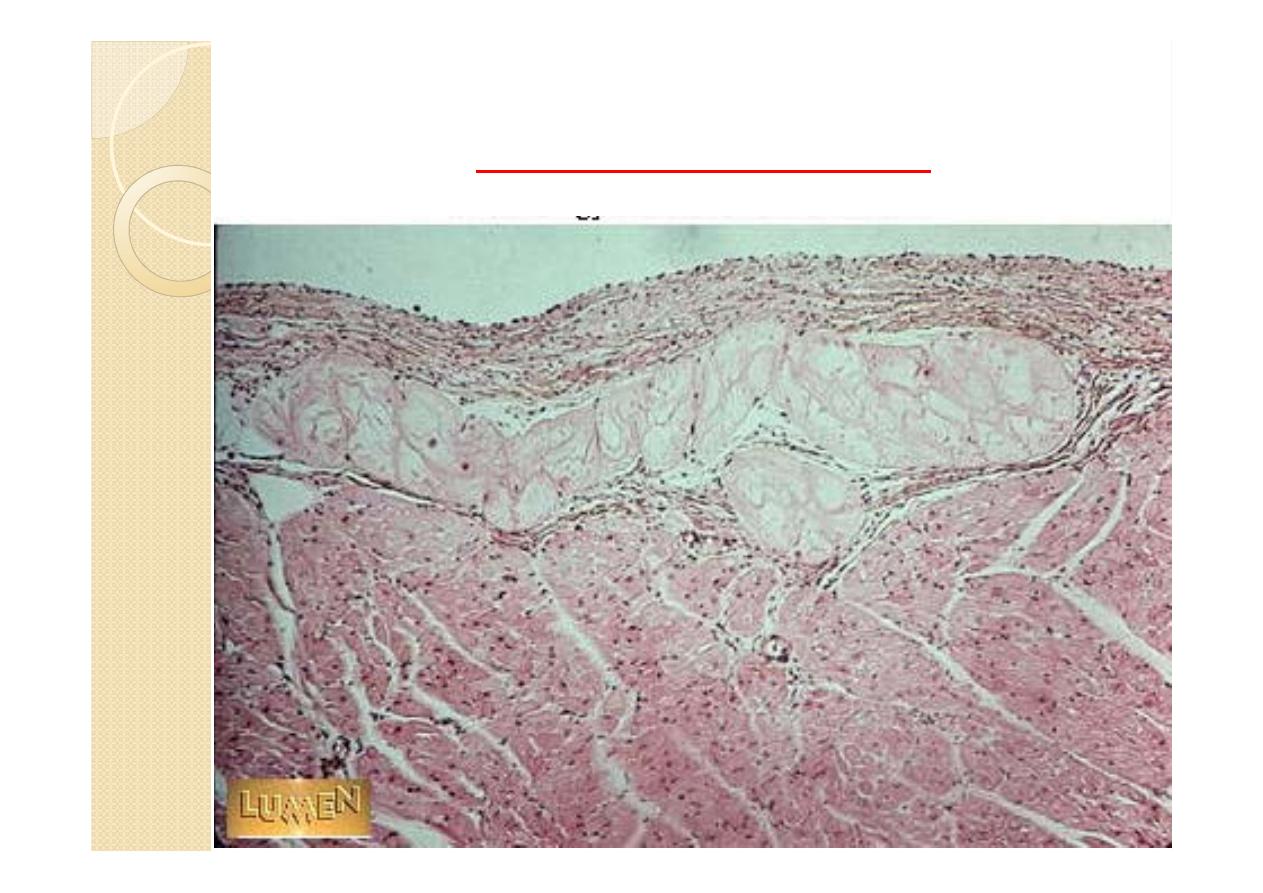
Purkinje fibers
SE ,subendocardial layer &purkinje
fibers

2-myocardium
The myocardium is the middle layer of the
heart and consists primarily of cardiac
muscle. The myocardium is a very vascular
tissue. The myocardium is the thinnest in the
atria and thickest in the left ventricle.
Cont.
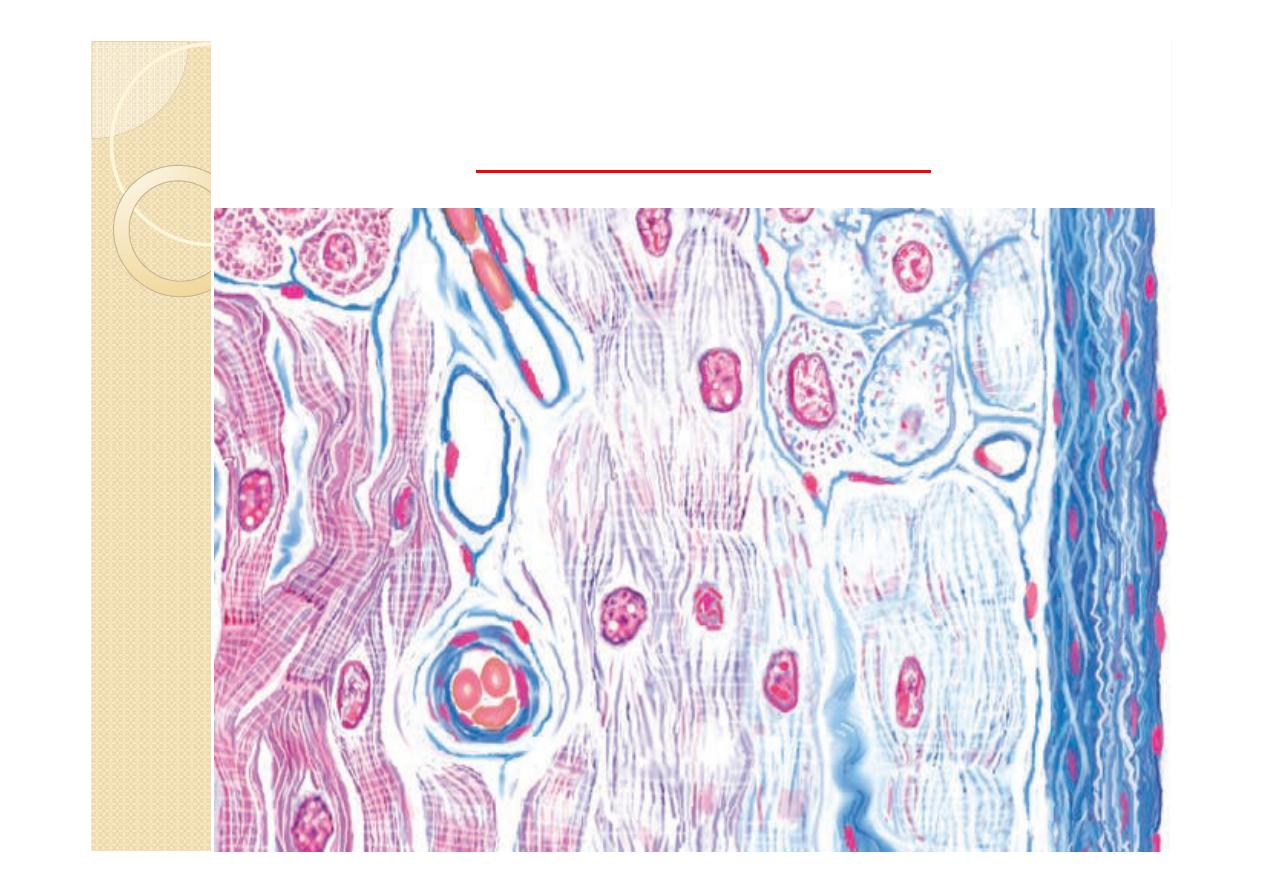
It consist of cardiac muscle cells =
myocytes .Different from smooth or skeletal
muscle cells due to placement of nuclei, cross
striations, and intercalated disks.
Intercalated disks
Junctional complexes that contain fascia
adherens, desmosomes, and gap junction to
provide connection and communication.
Bind myocytes and allow ion exchange to
facilitate electrical impulses to pass.

Gap junctions:
functionally couple all cardiac muscle
fibers to rapidly spread the stimuli for
contraction of the heart muscle.
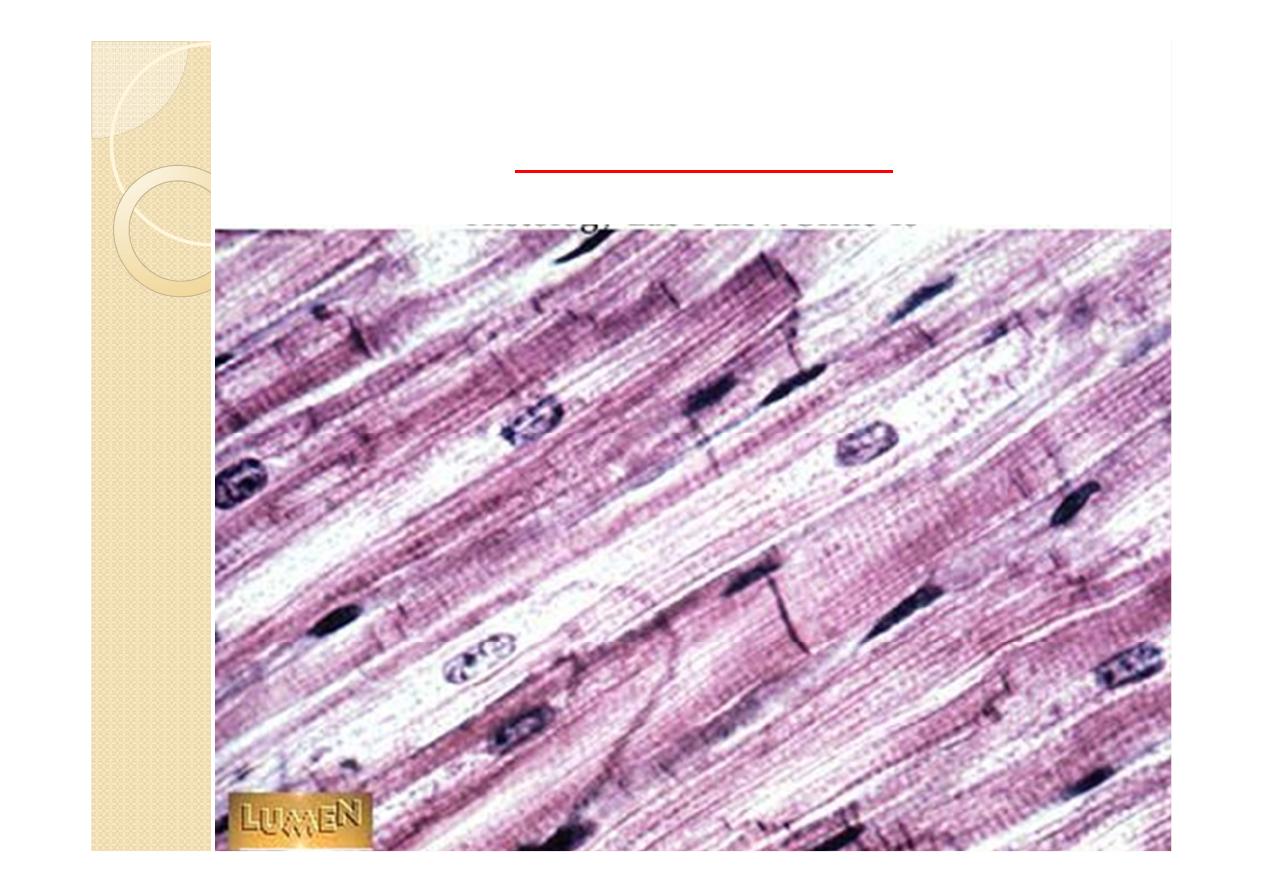
myocardium
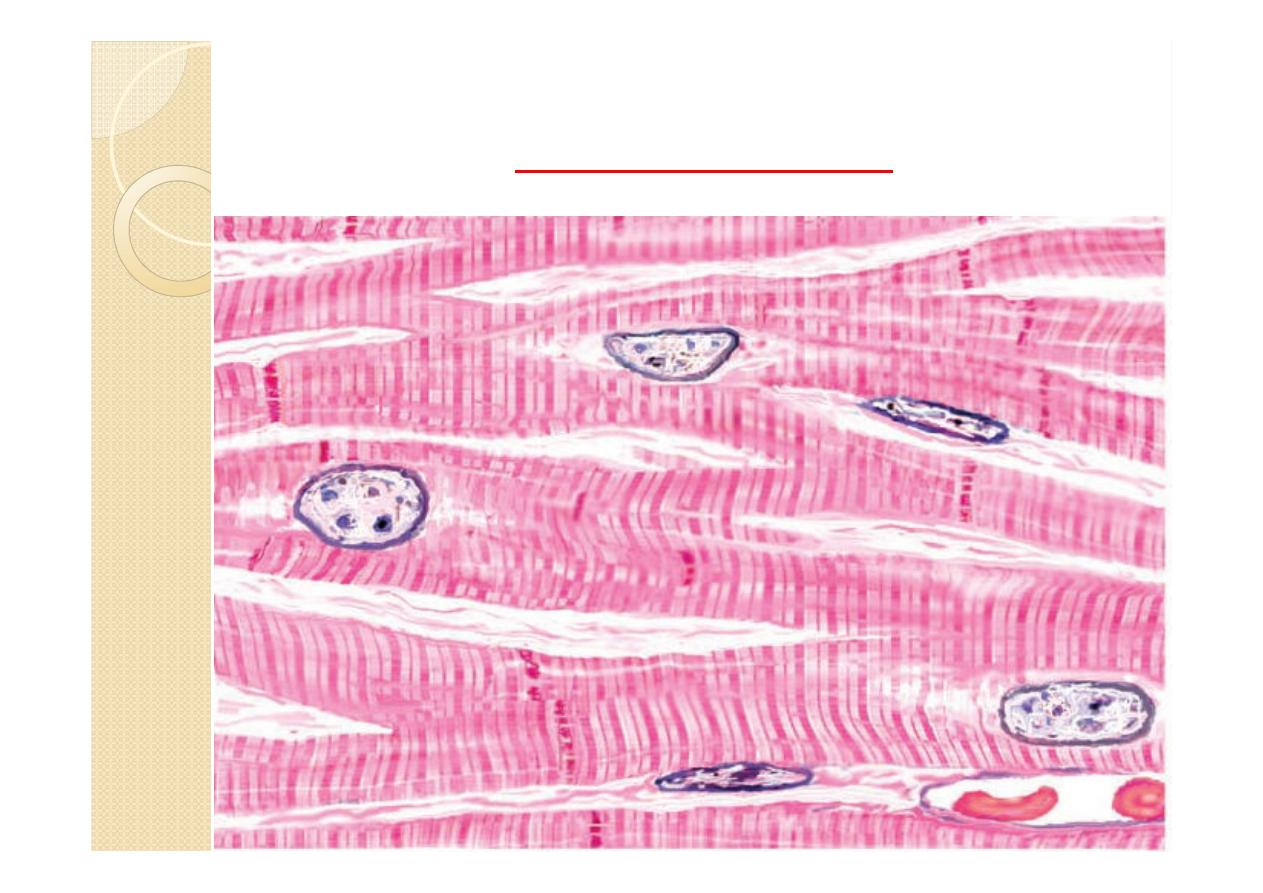
myocardium
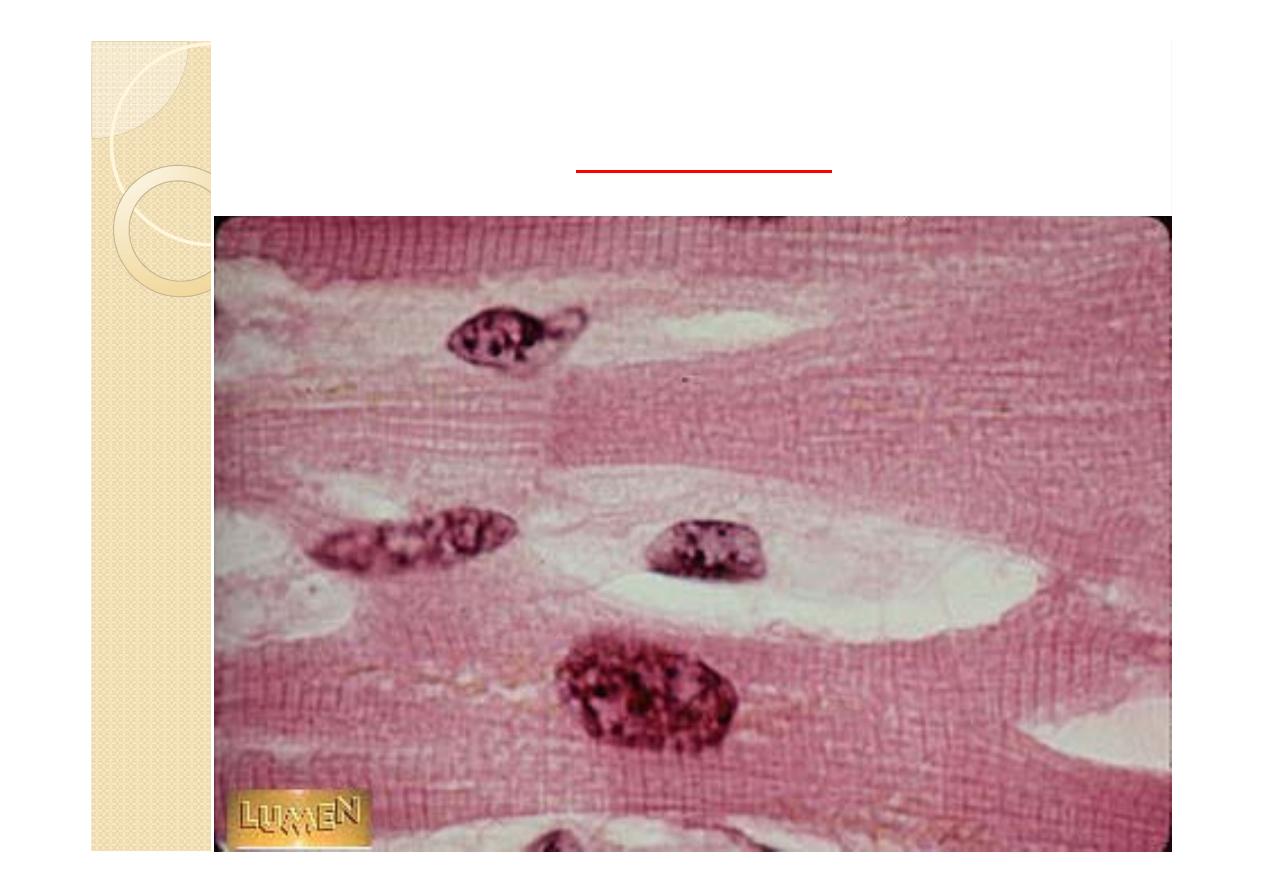
myocyte

Cont.
The capillaries completely surround
individual cardiac myocytes and are held in
close apposition to them by the enveloping
delicate connective tissue that occurs
between individual muscle cells. The
myocardium is arranged in layers that
form complex spirals about the atria and
ventricles.

Cont.
In the atria, the cardiac muscle cells are
smaller and contain a number of dense
granules not seen elsewhere in the heart.
These myocytes have properties associated
with endocrine cells. They are most
numerous in the right atrium and release the
secretory granules when stretched

Atrial Natriuretic Hormone
Certain cardiac muscle fibers in the atria
exhibit dense granules in their cytoplasm.
These granules contain atrial natriuretic
hormone, a chemical that is released in
response to atrial distension or stretching.
The main function of this hormone is to
decrease blood pressure by regulating blood
volume.

Cont.
This action is accomplished by inhibiting
the release of renin by the specialized cells
in the kidney and aldosterone from the
adrenal gland cortex. This induces the
kidney to lose more sodium and water
(diuresis).As a result, the blood volume and
blood pressure are reduced, and the
distension of the atrial wall is relieved.
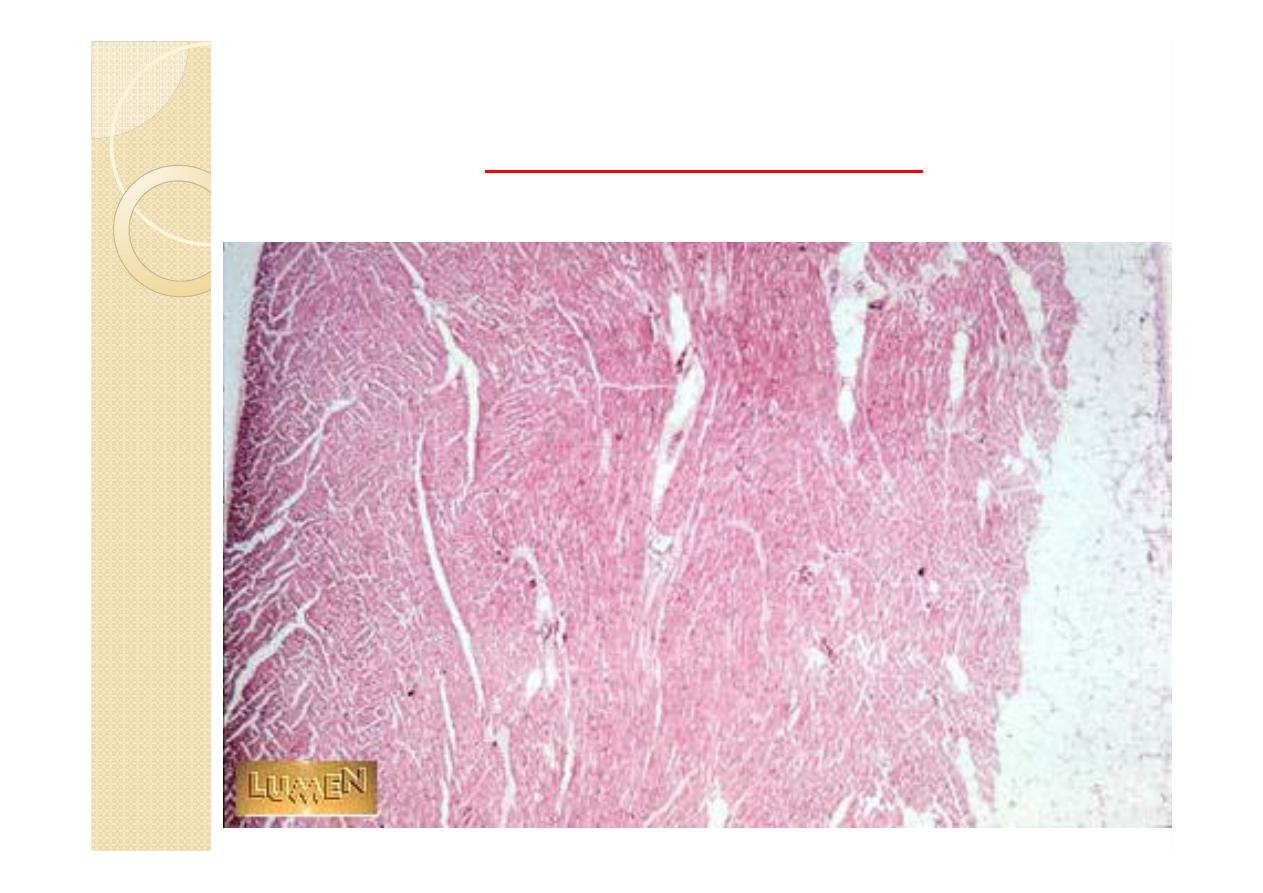
Heart Wall
